Kubernetes Job Controller源码分析
2017-09-21 11:35
519 查看
摘要: 对于一般用户,学习和使用Job,官方文档就足够了,但如果你是个变态,那你总会去想,Job Controller和Deployment Controller在管理Pod上,除了RestartPolicy等不同外,还有哪些不同呢?其实是因为最近在搞TensorFlow on Kubernetes项目,想通过Job映射分布式TensorFlow中的worker task,达到训练完数据,自动回收资源资源等目的。本博文通过Job Controller代码分析其内部主要流程。
Author: xidianwangtao@gmail.com
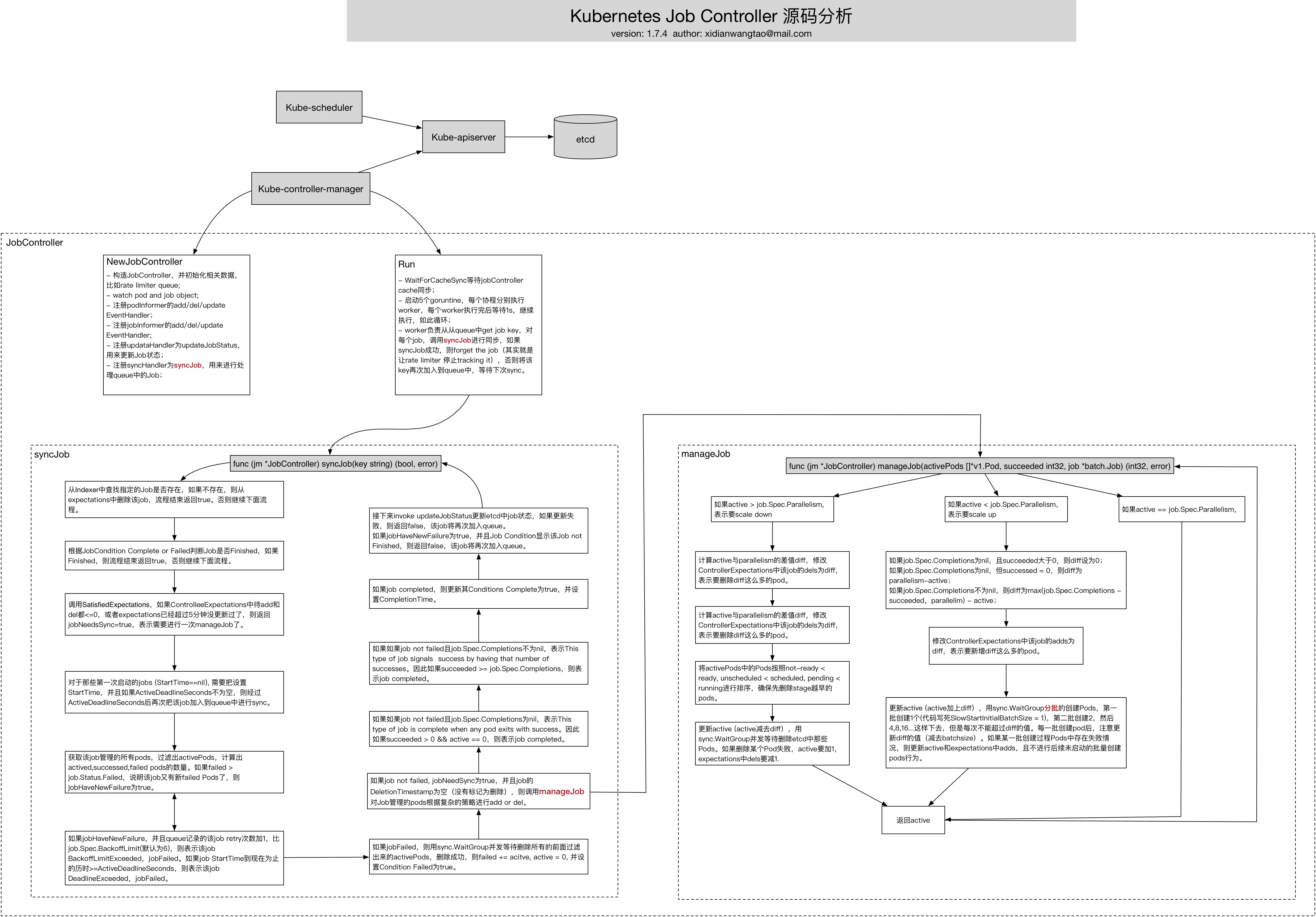
构造JobController,并初始化相关数据,比如rate limiter queue;
watch pod and job object;
注册podInformer的add/del/update EventHandler;
注册jobInformer的add/del/update EventHandler;
注册updataHandler为updateJobStatus,用来更新Job状态;
注册syncHandler为syncJob,用来进行处理queue中的Job;
WaitForCacheSync等待jobController cache同步;
启动5个goruntine,每个协程分别执行worker,每个worker执行完后等待1s,继续执行,如此循环;
worker负责从从queue中get job key,对每个job,调用syncJob进行同步,如果syncJob成功,则forget the job(其实就是让rate limiter 停止tracking it),否则将该key再次加入到queue中,等待下次sync。
从Indexer中查找指定的Job是否存在,如果不存在,则从expectations中删除该job,流程结束返回true。否则继续下面流程。
根据JobCondition Complete or Failed判断Job是否Finished,如果Finished,则流程结束返回true,否则继续下面流程。
调用SatisfiedExpectations,如果ControlleeExpectations中待add和del都<=0,或者expectations已经超过5分钟没更新过了,则返回jobNeedsSync=true,表示需要进行一次manageJob了。
对于那些第一次启动的jobs (StartTime==nil), 需要把设置StartTime,并且如果ActiveDeadlineSeconds不为空,则经过ActiveDeadlineSeconds后再次把该job加入到queue中进行sync。
获取该job管理的所有pods,过滤出activePods,计算出actived,successed,failed pods的数量。如果failed > job.Status.Failed,说明该job又有新failed Pods了,则jobHaveNewFailure为true。
