powermock 入门介绍及使用示例
2017-11-17 16:19
513 查看
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/rainbow702/article/details/51783285
相关框架
JUnit4、Mockit、PowerMock
相关maven依赖
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
代码base
后面的测试代码均是针对下面class的
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
相关注解:所有测试类均须加上以下注解
2
3
其中:
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class) :表明用 PowerMockerRunner来运行测试用例,否则无法使用PowerMock
PrepareForTest({UserController.class}):所有需要测试的类,列在此处,以逗号分隔
@PowerMockIgnore(“javax.management.*”):为了解决使用powermock后,提示classloader错误
2
3
4
5
@Autowired 属性的注入方式
2
3
4
5
6
7
几点需要注意一下:
上面的方式,将会mock出来一个 user service对象,将将其注入到 UserController 的实例 uc 中去。
uc后面的那个 new UserController() 也可以不需要的。
mock普通方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
上面的代码中,有两点需要注意一下:
userService.addUser() 和 uc.addUser() 所使用的参数值须保持一致,这样才能让powermock在运行的时候进行参数匹配。(本篇最后会讲到,如何进行模糊匹配参数。)
thenReturn() 返回的值需要与 userService.addUser() 方法声明的返回值的类型保持一致,否则编译将会出错。
mock语句不能写成下面这样的:
否则将报异常:
2
3
mock抛异常
2
3
4
5
6
7
有几点需要注意一下:
如果 user service 中的 delUser() 方法抛出的是 checked exception,那么,thenThrow() 里需要抛出 new Exception()或者其子类
如果delUser() 方法抛出的是 unchecked exception,那么,thenThrow() 里需要抛出 new RuntimeException()或其子类
mock静态方法
2
3
4
5
6
有几点需要注意一下:
需要在@PrepareForTest注解中加上 FileHelper.class
调用 PowerMockito.mockStatic(),参数为 FileHelper.class
mock 返回值为 void 的方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
mock私有方法
方法一
PS:该方法中,还介绍了 mock私有字段的值 的方法。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
需要注意的是:此处的uc2是mock出来的,不是 UserControllerTest 类中的成员变量 uc
方法二
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
使用spy方法可以避免执行被测类中的成员函数,即mock掉不想被执行的私有方法。
测试私有方法(注意: 是测试,不是mock)
方法一
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
方法二
2
3
4
5
6
mock新建对象
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
mock返回值为 void 的 static 方法 (此为后期补充,所以没有提供相关完整代码)
方法一
2
3
4
方法二
2
3
mock 同一方法,返回不同的值 (此为后期补充,所以没有提供相关完整代码)
2
3
4
5
6
上面这个代码,我们是想让schemaSet返回true,好让测试代码能进入while循环。但是我们又不能让它一直返回 true,否则,while将陷入死循环。针对这种需求,应该怎么来处理呢?请看:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
上面的关键步骤中,thenReturn()方法返回了两个值,一个是true,一个是false。它的意思是,当next()第一次被调用时,将会返回 true,第二次及第二次以后的调用将会返回false。这就满足了我们的需求啦。
mock 泛型 (此为后期补充,所以没有提供相关完整代码)
2
3
4
上面的代码,我们在进行Test时,一般都会把nodeService中的getAllChildren()方法给mock掉,但是这样会导致nodes这个List的内容一直为空(因为它的的返回值为void)。为了满足在getAllChildren()被mock掉的情况下,nodes的内容又不能为空这一需求,我们可以将 ArrayList 的 构造函数给mock掉。但是,ArrayList是一个泛型类,那么在mock它的构造函数时,要如何指定泛型的类型呢?
方法一
在构造ArrayList时,不指定泛型类型。
PS:此种方法中,nodes变量的类型必须是 ArrayList,不能是 List。
2
3
4
5
6
方法二
通过使用PowerMock的 Answer 机制。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
mock可变参数
2
3
4
像上面这种方法,它有一个被称为varargs的参数,像这种参数应该如何来模拟呢?
其实很简单,因为varargs参数实际上是被当成数组来处理的,所以,我们只需要像下面这样来处理即可:
mock final方法
final 与普通方法一样mock,但是需要将其所在class添加到@PrepareForTest注解中,即
2
3
4
不然,会报类似下面的异常,让人很迷惑(因为我们明显就是在 mock 出来的对象上调用的方法):
mock 私有内部静态类对象
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
对于上面这个类,如果我们想去测试InnerClassA类的run方法,该怎么做呢?
