人人都是 DBA(XIII)索引信息收集脚本汇编
2017-12-04 21:17
519 查看
什么?有个 SQL 执行了 8 秒!
哪里出了问题?臣妾不知道啊,得找 DBA 啊。DBA 人呢?离职了!!擦!!!
程序员在无处寻求帮助时,就得想办法自救,努力让自己变成 "伪 DBA"。
索引
找出哪些表的 Index 需要改进在指定数据库中查找哪些表的 Index 需要改进
根据缓存的查询计划判断 SP 是否需要优化
发现那些 Index 的写远多于读的表
查看 Index 的 Statistics 最后更新时间
查看哪些 Index 被修改的最频繁
查看 Index 碎片化指数
哪个 Index 上的读操作最活跃
哪个 Index 上的写操作最活跃
查看 Index 所使用的 Buffer 数量
按照 IO Latch 等待请求对索引进行排行
找出哪些表的 Index 需要改进
SELECT CONVERT(DECIMAL(18, 2), user_seeks * avg_total_user_cost * (avg_user_impact * 0.01)) AS [index_advantage] ,migs.last_user_seek ,mid.[statement] AS [Database.Schema.Table] ,mid.equality_columns ,mid.inequality_columns ,mid.included_columns ,migs.unique_compiles ,migs.user_seeks ,migs.avg_total_user_cost ,migs.avg_user_impact FROM sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats AS migs WITH (NOLOCK) INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_groups AS mig WITH (NOLOCK) ON migs.group_handle = mig.index_group_handle INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_details AS mid WITH (NOLOCK) ON mig.index_handle = mid.index_handle ORDER BY index_advantage DESC OPTION (RECOMPILE);
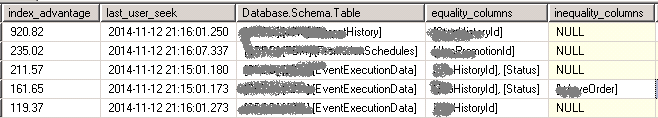
这里查询出的数据,只是说明数据寻址时间有点儿长,不一定就是缺少索引所引起的。
在指定数据库中查找哪些表的 Index 需要改进
SELECT DISTINCT CONVERT(DECIMAL(18, 2), user_seeks * avg_total_user_cost * (avg_user_impact * 0.01)) AS [index_advantage] ,migs.last_user_seek ,mid.[statement] AS [Database.Schema.Table] ,mid.equality_columns ,mid.inequality_columns ,mid.included_columns ,migs.unique_compiles ,migs.user_seeks ,migs.avg_total_user_cost ,migs.avg_user_impact ,OBJECT_NAME(mid.[object_id]) AS [Table Name] ,p.rows AS [Table Rows] FROM sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats AS migs WITH (NOLOCK) INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_groups AS mig WITH (NOLOCK) ON migs.group_handle = mig.index_group_handle INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_details AS mid WITH (NOLOCK) ON mig.index_handle = mid.index_handle INNER JOIN sys.partitions AS p WITH (NOLOCK) ON p.[object_id] = mid.[object_id] WHERE mid.database_id = DB_ID() ORDER BY index_advantage DESC OPTION (RECOMPILE);

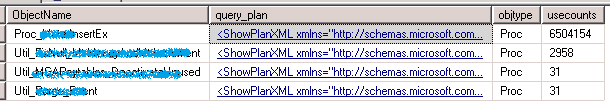
根据缓存的查询计划判断 SP 是否需要优化
SELECT TOP (25) OBJECT_NAME(objectid) AS [ObjectName] ,query_plan ,cp.objtype ,cp.usecounts FROM sys.dm_exec_cached_plans AS cp WITH (NOLOCK) CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_query_plan(cp.plan_handle) AS qp WHERE CAST(query_plan AS NVARCHAR(MAX)) LIKE N'%MissingIndex%' AND dbid = DB_ID() ORDER BY cp.usecounts DESC OPTION (RECOMPILE);
发现那些 Index 的写远多于读的表
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(s.[object_id]) AS [Table Name] ,i.[name] AS [Index Name] ,i.index_id ,i.is_disabled ,i.is_hypothetical ,i.has_filter ,i.fill_factor ,user_updates AS [Total Writes] ,user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups AS [Total Reads] ,user_updates - (user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups) AS [Difference] FROM sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats AS s WITH (NOLOCK) INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS i WITH (NOLOCK) ON s.[object_id] = i.[object_id] AND i.index_id = s.index_id WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(s.[object_id], 'IsUserTable') = 1 AND s.database_id = DB_ID() AND user_updates > (user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups) AND i.index_id > 1 ORDER BY [Difference] DESC ,[Total Writes] DESC ,[Total Reads] ASC OPTION (RECOMPILE);
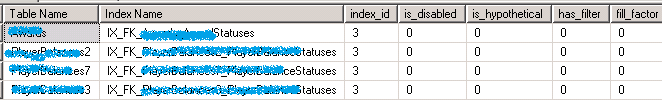
由于对索引的写操作远多于读操作,看起来 Index 的帮助不大,但需要根据业务需求来判断是否能够 Drop 掉该索引。
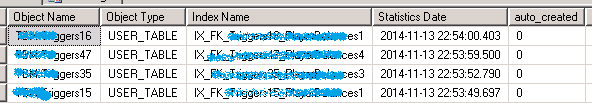
查看 Index 的 Statistics 最后更新时间