如果jobHaveNewFailure,并且queue记录的该job retry次数加1,比job.Spec.BackoffLimit(默认为6),则表示该job BackoffLimitExceeded,jobFailed。如果job StartTime到现在为止的历时>=ActiveDeadlineSeconds,则表示该job DeadlineExceeded,jobFailed。
如果jobFailed,则用sync.WaitGroup并发等待删除所有的前面过滤出来的activePods,删除成功,则failed += acitve, active = 0, 并设置Condition Failed为true。
如果job not failed, jobNeedSync为true,并且job的DeletionTimestamp为空(没有标记为删除),则调用manageJob对Job管理的pods根据复杂的策略进行add or del。
如果job not failed且job.Spec.Completions为nil,表示This type of job is complete when any pod exits with success。因此如果succeeded > 0 && active == 0,则表示job completed。
如果如果job not failed且job.Spec.Completions不为nil,表示This type of job signals success by having that number of successes。因此如果succeeded >= job.Spec.Completions,则表示job completed。
如果job completed,则更新其Conditions Complete为true,并设置CompletionTime。
接下来invoke updateJobStatus更新etcd中job状态,如果更新失败,则返回false,该job将再次加入queue。如果jobHaveNewFailure为true,并且Job Condition显示该Job not Finished,则返回false,该job将再次加入queue。
如果active > job.Spec.Parallelism, 表示要scale down:
计算active与parallelism的差值diff,修改ControllerExpectations中该job的dels为diff,表示要删除diff这么多的pod。
计算active与parallelism的差值diff,修改ControllerExpectations中该job的dels为diff,表示要删除diff这么多的pod。
将activePods中的Pods按照not-ready < ready, unscheduled < scheduled, pending < running进行排序,确保先删除stage越早的pods。
更新active (active减去diff),用sync.WaitGroup并发等待删除etcd中那些Pods。如果删除某个Pod失败,active要加1,expectations中dels要减1.
