详解Twitter开源分布式自增ID算法snowflake(附演算验证过程)
2017-10-16 12:17
696 查看
详解Twitter开源分布式自增ID算法snowflake,附演算验证过程
2017年01月22日 14:44:40
url: http://blog.csdn.net/li396864285/article/details/54668031
互联网快速发展的今天,分布式应用系统已经见怪不怪,在分布式系统中,我们需要各种各样的ID,既然是ID那么必然是要保证全局唯一,除此之外,不同当业务还需要不同的特性,比如像并发巨大的业务要求ID生成效率高,吞吐大;比如某些银行类业务,需要按每日日期制定交易流水号;又比如我们希望用户的ID是随机的,无序的,纯数字的,且位数长度是小于10位的。等等,不同的业务场景需要的ID特性各不一样,于是,衍生了各种ID生成器,但大多数利用数据库控制ID的生成,性能受数据库并发能力限制,那么有没有一款不需要依赖任何中间件(如数据库,分布式缓存服务等)的ID生成器呢?本着取之于开源,用之于开源的原则,今天,特此介绍Twitter开源的一款分布式自增ID算法snowflake,并附上算法原理推导和演算过程!
snowflake算法是一款本地生成的(ID生成过程不依赖任何中间件,无网络通信),保证ID全局唯一,并且ID总体有序递增,性能每秒生成300w+。
snowflake生产的ID二进制结构表示如下(每部分用-分开):
0 - 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 0 - 00000 - 00000 - 00000000 0000
第一位未使用,接下来的41位为毫秒级时间(41位的长度可以使用69年,从1970-01-01
08:00:00),然后是5位datacenterId(最大支持2^5=32个,二进制表示从00000-11111,也即是十进制0-31),和5位workerId(最大支持2^5=32个,原理同datacenterId),所以datacenterId*workerId最多支持部署1024个节点,最后12位是毫秒内的计数(12位的计数顺序号支持每个节点每毫秒产生2^12=4096个ID序号).
所有位数加起来共64位,恰好是一个Long型(转换为字符串长度为18).
单台机器实例,通过时间戳保证前41位是唯一的,分布式系统多台机器实例下,通过对每个机器实例分配不同的datacenterId和workerId避免中间的10位碰撞。最后12位每毫秒从0递增生产ID,再提一次:每毫秒最多生成4096个ID,每秒可达4096000个。理论上,只要CPU计算能力足够,单机每秒可生产400多万个,实测300w+,效率之高由此可见。
(该节改编自:http://www.cnblogs.com/relucent/p/4955340.html)
[java] view
plain copy
@ToString
@Slf4j
public class SnowflakeIdFactory {
private final long twepoch = 1288834974657L;
private final long workerIdBits = 5L;
private final long datacenterIdBits = 5L;
private final long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);
private final long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits);
private final long sequenceBits = 12L;
private final long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;
private final long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;
private final long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits;
private final long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits);
private long workerId;
private long datacenterId;
private long sequence = 0L;
private long lastTimestamp = -1L;
public SnowflakeIdFactory(long workerId, long datacenterId) {
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxWorkerId));
}
if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxDatacenterId));
}
this.workerId = workerId;
this.datacenterId = datacenterId;
}
public synchronized long nextId() {
long timestamp = timeGen();
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {
//服务器时钟被调整了,ID生成器停止服务.
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds", lastTimestamp - timestamp));
}
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);
}
} else {
sequence = 0L;
}
lastTimestamp = timestamp;
return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) | (workerId << workerIdShift) | sequence;
}
protected long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp) {
long timestamp = timeGen();
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = timeGen();
}
return timestamp;
}
protected long timeGen() {
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public static void testProductIdByMoreThread(int dataCenterId, int workerId, int n) throws InterruptedException {
List<Thread> tlist = new ArrayList<>();
Set<Long> setAll = new HashSet<>();
CountDownLatch cdLatch = new CountDownLatch(10);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int threadNo = dataCenterId;
Map<String,SnowflakeIdFactory> idFactories = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
//用线程名称做map key.
