Python进行数据分析(一)初步学习 对时区进行计数
2017-09-27 20:30
726 查看
time_zones[:10] Out[19]: [u'America/New_York', u'America/Denver', u'America/New_York', u'America/Sao_Paulo', u'America/New_York', u'America/New_York', u'Europe/Warsaw', u'', u'', u'']
接下来对时区进行计数,这里使用两种方法,一种使用Python标准库,另一个比较简(使用pandas)。
def get_counts(sequence):
counts = {}
for x in sequence:
if x in counts:
counts[x] += 1
else:
counts[x] = 1
return counts
get_counts(time_zones[:10])
Out[21]:
{u'': 3,
u'America/Denver': 1,
u'America/New_York': 4,
u'America/Sao_Paulo': 1,
u'Europe/Warsaw': 1}使用标准款,简洁版
from collections import defaultdict
def get_counts2(sequence):
counts = defaultdict(int) # 所有的值均会被初始化为0
for x in sequence:
counts[x] += 1
return counts
get_counts2(time_zones[:10])
Out[24]: defaultdict(<type 'int'>, {u'Europe/Warsaw': 1, u'America/Denver': 1, u'America/Sao_Paulo': 1, u'': 3, u'America/New_York': 4})要它对时区进行处理,传入time_zones传入即可:
counts = get_counts(time_zones) counts['America/New_York'] Out[27]: 1251 len(time_zones) Out[28]: 3440
得到前10位的时区及计数值:
def top_counts(count_dict, n = 10): value_key_pairs = [(count,tz) for tz,count in count_dict.items()] value_key_pairs.sort() return value_key_pairs[-n:] # 得到倒数第n个数到最后 top_counts(counts) Out[30]: [(33, u'America/Sao_Paulo'), (35, u'Europe/Madrid'), (36, u'Pacific/Honolulu'), (37, u'Asia/Tokyo'), (74, u'Europe/London'), (191, u'America/Denver'), (382, u'America/Los_Angeles'), (400, u'America/Chicago'), (521, u''), (1251, u'America/New_York')]
使用collection.Counter类,使这个任务变的简单:
from collections import Counter counts = Counter(time_zones) counts.most_common(10) Out[33]: [(u'America/New_York', 1251), (u'', 521), (u'America/Chicago', 400), (u'America/Los_Angeles', 382), (u'America/Denver', 191), (u'Europe/London', 74), (u'Asia/Tokyo', 37), (u'Pacific/Honolulu', 36), (u'Europe/Madrid', 35), (u'America/Sao_Paulo', 33)]
DataFrame是pandas中最重要的数据结构,用于将数据表示为一个表格。从一组数据中创建DataFrame:
from pandas import DataFrame, Series import pandas as pd; import numpy as np frame = DataFrame(records) frame Out[38]:
frame['tz'][:10] Out[40]: 0 America/New_York 1 America/Denver 2 America/New_York 3 America/Sao_Paulo 4 America/New_York 5 America/New_York 6 Europe/Warsaw 7 8 9 Name: tz, dtype: object
这里frame的输出形式是摘要视图,主要用于较大的DataFrame对象。frame['tz']所返回的Series对象有一个value_counts方法,改方法可以让我们得到所需的信息:
tz_counts = frame['tz'].value_counts() tz_counts[:10] Out[42]: America/New_York 1251 521 America/Chicago 400 America/Los_Angeles 382 America/Denver 191 Europe/London 74 Asia/Tokyo 37 Pacific/Honolulu 36 Europe/Madrid 35 America/Sao_Paulo 33 dtype: int64
利用绘图库(matplotlib)为这段数据生成一张的图片。
为此,先给记录中未知或缺失的时区填上一个替代值。fillna函数可以替代缺失值(NA),而未知值(空字符串)则可通过 布尔型数组索引加以替换:
clean_tz = frame['tz'].fillna('Missing') # 替换缺失值(NA)
clean_tz[clean_tz == ''] = 'Unknown' # 未知值通过布尔型数组索引加以替换,注意这里的 clean_tz是 Series对象
tz_counts = clean_tz.value_counts()
tz_counts[:10]
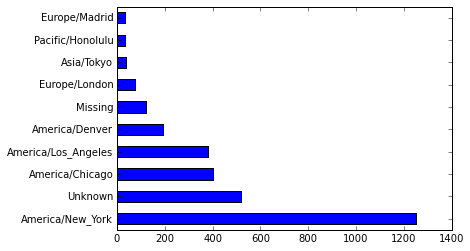
Out[46]:
America/New_York 1251
Unknown 521
America/Chicago 400
America/Los_Angeles 382
America/Denver 191
Missing 120
Europe/London 74
Asia/Tokyo 37
Pacific/Honolulu 36
Europe/Madrid 35
dtype: int64tz_counts[:10].plot(kind='barh', rot=0) Out[52]: <matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0xf6de430>