返回active
如果active < job.Spec.Parallelism,
表示要scale up:
如果job.Spec.Completions为nil,且succeeded大于0,则diff设为0;如果job.Spec.Completions为nil,但successed = 0,则diff为 parallelism-active;如果job.Spec.Completions不为nil,则diff为max(job.Spec.Completions - succeeded,parallelim) - active;
修改ControllerExpectations中该job的adds为diff,表示要新增diff这么多的pod。
更新active (active加上diff),用sync.WaitGroup分批的创建Pods,第一批创建1个(代码写死SlowStartInitialBatchSize = 1),第二批创建2,然后4,8,16...这样下去,但是每次不能超过diff的值。每一批创建pod后,注意更新diff的值(减去batchsize)。如果某一批创建过程Pods中存在失败情况,则更新active和expectations中adds,且不进行后续未启动的批量创建pods行为。
如果active == job.Spec.Parallelism,返回active。
Author: xidianwangtao@gmail.com
实现流程图
废话不多说,先把完整流程贴出来。
New JobController
type JobController struct {
kubeClient clientset.Interface
podControl controller.PodControlInterface
// To allow injection of updateJobStatus for testing.
updateHandler func(job *batch.Job) error
syncHandler func(jobKey string) (bool, error)
// podStoreSynced returns true if the pod store has been synced at least once.
// Added as a member to the struct to allow injection for testing.
podStoreSynced cache.InformerSynced
// jobStoreSynced returns true if the job store has been synced at least once.
// Added as a member to the struct to allow injection for testing.
jobStoreSynced cache.InformerSynced
// A TTLCache of pod creates/deletes each rc expects to see
expectations controller.ControllerExpectationsInterface
// A store of jobs
jobLister batchv1listers.JobLister
// A store of pods, populated by the podController
podStore corelisters.PodLister
// Jobs that need to be updated
queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface
recorder record.EventRecorder
}
func NewJobController(podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer, jobInformer batchinformers.JobInformer, kubeClient clientset.Interface) *JobController {
eventBroadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()
eventBroadcaster.StartLogging(glog.Infof)
// TODO: remove the wrapper when every clients have moved to use the clientset.
eventBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(&v1core.EventSinkImpl{Interface: v1core.New(kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient()).Events("")})
if kubeClient != nil && kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient().GetRateLimiter() != nil {
metrics.RegisterMetricAndTrackRateLimiterUsage("job_controller", kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient().GetRateLimiter())
}
jm := &JobController{
kubeClient: kubeClient,
podControl: controller.RealPodControl{
KubeClient: kubeClient,
Recorder: eventBroadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme.Scheme, v1.EventSource{Component: "job-controller"}),
},
expectations: controller.NewControllerExpectations(),
queue: workqueue.NewNamedRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(DefaultJobBackOff, MaxJobBackOff), "job"),
recorder: eventBroadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme.Scheme, v1.EventSource{Component: "job-controller"}),
}
jobInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: jm.enqueueController,
UpdateFunc: jm.updateJob,
DeleteFunc: jm.enqueueController,
})
jm.jobLister = jobInformer.Lister()
jm.jobStoreSynced = jobInformer.Informer().HasSynced
podInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: jm.addPod,
UpdateFunc: jm.updatePod,
DeleteFunc: jm.deletePod,
})
jm.podStore = podInformer.Lister()
jm.podStoreSynced = podInformer.Informer().HasSynced
jm.updateHandler = jm.updateJobStatus
jm.syncHandler = jm.syncJob
return jm
}构造JobController,并初始化相关数据,比如rate limiter queue;
watch pod and job object;
注册podInformer的add/del/update EventHandler;
注册jobInformer的add/del/update EventHandler;
注册updataHandler为updateJobStatus,用来更新Job状态;
注册syncHandler为syncJob,用来进行处理queue中的Job;
JobController Run
// Run the main goroutine responsible for watching and syncing jobs.
func (jm *JobController) Run(workers int, stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
defer jm.queue.ShutDown()
glog.Infof("Starting job controller")
defer glog.Infof("Shutting down job controller")
if !controller.WaitForCacheSync("job", stopCh, jm.podStoreSynced, jm.jobStoreSynced) {
return
}
for i := 0; i < workers; i++ {
go wait.Until(jm.worker, time.Second, stopCh)
}
<-stopCh
}// worker runs a worker thread that just dequeues items, processes them, and marks them done.
