浅谈webpack编译vue项目生成的代码探索
本文介绍了webpack编译vue项目生成的代码探索,分享给大家,具体如下:
前言
往 main.js 里写入最简单的 vue 项目结构如下
import Vue from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
new Vue({
el: '#app',
template: '<App/>',
components: {
App
}
})
App.vue 如下
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<h2>Essential Links</h2>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="https://vuejs.org" rel="external nofollow" target="_blank">Core Docs</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="https://forum.vuejs.org" rel="external nofollow" target="_blank">Forum</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="https://chat.vuejs.org" rel="external nofollow" target="_blank">Community Chat</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="https://twitter.com/vuejs" rel="external nofollow" target="_blank">Twitter</a>
</li>
</ul>
<h2>Ecosystem</h2>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="http://router.vuejs.org/" rel="external nofollow" target="_blank">vue-router</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="http://vuex.vuejs.org/" rel="external nofollow" target="_blank">vuex</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="http://vue-loader.vuejs.org/" rel="external nofollow" target="_blank">vue-loader</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="https://github.com/vuejs/awesome-vue" rel="external nofollow" target="_blank">awesome-vue</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'app',
data() {
return {
msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App'
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
h1,
h2 {
font-weight: normal;
}
ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
}
li {
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 10px;
}
a {
color: #42b983;
}
</style>
编译生成后得到一个316kb的文件,而在316Kb中包含着什么,我很好奇想探索一番。
npm run build > learning-in-vue@1.0.0 build /Users/everlose/workspace/github/learningInVue > cross-env NODE_ENV=production webpack --progress --hide-modules Hash: 18d868a423b48dc263e9 Version: webpack 3.9.1 Time: 3693ms Asset Size Chunks Chunk Names build.js 316 kB 0 [emitted] [big] main build.js.map 399 kB 0 [emitted] main
代码分解
按顺序往下解读,本篇编译后的代码在这儿,如果只想看结论那么请拉到最后有一张结构梳理图。
webpack 模块机制
前面70行还是熟悉的 webpack 模块机制的基础代码,关于它的细致解读参见上一篇webpack模块机制,编译后的代码格式如下,并且我做了代码美化,并且插上了中文注释
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ // 缓存模块,所有被加载过的模块都会成为installedModules对象的属性,靠函数__webpack_require__做到。
/******/ var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function 核心加载方法
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ // 检查模块是否已在缓存中,是则直接返回缓存中的模块不需要再次加载
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ // 创造一个新模块并放入缓存中,i是模块标识,l意为是否加载此模块完毕,exports是此模块执行后的输出对象
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {}
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ // 传入参数并执行模块函数
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded 标为true代表模块执行完成。
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module 返回此模块输出的对象
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/ // webpack 私有变量,保存传入的modules,即所有的模块组成的数组
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache
/******/ // 保存缓存中的模块数组
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/ // 为 es6 exports 定义 getter
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ // 如果 exports 输出的对象本身不包含 name 属性时,定义一个。
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {
/******/ configurable: false,
/******/ enumerable: true,
/******/ get: getter
/******/ });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/ // 解决 ES module 和 Common js module 的冲突,ES 则返回 module['default']
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ // 工具方法,判断是否object有property属性。
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__
/******/ // 大概和 webpack.config.js 的 output 有关吧,webpack 的公共路径
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "/dist/";
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports 执行第一个依赖模块并且返回它输出。
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0);
/******/ })
0号模块
导出一个全局变量,在web端就是指代window
/* 0 */
(function (module, exports) {
var g;
// This works in non-strict mode
g = (function () {
return this;
})();
try {
// This works if eval is allowed (see CSP)
g = g || Function("return this")() || (1, eval)("this");
} catch (e) {
// This works if the window reference is available
if (typeof window === "object")
g = window;
}
// g can still be undefined, but nothing to do about it...
