二叉树遍历方式和实现,以及二叉树查找、统计个数、比较、求深度
2017-11-28 11:52
375 查看
二叉树遍历方式和实现,以及二叉树查找、统计个数、比较、求深度
一、基本概念
每个结点最多有两棵子树,左子树和右子树,次序不可以颠倒。
性质:
1、非空二叉树的第n层上至多有2^(n-1)个元素。
2、深度为h的二叉树至多有2^h-1个结点。
满二叉树:所有终端都在同一层次,且非终端结点的度数为2。
在满二叉树中若其深度为h,则其所包含的结点数必为2^h-1。
完全二叉树:除了最大的层次即成为一颗满二叉树且层次最大那层所有的结点均向左靠齐,即集中在左面的位置上,不能有空位置。
对于完全二叉树,设一个结点为i则其父节点为i/2,2i为左子节点,2i+1为右子节点。
二、存储结构
顺序存储:
将数据结构存在一块固定的数组中。
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
#define LENGTH 100
typedef char datatype;
typedef struct node{
datatype data;
int lchild,rchild;
int parent;
}Node;
Node tree[LENGTH];
int length;
int root;
虽然在遍历速度上有一定的优势,但因所占空间比较大,是非主流二叉树。二叉树通常以链式存储。
链式存储:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
typedef char datatype;
typedef struct BinNode{
datatype data;
struct BinNode* lchild;
struct BinNode* rchild;
}BinNode;
typedef BinNode* bintree; //bintree本身是个指向结点的指针
三、二叉树的遍历
遍历即将树的所有结点访问且仅访问一次。按照根节点位置的不同分为前序遍历(先序遍历),中序遍历,后序遍历。另外还有一个遍历方式—层次遍历。
前序遍历:根节点->左子树->右子树
中序遍历:左子树->根节点->右子树
后序遍历:左子树->右子树->根节点
例如:求下面树的四种遍历
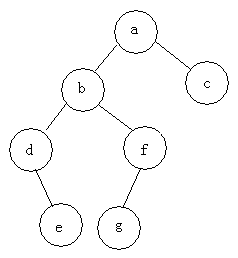
前序遍历:abdefgc
中序遍历:debgfac
后序遍历:edgfbca
层次遍历:abcdfeg
四、遍历的实现
递归实现(以前序遍历为例,其他的只是输出的位置稍有不同)
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
void preorder(bintree t){
if(t){
printf("%c ",t->data);
preorder(t->lchild);
preorder(t->rchild);
}
}
非递归的实现
因为当遍历过根节点之后还要回来,所以必须将其存起来。考虑到后进先出的特点,选用栈存储。数量确定,以顺序栈存储。
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
#define SIZE 100
typedef struct seqstack{
bintree data[SIZE];
int tag[SIZE]; //为后续遍历准备的
int top; //top为数组的下标
}seqstack;
void push(seqstack *s,bintree t){
if(s->top == SIZE){
printf("the stack is full\n");
}else{
s->top++;
s->data[s->top]=t;
}
}
bintree pop(seqstack *s){
if(s->top == -1){
return NULL;
}else{
s->top--;
return s->data[s->top+1];
}
}
1、前序遍历
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
void preorder_dev(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top = -1; //因为top在这里表示了数组中的位置,所以空为-1
if(!t){
printf("the tree is empty\n");
}else{
while(t || s.stop != -1){
while(t){ //只要结点不为空就应该入栈保存,与其左右结点无关
printf("%c ",t->data);
push(&s,t);
t= t->lchild;
}
t=pop(&s);
t=t->rchild;
}
}
}
2、中序遍历
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
void midorder(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top = -1;
if(!t){
printf("the tree is empty!\n");
}else{
while(t ||s.top != -1){
while(t){
push(&s,t);
t= t->lchild;
}
t=pop(&s);
printf("%c ",t->data);
t=t->rchild;
}
}
}
3、后序遍历
因为后序遍历最后还要要访问根结点一次,所以要访问根结点两次。采取夹标志位的方法解决这个问题。
这段代码非常纠结,对自己有信心的朋友可以尝试独立写一下。反正我是写了很长时间。逻辑不难,我画了一张逻辑图:
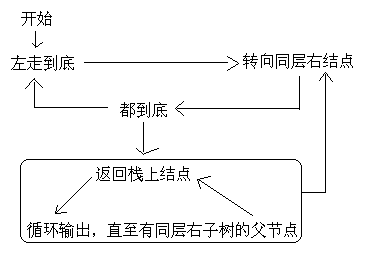
代码:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
void postorder_dev(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top = -1;
if(!t){
printf("the tree is empty!\n");
}else{
while(t || s.top != -1){ //栈空了的同时t也为空。
while(t){
push(&s,t);
s.tag[s.top] = 0; //设置访问标记,0为第一次访问,1为第二次访问
t= t->lchild;
}
if(s.tag[s.top] == 0){ //第一次访问时,转向同层右结点
t= s.data[s.top]; //左走到底时t是为空的,必须有这步!
