IO多路复用之select总结
2017-10-27 15:11
531 查看
1、基本概念
IO多路复用是指内核一旦发现进程指定的一个或者多个IO条件准备读取,它就通知该进程。IO多路复用适用如下场合:
(1)当客户处理多个描述字时(一般是交互式输入和网络套接口),必须使用I/O复用。
(2)当一个客户同时处理多个套接口时,而这种情况是可能的,但很少出现。
(3)如果一个TCP服务器既要处理监听套接口,又要处理已连接套接口,一般也要用到I/O复用。
(4)如果一个服务器即要处理TCP,又要处理UDP,一般要使用I/O复用。
(5)如果一个服务器要处理多个服务或多个协议,一般要使用I/O复用。
与多进程和多线程技术相比,I/O多路复用技术的最大优势是系统开销小,系统不必创建进程/线程,也不必维护这些进程/线程,从而大大减小了系统的开销。
2、select函数
该函数准许进程指示内核等待多个事件中的任何一个发送,并只在有一个或多个事件发生或经历一段指定的时间后才唤醒。函数原型如下:
函数参数介绍如下:
(1)第一个参数maxfdp1指定待测试的描述字个数,它的值是待测试的最大描述字加1(因此把该参数命名为maxfdp1),描述字0、1、2...maxfdp1-1均将被测试。
因为文件描述符是从0开始的。
(2)中间的三个参数readset、writeset和exceptset指定我们要让内核测试读、写和异常条件的描述字。如果对某一个的条件不感兴趣,就可以把它设为空指针。struct fd_set可以理解为一个集合,这个集合中存放的是文件描述符,可通过以下四个宏进行设置:
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *fdset); //清空集合
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *fdset); //将一个给定的文件描述符加入集合之中
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *fdset); //将一个给定的文件描述符从集合中删除
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *fdset); // 检查集合中指定的文件描述符是否可以读写
(3)timeout告知内核等待所指定描述字中的任何一个就绪可花多少时间。其timeval结构用于指定这段时间的秒数和微秒数。
struct timeval{
long tv_sec; //seconds
long tv_usec; //microseconds
};
这个参数有三种可能:
(1)永远等待下去:仅在有一个描述字准备好I/O时才返回。为此,把该参数设置为空指针NULL。
(2)等待一段固定时间:在有一个描述字准备好I/O时返回,但是不超过由该参数所指向的timeval结构中指定的秒数和微秒数。
(3)根本不等待:检查描述字后立即返回,这称为轮询。为此,该参数必须指向一个timeval结构,而且其中的定时器值必须为0。
原理图:

select 需要驱动程序的支持,驱动程序实现fops内的poll 函数。 select 通过每个设备文件对应的 poll 函数提供的信息判断当前是否有资源可用 ( 如可读或写 ) ,如果有的话则返回可用资源的文件描述符个数,没有的话则睡眠,等待有资源变为可用时再被唤醒继续执行。
下面我们分两个过程来分析 select :
2. select的睡眠过程
支持阻塞操作的设备驱动通常会实现一组自身的等待队列如读/写等待队列用于支持上层(用户层)所需的BLOCK或NONBLOCK操作。当应用程序通过设备驱 动访问该设备时(默 认为BLOCK操 作),若该设备当 前没有数据可读或写,则将该用户进程插入到该设备驱动对应的读/写等待队列让其睡眠一段时间,等到有数据可读/写时再将该进程唤醒。
select就是巧妙的利用等待队列机制让用户进程适当在没有资源可读/写时睡眠,有资源可读/写时唤醒。下面我们看看select睡眠的详细过程。select 会循环遍历它所监测的fd_set内的所有文件描述符对应的驱动程序的poll函数。驱动程序提供的poll函数首先会将调用select的用户进程插入到该设备驱动对应资源的等待队列(如读/写等待队列) ,然后返回一个bitmask告诉select当前资源哪些可用。当select循环遍历完s所有fd_set内指定的文件描述符对应的 poll 函数后,如果没有一个资源可用(即没有一个文件可供操作) ,则select让该进程睡眠,一直等到有资源可用为止,进程被唤醒(或者timeout)继续往下执行。
下面分析一下代码是如何实现的。
select的调用path如下: sys_select -> core_sys_select -> do_select
其中最重要的函数是do_select,最主要的工作是在这里,前面两个函数主要做一些准备工作。do_select 定义如下:
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
int do_select(int n, fd_set_bits *fds, s64 *timeout)
{
struct poll_wqueues table;
poll_table *wait;
int retval, i;
rcu_read_lock();
retval = max_select_fd(n, fds);
rcu_read_unlock();
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
n = retval;
poll_initwait(&table);
wait = &table.pt;
if (!*timeout)
wait = NULL;
retval = 0; //retval用于保存已经准备好的描述符数,初始为0
for (;;) {
unsigned long *rinp, *routp, *rexp, *inp, *outp, *exp;
long __timeout;
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); //将当前进程状态改为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE
inp = fds->in; outp = fds->out; exp = fds->ex;
rinp = fds->res_in; routp = fds->res_out; rexp = fds->res_ex;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++rinp, ++routp, ++rexp) { //遍历每个描述符
unsigned long in, out, ex, all_bits, bit = 1, mask, j;
unsigned long res_in = 0, res_out = 0, res_ex = 0;
const struct file_operations *f_op = NULL;
struct file *file = NULL;
in = *inp++; out = *outp++; ex = *exp++;
all_bits = in | out | ex;
if (all_bits == 0) {
i += __NFDBITS; // //如果这个字没有待查找的描述符, 跳过这个长字(32位)
continue;
}
for (j = 0; j < __NFDBITS; ++j, ++i, bit <<= 1) { //遍历每个长字里的每个位
int fput_needed;
if (i >= n)
break;
if (!(bit & all_bits))
continue;
file = fget_light(i, &fput_needed);
if (file) {
f_op = file->f_op;
MARK(fs_select, "%d %lld",