idFactories.put("snowflake"+i,new SnowflakeIdFactory(workerId, threadNo++));
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
Thread temp =new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Set<Long> setId = new HashSet<>();
SnowflakeIdFactory idWorker = idFactories.get(Thread.currentThread().getName());
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
setId.add(idWorker.nextId());
}
synchronized (setAll){
setAll.addAll(setId);
log.info("{}生产了{}个id,并成功加入到setAll中.",Thread.currentThread().getName(),n);
}
cdLatch.countDown();
}
},"snowflake"+i);
tlist.add(temp);
}
for(int j=0;j<10;j++){
tlist.get(j).start();
}
cdLatch.await();
long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
log.info("共耗时:{}毫秒,预期应该生产{}个id, 实际合并总计生成ID个数:{}",end1,10*n,setAll.size());
}
public static void testProductId(int dataCenterId, int workerId, int n){
SnowflakeIdFactory idWorker = new SnowflakeIdFactory(workerId, dataCenterId);
SnowflakeIdFactory idWorker2 = new SnowflakeIdFactory(workerId+1, dataCenterId);
Set<Long> setOne = new HashSet<>();
Set<Long> setTow = new HashSet<>();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
setOne.add(idWorker.nextId());//加入set
}
long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
log.info("第一批ID预计生成{}个,实际生成{}个<<<<*>>>>共耗时:{}",n,setOne.size(),end1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
setTow.add(idWorker2.nextId());//加入set
}
long end2 = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
log.info("第二批ID预计生成{}个,实际生成{}个<<<<*>>>>共耗时:{}",n,setTow.size(),end2);
setOne.addAll(setTow);
log.info("合并总计生成ID个数:{}",setOne.size());
}
public static void testPerSecondProductIdNums(){
SnowflakeIdFactory idWorker = new SnowflakeIdFactory(1, 2);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; System.currentTimeMillis()-start<1000; i++,count=i) {
/** 测试方法一: 此用法纯粹的生产ID,每秒生产ID个数为300w+ */
idWorker.nextId();
/** 测试方法二: 在log中打印,同时获取ID,此用法生产ID的能力受限于log.error()的吞吐能力.
* 每秒徘徊在10万左右. */
//log.error("{}",idWorker.nextId());
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
System.out.println(end);
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/** case1: 测试每秒生产id个数?
* 结论: 每秒生产id个数300w+ */
//testPerSecondProductIdNums();
/** case2: 单线程-测试多个生产者同时生产N个id,验证id是否有重复?
* 结论: 验证通过,没有重复. */
//testProductId(1,2,10000);//验证通过!
//testProductId(1,2,20000);//验证通过!
/** case3: 多线程-测试多个生产者同时生产N个id, 全部id在全局范围内是否会重复?
* 结论: 验证通过,没有重复. */
try {
testProductIdByMoreThread(1,2,100000);//单机测试此场景,性能损失至少折半!
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
测试用例:
说明:
演算使用的对象实例:SnowflakeIdFactory idWorker = new SnowflakeIdFactory(1, 2);
运行时数据workerId=1,datacenterId=2,分别表示机器实例的生产者编号,数据中心编号;
sequence=0表示每毫秒生产ID从0开始计数递增;
以下演算基于时间戳=1482394743339时刻进行推导。
一句话描述:以下演算模拟了1482394743339这一毫秒时刻,workerId=1,datacenterId=2的id生成器,生产第一个id的过程。

(图片原创,转载请注明出处,画图不易,谢谢!)
end!
https://github.com/twitter/snowflake http://www.cnblogs.com/relucent/p/4955340.html
2016年10月09日 19:48:56
url: http://blog.csdn.net/yangding_/article/details/52768906
Twitter Snowflake算法是用来在分布式场景下生成唯一ID的。
举个栗子:我们有10台分布式MySql服务器,我们的系统每秒能生成10W条数据插入到这10台机器里,现在我们需要为每一条数据生成一个全局唯一的ID, 并且这些 ID 有大致的顺序。

如图:最后生成的ID是一个long类型,long占64bit,符号位占1位,剩下63位,我们将这63位拆分成4段,就可以表示:某一毫秒内的某一集群内的某一机器的第几个ID。
有人会问:为什么时间戳要占41位?sequence要占12位?而其他两个要各占5位?