s.tag[s.top]=1;
t=t->rchild;
}else {
while (s.tag[s.top] == 1){ //找到栈中下一个第一次访问的结点,退出循环时并没有pop所以为其左子结点
t = pop(&s);
printf("%c ",t->data);
}
t = NULL; //必须将t置空。跳过向左走,直接向右走
}
}
}
}
4、层次遍历:即每一层从左向右输出
元素需要储存有先进先出的特性,所以选用队列存储。
队列的定义:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
#define MAX 1000
typedef struct seqqueue{
bintree data[MAX];
int front;
int rear;
}seqqueue;
void enter(seqqueue *q,bintree t){
if(q->rear == MAX){
printf("the queue is full!\n");
}else{
q->data[q->rear] = t;
q->rear++;
}
}
bintree del(seqqueue *q){
if(q->front == q->rear){
return NULL;
}else{
q->front++;
return q->data[q->front-1];
}
}
遍历实现
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
void level_tree(bintree t){
seqqueue q;
bintree temp;
q.front = q.rear = 0;
if(!t){
printf("the tree is empty\n");
return ;
}
enter(&q,t);
while(q.front != q.rear){
t=del(&q);
printf("%c ",t->data);
if(t->lchild){
enter(&q,t->lchild);
}
if(t->rchild){
enter(&q,t->rchild);
}
}
}
5、利用前序遍历的结果生成二叉树
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
//递归调用,不存点,想的时候只关注于一个点,因为还会回来的,不要跟踪程序运行,否则容易多加循环
void createtree(bintree *t){
datatype c;
if((c=getchar()) == '#')
*t = NULL;
else{
*t = (bintree)malloc(sizeof(BinNode));
(*t)->data = c;
createtree(&(*t)->lchild);
createtree(&(*t)->rchild);
}
}
6、二叉树的查找
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
bintree search_tree(bintree t,datatype x){
if(!t){
return NULL;
}
if(t->data == x){
return t;
}else{
if(!search_tree(t->lchild,x)){
return search_tree(t->rchild,x);
}
return t;
}
}
7、统计结点个数
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
int count_tree(bintree t){
if(t){
return (count_tree(t->lchild)+count_tree(t->rchild)+1);
}
return 0;
}
8、比较两个树是否相同
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
int is_equal(bintree t1,bintree t2){
if(!t1 && !t2){ //都为空就相等
return 1;
}
if(t1 && t2 && t1->data == t2->data){ //有一个为空或数据不同就不判断了
if(is_equal(t1->lchild,t2->lchild))
if(is_equal(t1->rchild,t2->rchild)){
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
9、求二叉树的深度
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
int hight_tree(bintree t){
int h,left,right;
if(!t){
return 0;
}
left = hight_tree(t->lchild);
right = hight_tree(t->rchild);
h = (left>right?left:right)+1;
return h;
}
转载地址:点击打开链接
一、基本概念
每个结点最多有两棵子树,左子树和右子树,次序不可以颠倒。
性质:
1、非空二叉树的第n层上至多有2^(n-1)个元素。
2、深度为h的二叉树至多有2^h-1个结点。
满二叉树:所有终端都在同一层次,且非终端结点的度数为2。
在满二叉树中若其深度为h,则其所包含的结点数必为2^h-1。
完全二叉树:除了最大的层次即成为一颗满二叉树且层次最大那层所有的结点均向左靠齐,即集中在左面的位置上,不能有空位置。
对于完全二叉树,设一个结点为i则其父节点为i/2,2i为左子节点,2i+1为右子节点。