i, (long long)*timeout);
mask = DEFAULT_POLLMASK;
if (f_op && f_op->poll)
/* 在这里循环调用所监测的fd_set内的所有文件描述符对应的驱动程序的poll函数 */
mask = (*f_op->poll)(file, retval ? NULL : wait);
fput_light(file, fput_needed);
if ((mask & POLLIN_SET) && (in & bit)) {
res_in |= bit; //如果是这个描述符可读, 将这个位置位
retval++; //返回描述符个数加1
}
if ((mask & POLLOUT_SET) && (out & bit)) {
res_out |= bit;
retval++;
}
if ((mask & POLLEX_SET) && (ex & bit)) {
res_ex |= bit;
retval++;
}
}
cond_resched();
}
//返回结果
if (res_in)
*rinp = res_in;
if (res_out)
*routp = res_out;
if (res_ex)
*rexp = res_ex;
}
wait = NULL;
/* 到这里遍历结束。retval保存了检测到的可操作的文件描述符的个数。如果有文件可操作,则跳出for(;;)循环,直接返回。若没有文件可操作且timeout时间未到同时没有收到signal,则执行schedule_timeout睡眠。睡眠时间长短由__timeout决定,一直等到该进程被唤醒。
那该进程是如何被唤醒的?被谁唤醒的呢?
我们看下面的select唤醒过程*/
if (retval || !*timeout || signal_pending(current))
break;
if(table.error) {
retval = table.error;
break;
}
if (*timeout < 0) {
/* Wait indefinitely */
__timeout = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT;
} else if (unlikely(*timeout >= (s64)MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT - 1)) {
/* Wait for longer than MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT. Do it in a loop */
__timeout = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT - 1;
*timeout -= __timeout;
} else {
__timeout = *timeout;
*timeout = 0;
}
__timeout = schedule_timeout(__timeout);
if (*timeout >= 0)
*timeout += __timeout;
}
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
poll_freewait(&table);
return retval;
}
3. select 的唤醒过程
前面介绍了 select 会循环遍历它所监测的 fd_set 内的所有文件描述符对应的驱动 程序的 poll 函 数。驱动程序提供的 poll 函数首先会将调用 select 的用户进程插入到该设备驱动对应资源的等待队列 ( 如读 / 写等待队列 ) ,然后返回一个 bitmask 告诉 select 当前资源哪些可用。
一个典型的驱动程序 poll 函数实现如下:
( 摘 自《 Linux Device Drivers – ThirdEdition 》 Page 165)
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
static unsigned int scull_p_poll(struct file *filp, poll_table *wait)
{
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
unsigned int mask = 0;
/*
* The buffer is circular; it is considered full
* if "wp" is right behind "rp" and empty if the
* two are equal.
*/
down(&dev->sem);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->inq, wait);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->outq, wait);
if (dev->rp != dev->wp)
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; /* readable */
if (spacefree(dev))
mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM; /* writable */
up(&dev->sem);
return mask;
}
将用户进程插入驱动的等待队列是通过poll_wait做的。Poll_wait定义如下:
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
static inline void poll_wait(struct file * filp, wait_queue_head_t * wait_address, poll_table *p)
{
if (p && wait_address)
p->qproc(filp, wait_address, p);
}
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
void poll_initwait(struct poll_wqueues *pwq)
{
init_poll_funcptr(&pwq->pt, __pollwait);
pwq->error = 0;
pwq->table = NULL;
pwq->inline_index = 0;
}
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
/* Add a new entry */
static void __pollwait(struct file *filp, wait_queue_head_t *wait_address,
poll_table *p)
{
struct poll_table_entry *entry = poll_get_entry(p);
if (!entry)
return;
get_file(filp);
entry->filp = filp;
entry->wait_address = wait_address;
init_waitqueue_entry(&entry->wait, current);
add_wait_queue(wait_address,&entry->wait);
}
入等待队列 wait_address 。 Wait_address 即在驱动 poll 函数内调用 poll_wait(filp,
&dev->inq, wait); 时传入的该驱动的 &dev->inq 或者 &dev->outq 等待队列。
到这里我们明白了 select 如何当前进程插入所有所监测的fd_set关联的驱动内的等待队列,那进 程究竟是何时让出 CPU 进入睡眠状态的呢?