答:这是根据具体需求来分的,你也可以自己再去将这63为重新拆分。例如:sequence占12位就可以在同一毫秒内的同一集群的同一机器上同时有2^12 - 1 个线程。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
问题1:twepoch 为什么要等于1288834974657L 而不等于其他数?
答: 1288834974657 是 (Thu, 04 Nov 2010 01:42:54 GMT) 这一时刻到1970-01-01 00:00:00时刻所经过的毫秒数。41位字节作为时间戳数值的话,大约68年就会用完,假如你2010年1月1日开始开发系统,如果不减去2010年1月1日的时间戳,那么白白浪费40年的时间戳啊!所有减去twepoch 可以让系统在41位字节作为时间戳的情况下的运行时间更长。1288834974657L可能就是该项目开始成立的时间。
问题2:类似这种long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);操作是什么意思?
答: -1L ^ (-1L << n)表示占n个bit的数字的最大值是多少。举个栗子:-1L ^ (-1L << 2)等于10进制的3 ,即二进制的11表示十进制3。
注意:计算机存放数字都是存放数字的补码,正数的原码、补码、反码都一样,负数的补码是其反码加一。符号位做取反操作时不变,做逻辑与、或、非、异或操作时要参与运算。
再来个栗子:
-1L原码 : 1000 0001
-1L反码 : 1111 1110
-1L补码 : 1111 1111
-1L<<5 : 1110 0000
1111 1111 ^ 1110 0000 : 0001 1111
0001 1111是正数,所以补码、反码、原码都一样,所以0001 1111是31
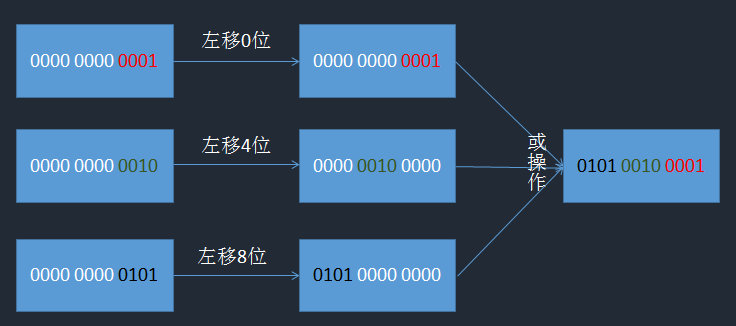
问题3:((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) | (workerId << workerIdShift) | sequence是什么意思?
答:我只发图不说话
2017年01月22日 14:44:40
url: http://blog.csdn.net/li396864285/article/details/54668031
1.snowflake简介
互联网快速发展的今天,分布式应用系统已经见怪不怪,在分布式系统中,我们需要各种各样的ID,既然是ID那么必然是要保证全局唯一,除此之外,不同当业务还需要不同的特性,比如像并发巨大的业务要求ID生成效率高,吞吐大;比如某些银行类业务,需要按每日日期制定交易流水号;又比如我们希望用户的ID是随机的,无序的,纯数字的,且位数长度是小于10位的。等等,不同的业务场景需要的ID特性各不一样,于是,衍生了各种ID生成器,但大多数利用数据库控制ID的生成,性能受数据库并发能力限制,那么有没有一款不需要依赖任何中间件(如数据库,分布式缓存服务等)的ID生成器呢?本着取之于开源,用之于开源的原则,今天,特此介绍Twitter开源的一款分布式自增ID算法snowflake,并附上算法原理推导和演算过程!snowflake算法是一款本地生成的(ID生成过程不依赖任何中间件,无网络通信),保证ID全局唯一,并且ID总体有序递增,性能每秒生成300w+。
2.snowflake算法原理
snowflake生产的ID二进制结构表示如下(每部分用-分开):0 - 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 0 - 00000 - 00000 - 00000000 0000
第一位未使用,接下来的41位为毫秒级时间(41位的长度可以使用69年,从1970-01-01
08:00:00),然后是5位datacenterId(最大支持2^5=32个,二进制表示从00000-11111,也即是十进制0-31),和5位workerId(最大支持2^5=32个,原理同datacenterId),所以datacenterId*workerId最多支持部署1024个节点,最后12位是毫秒内的计数(12位的计数顺序号支持每个节点每毫秒产生2^12=4096个ID序号).