首先,因为InnerClassA是一个private的内部类,所以我们是无法像下面这样来mock它的(编译就会报错,这个内部类是不可见的):
这种情况下,能想到的办法就是通过反射获取到InnerClassA的构造函数,然后生成一个对象。
那么如何来做呢?Whitebox可以帮你实现这一点:
2
3
4
5
6
mock super关键字
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
对于上面这个类的init方法,我们在测试时,一个难点就是,如何把父类中的init给mock掉。因为它不像我们其他情况下的方法调用,所以不好通过when().xxx()这种方式来mock。这种情况下,就轮到suppress方法出面了,下面直接给出mock方式:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
这里为什么是GenericServlet.class而不是HttpServlet.class,因为init(ServletConfig config)这个方法是定义在GenericServlet中而非HttpServlet中。
spy 使用的注意点
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
我本意是要测试getAllChildren()这个方法,在这个方法中,它调用了getChildren()方法,自然而然地,我准备将getChildren() mock掉,所以我写了下面的mock语句:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
本以为这样写,测试肯定可以通过的。
但是事实总是残酷的,运行之后,一直报错,说result.size()的值是0不是2。
这我就很纳闷了啊,明明返回的是长度为2的list啊,为什么却一直是0呢?
就是这么一个不起眼的问题,花了我5个小时来检查。
最终在网上一个贴子的点醒下,发现了问题所在。
问题出就出在下面这句看似理所当然的mock语句上:
它的目的是当ns的getChildren()被调用且参数是任意int类型的值时,都返回nodes这个list。但是这样写的话,它相当于只是mock了当参数为0的场合下才返回nodes这个list。具体原因如下(摘自org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito.doReturn()方法的javadoc)
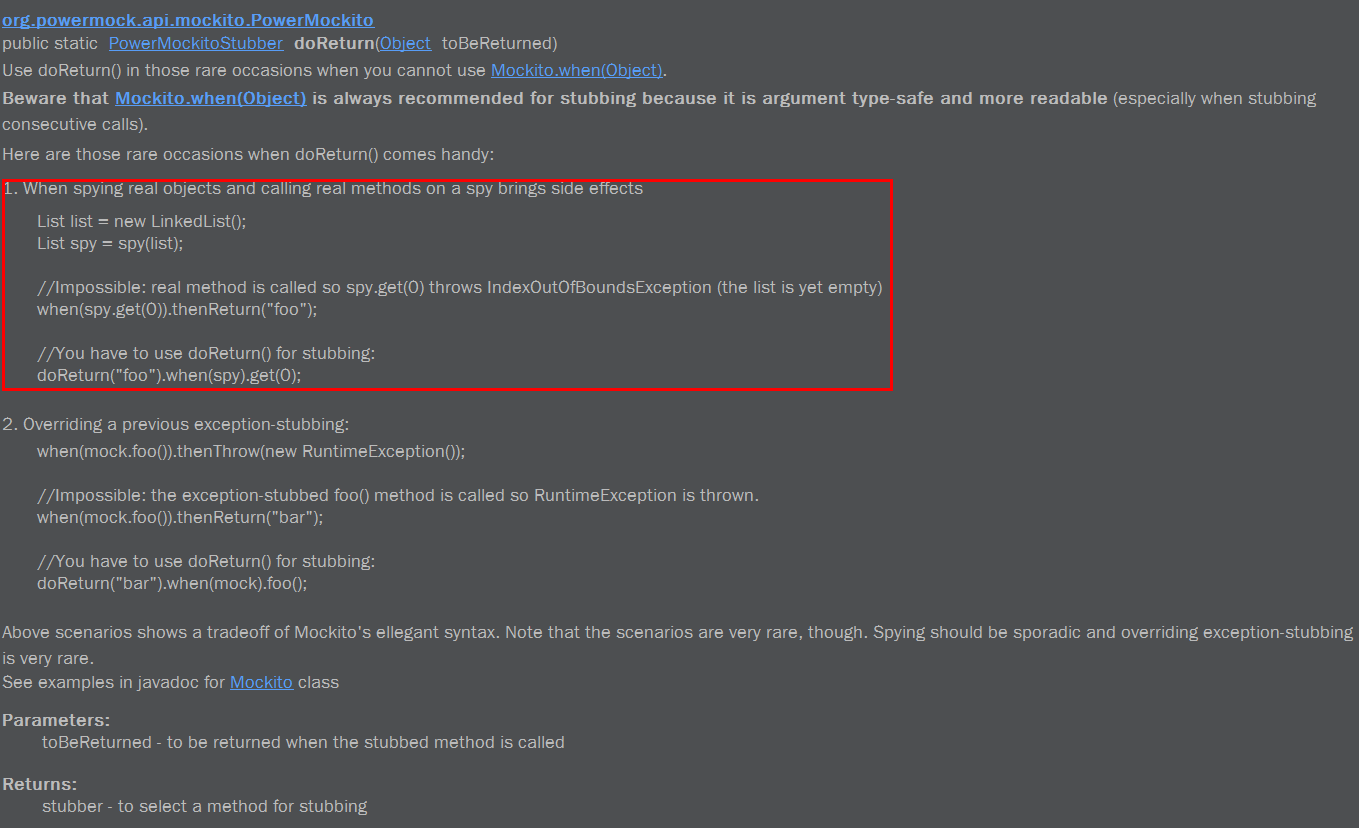
从这里的说明,我们知道我们的问题是什么了,上面的那种mock写法,其实就是相当于:
因为Matchers.anyInt()的返回值就是0.
