Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
2017-09-05 15:02
591 查看
传送门
A. Five Dimensional Points
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
You are given set of n points in 5-dimensional space. The points are labeled from 1 to n.
No two points coincide.
We will call point a bad if there are different points b and c,
not equal to a, from the given set such that angle between vectors
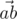
and
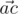
is
acute (i.e. strictly less than
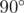
).
Otherwise, the point is called good.
The angle between vectors
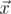
and
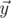
in
5-dimensional space is defined as
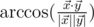
,
where
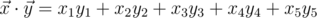
is
the scalar product and
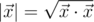
is
length of
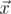
.
Given the list of points, print the indices of the good points in ascending order.
Input
The first line of input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 103) —
the number of points.
The next n lines of input contain five integers ai, bi, ci, di, ei (|ai|, |bi|, |ci|, |di|, |ei| ≤ 103)
— the coordinates of the i-th point. All points are distinct.
Output
First, print a single integer k — the number of good points.
Then, print k integers, each on their own line — the indices of the good points in ascending order.
Examples
input
output
input
output
Note
In the first sample, the first point forms exactly a
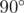
angle
with all other pairs of points, so it is good.
In the second sample, along the cd plane, we can see the points look as follows:
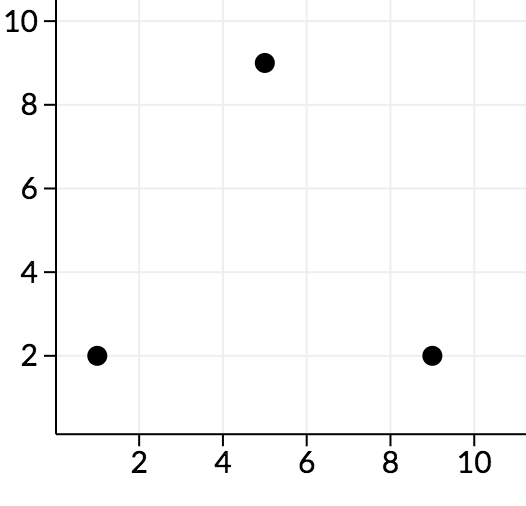
We can see that all angles here are acute, so no points are good.
n^3。
暴力怼
//china no.1
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <list>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cctype>
#include <sstream>
#include <functional>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define s_1(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define s_2(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)
#define s_3(x,y,z) scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z)
#define PI acos(-1)
#define endl '\n'
#define srand() srand(time(0));
#define me(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x));
#define foreach(it,a) for(__typeof((a).begin()) it=(a).begin();it!=(a).end();it++)
#define close() ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
#define FOR(x,n,i) for(int i=x;i<=n;i++)
#define FOr(x,n,i) for(int i=x;i<n;i++)
#define fOR(n,x,i) for(int i=n;i>=x;i--)
#define fOr(n,x,i) for(int i=n;i>x;i--)
#define W while
#define sgn(x) ((x) < 0 ? -1 : (x) > 0)
#define bug printf("***********\n");
#define db double
#define ll long long
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
typedef long long LL;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LINF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
const int dx[]={-1,0,1,0,1,-1,-1,1};
const int dy[]={0,1,0,-1,-1,1,-1,1};
const int maxn=1e3+10;
const int maxx=1e6+100;
const double EPS=1e-8;
const double eps=1e-8;
const int mod=1e9+7;
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c) { return min(min(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c) { return max(max(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return min(min(a,b),min(c,d));}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return max(max(a,b),max(c,d));}
template <class T>
inline bool scan_d(T &ret){char c;int sgn;if (c = getchar(), c == EOF){return 0;}
while (c != '-' && (c < '0' || c > '9')){c = getchar();}sgn = (c == '-') ? -1 : 1;ret = (c == '-') ? 0 : (c - '0');