二、存储结构
顺序存储:
将数据结构存在一块固定的数组中。
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
#define LENGTH 100
typedef char datatype;
typedef struct node{
datatype data;
int lchild,rchild;
int parent;
}Node;
Node tree[LENGTH];
int length;
int root;
虽然在遍历速度上有一定的优势,但因所占空间比较大,是非主流二叉树。二叉树通常以链式存储。
链式存储:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
typedef char datatype;
typedef struct BinNode{
datatype data;
struct BinNode* lchild;
struct BinNode* rchild;
}BinNode;
typedef BinNode* bintree; //bintree本身是个指向结点的指针
三、二叉树的遍历
遍历即将树的所有结点访问且仅访问一次。按照根节点位置的不同分为前序遍历(先序遍历),中序遍历,后序遍历。另外还有一个遍历方式—层次遍历。
前序遍历:根节点->左子树->右子树
中序遍历:左子树->根节点->右子树
后序遍历:左子树->右子树->根节点
例如:求下面树的四种遍历

前序遍历:abdefgc
中序遍历:debgfac
后序遍历:edgfbca
层次遍历:abcdfeg
四、遍历的实现
递归实现(以前序遍历为例,其他的只是输出的位置稍有不同)
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
void preorder(bintree t){
if(t){
printf("%c ",t->data);
preorder(t->lchild);
preorder(t->rchild);
}
}
非递归的实现
因为当遍历过根节点之后还要回来,所以必须将其存起来。考虑到后进先出的特点,选用栈存储。数量确定,以顺序栈存储。
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
#define SIZE 100
typedef struct seqstack{
bintree data[SIZE];
int tag[SIZE]; //为后续遍历准备的
int top; //top为数组的下标
}seqstack;
void push(seqstack *s,bintree t){
if(s->top == SIZE){
printf("the stack is full\n");
}else{
s->top++;
s->data[s->top]=t;
}
}
bintree pop(seqstack *s){
if(s->top == -1){
return NULL;
}else{
s->top--;
return s->data[s->top+1];
}
}
1、前序遍历
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
void preorder_dev(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top = -1; //因为top在这里表示了数组中的位置,所以空为-1
if(!t){
printf("the tree is empty\n");
}else{
while(t || s.stop != -1){
while(t){ //只要结点不为空就应该入栈保存,与其左右结点无关
printf("%c ",t->data);
push(&s,t);
t= t->lchild;
}
t=pop(&s);
t=t->rchild;
}
}
}
2、中序遍历
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
void midorder(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top = -1;
if(!t){
printf("the tree is empty!\n");
}else{
while(t ||s.top != -1){
while(t){
push(&s,t);
t= t->lchild;
}
t=pop(&s);
printf("%c ",t->data);
t=t->rchild;
}
}
}
3、后序遍历
因为后序遍历最后还要要访问根结点一次,所以要访问根结点两次。采取夹标志位的方法解决这个问题。
这段代码非常纠结,对自己有信心的朋友可以尝试独立写一下。反正我是写了很长时间。逻辑不难,我画了一张逻辑图:

代码:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
void postorder_dev(bintree t){
seqstack s;
s.top = -1;
if(!t){
printf("the tree is empty!\n");
}else{
while(t || s.top != -1){ //栈空了的同时t也为空。
while(t){
push(&s,t);
s.tag[s.top] = 0; //设置访问标记,0为第一次访问,1为第二次访问
t= t->lchild;
}
if(s.tag[s.top] == 0){ //第一次访问时,转向同层右结点
t= s.data[s.top]; //左走到底时t是为空的,必须有这步!