所以,只有当参数值为0的时候,它才会返回nodes这个list。
然后,根据Javadoc,我们只需要按照如下来修改一下mock语句即可:
参数的模糊匹配
上面的测试用例中,在mock一个方法时,这个方法的参数都是事先准备好的。那么,有没有什么方式,使用在mock方法时,可以无视方法所需要的参数值呢?答案肯定有的,它就是org.mockito.Matchers。在这个类中,提供了很多 any*的方法,如:
anyObject()
anyString
anyList()
……
我们可以使用这些方法去避免构建那些难以模拟的输入参数,如:
2
3
4
5
6
7
Matchers的方便之处,各位可以自己尝试,包你用得爽~
不过,有一点需要注意一下:如果对某一个参数使用了Matcher,那么,这个方法的所有其他参数也必须使用Matcher,否则将会报错。
Power Mock 实现原理(转)
当某个测试方法被注解@PrepareForTest标注以后,在运行测试用例时,会创建一个新的org.powermock.core.classloader.MockClassLoader实例,然后加载该测试用例使用到的类(系统类除外)。
PowerMock会根据你的mock要求,去修改写在注解@PrepareForTest里的class文件(当前测试类会自动加入注解中),以满足特殊的mock需求。例如:去除final方法的final标识,在静态方法的最前面加入自己的虚拟实现等。
如果需要mock的是系统类的final方法和静态方法,PowerMock不会直接修改系统类的class文件,而是修改调用系统类的class文件,以满足mock需求。
参考文档:
官方文档:https://github.com/jayway/powermock
WhiteBox 介绍:https://github.com/jayway/powermock/wiki/BypassEncapsulation
官方spring sample: https://github.com/jayway/powermock/tree/master/examples/spring-mockito
关于 @Autowired 的注入问题:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/36799240/mock-final-class-and-inject-it-to-autowired-data-member-and-overcome-postconstru
http://agiledon.github.io/blog/2013/11/21/play-trick-with-powermock/
http://blog.csdn.net/jackiehff/article/details/14000779
http://www.cnblogs.com/jiyuqi/p/3564621.html
http://blog.csdn.net/dfqin/article/details/6604610
http://blog.csdn.net/booboo2006/article/details/7495863
最后附上测试类完整代码
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
相关框架
JUnit4、Mockit、PowerMock
相关maven依赖
<dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.powermock</groupId> <artifactId>powermock-module-junit4</artifactId> <version>1.6.5</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.powermock</groupId> <artifactId>powermock-api-mockito</artifactId> <version>1.6.5</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
代码base
后面的测试代码均是针对下面class的
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
public boolean addUser(UserDto userDto) {
int added = userService.addUser(userDto);
if (added <= 0) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
public boolean delUser(int id) {
try {
userService.delUser(id);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
public void saveUser(UserDto userDto) {
userService.saveUser(userDto);
}
public int countUser() {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
int count = 0;
if (ud.getId() > 0) {
count += 1;
}
return count;
}
public boolean modUser(UserDto userDto) {
int moded = userService.modUser(userDto);
return verifyMod(moded);
}
private boolean verifyMod(int moded) {
if (moded <= 0) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
public interface UserService {
int addUser(UserDto userDto);
int delUser(int id) throws Exception;
int modUser(UserDto userDto);
void saveUser(UserDto userDto);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class UserDto {
private int id;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class FileHelper {
public static String getName(String name) {
return "A_" + name;
}
}12
3
4
5
6
相关注解:所有测试类均须加上以下注解
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest({UserController.class, FileHelper.class})
@PowerMockIgnore("javax.management.*")12
3
其中:
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class) :表明用 PowerMockerRunner来运行测试用例,否则无法使用PowerMock
PrepareForTest({UserController.class}):所有需要测试的类,列在此处,以逗号分隔
@PowerMockIgnore(“javax.management.*”):为了解决使用powermock后,提示classloader错误