进入睡眠状态是在do_select内调用schedule_timeout(__timeout) 实现的。当select遍历完fd_set内的所有设备文件,发现没有文件可操作时(即retval=0), 则调用schedule_timeout(__timeout)进入睡眠状态。
唤醒该进程的过程通常是在所监测文件的设备驱动内实现的, 驱动程序维护了针对自身资源读写的等待队列。当设备驱动发现自身资源变为可读写并且有进程睡眠在该资源的等待队列上时,就会唤醒这个资源等待队列上的进 程。
到这里明白了 select 进程被唤醒的过程。由于该进程是阻塞在所有监测的文件对应的设备等待队列上的,因此在timeout 时间内,只要任意个设备变为可操作,都会立即唤醒该进程,从而继续往下执行。这就实现了 select 的当有一个文件描述符可操作时
就立即唤醒执行的基本原理。
4、测试程序
写一个TCP回射程序,程序的功能是:客户端向服务器发送信息,服务器接收并原样发送给客户端,客户端显示出接收到的信息。
服务端程序如下:
客户端程序如下:
5、程序结果
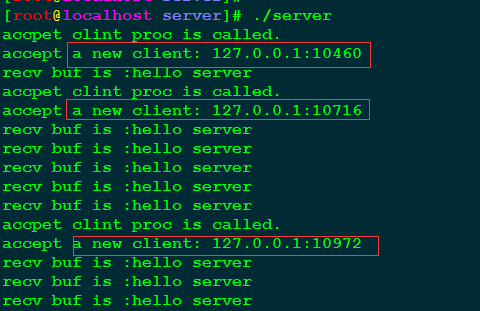
启动服务程序,执行三个个客户程序进行测试,结果如下图所示:
参考:
http://konglingchun.is-programmer.com/posts/12146.html
http://blog.163.com/smileface100@126/blog/static/27720874200951024532966/
IO多路复用是指内核一旦发现进程指定的一个或者多个IO条件准备读取,它就通知该进程。IO多路复用适用如下场合:
(1)当客户处理多个描述字时(一般是交互式输入和网络套接口),必须使用I/O复用。
(2)当一个客户同时处理多个套接口时,而这种情况是可能的,但很少出现。
(3)如果一个TCP服务器既要处理监听套接口,又要处理已连接套接口,一般也要用到I/O复用。
(4)如果一个服务器即要处理TCP,又要处理UDP,一般要使用I/O复用。
(5)如果一个服务器要处理多个服务或多个协议,一般要使用I/O复用。
与多进程和多线程技术相比,I/O多路复用技术的最大优势是系统开销小,系统不必创建进程/线程,也不必维护这些进程/线程,从而大大减小了系统的开销。
2、select函数
该函数准许进程指示内核等待多个事件中的任何一个发送,并只在有一个或多个事件发生或经历一段指定的时间后才唤醒。函数原型如下:
#include <sys/select.h> #include <sys/time.h> int select(int maxfdp1,fd_set *readset,fd_set *writeset,fd_set *exceptset,const struct timeval *timeout) 返回值:就绪描述符的数目,超时返回0,出错返回-1
函数参数介绍如下:
(1)第一个参数maxfdp1指定待测试的描述字个数,它的值是待测试的最大描述字加1(因此把该参数命名为maxfdp1),描述字0、1、2...maxfdp1-1均将被测试。
因为文件描述符是从0开始的。
(2)中间的三个参数readset、writeset和exceptset指定我们要让内核测试读、写和异常条件的描述字。如果对某一个的条件不感兴趣,就可以把它设为空指针。struct fd_set可以理解为一个集合,这个集合中存放的是文件描述符,可通过以下四个宏进行设置:
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *fdset); //清空集合
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *fdset); //将一个给定的文件描述符加入集合之中
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *fdset); //将一个给定的文件描述符从集合中删除
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *fdset); // 检查集合中指定的文件描述符是否可以读写
(3)timeout告知内核等待所指定描述字中的任何一个就绪可花多少时间。其timeval结构用于指定这段时间的秒数和微秒数。
struct timeval{
long tv_sec; //seconds
long tv_usec; //microseconds
};
这个参数有三种可能:
(1)永远等待下去:仅在有一个描述字准备好I/O时才返回。为此,把该参数设置为空指针NULL。
(2)等待一段固定时间:在有一个描述字准备好I/O时返回,但是不超过由该参数所指向的timeval结构中指定的秒数和微秒数。
(3)根本不等待:检查描述字后立即返回,这称为轮询。为此,该参数必须指向一个timeval结构,而且其中的定时器值必须为0。
原理图:

select 需要驱动程序的支持,驱动程序实现fops内的poll 函数。 select 通过每个设备文件对应的 poll 函数提供的信息判断当前是否有资源可用 ( 如可读或写 ) ,如果有的话则返回可用资源的文件描述符个数,没有的话则睡眠,等待有资源变为可用时再被唤醒继续执行。
下面我们分两个过程来分析 select :
2. select的睡眠过程
支持阻塞操作的设备驱动通常会实现一组自身的等待队列如读/写等待队列用于支持上层(用户层)所需的BLOCK或NONBLOCK操作。当应用程序通过设备驱 动访问该设备时(默 认为BLOCK操 作),若该设备当 前没有数据可读或写,则将该用户进程插入到该设备驱动对应的读/写等待队列让其睡眠一段时间,等到有数据可读/写时再将该进程唤醒。