SELECT SCHEMA_NAME(o.[schema_id]) + N'.' + o.[name] AS [Object Name] ,o.type_desc AS [Object Type] ,i.[name] AS [Index Name] ,STATS_DATE(i.[object_id], i.index_id) AS [Statistics Date] ,s.auto_created ,s.no_recompute ,s.user_created ,st.row_count ,st.used_page_count FROM sys.objects AS o WITH (NOLOCK) INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS i WITH (NOLOCK) ON o.[object_id] = i.[object_id] INNER JOIN sys.stats AS s WITH (NOLOCK) ON i.[object_id] = s.[object_id] AND i.index_id = s.stats_id INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_partition_stats AS st WITH (NOLOCK) ON o.[object_id] = st.[object_id] AND i.[index_id] = st.[index_id] WHERE o.[type] IN ( 'U' ,'V' ) AND st.row_count > 0 ORDER BY STATS_DATE(i.[object_id], i.index_id) DESC OPTION (RECOMPILE);
参考资料:
Statistics
UPDATE STATISTICS (Transact-SQL)
sp_updatestats (Transact-SQL)
Rebuilding Indexes vs. Updating Statistics
Does a re-index update statistics?
SQL Server Index and Statistics Maintenance
查看哪些 Index 被修改的最频繁
SQL Server 2008 R2SELECT TableName = OBJECT_NAME(s.[object_id]) ,SchemaName = SCHEMA_NAME(o.[schema_id]) ,IndexName = i.[name] ,user_updates ,i.is_primary_key FROM sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats s JOIN sys.objects O ON s.[object_id] = O.[object_id] JOIN sys.indexes i ON s.[object_id] = i.[object_id] AND s.index_id = i.index_id WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(s.[object_id], 'IsMsShipped') = 0 AND user_seeks = 0 AND user_scans = 0 AND user_lookups = 0 AND i.NAME IS NOT NULL -- Ignore HEAP indexes. ORDER BY user_updates DESC
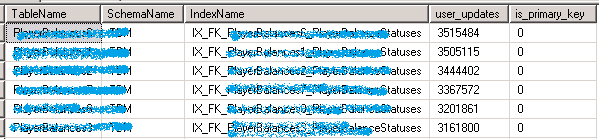
The user_updates counter indicates the level of maintenance on the index caused by insert, update, or delete operations on the underlying table or view.
SQL Server 2012
SELECT o.[name] AS [Object Name] ,o.[object_id] ,o.type_desc ,s.[name] AS [Statistics Name] ,s.stats_id ,s.no_recompute ,s.auto_created ,sp.modification_counter ,sp.rows ,sp.rows_sampled ,sp.last_updated FROM sys.objects AS o WITH (NOLOCK) INNER JOIN sys.stats AS s WITH (NOLOCK) ON s.object_id = o.object_id CROSS APPLY sys.dm_db_stats_properties(s.object_id, s.stats_id) AS sp WHERE o.type_desc NOT IN ( N'SYSTEM_TABLE' ,N'INTERNAL_TABLE' ) AND sp.modification_counter > 0 ORDER BY sp.modification_counter DESC ,o.[name] OPTION (RECOMPILE);
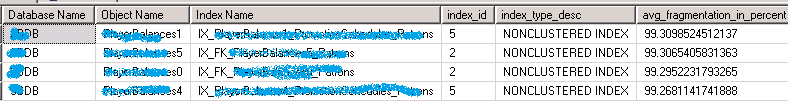
查看 Index 碎片化指数
SELECT DB_NAME(ps.database_id) AS [Database Name] ,OBJECT_NAME(ps.[object_id]) AS [Object Name] ,i.[name] AS [Index Name] ,ps.index_id ,ps.index_type_desc ,ps.avg_fragmentation_in_percent ,ps.fragment_count ,ps.page_count ,i.fill_factor ,i.has_filter ,i.filter_definition FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats(DB_ID(), NULL, NULL, NULL, N'LIMITED') AS ps INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS i WITH (NOLOCK) ON ps.[object_id] = i.[object_id] AND ps.index_id = i.index_id WHERE ps.database_id = DB_ID() AND ps.page_count > 2500 ORDER BY ps.avg_fragmentation_in_percent DESC OPTION (RECOMPILE);
参考资料:
Stop Worrying About SQL Server Fragmentation
Importance of index maintenance
Reorganize and Rebuild Indexes
Fragmentation and Index Maintenance Tips
Index Fragmentation–"If it isn’t broken, don’t fix it"
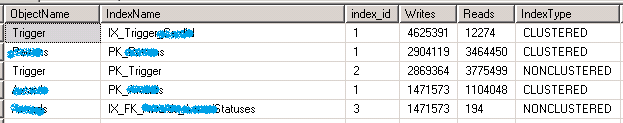
哪个 Index 上的读操作最活跃
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(s.[object_id]) AS [ObjectName] ,i.[name] AS [IndexName] ,i.index_id ,user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups AS [Reads] ,s.user_updates AS [Writes] ,i.type_desc AS [IndexType] ,i.fill_factor AS [FillFactor] ,i.has_filter ,i.filter_definition ,s.last_user_scan ,s.last_user_lookup ,s.last_user_seek FROM sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats AS s WITH (NOLOCK) INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS i WITH (NOLOCK) ON s.[object_id] = i.[object_id] WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(s.[object_id], 'IsUserTable') = 1 AND i.index_id = s.index_id AND s.database_id = DB_ID() ORDER BY user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups DESC OPTION (RECOMPILE);