java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: com.ibm.mq.jms.MQQueueConnectionFactory$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$7cb492ab (initialization failure) at java.lang.J9VMInternals.initialize(J9VMInternals.java:140) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:60) ……1
2
3
4
5
@Autowired 属性的注入方式
public class UserControllerTest {
@Mock
private UserService userService;
@InjectMocks
private UserController uc = new UserController();
}12
3
4
5
6
7
几点需要注意一下:
上面的方式,将会mock出来一个 user service对象,将将其注入到 UserController 的实例 uc 中去。
uc后面的那个 new UserController() 也可以不需要的。
mock普通方法
@Test
public void testAddUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
PowerMockito.when(userService.addUser(ud)).thenReturn(1);
// can not stub like this
// PowerMockito.doReturn(1).when(userService.addUser(ud));
boolean result = uc.addUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
上面的代码中,有两点需要注意一下:
userService.addUser() 和 uc.addUser() 所使用的参数值须保持一致,这样才能让powermock在运行的时候进行参数匹配。(本篇最后会讲到,如何进行模糊匹配参数。)
thenReturn() 返回的值需要与 userService.addUser() 方法声明的返回值的类型保持一致,否则编译将会出错。
mock语句不能写成下面这样的:
PowerMockito.doReturn(1).when(userService.addUser(ud));1
否则将报异常:
org.mockito.exceptions.misusing.UnfinishedStubbingException: Unfinished stubbing detected here: ……1
2
3
mock抛异常
@Test
public void testDelUser() throws Exception {
int toDelete = 1;
PowerMockito.when(userService.delUser(toDelete)).thenThrow(new Exception("mock exception"));
boolean result = uc.delUser(toDelete);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
有几点需要注意一下:
如果 user service 中的 delUser() 方法抛出的是 checked exception,那么,thenThrow() 里需要抛出 new Exception()或者其子类
如果delUser() 方法抛出的是 unchecked exception,那么,thenThrow() 里需要抛出 new RuntimeException()或其子类
mock静态方法
@Test
public void mockFileHelper() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(FileHelper.class);
PowerMockito.when(FileHelper.getName("lucy")).thenReturn("lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("lucy"), "lily");
}12
3
4
5
6
有几点需要注意一下:
需要在@PrepareForTest注解中加上 FileHelper.class
调用 PowerMockito.mockStatic(),参数为 FileHelper.class
mock 返回值为 void 的方法
@Test
public void testSaveUser() throws Exception {
UserDto userDto = new UserDto();
// way one:
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(userService, "saveUser", userDto);
// way two:
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(userService).saveUser(userDto);
uc.saveUser(userDto);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
mock私有方法
方法一
PS:该方法中,还介绍了 mock私有字段的值 的方法。
@Test
public void testModUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
int moded = 1;
PowerMockito.when(userService.modUser(ud)).thenReturn(moded);
UserController uc2 = PowerMockito.mock(UserController.class);
// 给没有 setter 方法的 私有字段 赋值。
Whitebox.setInternalState(uc2, "userService", userService);
// 因为要测试的是 modUser() 方法,
// 所以,当调用这个方法时,应该让它调用真实的方法,而非被mock掉的方法
PowerMockito.when(uc2.modUser(ud)).thenCallRealMethod();
// 在modUser()方法中会调用verifyMod()这个私有方法,所以,需要将mock掉
PowerMockito.when(uc2, "verifyMod", moded).thenReturn(true);
boolean result = uc2.modUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
需要注意的是:此处的uc2是mock出来的,不是 UserControllerTest 类中的成员变量 uc
方法二
@Test
public void testModUser2() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
int moded = 1;
PowerMockito.when(userService.modUser(ud)).thenReturn(moded);
// 对uc进行监视
uc = PowerMockito.spy(uc);
// 当uc的verifyMod被执行时,将被mock掉
PowerMockito.when(uc, "verifyMod", moded).thenReturn(true);
boolean result = uc.modUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