while (c = getchar(), c >= '0' && c <= '9'){ret = ret * 10 + (c - '0');}ret *= sgn;return 1;}
inline bool scan_lf(double &num){char in;double Dec=0.1;bool IsN=false,IsD=false;in=getchar();if(in==EOF) return false;
while(in!='-'&&in!='.'&&(in<'0'||in>'9'))in=getchar();if(in=='-'){IsN=true;num=0;}else if(in=='.'){IsD=true;num=0;}
else num=in-'0';if(!IsD){while(in=getchar(),in>='0'&&in<='9'){num*=10;num+=in-'0';}}
if(in!='.'){if(IsN) num=-num;return true;}else{while(in=getchar(),in>='0'&&in<='9'){num+=Dec*(in-'0');Dec*=0.1;}}
if(IsN) num=-num;return true;}
void Out(LL a){if(a < 0) { putchar('-'); a = -a; }if(a >= 10) Out(a / 10);putchar(a % 10 + '0');}
void print(LL a){ Out(a),puts("");}
//freopen( "in.txt" , "r" , stdin );
//freopen( "data.txt" , "w" , stdout );
//cerr << "run time is " << clock() << endl;
//cf-535C Tavas and Pashmaks
int n;
int vis[maxn];
struct node
{
double a,b,c,d,e;
}Q[maxn];
typedef node Vector;
double Dot(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.a*B.a + A.b*B.b+
A.c*B.c+A.d*B.d+A.e*B.e; }
double Length(Vector A) { return sqrt(Dot(A,A));}
double Angle(Vector A, Vector B) { return acos(Dot(A, B) / Length(A) / Length(B)); }
Vector vv(node A,node B)
{
Vector v1;
v1.a=A.a-B.a;
v1.b=A.b-B.b;
v1.c=A.c-B.c;
v1.d=A.d-B.d;
v1.e=A.e-B.e;
return v1;
}
int main()
{
scan_d(n);
FOR(1,n,i)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf",
&Q[i].a,&Q[i].b,&Q[i].c,&Q[i].d,&Q[i].e);
}
/*if(n>243)
{
puts("0");
return 0;
}*/
Vector v1,v2;
int cnt=0;
FOR(1,n,i)
{
int flag=0;
FOR(1,n,j)
{
if(i==j)
continue;
FOR(1,n,k)
{
if(j==k||k==i)
continue;
//cout<<i<<" "<<j<<" "<<k<<endl;
v1=vv(Q[i],Q[j]);
v2=vv(Q[i],Q[k]);
db ang=Angle(v1,v2);
// printf("%f %f\n",ang,pi/2.0-eps);
if(ang<pi/2.0-eps)
{
// printf("%f %f\n",ang,pi/2.0-eps);
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
break;
}
if(!flag)
{
vis[cnt++]=i;
}
}
print(cnt);
FOr(0,cnt,i)
print(vis[i]);
}
A. Five Dimensional Points
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
You are given set of n points in 5-dimensional space. The points are labeled from 1 to n.
No two points coincide.
We will call point a bad if there are different points b and c,
not equal to a, from the given set such that angle between vectors
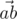
and
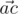
is
acute (i.e. strictly less than
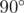
).
Otherwise, the point is called good.
The angle between vectors
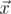
and
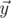
in
5-dimensional space is defined as
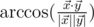
,
where
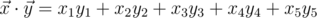
is
the scalar product and
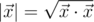
is
length of
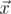
.
Given the list of points, print the indices of the good points in ascending order.
Input
The first line of input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 103) —
the number of points.
The next n lines of input contain five integers ai, bi, ci, di, ei (|ai|, |bi|, |ci|, |di|, |ei| ≤ 103)
— the coordinates of the i-th point. All points are distinct.
Output
First, print a single integer k — the number of good points.
Then, print k integers, each on their own line — the indices of the good points in ascending order.
Examples
input
6 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
output
1 1
input
3 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 9 2 0 0 0 5 9 0
output
0
Note
In the first sample, the first point forms exactly a
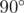
angle
with all other pairs of points, so it is good.
In the second sample, along the cd plane, we can see the points look as follows:

We can see that all angles here are acute, so no points are good.