所有位数加起来共64位,恰好是一个Long型(转换为字符串长度为18).
单台机器实例,通过时间戳保证前41位是唯一的,分布式系统多台机器实例下,通过对每个机器实例分配不同的datacenterId和workerId避免中间的10位碰撞。最后12位每毫秒从0递增生产ID,再提一次:每毫秒最多生成4096个ID,每秒可达4096000个。理论上,只要CPU计算能力足够,单机每秒可生产400多万个,实测300w+,效率之高由此可见。
(该节改编自:http://www.cnblogs.com/relucent/p/4955340.html)
3.snowflake算法源码(java版)
[java] viewplain copy
@ToString
@Slf4j
public class SnowflakeIdFactory {
private final long twepoch = 1288834974657L;
private final long workerIdBits = 5L;
private final long datacenterIdBits = 5L;
private final long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);
private final long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits);
private final long sequenceBits = 12L;
private final long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;
private final long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;
private final long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits;
private final long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits);
private long workerId;
private long datacenterId;
private long sequence = 0L;
private long lastTimestamp = -1L;
public SnowflakeIdFactory(long workerId, long datacenterId) {
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxWorkerId));
}
if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxDatacenterId));
}
this.workerId = workerId;
this.datacenterId = datacenterId;
}
public synchronized long nextId() {
long timestamp = timeGen();
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {
//服务器时钟被调整了,ID生成器停止服务.
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds", lastTimestamp - timestamp));
}
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);
}
} else {
sequence = 0L;
}
lastTimestamp = timestamp;
return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) | (workerId << workerIdShift) | sequence;
}
protected long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp) {
long timestamp = timeGen();
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = timeGen();
}
return timestamp;
}
protected long timeGen() {
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public static void testProductIdByMoreThread(int dataCenterId, int workerId, int n) throws InterruptedException {
List<Thread> tlist = new ArrayList<>();
Set<Long> setAll = new HashSet<>();
CountDownLatch cdLatch = new CountDownLatch(10);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int threadNo = dataCenterId;
Map<String,SnowflakeIdFactory> idFactories = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
//用线程名称做map key.
idFactories.put("snowflake"+i,new SnowflakeIdFactory(workerId, threadNo++));
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
Thread temp =new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Set<Long> setId = new HashSet<>();
SnowflakeIdFactory idWorker = idFactories.get(Thread.currentThread().getName());
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
setId.add(idWorker.nextId());
}
synchronized (setAll){
setAll.addAll(setId);
log.info("{}生产了{}个id,并成功加入到setAll中.",Thread.currentThread().getName(),n);
}
cdLatch.countDown();
}
},"snowflake"+i);
tlist.add(temp);
}
for(int j=0;j<10;j++){
tlist.get(j).start();
}
cdLatch.await();
long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
log.info("共耗时:{}毫秒,预期应该生产{}个id, 实际合并总计生成ID个数:{}",end1,10*n,setAll.size());
}
public static void testProductId(int dataCenterId, int workerId, int n){
SnowflakeIdFactory idWorker = new SnowflakeIdFactory(workerId, dataCenterId);
SnowflakeIdFactory idWorker2 = new SnowflakeIdFactory(workerId+1, dataCenterId);
Set<Long> setOne = new HashSet<>();
Set<Long> setTow = new HashSet<>();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
setOne.add(idWorker.nextId());//加入set
}
long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
log.info("第一批ID预计生成{}个,实际生成{}个<<<<*>>>>共耗时:{}",n,setOne.size(),end1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
setTow.add(idWorker2.nextId());//加入set
}
long end2 = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
log.info("第二批ID预计生成{}个,实际生成{}个<<<<*>>>>共耗时:{}",n,setTow.size(),end2);
setOne.addAll(setTow);
log.info("合并总计生成ID个数:{}",setOne.size());
}
public static void testPerSecondProductIdNums(){
SnowflakeIdFactory idWorker = new SnowflakeIdFactory(1, 2);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; System.currentTimeMillis()-start<1000; i++,count=i) {
/** 测试方法一: 此用法纯粹的生产ID,每秒生产ID个数为300w+ */
idWorker.nextId();
/** 测试方法二: 在log中打印,同时获取ID,此用法生产ID的能力受限于log.error()的吞吐能力.