使用spy方法可以避免执行被测类中的成员函数,即mock掉不想被执行的私有方法。
测试私有方法(注意: 是测试,不是mock)
方法一
@Test
public void testVerifyMod() throws Exception {
// 获取Method对象,
Method method = PowerMockito.method(UserController.class, "verifyMod", int.class);
// 调用Method的invoke方法来执行
boolean result = (boolean) method.invoke(uc, 1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
方法二
@Test
public void testVerifyMod2() throws Exception {
// 通过 Whitebox 来执行
boolean result = Whitebox.invokeMethod(uc, "verifyMod", 1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}12
3
4
5
6
mock新建对象
@Test
public void testCountUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
ud.setId(1);
PowerMockito.whenNew(UserDto.class).withNoArguments().thenReturn(ud);
int count = uc.countUser();
Assert.assertEquals(count, 1);
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
mock返回值为 void 的 static 方法 (此为后期补充,所以没有提供相关完整代码)
方法一
// "xxxUtil" 是类名 // "xxxStaticMethod" 是 static 方法的方法名 // 这里假设 "xxxStaticMethod" 需要两个参数,一个是 int 型,一个是 String 型 PowerMockito.doNothing().when(xxxUtil.class, "xxxStaticMethod", 1,"mysql");1
2
3
4
方法二
// 这种方式下,可以把所有需要模拟的 "static void" 方法,都列出来 PowerMockito.doNothing().when(xxxUtil.class); xxxUtil.xxxStaticMethod(1, 2);1
2
3
mock 同一方法,返回不同的值 (此为后期补充,所以没有提供相关完整代码)
// 待测试代码
DatabaseMetaData dbMetaData = connection.getMetaData();
ResultSet schemaSet = dbMetaData.getSchemas();
while (schemaSet.next()) {
schemaList.add(schemaSet.getString("TABLE_SCHEM"));
}12
3
4
5
6
上面这个代码,我们是想让schemaSet返回true,好让测试代码能进入while循环。但是我们又不能让它一直返回 true,否则,while将陷入死循环。针对这种需求,应该怎么来处理呢?请看:
Connection connection = PowerMockito.mock(Connection.class);
DatabaseMetaData databaseMetaData = PowerMockito.mock(DatabaseMetaData.class);
ResultSet resultSet = PowerMockito.mock(ResultSet.class);
PowerMockito.when(connection.getMetaData()).thenReturn(databaseMetaData);
PowerMockito.when(databaseMetaData.getSchemas()).thenReturn(resultSet);
// 关键步骤
PowerMockito.when(resultSet.next()).thenReturn(true, false);
PowerMockito.when(resultSet.getString("TABLE_SCHEM")).thenReturn("mock schema");12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
上面的关键步骤中,thenReturn()方法返回了两个值,一个是true,一个是false。它的意思是,当next()第一次被调用时,将会返回 true,第二次及第二次以后的调用将会返回false。这就满足了我们的需求啦。
mock 泛型 (此为后期补充,所以没有提供相关完整代码)
// 待测试代码 List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<>(); // getAllChildren() 是一个递归方法,且返回值为 void nodeService.getAllChildren(nodeId, nodes);1
2
3
4
上面的代码,我们在进行Test时,一般都会把nodeService中的getAllChildren()方法给mock掉,但是这样会导致nodes这个List的内容一直为空(因为它的的返回值为void)。为了满足在getAllChildren()被mock掉的情况下,nodes的内容又不能为空这一需求,我们可以将 ArrayList 的 构造函数给mock掉。但是,ArrayList是一个泛型类,那么在mock它的构造函数时,要如何指定泛型的类型呢?
方法一
在构造ArrayList时,不指定泛型类型。
PS:此种方法中,nodes变量的类型必须是 ArrayList,不能是 List。
ArrayList nodes = new ArrayList() {{
Node n = new Node();
n.setId(1);
this.add(n);
}};
PowerMockito.whenNew(ArrayList.class).withNoArguments().thenReturn(nodes);12
3
4
5
6
方法二
通过使用PowerMock的 Answer 机制。
final List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>() {{
Node n = new Node();
n.setId(1);
this.add(n);
}};
PowerMockito.whenNew(ArrayList.class).withNoArguments().thenAnswer(new Answer<List<Node>>() {
@Override
public List<Node> answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) throws Throwable {
return nodes;
}
});12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
mock可变参数
// 待mock方法
public List<Node> getFlowByPrjId(int prjId, Integer ...status) {
// do something
}12
3
4
像上面这种方法,它有一个被称为varargs的参数,像这种参数应该如何来模拟呢?