select就是巧妙的利用等待队列机制让用户进程适当在没有资源可读/写时睡眠,有资源可读/写时唤醒。下面我们看看select睡眠的详细过程。select 会循环遍历它所监测的fd_set内的所有文件描述符对应的驱动程序的poll函数。驱动程序提供的poll函数首先会将调用select的用户进程插入到该设备驱动对应资源的等待队列(如读/写等待队列) ,然后返回一个bitmask告诉select当前资源哪些可用。当select循环遍历完s所有fd_set内指定的文件描述符对应的 poll 函数后,如果没有一个资源可用(即没有一个文件可供操作) ,则select让该进程睡眠,一直等到有资源可用为止,进程被唤醒(或者timeout)继续往下执行。
下面分析一下代码是如何实现的。
select的调用path如下: sys_select -> core_sys_select -> do_select
其中最重要的函数是do_select,最主要的工作是在这里,前面两个函数主要做一些准备工作。do_select 定义如下:
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
int do_select(int n, fd_set_bits *fds, s64 *timeout)
{
struct poll_wqueues table;
poll_table *wait;
int retval, i;
rcu_read_lock();
retval = max_select_fd(n, fds);
rcu_read_unlock();
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
n = retval;
poll_initwait(&table);
wait = &table.pt;
if (!*timeout)
wait = NULL;
retval = 0; //retval用于保存已经准备好的描述符数,初始为0
for (;;) {
unsigned long *rinp, *routp, *rexp, *inp, *outp, *exp;
long __timeout;
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); //将当前进程状态改为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE
inp = fds->in; outp = fds->out; exp = fds->ex;
rinp = fds->res_in; routp = fds->res_out; rexp = fds->res_ex;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++rinp, ++routp, ++rexp) { //遍历每个描述符
unsigned long in, out, ex, all_bits, bit = 1, mask, j;
unsigned long res_in = 0, res_out = 0, res_ex = 0;
const struct file_operations *f_op = NULL;
struct file *file = NULL;
in = *inp++; out = *outp++; ex = *exp++;
all_bits = in | out | ex;
if (all_bits == 0) {
i += __NFDBITS; // //如果这个字没有待查找的描述符, 跳过这个长字(32位)
continue;
}
for (j = 0; j < __NFDBITS; ++j, ++i, bit <<= 1) { //遍历每个长字里的每个位
int fput_needed;
if (i >= n)
break;
if (!(bit & all_bits))
continue;
file = fget_light(i, &fput_needed);
if (file) {
f_op = file->f_op;
MARK(fs_select, "%d %lld",
i, (long long)*timeout);
mask = DEFAULT_POLLMASK;
if (f_op && f_op->poll)
/* 在这里循环调用所监测的fd_set内的所有文件描述符对应的驱动程序的poll函数 */
mask = (*f_op->poll)(file, retval ? NULL : wait);
fput_light(file, fput_needed);
if ((mask & POLLIN_SET) && (in & bit)) {
res_in |= bit; //如果是这个描述符可读, 将这个位置位
retval++; //返回描述符个数加1
}
if ((mask & POLLOUT_SET) && (out & bit)) {
res_out |= bit;
retval++;
}
if ((mask & POLLEX_SET) && (ex & bit)) {
res_ex |= bit;
retval++;
}
}
cond_resched();
}
//返回结果
if (res_in)
*rinp = res_in;
if (res_out)
*routp = res_out;
if (res_ex)
*rexp = res_ex;
}
wait = NULL;
/* 到这里遍历结束。retval保存了检测到的可操作的文件描述符的个数。如果有文件可操作,则跳出for(;;)循环,直接返回。若没有文件可操作且timeout时间未到同时没有收到signal,则执行schedule_timeout睡眠。睡眠时间长短由__timeout决定,一直等到该进程被唤醒。
那该进程是如何被唤醒的?被谁唤醒的呢?