* 每秒徘徊在10万左右. */
//log.error("{}",idWorker.nextId());
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
System.out.println(end);
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/** case1: 测试每秒生产id个数?
* 结论: 每秒生产id个数300w+ */
//testPerSecondProductIdNums();
/** case2: 单线程-测试多个生产者同时生产N个id,验证id是否有重复?
* 结论: 验证通过,没有重复. */
//testProductId(1,2,10000);//验证通过!
//testProductId(1,2,20000);//验证通过!
/** case3: 多线程-测试多个生产者同时生产N个id, 全部id在全局范围内是否会重复?
* 结论: 验证通过,没有重复. */
try {
testProductIdByMoreThread(1,2,100000);//单机测试此场景,性能损失至少折半!
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
测试用例:
/** case1: 测试每秒生产id个数?
* 结论: 每秒生产id个数300w+ */
//testPerSecondProductIdNums();
/** case2: 单线程-测试多个生产者同时生产N个id,验证id是否有重复?
* 结论: 验证通过,没有重复. */
//testProductId(1,2,10000);//验证通过!
//testProductId(1,2,20000);//验证通过!
/** case3: 多线程-测试多个生产者同时生产N个id, 全部id在全局范围内是否会重复?
* 结论: 验证通过,没有重复. */
try {
testProductIdByMoreThread(1,2,100000);//单机测试此场景,性能损失至少折半!
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
4.snowflake算法推导和演算过程
说明:演算使用的对象实例:SnowflakeIdFactory idWorker = new SnowflakeIdFactory(1, 2);
运行时数据workerId=1,datacenterId=2,分别表示机器实例的生产者编号,数据中心编号;
sequence=0表示每毫秒生产ID从0开始计数递增;
以下演算基于时间戳=1482394743339时刻进行推导。
一句话描述:以下演算模拟了1482394743339这一毫秒时刻,workerId=1,datacenterId=2的id生成器,生产第一个id的过程。

(图片原创,转载请注明出处,画图不易,谢谢!)
end!
参考
https://github.com/twitter/snowflake http://www.cnblogs.com/relucent/p/4955340.html
Twitter Snowflake算法详解
2016年10月09日 19:48:56url: http://blog.csdn.net/yangding_/article/details/52768906
一、简介
Twitter Snowflake算法是用来在分布式场景下生成唯一ID的。举个栗子:我们有10台分布式MySql服务器,我们的系统每秒能生成10W条数据插入到这10台机器里,现在我们需要为每一条数据生成一个全局唯一的ID, 并且这些 ID 有大致的顺序。
二、算法图解

如图:最后生成的ID是一个long类型,long占64bit,符号位占1位,剩下63位,我们将这63位拆分成4段,就可以表示:某一毫秒内的某一集群内的某一机器的第几个ID。
有人会问:为什么时间戳要占41位?sequence要占12位?而其他两个要各占5位?