// We return undefined, instead of nothing here, so it's
// easier to handle this case. if(!global) { ...}
module.exports = g;
/***/
}),
1号模块
实际上做的事情很明显,就是导出了 main.js 的代码,一个vue实例对象
/* 1 */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
Object.defineProperty(__webpack_exports__, "__esModule", { value: true });
/* harmony import */ var __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0_vue__ = __webpack_require__(2);
/* harmony import */ var __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__App_vue__ = __webpack_require__(6);
// 从2号模块导出的一个叫a的变量,就是Vue对象本身
new __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0_vue__["a" /* default */]({
el: '#app',
template: '<App/>',
components: {
App: __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__App_vue__["a" /* default */]
}
});
/***/ })
2号模块
即是 Vue 源码本身,从114行一直到了10818行,一共是10705行代码,啧啧啧
webpack 有所配置,所以导出的 Vue 实际上是 vue/dist/vue.esm.js 的完整编译版本。
/* 2 */
/***/ (function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
/*!
* Vue.js v2.5.9
* (c) 2014-2017 Evan You
* Released under the MIT License.
*/
// 作用域指向__webpack_exports__,并把__webpack_require__(0)作为global,实际上就是window
// __webpack_require__(3).setImmediate)作为setsetImmediate参数传入函数
(function (global, setImmediate) {
// 省略近1w行的代码,关于vue原本本身的解读以后再做......
// 最终 export 出来一个叫 Vue$3的对象
/* harmony default export */
__webpack_exports__["a"] = (Vue$3);
/* WEBPACK VAR INJECTION */
}.call(__webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__(0), __webpack_require__(3).setImmediate))
}),
3,4,5号模块
都和 node_modules/setimmediate 有关,由于 vue 的 DOM 异步更新机制使用到了它,所以被引入。
这里也不做详解,只给出结构。
/* 3 */
/***/
(function (module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
// 省略代码...
// setimmediate attaches itself to the global object
__webpack_require__(4);
exports.setImmediate = setImmediate;
exports.clearImmediate = clearImmediate;
/***/
}),
/* 4 */
/***/
(function (module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
/* WEBPACK VAR INJECTION */
(function (global, process) {
// 省略代码...
}.call(exports, __webpack_require__(0), __webpack_require__(5)))
/***/
}),
/* 5 */
/***/
(function (module, exports) {
// shim for using process in browser
var process = module.exports = {};
// 省略代码...
process.cwd = function () {
return '/'
};
process.chdir = function (dir) {
throw new Error('process.chdir is not supported');
};
process.umask = function () {
return 0;
};
/***/
}),
6号模块
和 App.vue 的解析有关,把 App.vue 中的 template 和 script 编译为一个 vue components,并把 style 标签内的样式插入到DOM中。
/* 6 */
/***/
(function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
// 返回具体 App.vue 中 的script 中的代码
var __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__babel_loader_node_modules_vue_loader_lib_selector_type_script_index_0_App_vue__ = __webpack_require__(13);
// 把App.vue 的 template 解析为一堆 vue render 函数。
var __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__node_modules_vue_loader_lib_template_compiler_index_id_data_v_66ce2159_hasScoped_false_buble_transforms_node_modules_vue_loader_lib_selector_type_template_index_0_App_vue__ = __webpack_require__(14);
// 注入vue文件里写入的css函数
function injectStyle(ssrContext) {
// 由此可知7号模块是编译并插入vue中的css到DOM上的
__webpack_require__(7)
}
// 12号模块用于输出components渲染函数
var normalizeComponent = __webpack_require__(12)
/* script */
/* template */
/* template functional */
var __vue_template_functional__ = false
/* styles */
var __vue_styles__ = injectStyle
/* scopeId */
var __vue_scopeId__ = null
/* moduleIdentifier (server only) */
var __vue_module_identifier__ = null
// 编译模块,混杂template和script。
var Component = normalizeComponent(
__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__babel_loader_node_modules_vue_loader_lib_selector_type_script_index_0_App_vue__["a" /* default */ ],
__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_1__node_modules_vue_loader_lib_template_compiler_index_id_data_v_66ce2159_hasScoped_false_buble_transforms_node_modules_vue_loader_lib_selector_type_template_index_0_App_vue__["a" /* default */ ],
__vue_template_functional__,
__vue_styles__,
__vue_scopeId__,
__vue_module_identifier__
)