results = Series([x.split()[0] for x in frame.a.dropna()]) results[:5] Out[65]: 0 Mozilla/5.0 1 GoogleMaps/RochesterNY 2 Mozilla/4.0 3 Mozilla/5.0 4 Mozilla/5.0 dtype: object results.value_counts()[:8] Out[66]: Mozilla/5.0 2594 Mozilla/4.0 601 GoogleMaps/RochesterNY 121 Opera/9.80 34 TEST_INTERNET_AGENT 24 GoogleProducer 21 Mozilla/6.0 5 BlackBerry8520/5.0.0.681 4 dtype: int64
按Windows和非Windows用户对时区统计信息进行分解。
由于有agent缺失值,首先将他们从数据中移除:
cframe = frame[frame.a.notull()]
根据a值计算出各行是否是Windows:
根据时区和新得到的操作系统列表对数据进行分组
通过size对分组结果进行计数(类似上面value_counts()),并用unstack()对计数结果进行重塑:
operating_system = np.where(cframe['a'].str.contains('Windows'),
'Windows', 'Not Windows')
operating_system[:5]
Out[79]:
array(['Windows', 'Not Windows', 'Windows', 'Not Windows', 'Windows'],
dtype='|S11')
by_tz_os = cframe.groupby(['tz', operating_system])
by_tz_os
Out[81]: <pandas.core.groupby.DataFrameGroupBy object at 0x0F9C4D30>
agg_counts = by_tz_os.size().unstack().fillna(0) # 拆分列
agg_counts[:10]
Out[83]:
Not Windows Windows
tz
245 276
Africa/Cairo 0 3
Africa/Casablanca 0 1
Africa/Ceuta 0 2
Africa/Johannesburg 0 1
Africa/Lusaka 0 1
America/Anchorage 4 1
America/Argentina/Buenos_Aires 1 0
America/Argentina/Cordoba 0 1
America/Argentina/Mendoza 0 1没有拆分列是这种效果(unstack):
Out[87]: tz Not Windows 245 Windows 276 Africa/Cairo Windows 3 Africa/Casablanca Windows 1 Africa/Ceuta Windows 2 dtype: int64
# 用于按升序排列 # 行相加(win+nowin之和,排序),返回数值从小到大的索引值 indexer = agg_counts.sum(1).argsort() indexer[:10] Out[90]: tz 24 Africa/Cairo 20 Africa/Casablanca 21 Africa/Ceuta 92 Africa/Johannesburg 87 Africa/Lusaka 53 America/Anchorage 54 America/Argentina/Buenos_Aires 57 America/Argentina/Cordoba 26 America/Argentina/Mendoza 55 dtype: int64
通过take,截取了最后10行:(根据索引截取数据)
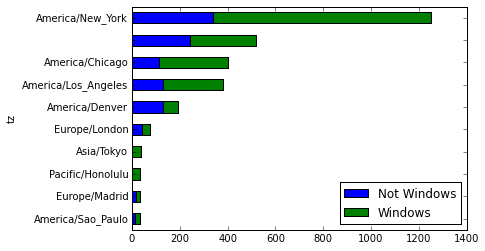
count_subset = agg_counts.take(indexer)[-10:] count_subset Out[97]: Not Windows Windows tz America/Sao_Paulo 13 20 Europe/Madrid 16 19 Pacific/Honolulu 0 36 Asia/Tokyo 2 35 Europe/London 43 31 America/Denver 132 59 America/Los_Angeles 130 252 America/Chicago 115 285 245 276 America/New_York 339 912
生成一张条形图,使用stacked=True 来生成一张堆积条形图
count_subset.plot(kind='barh', stacked=True) Out[98]: <matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0xfd535f0>
将各行规划化为“总计为1”,并重新绘图
normed_subset = count_subset.div(count_subset.sum(1), axis=0) normed_subset.plot(kind='barh', stacked=True) Out[100]: <matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0xfd53990>

相关文章推荐
- 转载]利用Python进行数据分析——绘图和可视化 xticks-学习笔记
- 『利用Python进行数据分析学习』第四章:numpy基础学习
- 《利用Python进行数据分析: Python for Data Analysis 》学习随笔
- 【利用python进行数据分析】附录A Python 学习
- 学习笔记:利用Python进行数据分析
- 利用python进行数据分析(O'Relly)学习笔记
- 利用Pythonj进行数据分析学习笔记——第五章 pandas入门
- 利用python进行数据分析(学习笔记)
- 利用Python进行数据分析 学习笔记
- Python: 利用Python进行数据分析 学习记录
- 【利用python进行数据分析-学习记录】python-matplotlib中Basemap插件的安装
- python学习-文本数据分析2(文本分类)
- 快速学习 Python 数据分析包 之 pandas
- Comprehensive learning path – Data Science in Python深度学习路径-用python进行数据学习
- [python和大数据-1]利用爬虫登录知乎进行BFS搜索抓取用户信息本地mysql分析【PART1】
- 利用python进行数据分析之数据加载存储与文件格式
- linux下利用python进行数据分析(1)Anaconda 安装
- python学习-文本数据分析1(主题提取+词向量化)
- 利用Python进行数据分析--数据加载、存储与文件格式
- python学习-数据分析2(分类型数据处理+SVM建模)