n^3。
暴力怼
//china no.1
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <list>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cctype>
#include <sstream>
#include <functional>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define s_1(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define s_2(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)
#define s_3(x,y,z) scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z)
#define PI acos(-1)
#define endl '\n'
#define srand() srand(time(0));
#define me(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x));
#define foreach(it,a) for(__typeof((a).begin()) it=(a).begin();it!=(a).end();it++)
#define close() ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
#define FOR(x,n,i) for(int i=x;i<=n;i++)
#define FOr(x,n,i) for(int i=x;i<n;i++)
#define fOR(n,x,i) for(int i=n;i>=x;i--)
#define fOr(n,x,i) for(int i=n;i>x;i--)
#define W while
#define sgn(x) ((x) < 0 ? -1 : (x) > 0)
#define bug printf("***********\n");
#define db double
#define ll long long
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
typedef long long LL;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LINF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
const int dx[]={-1,0,1,0,1,-1,-1,1};
const int dy[]={0,1,0,-1,-1,1,-1,1};
const int maxn=1e3+10;
const int maxx=1e6+100;
const double EPS=1e-8;
const double eps=1e-8;
const int mod=1e9+7;
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c) { return min(min(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c) { return max(max(a,b),c);}
template<class T>inline T min(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return min(min(a,b),min(c,d));}
template<class T>inline T max(T a,T b,T c,T d) { return max(max(a,b),max(c,d));}
template <class T>
inline bool scan_d(T &ret){char c;int sgn;if (c = getchar(), c == EOF){return 0;}
while (c != '-' && (c < '0' || c > '9')){c = getchar();}sgn = (c == '-') ? -1 : 1;ret = (c == '-') ? 0 : (c - '0');
while (c = getchar(), c >= '0' && c <= '9'){ret = ret * 10 + (c - '0');}ret *= sgn;return 1;}
inline bool scan_lf(double &num){char in;double Dec=0.1;bool IsN=false,IsD=false;in=getchar();if(in==EOF) return false;
while(in!='-'&&in!='.'&&(in<'0'||in>'9'))in=getchar();if(in=='-'){IsN=true;num=0;}else if(in=='.'){IsD=true;num=0;}
else num=in-'0';if(!IsD){while(in=getchar(),in>='0'&&in<='9'){num*=10;num+=in-'0';}}
if(in!='.'){if(IsN) num=-num;return true;}else{while(in=getchar(),in>='0'&&in<='9'){num+=Dec*(in-'0');Dec*=0.1;}}
if(IsN) num=-num;return true;}
void Out(LL a){if(a < 0) { putchar('-'); a = -a; }if(a >= 10) Out(a / 10);putchar(a % 10 + '0');}
void print(LL a){ Out(a),puts("");}
//freopen( "in.txt" , "r" , stdin );
//freopen( "data.txt" , "w" , stdout );
//cerr << "run time is " << clock() << endl;
//cf-535C Tavas and Pashmaks
int n;
int vis[maxn];
struct node
{
double a,b,c,d,e;
}Q[maxn];
typedef node Vector;
double Dot(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.a*B.a + A.b*B.b+
A.c*B.c+A.d*B.d+A.e*B.e; }
double Length(Vector A) { return sqrt(Dot(A,A));}
double Angle(Vector A, Vector B) { return acos(Dot(A, B) / Length(A) / Length(B)); }
Vector vv(node A,node B)
{
Vector v1;
v1.a=A.a-B.a;
v1.b=A.b-B.b;
v1.c=A.c-B.c;
v1.d=A.d-B.d;
v1.e=A.e-B.e;
return v1;
}
int main()
{
scan_d(n);
FOR(1,n,i)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf",
&Q[i].a,&Q[i].b,&Q[i].c,&Q[i].d,&Q[i].e);
}
/*if(n>243)
{
puts("0");
return 0;
}*/
Vector v1,v2;
int cnt=0;
FOR(1,n,i)
{
int flag=0;
FOR(1,n,j)
{
if(i==j)
continue;
FOR(1,n,k)
{
if(j==k||k==i)
continue;
//cout<<i<<" "<<j<<" "<<k<<endl;
v1=vv(Q[i],Q[j]);
v2=vv(Q[i],Q[k]);
db ang=Angle(v1,v2);
// printf("%f %f\n",ang,pi/2.0-eps);
if(ang<pi/2.0-eps)
{
// printf("%f %f\n",ang,pi/2.0-eps);
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
break;
}
if(!flag)
{
vis[cnt++]=i;
}
}
print(cnt);
FOr(0,cnt,i)
print(vis[i]);
}
相关文章推荐
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)C. Five Dimensional Points
- 【推导】【暴力】Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017) C. Five Dimensional Points
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017) C
- 【推导】Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017) B. Arpa and an exam about geometry
- CF——Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017) A
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017)
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017) B
- Codeforces Round #432 (Div. 2, based on IndiaHacks Final Round 2017) D