其实很简单,因为varargs参数实际上是被当成数组来处理的,所以,我们只需要像下面这样来处理即可:
when(xxxClass.getFlowByPrjId(Matchers.anyInt(), (Integer[])Matchers.anyVararg())).thenReturn(nodeList);1
mock final方法
final 与普通方法一样mock,但是需要将其所在class添加到@PrepareForTest注解中,即
@PrepareForTest({XXXClassWithFinalMethod.class})
XXXClassWithFinalMethod obj = mock(XXXClassWithFinalMethod.class);
when(obj.xxxFinalMethod()).thenReturn(xxxxxxx);12
3
4
不然,会报类似下面的异常,让人很迷惑(因为我们明显就是在 mock 出来的对象上调用的方法):
when() requires an argument which has to be 'a method call on a mock'1
mock 私有内部静态类对象
public class ClassA {
private static class InnerClassA {
private InnerClassA(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// do something
}
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
对于上面这个类,如果我们想去测试InnerClassA类的run方法,该怎么做呢?
首先,因为InnerClassA是一个private的内部类,所以我们是无法像下面这样来mock它的(编译就会报错,这个内部类是不可见的):
ClassA.InnerClassA aaa = mock(ClassA.InnerClassA.class);1
这种情况下,能想到的办法就是通过反射获取到InnerClassA的构造函数,然后生成一个对象。
那么如何来做呢?Whitebox可以帮你实现这一点:
Class clazz = Whitebox.getInnerClassType(ClassA.class, "InnerClassA");
Constructor constructor = Whitebox.getConstructor(clazz, String.class);
// the constructor needs a string parameter
Object object = constructor.newInstance("mock name");
// run the 'run' method
Whitebox.invokeMethod(object, "run");12
3
4
5
6
mock super关键字
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
super.init(config);
// do some thing
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
// do something
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
对于上面这个类的init方法,我们在测试时,一个难点就是,如何把父类中的init给mock掉。因为它不像我们其他情况下的方法调用,所以不好通过when().xxx()这种方式来mock。这种情况下,就轮到suppress方法出面了,下面直接给出mock方式:
@Test
public void testInit() throws Exception {
DispatcherServlet ds = spy(new DispatcherServlet());
// use "method()" to get the "init" method which is defined in "GenericServlet"
// use "suppress()" to suppress the "init" method
suppress(method(GenericServlet.class, "init", ServletConfig.class));
ds.init(mock(ServletConfig.class))
// other to do ...
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
这里为什么是GenericServlet.class而不是HttpServlet.class,因为init(ServletConfig config)这个方法是定义在GenericServlet中而非HttpServlet中。
spy 使用的注意点
// 待测试代码
public void getAllChildren(int parentNodeId, List<Node> allChildren) {
List<Node> children = getChildren(parentNodeId);
// some other logic
allChildren.addAll(children);
}
public List<Node> getChildren(int nodeId) {
List<Node> children = nodeMapper.getChildren(nodeId);
return children;
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
我本意是要测试getAllChildren()这个方法,在这个方法中,它调用了getChildren()方法,自然而然地,我准备将getChildren() mock掉,所以我写了下面的mock语句:
private XXXService ns = new XXXService(); ns = spy(ns); // nodes 是包含了2个 Node 的 List when(ns.getChildren(Matchers.anyInt())).thenReturn(nodes); List<Node> result = new ArrayList<>(); ns.getAllChildren(1, result); assertEquals(result.size(), 2);1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
本以为这样写,测试肯定可以通过的。
但是事实总是残酷的,运行之后,一直报错,说result.size()的值是0不是2。
这我就很纳闷了啊,明明返回的是长度为2的list啊,为什么却一直是0呢?
就是这么一个不起眼的问题,花了我5个小时来检查。
最终在网上一个贴子的点醒下,发现了问题所在。
问题出就出在下面这句看似理所当然的mock语句上:
when(ns.getChildren(Matchers.anyInt())).thenReturn(nodes);1
它的目的是当ns的getChildren()被调用且参数是任意int类型的值时,都返回nodes这个list。但是这样写的话,它相当于只是mock了当参数为0的场合下才返回nodes这个list。具体原因如下(摘自org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito.doReturn()方法的javadoc)

从这里的说明,我们知道我们的问题是什么了,上面的那种mock写法,其实就是相当于:
when(ns.getChildren(0)).thenReturn(nodes);1
因为Matchers.anyInt()的返回值就是0.