s.tag[s.top]=1;
t=t->rchild;
}else {
while (s.tag[s.top] == 1){ //找到栈中下一个第一次访问的结点,退出循环时并没有pop所以为其左子结点
t = pop(&s);
printf("%c ",t->data);
}
t = NULL; //必须将t置空。跳过向左走,直接向右走
}
}
}
}
4、层次遍历:即每一层从左向右输出
元素需要储存有先进先出的特性,所以选用队列存储。
队列的定义:
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
#define MAX 1000
typedef struct seqqueue{
bintree data[MAX];
int front;
int rear;
}seqqueue;
void enter(seqqueue *q,bintree t){
if(q->rear == MAX){
printf("the queue is full!\n");
}else{
q->data[q->rear] = t;
q->rear++;
}
}
bintree del(seqqueue *q){
if(q->front == q->rear){
return NULL;
}else{
q->front++;
return q->data[q->front-1];
}
}
遍历实现
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
void level_tree(bintree t){
seqqueue q;
bintree temp;
q.front = q.rear = 0;
if(!t){
printf("the tree is empty\n");
return ;
}
enter(&q,t);
while(q.front != q.rear){
t=del(&q);
printf("%c ",t->data);
if(t->lchild){
enter(&q,t->lchild);
}
if(t->rchild){
enter(&q,t->rchild);
}
}
}
5、利用前序遍历的结果生成二叉树
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
//递归调用,不存点,想的时候只关注于一个点,因为还会回来的,不要跟踪程序运行,否则容易多加循环
void createtree(bintree *t){
datatype c;
if((c=getchar()) == '#')
*t = NULL;
else{
*t = (bintree)malloc(sizeof(BinNode));
(*t)->data = c;
createtree(&(*t)->lchild);
createtree(&(*t)->rchild);
}
}
6、二叉树的查找
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
bintree search_tree(bintree t,datatype x){
if(!t){
return NULL;
}
if(t->data == x){
return t;
}else{
if(!search_tree(t->lchild,x)){
return search_tree(t->rchild,x);
}
return t;
}
}
7、统计结点个数
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
int count_tree(bintree t){
if(t){
return (count_tree(t->lchild)+count_tree(t->rchild)+1);
}
return 0;
}
8、比较两个树是否相同
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
int is_equal(bintree t1,bintree t2){
if(!t1 && !t2){ //都为空就相等
return 1;
}
if(t1 && t2 && t1->data == t2->data){ //有一个为空或数据不同就不判断了
if(is_equal(t1->lchild,t2->lchild))
if(is_equal(t1->rchild,t2->rchild)){
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
9、求二叉树的深度
[cpp] view
plain copy
print?
int hight_tree(bintree t){
int h,left,right;
if(!t){
return 0;
}
left = hight_tree(t->lchild);
right = hight_tree(t->rchild);
h = (left>right?left:right)+1;
return h;
}
转载地址:点击打开链接
相关文章推荐
- 数据结构(六)——二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 数据结构 ——二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 数据结构(一)——二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 数据结构(六)——二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 数据结构(六)——二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 【基础备忘】二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 二叉树遍历及查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 用非递归实现二叉树的前序、中序、后序、层次遍历,用递归实现查找、统计个数、比较、求深度
- 二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 数据结构——二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 数据结构(六)——二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 数据结构(六)——二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 数据结构(六)——二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 数据结构 —— 二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
- 数据结构(六)——二叉树 前序、中序、后序、层次遍历及非递归实现 查找、统计个数、比较、求深度的递归实现