我们看下面的select唤醒过程*/
if (retval || !*timeout || signal_pending(current))
break;
if(table.error) {
retval = table.error;
break;
}
if (*timeout < 0) {
/* Wait indefinitely */
__timeout = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT;
} else if (unlikely(*timeout >= (s64)MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT - 1)) {
/* Wait for longer than MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT. Do it in a loop */
__timeout = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT - 1;
*timeout -= __timeout;
} else {
__timeout = *timeout;
*timeout = 0;
}
__timeout = schedule_timeout(__timeout);
if (*timeout >= 0)
*timeout += __timeout;
}
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
poll_freewait(&table);
return retval;
}
int do_select(int n, fd_set_bits *fds, s64 *timeout)
{
struct poll_wqueues table;
poll_table *wait;
int retval, i;
rcu_read_lock();
retval = max_select_fd(n, fds);
rcu_read_unlock();
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
n = retval;
poll_initwait(&table);
wait = &table.pt;
if (!*timeout)
wait = NULL;
retval = 0; //retval用于保存已经准备好的描述符数,初始为0
for (;;) {
unsigned long *rinp, *routp, *rexp, *inp, *outp, *exp;
long __timeout;
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); //将当前进程状态改为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE
inp = fds->in; outp = fds->out; exp = fds->ex;
rinp = fds->res_in; routp = fds->res_out; rexp = fds->res_ex;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++rinp, ++routp, ++rexp) { //遍历每个描述符
unsigned long in, out, ex, all_bits, bit = 1, mask, j;
unsigned long res_in = 0, res_out = 0, res_ex = 0;
const struct file_operations *f_op = NULL;
struct file *file = NULL;
in = *inp++; out = *outp++; ex = *exp++;
all_bits = in | out | ex;
if (all_bits == 0) {
i += __NFDBITS; // //如果这个字没有待查找的描述符, 跳过这个长字(32位)
continue;
}
for (j = 0; j < __NFDBITS; ++j, ++i, bit <<= 1) { //遍历每个长字里的每个位
int fput_needed;
if (i >= n)
break;
if (!(bit & all_bits))
continue;
file = fget_light(i, &fput_needed);
if (file) {
f_op = file->f_op;
MARK(fs_select, "%d %lld",
i, (long long)*timeout);
mask = DEFAULT_POLLMASK;
if (f_op && f_op->poll)
/* 在这里循环调用所监测的fd_set内的所有文件描述符对应的驱动程序的poll函数 */
mask = (*f_op->poll)(file, retval ? NULL : wait);
fput_light(file, fput_needed);
if ((mask & POLLIN_SET) && (in & bit)) {
res_in |= bit; //如果是这个描述符可读, 将这个位置位
retval++; //返回描述符个数加1
}
if ((mask & POLLOUT_SET) && (out & bit)) {
res_out |= bit;
retval++;
}
if ((mask & POLLEX_SET) && (ex & bit)) {
res_ex |= bit;
retval++;
}
}
cond_resched();
}
//返回结果
if (res_in)
*rinp = res_in;
if (res_out)
*routp = res_out;
if (res_ex)
*rexp = res_ex;
}
wait = NULL;
/* 到这里遍历结束。retval保存了检测到的可操作的文件描述符的个数。如果有文件可操作,则跳出for(;;)循环,直接返回。若没有文件可操作且timeout时间未到同时没有收到signal,则执行schedule_timeout睡眠。睡眠时间长短由__timeout决定,一直等到该进程被唤醒。
那该进程是如何被唤醒的?被谁唤醒的呢?
我们看下面的select唤醒过程*/
if (retval || !*timeout || signal_pending(current))
break;
if(table.error) {
retval = table.error;
break;
}
if (*timeout < 0) {
/* Wait indefinitely */
__timeout = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT;
} else if (unlikely(*timeout >= (s64)MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT - 1)) {
/* Wait for longer than MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT. Do it in a loop */
__timeout = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT - 1;
*timeout -= __timeout;
} else {
__timeout = *timeout;
*timeout = 0;
}
__timeout = schedule_timeout(__timeout);
if (*timeout >= 0)
*timeout += __timeout;
}
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
poll_freewait(&table);
return retval;
}3. select 的唤醒过程
前面介绍了 select 会循环遍历它所监测的 fd_set 内的所有文件描述符对应的驱动 程序的 poll 函 数。驱动程序提供的 poll 函数首先会将调用 select 的用户进程插入到该设备驱动对应资源的等待队列 ( 如读 / 写等待队列 ) ,然后返回一个 bitmask 告诉 select 当前资源哪些可用。
一个典型的驱动程序 poll 函数实现如下:
( 摘 自《 Linux Device Drivers – ThirdEdition 》 Page 165)
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
static unsigned int scull_p_poll(struct file *filp, poll_table *wait)
{
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
unsigned int mask = 0;
/*
* The buffer is circular; it is considered full
* if "wp" is right behind "rp" and empty if the
* two are equal.