所以,只有当参数值为0的时候,它才会返回nodes这个list。
然后,根据Javadoc,我们只需要按照如下来修改一下mock语句即可:
doReturn(nodes).when(ns).getChildren(Matchers.anyInt());1
参数的模糊匹配
上面的测试用例中,在mock一个方法时,这个方法的参数都是事先准备好的。那么,有没有什么方式,使用在mock方法时,可以无视方法所需要的参数值呢?答案肯定有的,它就是org.mockito.Matchers。在这个类中,提供了很多 any*的方法,如:
anyObject()
anyString
anyList()
……
我们可以使用这些方法去避免构建那些难以模拟的输入参数,如:
@Test
public void mockFileHelper2() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(FileHelper.class);
PowerMockito.when(FileHelper.getName(Matchers.anyString())).thenReturn("lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("lucy"), "lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("hanmeimei"), "lily");
}12
3
4
5
6
7
Matchers的方便之处,各位可以自己尝试,包你用得爽~
不过,有一点需要注意一下:如果对某一个参数使用了Matcher,那么,这个方法的所有其他参数也必须使用Matcher,否则将会报错。
Power Mock 实现原理(转)
当某个测试方法被注解@PrepareForTest标注以后,在运行测试用例时,会创建一个新的org.powermock.core.classloader.MockClassLoader实例,然后加载该测试用例使用到的类(系统类除外)。
PowerMock会根据你的mock要求,去修改写在注解@PrepareForTest里的class文件(当前测试类会自动加入注解中),以满足特殊的mock需求。例如:去除final方法的final标识,在静态方法的最前面加入自己的虚拟实现等。
如果需要mock的是系统类的final方法和静态方法,PowerMock不会直接修改系统类的class文件,而是修改调用系统类的class文件,以满足mock需求。
参考文档:
官方文档:https://github.com/jayway/powermock
WhiteBox 介绍:https://github.com/jayway/powermock/wiki/BypassEncapsulation
官方spring sample: https://github.com/jayway/powermock/tree/master/examples/spring-mockito
关于 @Autowired 的注入问题:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/36799240/mock-final-class-and-inject-it-to-autowired-data-member-and-overcome-postconstru
http://agiledon.github.io/blog/2013/11/21/play-trick-with-powermock/
http://blog.csdn.net/jackiehff/article/details/14000779
http://www.cnblogs.com/jiyuqi/p/3564621.html
http://blog.csdn.net/dfqin/article/details/6604610
http://blog.csdn.net/booboo2006/article/details/7495863
最后附上测试类完整代码
import org.junit.Assert;1
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.mockito.InjectMocks;
import org.mockito.Matchers;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.powermock.api.mockito.PowerMockito;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.PowerMockIgnore;
import org.powermock.core.classloader.annotations.PrepareForTest;
import org.powermock.modules.junit4.PowerMockRunner;
import org.powermock.reflect.Whitebox;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
// 相关注解
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class) @PrepareForTest({UserController.class, FileHelper.class}) @PowerMockIgnore("javax.management.*")
public class UserControllerTest {
// @Autowired 属性的注入方式: 联合使用 @Mock 和 @InjectMocks
// 下面的方式,将会mock出来一个 user service对象,将将其注入到 UserController 的实例 uc 中去。
@Mock
private UserService userService;
@InjectMocks
private UserController uc;
/**
* mock普通方法
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testAddUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
PowerMockito.when(userService.addUser(ud)).thenReturn(1);
// can not stub like this
// PowerMockito.doReturn(1).when(userService.addUser(ud));
boolean result = uc.addUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
/**
* mock抛异常
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testDelUser() throws Exception {
int toDelete = 1;
// 如果 user service 中的 delUser() 方法抛出的是 checked exception,那么,thenThrow() 里需要抛出 Exception()或者其子类;
// 如果delUser() 方法抛出的是 unchecked exception,那么,thenThrow() 里需要抛出 RuntimeException()或其子类
PowerMockito.when(userService.delUser(toDelete)).thenThrow(new Exception("mock exception"));
boolean result = uc.delUser(toDelete);
Assert.assertEquals(result, false);
}
/**
* mock静态方法
*/
@Test
public void mockFileHelper() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(FileHelper.class);