// It enforces that the syncHandler is never invoked concurrently with the same key.
func (jm *JobController) worker() {
for jm.processNextWorkItem() {
}
}
func (jm *JobController) processNextWorkItem() bool {
key, quit := jm.queue.Get()
if quit {
return false
}
defer jm.queue.Done(key)
forget, err := jm.syncHandler(key.(string))
if err == nil {
if forget {
jm.queue.Forget(key)
}
return true
}
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("Error syncing job: %v", err))
jm.queue.AddRateLimited(key)
return true
}WaitForCacheSync等待jobController cache同步;
启动5个goruntine,每个协程分别执行worker,每个worker执行完后等待1s,继续执行,如此循环;
worker负责从从queue中get job key,对每个job,调用syncJob进行同步,如果syncJob成功,则forget the job(其实就是让rate limiter 停止tracking it),否则将该key再次加入到queue中,等待下次sync。
syncJob
// syncJob will sync the job with the given key if it has had its expectations fulfilled, meaning
// it did not expect to see any more of its pods created or deleted. This function is not meant to be invoked
// concurrently with the same key.
func (jm *JobController) syncJob(key string) (bool, error) {
startTime := time.Now()
defer func() {
glog.V(4).Infof("Finished syncing job %q (%v)", key, time.Now().Sub(startTime))
}()
ns, name, err := cache.SplitMetaNamespaceKey(key)
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
if len(ns) == 0 || len(name) == 0 {
return false, fmt.Errorf("invalid job key %q: either namespace or name is missing", key)
}
sharedJob, err := jm.jobLister.Jobs(ns).Get(name)
if err != nil {
if errors.IsNotFound(err) {
glog.V(4).Infof("Job has been deleted: %v", key)
jm.expectations.DeleteExpectations(key)
return true, nil
}
return false, err
}
job := *sharedJob
// if job was finished previously, we don't want to redo the termination
if IsJobFinished(&job) {
return true, nil
}
// retrieve the previous number of retry
previousRetry := jm.queue.NumRequeues(key)
// Check the expectations of the job before counting active pods, otherwise a new pod can sneak in
// and update the expectations after we've retrieved active pods from the store. If a new pod enters
// the store after we've checked the expectation, the job sync is just deferred till the next relist.
jobNeedsSync := jm.expectations.SatisfiedExpectations(key)
pods, err := jm.getPodsForJob(&job)
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
activePods := controller.FilterActivePods(pods)
active := int32(len(activePods))
succeeded, failed := getStatus(pods)
conditions := len(job.Status.Conditions)
// job first start
if job.Status.StartTime == nil {
now := metav1.Now()
job.Status.StartTime = &now
// enqueue a sync to check if job past ActiveDeadlineSeconds
if job.Spec.ActiveDeadlineSeconds != nil {
glog.V(4).Infof("Job %s have ActiveDeadlineSeconds will sync after %d seconds",
key, *job.Spec.ActiveDeadlineSeconds)
jm.queue.AddAfter(key, time.Duration(*job.Spec.ActiveDeadlineSeconds)*time.Second)
}
}
var manageJobErr error
jobFailed := false
var failureReason string
var failureMessage string
jobHaveNewFailure := failed > job.Status.Failed
// check if the number of failed jobs increased since the last syncJob
if jobHaveNewFailure && (int32(previousRetry)+1 > *job.Spec.BackoffLimit) {
jobFailed = true
failureReason = "BackoffLimitExceeded"
failureMessage = "Job has reach the specified backoff limit"
} else if pastActiveDeadline(&job) {
jobFailed = true
failureReason = "DeadlineExceeded"
failureMessage = "Job was active longer than specified deadline"
}
if jobFailed {
errCh := make(chan error, active)
jm.deleteJobPods(&job, activePods, errCh)
select {
case manageJobErr = <-errCh:
if manageJobErr != nil {
break
}
default:
}
// update status values accordingly
failed += active
active = 0
job.Status.Conditions = append(job.Status.Conditions, newCondition(batch.JobFailed, failureReason, failureMessage))
jm.recorder.Event(&job, v1.EventTypeWarning, failureReason, failureMessage)
} else {
if jobNeedsSync && job.DeletionTimestamp == nil {
active, manageJobErr = jm.manageJob(activePods, succeeded, &job)
}
completions := succeeded
complete := false
if job.Spec.Completions == nil {
// This type of job is complete when any pod exits with success.