*/
down(&dev->sem);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->inq, wait);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->outq, wait);
if (dev->rp != dev->wp)
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; /* readable */
if (spacefree(dev))
mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM; /* writable */
up(&dev->sem);
return mask;
}
static unsigned int scull_p_poll(struct file *filp, poll_table *wait)
{
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
unsigned int mask = 0;
/*
* The buffer is circular; it is considered full
* if "wp" is right behind "rp" and empty if the
* two are equal.
*/
down(&dev->sem);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->inq, wait);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->outq, wait);
if (dev->rp != dev->wp)
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; /* readable */
if (spacefree(dev))
mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM; /* writable */
up(&dev->sem);
return mask;
}将用户进程插入驱动的等待队列是通过poll_wait做的。Poll_wait定义如下:
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
static inline void poll_wait(struct file * filp, wait_queue_head_t * wait_address, poll_table *p)
{
if (p && wait_address)
p->qproc(filp, wait_address, p);
}
static inline void poll_wait(struct file * filp, wait_queue_head_t * wait_address, poll_table *p)
{
if (p && wait_address)
p->qproc(filp, wait_address, p);
}这里的p->qproc在do_select内poll_initwait(&table)被初始化为__pollwait,如下:[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
void poll_initwait(struct poll_wqueues *pwq)
{
init_poll_funcptr(&pwq->pt, __pollwait);
pwq->error = 0;
pwq->table = NULL;
pwq->inline_index = 0;
}
void poll_initwait(struct poll_wqueues *pwq)
{
init_poll_funcptr(&pwq->pt, __pollwait);
pwq->error = 0;
pwq->table = NULL;
pwq->inline_index = 0;
}__pollwait定义如下:[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
/* Add a new entry */
static void __pollwait(struct file *filp, wait_queue_head_t *wait_address,
poll_table *p)
{
struct poll_table_entry *entry = poll_get_entry(p);
if (!entry)
return;
get_file(filp);
entry->filp = filp;
entry->wait_address = wait_address;
init_waitqueue_entry(&entry->wait, current);
add_wait_queue(wait_address,&entry->wait);
}
/* Add a new entry */
static void __pollwait(struct file *filp, wait_queue_head_t *wait_address,
poll_table *p)
{
struct poll_table_entry *entry = poll_get_entry(p);
if (!entry)
return;
get_file(filp);
entry->filp = filp;
entry->wait_address = wait_address;
init_waitqueue_entry(&entry->wait, current);
add_wait_queue(wait_address,&entry->wait);
}通过 init_waitqueue_entry 初始化一个等待队列项,这个等待队列项关联的进程即当前调用 select 的进程。然后将这个等待队列项插入等待队列 wait_address 。 Wait_address 即在驱动 poll 函数内调用 poll_wait(filp,
&dev->inq, wait); 时传入的该驱动的 &dev->inq 或者 &dev->outq 等待队列。
到这里我们明白了 select 如何当前进程插入所有所监测的fd_set关联的驱动内的等待队列,那进 程究竟是何时让出 CPU 进入睡眠状态的呢?
进入睡眠状态是在do_select内调用schedule_timeout(__timeout) 实现的。当select遍历完fd_set内的所有设备文件,发现没有文件可操作时(即retval=0), 则调用schedule_timeout(__timeout)进入睡眠状态。
唤醒该进程的过程通常是在所监测文件的设备驱动内实现的, 驱动程序维护了针对自身资源读写的等待队列。当设备驱动发现自身资源变为可读写并且有进程睡眠在该资源的等待队列上时,就会唤醒这个资源等待队列上的进 程。
到这里明白了 select 进程被唤醒的过程。由于该进程是阻塞在所有监测的文件对应的设备等待队列上的,因此在timeout 时间内,只要任意个设备变为可操作,都会立即唤醒该进程,从而继续往下执行。这就实现了 select 的当有一个文件描述符可操作时
就立即唤醒执行的基本原理。
4、测试程序
写一个TCP回射程序,程序的功能是:客户端向服务器发送信息,服务器接收并原样发送给客户端,客户端显示出接收到的信息。
服务端程序如下:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4 #include <errno.h>
5 #include <netinet/in.h>
6 #include <sys/socket.h>
7 #include <sys/select.h>
8 #include <sys/types.h>
9 #include <netinet/in.h>
10 #include <arpa/inet.h>
11 #include <unistd.h>
12 #include <assert.h>
13
14 #define IPADDR "127.0.0.1"
15 #define PORT 8787
16 #define MAXLINE 1024
17 #define LISTENQ 5
18 #define SIZE 10
19
20 typedef struct server_context_st
21 {
22 int cli_cnt; /*客户端个数*/
23 int clifds[SIZE]; /*客户端的个数*/
24 fd_set allfds; /*句柄集合*/