PowerMockito.when(FileHelper.getName("lucy")).thenReturn("lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("lucy"), "lily");
}
/**
* mock 返回值为 void 的方法
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testSaveUser() throws Exception {
UserDto userDto = new UserDto();
// way one:
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(userService, "saveUser", userDto);
// way two:
PowerMockito.doNothing().when(userService).saveUser(userDto);
uc.saveUser(userDto);
}
/**
* mock私有方法<br />
* 方法一<br />
* PS:该方法中,还介绍了 mock私有字段的值 的方法。
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testModUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
int moded = 1;
PowerMockito.when(userService.modUser(ud)).thenReturn(moded);
UserController uc2 = PowerMockito.mock(UserController.class);
// 给没有 setter 方法的 私有字段 赋值。
Whitebox.setInternalState(uc2, "userService", userService);
// 因为要测试的是 modUser() 方法,
// 所以,当调用这个方法时,应该让它调用真实的方法,而非被mock掉的方法
PowerMockito.when(uc2.modUser(ud)).thenCallRealMethod();
// 在modUser()方法中会调用verifyMod()这个私有方法,所以,需要将mock掉
PowerMockito.when(uc2, "verifyMod", moded).thenReturn(true);
boolean result = uc2.modUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
/**
* mock私有方法<br />
* 方法二
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testModUser2() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
int moded = 1;
PowerMockito.when(userService.modUser(ud)).thenReturn(moded);
// 对uc进行监视
uc = PowerMockito.spy(uc);
// 当uc的verifyMod被执行时,将被mock掉
PowerMockito.when(uc, "verifyMod", moded).thenReturn(true);
boolean result = uc.modUser(ud);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
/**
* 测试私有方法(注意: 是测试,不是mock)<br />
* 方法一
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testVerifyMod() throws Exception {
// 获取Method对象,
Method method = PowerMockito.method(UserController.class, "verifyMod", int.class);
// 调用Method的invoke方法来执行
boolean result = (boolean) method.invoke(uc, 1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
/**
* 测试私有方法(注意: 是测试,不是mock)<br />
* 方法二
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testVerifyMod2() throws Exception {
// 通过 Whitebox 来执行
boolean result = Whitebox.invokeMethod(uc, "verifyMod", 1);
Assert.assertEquals(result, true);
}
/**
* mock新建对象
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testCountUser() throws Exception {
UserDto ud = new UserDto();
ud.setId(1);
PowerMockito.whenNew(UserDto.class).withNoArguments().thenReturn(ud);
int count = uc.countUser();
Assert.assertEquals(count, 1);
}
/**
* 参数的模糊匹配
*/
@Test
public void mockFileHelper2() {
PowerMockito.mockStatic(FileHelper.class);
PowerMockito.when(FileHelper.getName(Matchers.anyString())).thenReturn("lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("lucy"), "lily");
Assert.assertEquals(FileHelper.getName("hanmeimei"), "lily");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
相关文章推荐
- power mock 入门介绍及使用示例
- phonegap 开发入门 PhoneGap官方网站上有详细的入门示例教程,这里,我针对使用PhoneGap进行Android移动应用的开发对其官网的Get Started进行一些介绍、补充。 Ste
- Solr 使用入门介绍,以搜索论坛帖子为示例
- Spring入门示例及相关概念介绍
- NHibernate使用入门示例
- Windows WorkFlow Foundation 入门之二(使用WF开发介绍)
- NHibernate使用入门示例
- PHP快速入门教程:WHILE循环的使用示例
- 通用usb驱动libusb介绍和使用示例
- python html parser库lxml的介绍和使用(快速入门)
- Java基础系列之五:Spring使用入门示例
- 使用套件示例@GTK+ 2.0 中文教程连载 现在我们已经介绍了难的办法,这里介绍怎样用 gtk_item_factory 调用来做。
- jQuery powerFloat万能浮动层下拉层插件使用介绍
- jQuery powerFloat万能浮动层下拉层插件使用介绍
- Eclipse 入门及其基本的使用介绍
- 使用java操作Excel入门 ---- jxl介绍
- maven使用入门介绍
- GWT入门介绍(使用JSON格式的数据通讯)
- JAVA中常用接口的介绍及使用示例:java.lang.Comparable
- PHP快速入门教程:WHILE循环的使用示例