// Each pod is capable of
// determining whether or not the entire Job is done. Subsequent pods are
// not expected to fail, but if they do, the failure is ignored. Once any
// pod succeeds, the controller waits for remaining pods to finish, and
// then the job is complete.
if succeeded > 0 && active == 0 {
complete = true
}
} else {
// Job specifies a number of completions. This type of job signals
// success by having that number of successes. Since we do not
// start more pods than there are remaining completions, there should
// not be any remaining active pods once this count is reached.
if completions >= *job.Spec.Completions {
complete = true
if active > 0 {
jm.recorder.Event(&job, v1.EventTypeWarning, "TooManyActivePods", "Too many active pods running after completion count reached")
}
if completions > *job.Spec.Completions {
jm.recorder.Event(&job, v1.EventTypeWarning, "TooManySucceededPods", "Too many succeeded pods running after completion count reached")
}
}
}
if complete {
job.Status.Conditions = append(job.Status.Conditions, newCondition(batch.JobComplete, "", ""))
now := metav1.Now()
job.Status.CompletionTime = &now
}
}
forget := false
// no need to update the job if the status hasn't changed since last time
if job.Status.Active != active || job.Status.Succeeded != succeeded || job.Status.Failed != failed || len(job.Status.Conditions) != conditions {
job.Status.Active = active
job.Status.Succeeded = succeeded
job.Status.Failed = failed
if err := jm.updateHandler(&job); err != nil {
return false, err
}
if jobHaveNewFailure && !IsJobFinished(&job) {
// returning an error will re-enqueue Job after the backoff period
return false, fmt.Errorf("failed pod(s) detected for job key %q", key)
}
forget = true
}
return forget, manageJobErr
}从Indexer中查找指定的Job是否存在,如果不存在,则从expectations中删除该job,流程结束返回true。否则继续下面流程。
根据JobCondition Complete or Failed判断Job是否Finished,如果Finished,则流程结束返回true,否则继续下面流程。
调用SatisfiedExpectations,如果ControlleeExpectations中待add和del都<=0,或者expectations已经超过5分钟没更新过了,则返回jobNeedsSync=true,表示需要进行一次manageJob了。
对于那些第一次启动的jobs (StartTime==nil), 需要把设置StartTime,并且如果ActiveDeadlineSeconds不为空,则经过ActiveDeadlineSeconds后再次把该job加入到queue中进行sync。
获取该job管理的所有pods,过滤出activePods,计算出actived,successed,failed pods的数量。如果failed > job.Status.Failed,说明该job又有新failed Pods了,则jobHaveNewFailure为true。
如果jobHaveNewFailure,并且queue记录的该job retry次数加1,比job.Spec.BackoffLimit(默认为6),则表示该job BackoffLimitExceeded,jobFailed。如果job StartTime到现在为止的历时>=ActiveDeadlineSeconds,则表示该job DeadlineExceeded,jobFailed。
如果jobFailed,则用sync.WaitGroup并发等待删除所有的前面过滤出来的activePods,删除成功,则failed += acitve, active = 0, 并设置Condition Failed为true。
如果job not failed, jobNeedSync为true,并且job的DeletionTimestamp为空(没有标记为删除),则调用manageJob对Job管理的pods根据复杂的策略进行add or del。
如果job not failed且job.Spec.Completions为nil,表示This type of job is complete when any pod exits with success。因此如果succeeded > 0 && active == 0,则表示job completed。
如果如果job not failed且job.Spec.Completions不为nil,表示This type of job signals success by having that number of successes。因此如果succeeded >= job.Spec.Completions,则表示job completed。
如果job completed,则更新其Conditions Complete为true,并设置CompletionTime。
接下来invoke updateJobStatus更新etcd中job状态,如果更新失败,则返回false,该job将再次加入queue。如果jobHaveNewFailure为true,并且Job Condition显示该Job not Finished,则返回false,该job将再次加入queue。
manageJob
// manageJob is the core method responsible for managing the number of running
// pods according to what is specified in the job.Spec.