25 int maxfd; /*句柄最大值*/
26 } server_context_st;
27 static server_context_st *s_srv_ctx = NULL;
28 /*===========================================================================
29 * ==========================================================================*/
30 static int create_server_proc(const char* ip,int port)
31 {
32 int fd;
33 struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
34 fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM,0);
35 if (fd == -1) {
36 fprintf(stderr, "create socket fail,erron:%d,reason:%s\n",
37 errno, strerror(errno));
38 return -1;
39 }
40
41 /*一个端口释放后会等待两分钟之后才能再被使用,SO_REUSEADDR是让端口释放后立即就可以被再次使用。*/
42 int reuse = 1;
43 if (setsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &reuse, sizeof(reuse)) == -1) {
44 return -1;
45 }
46
47 bzero(&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr));
48 servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
49 inet_pton(AF_INET,ip,&servaddr.sin_addr);
50 servaddr.sin_port = htons(port);
51
52 if (bind(fd,(struct sockaddr*)&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr)) == -1) {
53 perror("bind error: ");
54 return -1;
55 }
56
57 listen(fd,LISTENQ);
58
59 return fd;
60 }
61
62 static int accept_client_proc(int srvfd)
63 {
64 struct sockaddr_in cliaddr;
65 socklen_t cliaddrlen;
66 cliaddrlen = sizeof(cliaddr);
67 int clifd = -1;
68
69 printf("accpet clint proc is called.\n");
70
71 ACCEPT:
72 clifd = accept(srvfd,(struct sockaddr*)&cliaddr,&cliaddrlen);
73
74 if (clifd == -1) {
75 if (errno == EINTR) {
76 goto ACCEPT;
77 } else {
78 fprintf(stderr, "accept fail,error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
79 return -1;
80 }
81 }
82
83 fprintf(stdout, "accept a new client: %s:%d\n",
84 inet_ntoa(cliaddr.sin_addr),cliaddr.sin_port);
85
86 //将新的连接描述符添加到数组中
87 int i = 0;
88 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
89 if (s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] < 0) {
90 s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] = clifd;
91 s_srv_ctx->cli_cnt++;
92 break;
93 }
94 }
95
96 if (i == SIZE) {
97 fprintf(stderr,"too many clients.\n");
98 return -1;
99 }
100
101 }
102
103 static int handle_client_msg(int fd, char *buf)
104 {
105 assert(buf);
106 printf("recv buf is :%s\n", buf);
107 write(fd, buf, strlen(buf) +1);
108 return 0;
109 }
110
111 static void recv_client_msg(fd_set *readfds)
112 {
113 int i = 0, n = 0;
114 int clifd;
115 char buf[MAXLINE] = {0};
116 for (i = 0;i <= s_srv_ctx->cli_cnt;i++) {
117 clifd = s_srv_ctx->clifds[i];
118 if (clifd < 0) {
119 continue;
120 }
121 /*判断客户端套接字是否有数据*/
122 if (FD_ISSET(clifd, readfds)) {
123 //接收客户端发送的信息
124 n = read(clifd, buf, MAXLINE);
125 if (n <= 0) {
126 /*n==0表示读取完成,客户都关闭套接字*/
127 FD_CLR(clifd, &s_srv_ctx->allfds);
128 close(clifd);
129 s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] = -1;
130 continue;
131 }
132 handle_client_msg(clifd, buf);
133 }
134 }
135 }
136 static void handle_client_proc(int srvfd)
137 {
138 int clifd = -1;
139 int retval = 0;
140 fd_set *readfds = &s_srv_ctx->allfds;
141 struct timeval tv;
142 int i = 0;
143
144 while (1) {
145 /*每次调用select前都要重新设置文件描述符和时间,因为事件发生后,文件描述符和时间都被内核修改啦*/
146 FD_ZERO(readfds);
147 /*添加监听套接字*/
148 FD_SET(srvfd, readfds);
149 s_srv_ctx->maxfd = srvfd;
150
151 tv.tv_sec = 30;
152 tv.tv_usec = 0;
153 /*添加客户端套接字*/
154 for (i = 0; i < s_srv_ctx->cli_cnt; i++) {
155 clifd = s_srv_ctx->clifds[i];
156 /*去除无效的客户端句柄*/
157 if (clifd != -1) {
158 FD_SET(clifd, readfds);
159 }
160 s_srv_ctx->maxfd = (clifd > s_srv_ctx->maxfd ? clifd : s_srv_ctx->maxfd);
161 }
162
163 /*开始轮询接收处理服务端和客户端套接字*/
164 retval = select(s_srv_ctx->maxfd + 1, readfds, NULL, NULL, &tv);
165 if (retval == -1) {
166 fprintf(stderr, "select error:%s.\n", strerror(errno));
167 return;
168 }
169 if (retval == 0) {
170 fprintf(stdout, "select is timeout.\n");