/* harmony default export */
__webpack_exports__["a"] = (Component.exports);
/***/
}),
7、8、9、10、11
都和样式有关,简言之就是7号模块加载8号模块获取css代码作为参数,并作为参数传入10号模块进行插入
太长也只大意上列出结构
- 7号模块由 style-loader 带入,把所有的css插入到 style 标签里
- 8号模块加载具体的css代码,
- 9号模块由css-loader代入,用于做css的sourceMap
- 10号模块返回具体插入动作函数,供7号模块调用
- 11号模块把所有的样式组成的数组转为字符串,给10号模块做插入。
/* 7 */
/***/
(function (module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
// style-loader: Adds some css to the DOM by adding a <style> tag
// load the styles
var content = __webpack_require__(8);
if (typeof content === 'string') content = [
[module.i, content, '']
];
if (content.locals) module.exports = content.locals;
// add the styles to the DOM
var update = __webpack_require__(10)("15459d21", content, true);
/***/
}),
/* 8 */
/***/
(function (module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
// css-loader 用于做css的sourceMap
exports = module.exports = __webpack_require__(9)(undefined);
// imports
// module
// 这就是 App.vue 文件中 style 里的的 css
exports.push([module.i, "#app{font-family:Avenir,Helvetica,Arial,sans-serif;-webkit-font-smoothing:antialiased;-moz-osx-font-smoothing:grayscale;text-align:center;color:#2c3e50;margin-top:60px}h1,h2{font-weight:400}ul{list-style-type:none;padding:0}li{display:inline-block;margin:0 10px}a{color:#42b983}", ""]);
// exports
/***/
}),
/* 9 */
/***/
(function (module, exports) {
// css base code, injected by the css-loader
module.exports = function (useSourceMap) {
// 省略代码...
}
}),
/* 10 */
/***/
(function (module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
/*
MIT License http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php
Author Tobias Koppers @sokra
Modified by Evan You @yyx990803
*/
// ...太长只贴了关键步骤,总之关键的函数就是这些
var hasDocument = typeof document !== 'undefined'
// ...
var listToStyles = __webpack_require__(11)
// ...
var head = hasDocument && (document.head || document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0])
// ...
module.exports = function (parentId, list, _isProduction) {
// ...
var styles = listToStyles(parentId, list)
addStylesToDom(styles)
return function update (newList) {
// ...
}
}
function addStylesToDom (styles /* Array<StyleObject> */) {
for (var i = 0; i < styles.length; i++) {
// ...
domStyle.parts.push(addStyle(item.parts[j]))
// ....
}
}
// 总之先调用了addStylesToDom,接着是addStyle,再是createStyleElement插入样式到head中。
function createStyleElement () {
var styleElement = document.createElement('style')
styleElement.type = 'text/css'
head.appendChild(styleElement)
return styleElement
}
function addStyle (obj /* StyleObjectPart */) {
// ...
styleElement = createStyleElement()
// ...
}
/***/
}),
/* 11 */
/***/
(function (module, exports) {
/**
* Translates the list format produced by css-loader into something
* easier to manipulate.
*/
module.exports = function listToStyles(parentId, list) {
var styles = []
var newStyles = {}
for (var i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
var item = list[i]
var id = item[0]
var css = item[1]
var media = item[2]
var sourceMap = item[3]
var part = {
id: parentId + ':' + i,
css: css,
media: media,
sourceMap: sourceMap
}
if (!newStyles[id]) {
styles.push(newStyles[id] = {
id: id,
parts: [part]
})
} else {
newStyles[id].parts.push(part)
}
}
return styles
}
/***/
}),
12、13、14号模块
12号做 .vue 文件中的 template 和 script 解析并供6号输出,最终返回了一个 vue components 对象,在浏览器控制台打印如下:
Object
beforeCreate: [ƒ]
data: ƒ data()
inject: {}
name: "app"
render: ƒ ()
staticRenderFns: (2) [ƒ, ƒ, cached: Array(2)]
_Ctor: {0: ƒ}
_compiled: true
__proto__: Object
而13号模块返回具体 script 中的代码,而14号模块则是把 template 解析为一堆 vue render 函数。
/* 12 */
/***/
(function (module, exports) {
/* globals __VUE_SSR_CONTEXT__ */
// IMPORTANT: Do NOT use ES2015 features in this file.