// Does NOT modify <activePods>.
func (jm *JobController) manageJob(activePods []*v1.Pod, succeeded int32, job *batch.Job) (int32, error) {
var activeLock sync.Mutex
active := int32(len(activePods))
parallelism := *job.Spec.Parallelism
jobKey, err := controller.KeyFunc(job)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("Couldn't get key for job %#v: %v", job, err))
return 0, nil
}
var errCh chan error
if active > parallelism {
diff := active - parallelism
errCh = make(chan error, diff)
jm.expectations.ExpectDeletions(jobKey, int(diff))
glog.V(4).Infof("Too many pods running job %q, need %d, deleting %d", jobKey, parallelism, diff)
// Sort the pods in the order such that not-ready < ready, unscheduled
// < scheduled, and pending < running. This ensures that we delete pods
// in the earlier stages whenever possible.
sort.Sort(controller.ActivePods(activePods))
active -= diff
wait := sync.WaitGroup{}
wait.Add(int(diff))
for i := int32(0); i < diff; i++ {
go func(ix int32) {
defer wait.Done()
if err := jm.podControl.DeletePod(job.Namespace, activePods[ix].Name, job); err != nil {
defer utilruntime.HandleError(err)
// Decrement the expected number of deletes because the informer won't observe this deletion
glog.V(2).Infof("Failed to delete %v, decrementing expectations for job %q/%q", activePods[ix].Name, job.Namespace, job.Name)
jm.expectations.DeletionObserved(jobKey)
activeLock.Lock()
active++
activeLock.Unlock()
errCh <- err
}
}(i)
}
wait.Wait()
} else if active < parallelism {
wantActive := int32(0)
if job.Spec.Completions == nil {
// Job does not specify a number of completions. Therefore, number active
// should be equal to parallelism, unless the job has seen at least
// once success, in which leave whatever is running, running.
if succeeded > 0 {
wantActive = active
} else {
wantActive = parallelism
}
} else {
// Job specifies a specific number of completions. Therefore, number
// active should not ever exceed number of remaining completions.
wantActive = *job.Spec.Completions - succeeded
if wantActive > parallelism {
wantActive = parallelism
}
}
diff := wantActive - active
if diff < 0 {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("More active than wanted: job %q, want %d, have %d", jobKey, wantActive, active))
diff = 0
}
jm.expectations.ExpectCreations(jobKey, int(diff))
errCh = make(chan error, diff)
glog.V(4).Infof("Too few pods running job %q, need %d, creating %d", jobKey, wantActive, diff)
active += diff
wait := sync.WaitGroup{}
// Batch the pod creates. Batch sizes start at SlowStartInitialBatchSize
// and double with each successful iteration in a kind of "slow start".
// This handles attempts to start large numbers of pods that would
// likely all fail with the same error. For example a project with a
// low quota that attempts to create a large number of pods will be
// prevented from spamming the API service with the pod create requests
// after one of its pods fails. Conveniently, this also prevents the
// event spam that those failures would generate.
for batchSize := int32(integer.IntMin(int(diff), controller.SlowStartInitialBatchSize)); diff > 0; batchSize = integer.Int32Min(2*batchSize, diff) {
errorCount := len(errCh)
wait.Add(int(batchSize))
for i := int32(0); i < batchSize; i++ {
go func() {
defer wait.Done()
err := jm.podControl.CreatePodsWithControllerRef(job.Namespace, &job.Spec.Template, job, metav1.NewControllerRef(job, controllerKind))
if err != nil && errors.IsTimeout(err) {
// Pod is created but its initialization has timed out.
// If the initialization is successful eventually, the
// controller will observe the creation via the informer.