171 continue;
172 }
173 if (FD_ISSET(srvfd, readfds)) {
174 /*监听客户端请求*/
175 accept_client_proc(srvfd);
176 } else {
177 /*接受处理客户端消息*/
178 recv_client_msg(readfds);
179 }
180 }
181 }
182
183 static void server_uninit()
184 {
185 if (s_srv_ctx) {
186 free(s_srv_ctx);
187 s_srv_ctx = NULL;
188 }
189 }
190
191 static int server_init()
192 {
193 s_srv_ctx = (server_context_st *)malloc(sizeof(server_context_st));
194 if (s_srv_ctx == NULL) {
195 return -1;
196 }
197
198 memset(s_srv_ctx, 0, sizeof(server_context_st));
199
200 int i = 0;
201 for (;i < SIZE; i++) {
202 s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] = -1;
203 }
204
205 return 0;
206 }
207
208 int main(int argc,char *argv[])
209 {
210 int srvfd;
211 /*初始化服务端context*/
212 if (server_init() < 0) {
213 return -1;
214 }
215 /*创建服务,开始监听客户端请求*/
216 srvfd = create_server_proc(IPADDR, PORT);
217 if (srvfd < 0) {
218 fprintf(stderr, "socket create or bind fail.\n");
219 goto err;
220 }
221 /*开始接收并处理客户端请求*/
222 handle_client_proc(srvfd);
223 server_uninit();
224 return 0;
225 err:
226 server_uninit();
227 return -1;
228 }客户端程序如下:
1 #include <netinet/in.h>
2 #include <sys/socket.h>
3 #include <stdio.h>
4 #include <string.h>
5 #include <stdlib.h>
6 #include <sys/select.h>
7 #include <time.h>
8 #include <unistd.h>
9 #include <sys/types.h>
10 #include <errno.h>
11
12 #define MAXLINE 1024
13 #define IPADDRESS "127.0.0.1"
14 #define SERV_PORT 8787
15
16 #define max(a,b) (a > b) ? a : b
17
18 static void handle_recv_msg(int sockfd, char *buf)
19 {
20 printf("client recv msg is:%s\n", buf);
21 sleep(5);
22 write(sockfd, buf, strlen(buf) +1);
23 }
24
25 static void handle_connection(int sockfd)
26 {
27 char sendline[MAXLINE],recvline[MAXLINE];
28 int maxfdp,stdineof;
29 fd_set readfds;
30 int n;
31 struct timeval tv;
32 int retval = 0;
33
34 while (1) {
35
36 FD_ZERO(&readfds);
37 FD_SET(sockfd,&readfds);
38 maxfdp = sockfd;
39
40 tv.tv_sec = 5;
41 tv.tv_usec = 0;
42
43 retval = select(maxfdp+1,&readfds,NULL,NULL,&tv);
44
45 if (retval == -1) {
46 return ;
47 }
48
49 if (retval == 0) {
50 printf("client timeout.\n");
51 continue;
52 }
53
54 if (FD_ISSET(sockfd, &readfds)) {
55 n = read(sockfd,recvline,MAXLINE);
56 if (n <= 0) {
57 fprintf(stderr,"client: server is closed.\n");
58 close(sockfd);
59 FD_CLR(sockfd,&readfds);
60 return;
61 }
62
63 handle_recv_msg(sockfd, recvline);
64 }
65 }
66 }
67
68 int main(int argc,char *argv[])
69 {
70 int sockfd;
71 struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
72
73 sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
74
75 bzero(&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr));
76 servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
77 servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
78 inet_pton(AF_INET,IPADDRESS,&servaddr.sin_addr);
79
80 int retval = 0;
81 retval = connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr));
82 if (retval < 0) {
83 fprintf(stderr, "connect fail,error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
84 return -1;
85 }
86
87 printf("client send to server .\n");
88 write(sockfd, "hello server", 32);
89
90 handle_connection(sockfd);
91
92 return 0;
93 }5、程序结果
启动服务程序,执行三个个客户程序进行测试,结果如下图所示:

参考:
http://konglingchun.is-programmer.com/posts/12146.html
http://blog.163.com/smileface100@126/blog/static/27720874200951024532966/
相关文章推荐
- IO多路复用之select总结
- io多路复用之select,poll,epoll总结
- IO多路复用之select总结
- IO多路复用之select总结
- IO多路复用之select总结
- IO多路复用总结:select pool epoll
- IO多路复用之select总结
- 【网络编程】IO 多路复用之 select 总结
- python网络编程——IO多路复用总结(select/poll/epoll)
- 同步和异步 阻塞和非阻塞 IO多路复用和select总结
- IO多路复用之select总结
- IO多路复用之select总结
- IO多路复用之select总结
- 聊聊IO多路复用之select、poll、epoll详解
- I/O多路复用之select总结
- 多路复用io接口-select()
- IO多路复用之epoll总结(转)
- IO多路复用之select
- 聊聊IO多路复用之select、poll、epoll详解
- 聊聊IO多路复用之select、poll、epoll详解