答:这是根据具体需求来分的,你也可以自己再去将这63为重新拆分。例如:sequence占12位就可以在同一毫秒内的同一集群的同一机器上同时有2^12 - 1 个线程。
三、快快上码
public class IdWorker {
protected static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(IdWorker.class);
private long workerId;
private long datacenterId;
private long sequence = 0L;
private long twepoch = 1288834974657L;
private long workerIdBits = 5L;
private long datacenterIdBits = 5L;
private long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);
private long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits);
private long sequenceBits = 12L;
private long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;
private long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;
private long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits;
private long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits);
private long lastTimestamp = -1L;
public IdWorker(long workerId, long datacenterId) {
// sanity check for workerId
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxWorkerId));
}
if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxDatacenterId));
}
this.workerId = workerId;
this.datacenterId = datacenterId;
LOG.info(String.format("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter id bits %d, worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d", timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits, workerId));
}
public synchronized long nextId() {
long timestamp = timeGen();
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {
LOG.error(String.format("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.", lastTimestamp));
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds", lastTimestamp - timestamp));
}
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);
}
} else {
sequence = 0L;
}
lastTimestamp = timestamp;
return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) | (workerId << workerIdShift) | sequence;
}
protected long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp) {
long timestamp = timeGen();
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = timeGen();
}
return timestamp;
}
protected long timeGen() {
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
四、Q&A
问题1:twepoch 为什么要等于1288834974657L 而不等于其他数? 答: 1288834974657 是 (Thu, 04 Nov 2010 01:42:54 GMT) 这一时刻到1970-01-01 00:00:00时刻所经过的毫秒数。41位字节作为时间戳数值的话,大约68年就会用完,假如你2010年1月1日开始开发系统,如果不减去2010年1月1日的时间戳,那么白白浪费40年的时间戳啊!所有减去twepoch 可以让系统在41位字节作为时间戳的情况下的运行时间更长。1288834974657L可能就是该项目开始成立的时间。
问题2:类似这种long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);操作是什么意思?
答: -1L ^ (-1L << n)表示占n个bit的数字的最大值是多少。举个栗子:-1L ^ (-1L << 2)等于10进制的3 ,即二进制的11表示十进制3。
注意:计算机存放数字都是存放数字的补码,正数的原码、补码、反码都一样,负数的补码是其反码加一。符号位做取反操作时不变,做逻辑与、或、非、异或操作时要参与运算。
再来个栗子:
-1L原码 : 1000 0001
-1L反码 : 1111 1110
-1L补码 : 1111 1111
-1L<<5 : 1110 0000
1111 1111 ^ 1110 0000 : 0001 1111
0001 1111是正数,所以补码、反码、原码都一样,所以0001 1111是31
问题3:((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | (datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) | (workerId << workerIdShift) | sequence是什么意思?
答:我只发图不说话

相关文章推荐
- 详解Twitter开源分布式自增ID算法snowflake,附演算验证过程
- Twitter开源分布式自增ID算法snowflake(Java)
- Twitter的分布式自增ID算法snowflake
- Twitter-Snowflake,64位自增ID算法详解
- Twitter的分布式自增ID算法snowflake (Java版)
- Twitter-Snowflake,64位自增ID算法详解
- Twitter的分布式自增ID算法snowflake (Java版)
- Twitter的分布式雪花算法 SnowFlake 每秒自增生成26个万个可排序的ID (Java版)
- Twitter的分布式自增ID算法snowflake
- Twitter的分布式自增ID算法snowflake - C#版
- Twitter的分布式自增ID算法snowflake(Java版)
- Twitter-Snowflake(64位分布式ID算法)分析与JAVA实现
- Twitter的分布式雪花算法 SnowFlake 每秒自增生成26个万个可排序的ID (Java版)
- Twitter的分布式自增ID算法snowflake (Java版)
- Twitter-Snowflake,64位自增ID算法详解
- 分布式全局ID的Twitter的Snowflake(雪花算法)
- Twitter的分布式自增ID算法snowflake (Java版)
- Twitter的分布式自增ID算法snowflake (Java版)
- Twitter-Snowflake,64位自增ID算法详解
- Twitter-Snowflake,64位自增ID算法详解