哪个 Index 上的写操作最活跃
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(s.[object_id]) AS [ObjectName] ,i.[name] AS [IndexName] ,i.index_id ,s.user_updates AS [Writes] ,user_seeks + user_scans + user_lookups AS [Reads] ,i.type_desc AS [IndexType] ,i.fill_factor AS [FillFactor] ,i.has_filter ,i.filter_definition ,s.last_system_update ,s.last_user_update FROM sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats AS s WITH (NOLOCK) INNER JOIN sys.indexes AS i WITH (NOLOCK) ON s.[object_id] = i.[object_id] WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(s.[object_id], 'IsUserTable') = 1 AND i.index_id = s.index_id AND s.database_id = DB_ID() ORDER BY s.user_updates DESC OPTION (RECOMPILE);
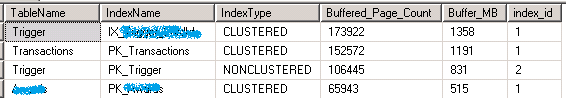
查看 Index 所使用的 Buffer 数量
SELECT TOP 25 obj.[name] AS TableName ,i.[name] AS IndexName ,i.[type_desc] AS IndexType ,count(*) AS Buffered_Page_Count ,count(*) * 8192 / (1024 * 1024) AS Buffer_MB ,obj.index_id FROM sys.dm_os_buffer_descriptors AS bd INNER JOIN ( SELECT object_name(object_id) AS NAME ,index_id ,allocation_unit_id ,object_id FROM sys.allocation_units AS au INNER JOIN sys.partitions AS p ON au.container_id = p.hobt_id AND ( au.type = 1 OR au.type = 3 ) UNION ALL SELECT object_name(object_id) AS NAME ,index_id ,allocation_unit_id ,object_id FROM sys.allocation_units AS au INNER JOIN sys.partitions AS p ON au.container_id = p.hobt_id AND au.type = 2 ) AS obj ON bd.allocation_unit_id = obj.allocation_unit_id LEFT JOIN sys.indexes i ON i.object_id = obj.object_id AND i.index_id = obj.index_id WHERE database_id = db_id() GROUP BY obj.NAME ,obj.index_id ,i.[name] ,i.[type_desc] ORDER BY Buffered_Page_Count DESC
按照 IO Latch 等待请求对索引进行排行
SELECT OBJECT_SCHEMA_NAME(ios.object_id) + '.' + OBJECT_NAME(ios.object_id) AS table_name ,i.[name] AS index_name ,page_io_latch_wait_count ,page_io_latch_wait_in_ms ,CAST(1. * page_io_latch_wait_in_ms / NULLIF(page_io_latch_wait_count, 0) AS DECIMAL(12, 2)) AS page_io_avg_lock_wait_ms ,page_latch_wait_count ,page_latch_wait_in_ms ,CAST(1. * page_latch_wait_in_ms / NULLIF(page_latch_wait_count, 0) AS DECIMAL(12, 2)) AS page_avg_lock_wait_ms FROM sys.dm_db_index_operational_stats(DB_ID(), NULL, NULL, NULL) ios INNER JOIN sys.indexes i ON i.object_id = ios.object_id AND i.index_id = ios.index_id WHERE OBJECTPROPERTY(ios.object_id, 'IsUserTable') = 1 ORDER BY 3 DESC

《人人都是 DBA》系列文章索引:
相关文章推荐
- 人人都是 DBA(XIII)索引信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(XIII)索引信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(IX)服务器信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(X)资源信息收集脚本汇编 (转)
- 人人都是 DBA(X)资源信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(XI)I/O 信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(XIV)存储过程信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(XV)锁信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(XIV)存储过程信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(IX)服务器信息收集脚本汇编 (转)
- 人人都是 DBA(XV)锁信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(IX)服务器信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(XII)查询信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(XI)I/O 信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(X)资源信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(XII)查询信息收集脚本汇编
- 人人都是 DBA(XI)I/O 信息收集脚本汇编(转)
- windows 信息收集脚本
- 收集服务器基本信息的脚本
- 一个mysql数据库的脚本帮助dba简单的管理数据库信息