// If the initialization fails, or if the pod keeps
// uninitialized for a long time, the informer will not
// receive any update, and the controller will create a new
// pod when the expectation expires.
return
}
if err != nil {
defer utilruntime.HandleError(err)
// Decrement the expected number of creates because the informer won't observe this pod
glog.V(2).Infof("Failed creation, decrementing expectations for job %q/%q", job.Namespace, job.Name)
jm.expectations.CreationObserved(jobKey)
activeLock.Lock()
active--
activeLock.Unlock()
errCh <- err
}
}()
}
wait.Wait()
// any skipped pods that we never attempted to start shouldn't be expected.
skippedPods := diff - batchSize
if errorCount < len(errCh) && skippedPods > 0 {
glog.V(2).Infof("Slow-start failure. Skipping creation of %d pods, decrementing expectations for job %q/%q", skippedPods, job.Namespace, job.Name)
active -= skippedPods
for i := int32(0); i < skippedPods; i++ {
// Decrement the expected number of creates because the informer won't observe this pod
jm.expectations.CreationObserved(jobKey)
}
// The skipped pods will be retried later. The next controller resync will
// retry the slow start process.
break
}
diff -= batchSize
}
}
select {
case err := <-errCh:
// all errors have been reported before, we only need to inform the controller that there was an error and it should re-try this job once more next time.
if err != nil {
return active, err
}
default:
}
return active, nil
}如果active > job.Spec.Parallelism, 表示要scale down:
计算active与parallelism的差值diff,修改ControllerExpectations中该job的dels为diff,表示要删除diff这么多的pod。
计算active与parallelism的差值diff,修改ControllerExpectations中该job的dels为diff,表示要删除diff这么多的pod。
将activePods中的Pods按照not-ready < ready, unscheduled < scheduled, pending < running进行排序,确保先删除stage越早的pods。
更新active (active减去diff),用sync.WaitGroup并发等待删除etcd中那些Pods。如果删除某个Pod失败,active要加1,expectations中dels要减1.
返回active
如果active < job.Spec.Parallelism,
表示要scale up:
如果job.Spec.Completions为nil,且succeeded大于0,则diff设为0;如果job.Spec.Completions为nil,但successed = 0,则diff为 parallelism-active;如果job.Spec.Completions不为nil,则diff为max(job.Spec.Completions - succeeded,parallelim) - active;
修改ControllerExpectations中该job的adds为diff,表示要新增diff这么多的pod。
更新active (active加上diff),用sync.WaitGroup分批的创建Pods,第一批创建1个(代码写死SlowStartInitialBatchSize = 1),第二批创建2,然后4,8,16...这样下去,但是每次不能超过diff的值。每一批创建pod后,注意更新diff的值(减去batchsize)。如果某一批创建过程Pods中存在失败情况,则更新active和expectations中adds,且不进行后续未启动的批量创建pods行为。
如果active == job.Spec.Parallelism,返回active。
总结
关于Job工作原理及配置,请直接阅读官方文档 jobs run to completion,那里有关于job配置.spec.completions,
.spec.parallelism,
spec.activeDeadlineSeconds的使用说明,但是并没有把真正内部怎么工作的讲清楚,本博文就是希望能把这些东西讲清楚。
相关文章推荐
- Kubernetes Nginx Ingress Controller源码分析
- Kubernetes PodGC Controller源码分析
- Kubernetes中controller-manager源码分析--启动流程
- Kubernetes ResourceQuotaController内部实现原理及源码分析
- Kubernetes Node Controller源码分析之Taint Controller
- Kubernetes ReplicationController源码分析
- Kubernetes Node Controller源码分析之配置篇
- Elastic-Job项目源码分析1--核心骨架JobScheduler
- CI框架源码完全分析之核心文件(超级控制器)Controller.php
- spark源码分析之DAGScheduler提交作业(job)过程、stage阶段说明
- hadoop中job提交的源码分析
- Elastic-Job项目源码分析2--console执行一窥
- springMVC源码分析--ControllerBeanNameHandlerMapping(八)
- 详解SpringMVC中Controller的方法中参数的工作原理[附带源码分析]
- JobService的使用及源码分析
- SpringMVC源码分析(二)之请求如何转发到对应的Controller
- Hadoop源码分析30 JobInProgress 的 TaskInProgress 执行情况
- asp.net mvc源码分析-Controllerl篇 如何创建Controller实例
- 详解SpringMVC中Controller的方法中参数的工作原理[附带源码分析]
- Spark中job、stage、task的划分+源码执行过程分析