// This module is a runtime utility for cleaner component module output and will
// be included in the final webpack user bundle.
module.exports = function normalizeComponent(
rawScriptExports,
compiledTemplate,
functionalTemplate,
injectStyles,
scopeId,
moduleIdentifier /* server only */
) {
var esModule
var scriptExports = rawScriptExports = rawScriptExports || {}
// ES6 modules interop
var type = typeof rawScriptExports.default
if (type === 'object' || type === 'function') {
esModule = rawScriptExports
scriptExports = rawScriptExports.default
}
// Vue.extend constructor export interop
var options = typeof scriptExports === 'function' ?
scriptExports.options :
scriptExports
// render functions
if (compiledTemplate) {
options.render = compiledTemplate.render
options.staticRenderFns = compiledTemplate.staticRenderFns
options._compiled = true
}
// functional template
if (functionalTemplate) {
options.functional = true
}
// scopedId
if (scopeId) {
options._scopeId = scopeId
}
var hook
if (moduleIdentifier) { // server build
hook = function (context) {
// 2.3 injection
context =
context || // cached call
(this.$vnode && this.$vnode.ssrContext) || // stateful
(this.parent && this.parent.$vnode && this.parent.$vnode.ssrContext) // functional
// 2.2 with runInNewContext: true
if (!context && typeof __VUE_SSR_CONTEXT__ !== 'undefined') {
context = __VUE_SSR_CONTEXT__
}
// inject component styles
if (injectStyles) {
injectStyles.call(this, context)
}
// register component module identifier for async chunk inferrence
if (context && context._registeredComponents) {
context._registeredComponents.add(moduleIdentifier)
}
}
// used by ssr in case component is cached and beforeCreate
// never gets called
options._ssrRegister = hook
} else if (injectStyles) {
hook = injectStyles
}
if (hook) {
var functional = options.functional
var existing = functional ?
options.render :
options.beforeCreate
if (!functional) {
// inject component registration as beforeCreate hook
options.beforeCreate = existing ?
[].concat(existing, hook) :
[hook]
} else {
// for template-only hot-reload because in that case the render fn doesn't
// go through the normalizer
options._injectStyles = hook
// register for functioal component in vue file
options.render = function renderWithStyleInjection(h, context) {
hook.call(context)
return existing(h, context)
}
}
}
return {
esModule: esModule,
exports: scriptExports,
options: options
}
}
/***/
}),
/* 13 */
/***/
(function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
/* harmony default export */
// 这就是 App.vue 中 script 的部分
__webpack_exports__["a"] = ({
name: 'app',
data: function data() {
return {
msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App'
};
}
});
/***/
}),
/* 14 */
/***/
(function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
// 把template 解析为一堆 render 函数,扔给vue处理最终编译成Vnode节点在渲染成DOM输出到视图
var render = function () {
var _vm = this;
var _h = _vm.$createElement;
var _c = _vm._self._c || _h;
return _c('div', {
attrs: {
"id": "app"
}
}, [_c('h1', [_vm._v(_vm._s(_vm.msg))]), _vm._v(" "), _c('h2', [_vm._v("Essential Links")]), _vm._v(" "), _vm._m(0, false, false), _vm._v(" "), _c('h2', [_vm._v("Ecosystem")]), _vm._v(" "), _vm._m(1, false, false)])
}
var staticRenderFns = [function () {
var _vm = this;
var _h = _vm.$createElement;
var _c = _vm._self._c || _h;
return _c('ul', [_c('li', [_c('a', {
attrs: {
"href": "https://vuejs.org",
"target": "_blank"
}
}, [_vm._v("Core Docs")])]), _vm._v(" "), _c('li', [_c('a', {
attrs: {
"href": "https://forum.vuejs.org",
"target": "_blank"
}
}, [_vm._v("Forum")])]), _vm._v(" "), _c('li', [_c('a', {
attrs: {
"href": "https://chat.vuejs.org",
"target": "_blank"
}
}, [_vm._v("Community Chat")])]), _vm._v(" "), _c('li', [_c('a', {
attrs: {
"href": "https://twitter.com/vuejs",
"target": "_blank"
}
}, [_vm._v("Twitter")])])])
}, function () {
var _vm = this;
var _h = _vm.$createElement;
var _c = _vm._self._c || _h;
return _c('ul', [_c('li', [_c('a', {
attrs: {
"href": "http://router.vuejs.org/",
"target": "_blank"
}
}, [_vm._v("vue-router")])]), _vm._v(" "), _c('li', [_c('a', {
attrs: {
"href": "http://vuex.vuejs.org/",
"target": "_blank"
}
}, [_vm._v("vuex")])]), _vm._v(" "), _c('li', [_c('a', {
attrs: {
"href": "http://vue-loader.vuejs.org/",
"target": "_blank"
}
}, [_vm._v("vue-loader")])]), _vm._v(" "), _c('li', [_c('a', {
attrs: {
"href": "https://github.com/vuejs/awesome-vue",
"target": "_blank"
}
}, [_vm._v("awesome-vue")])])])
}]
var esExports = {
render: render,
staticRenderFns: staticRenderFns
}
/* harmony default export */
__webpack_exports__["a"] = (esExports);
/***/
})
总结
结构梳理,一图胜千言
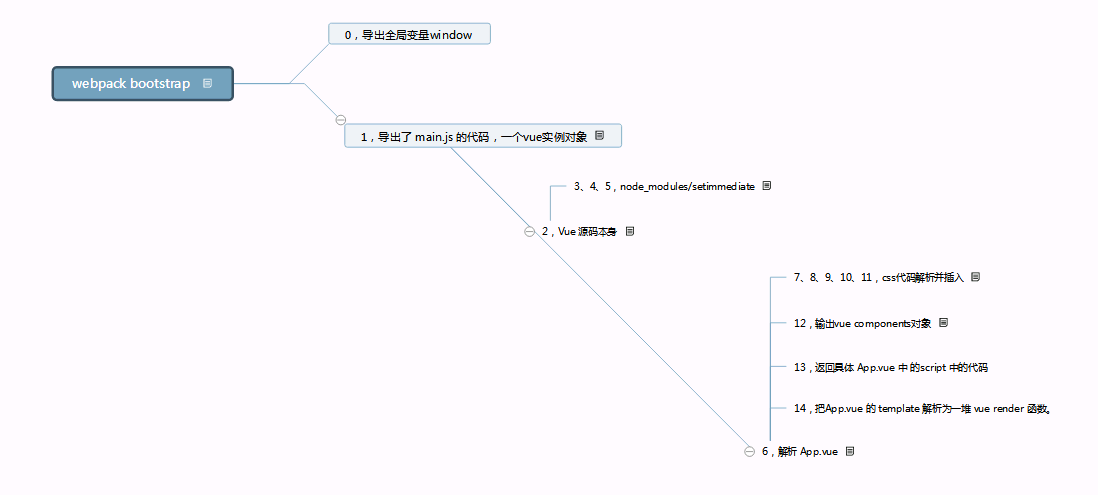
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
您可能感兴趣的文章:
- vue-cli+webpack在生成的项目中使用bootstrap实例代码
- vue-cli+webpack在生成的项目中使用bootstrap方法(一)
- 浅谈vue+webpack项目调试方法
- webpack+vue+vueRouter模块化构建完整项目实例超详细步骤(附截图、代码、入门篇)
- 浅谈vue+webpack项目调试方法
- 让Vue-cli生成vue+webpack的项目为vue1.0版本以及端口占用问题解决办法
- 用Vue-cli生成vue+webpack的项目模板
- vue-cli生成项目下webpack运行测试数据
- vue-cli生成vue+webpack的项目模板怎么设置为vue1.0
- vue-cli+webpack在生成的项目中使用bootstrap方法(二)
- 用Vue-cli生成vue+webpack的项目模板怎么设置为vue1.0版本?
- 浅谈vue+webpack项目调试方法步骤
- 用Vue-cli生成vue+webpack的项目模板怎么设置为vue1.0版本?
- webpack4.0.1_vue脚手架的项目与json-server结合,vue开发前端时用json-server模拟数据,fetch的请求代码
- webpack编译多页面vue项目的配置问题
- vue项目通过webpack打包生成的dist文件放到express里边运行(vue+webpack+express)
- 详解webpack编译多页面vue项目的配置问题
- 浅谈vue项目优化之页面的按需加载(vue+webpack)
- webpack+vue+vueRouter模块化构建完整项目实例超详细步骤(附截图、代码、入门篇)
- vue-cli + webpack自动生成项目
