TensorFlow搭建CNN卷积神经网络
2017-08-19 00:40
411 查看
TensorFlow搭建CNN卷积神经网络
该教程采用TernsorFlow搭建CNN卷积神经网络,并利用MNIST数据集进行数字的手写识别数据结构
mnist原始图片输入,原始图片的尺寸为28×28,导入后会自动展开为28×28=784的listtensor : shape=[784]
卷积层输入input_image: shape=[batch, height, width, channels]
bacth : 取样数
height, width : 图片的尺寸
channels : 图片的深度;如果是灰度图像,则为1,rgb图像,则为3
卷积核filter: shape=[height, width, in_channels, out_channels]
height, width: 图片的尺寸
in_channels: 图片的深度
out_channels: 卷积核的数量
对于in_channels,灰度图为1,rgb图为3
函数
TensorFlow自带的CNN操作函数卷积函数[tf.nn.conv2d(x, filter, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding=’SAME’)]
x: 卷积层输入 shape=[batch, height, width, channels]
filter: 卷积核 shape=[height, width, in_channels, out_channels]
stride: 卷积步长 shape=[batch_stride, height_stride, width_stride, channels_stride]
padding: 控制卷积核处理边界的策略
stride表示卷积核filter对应了input_image各维度下移动的步长;第一个参数对应input_image的batch方向上的移动步长,第二、三参数对应高宽方向上的步长,决定了卷积后图像的尺寸,最后一个参数对应channels方向上的步长
padding=’SAME’表示给图像边界加上padding,让filter卷积后的图像尺寸与原图相同;’VALID’表示卷积后imgaeHeight_aterFiltered=imageHeight_inital-filterHeight+strideHeight,宽同理
池化函数tf.nn.max_pool(x, k_size=[1,2,2,1], strides=[1,2,2,1], padding=’SAME’)
x: 池化输入input_image: shape=[batch, height, width, channels]
ksize: 池化窗口的尺寸
strides: 池化步长
padding: 处理边界策略
池化输入,tensor的shape同input_image, 一般为卷积后图像feature_map
ksize对应输入图像各维度的池化尺寸;第一个参数对应batch方向上的池化尺寸,第二、三参数对应图像高宽上的池化尺寸,第四个参数对应channels方向上的池化尺寸,一般不在batch和channel方向上做池化,因此通常为[1,height,width,1]
strides与padding同卷积函数tf.nn.conv2d()
为了方便后续搭建,需要自己定义一些函数
卷积核filter初始化weight_variable(shape)
def weight_variable(shape): initial=tf.truncated_normal(shape, mean=0.0, stddev=0.1) return tf.Variable(inital)
对于CNN来说,weight实际上就是卷积核filter,因此shape应该与tf.nn.conv2d中filter的shape一致,即shape=[height, width, in_channels, out_channels]
tf.truncated_normal()表示截断正态分布,即保留[mean-2×stddev,mean+2×stddev]范围内的随机数,mean表示平均数,stddev为方差
偏置初始化bias_variable(shape)
def bias_variable(shape): initial=tf.constant(0,1,shape=shape) return tf.Vatiable(initial)
针对tensorFlow函数更详细的使用,参见tensorFlow常用函数汇总
思路
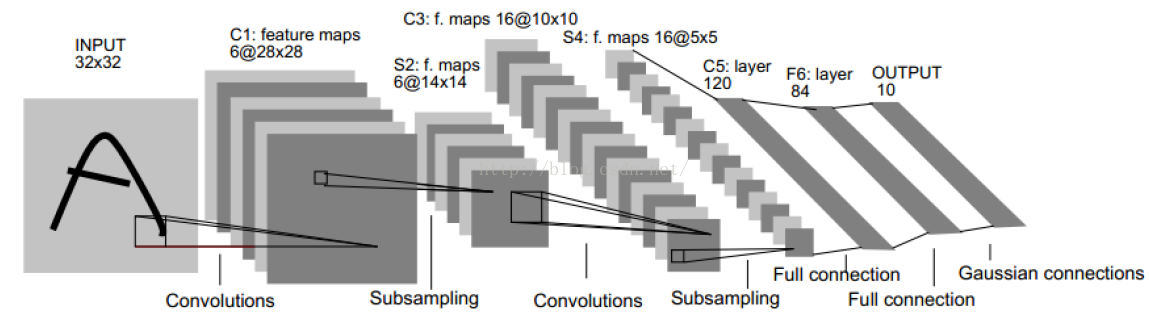
详细CNN过程
MNIST数据导入
代码这一行就是用于下载mnist数据,实际操作过程往往会出现socket error,因此需要事先下载好from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
在程序的文件夹下建立MNIST_data文件夹,在执行完上述代码后,会自动生成该文件夹
进入MNIST_data文件后,从github上直接下载数据集合
cd MNIST_data git clone https://github.com/HIPS/hypergrad.git #下载完成后,将下载文件中data/mnist下所有数据copy进MNIST_data中即可

完整代码
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
#获取mnist训练集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
#交互式session
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
#已将32×32的图片展开成行向量,None代表该维度上数量不确定,程序中指的是取样的图像数量不确定
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None,784])
#图片的标签
y_label=tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None,10])
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
#第一层网络
#reshape()将按照设定的shape=[-1,28,28,1]对x:shape=[None,784]的结构进行重新构建
#参数-1代表该维度上数量不确定,由系统自动计算
x_image = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1,28,28,1])
#32个卷积核,卷积核大小5×5
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,1,32])
#32个前置,对应32个卷积核输出
b_conv1 = bias_varibale([32])
#卷积操作
layer_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
#池化操作
layer_pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(layer_conv1)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
#第二层网络
#64个卷积核,卷积核大小5×5,32个channel
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,32,64])
#64个前置,对应64个卷积核输出
b_conv2 = bias_varibale([64])
#卷积操作
layer_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(layer_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
#池化操作
layer_pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(layer_conv2)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
#full-connected网络
#图片尺寸变化28×28-->14×14-->7×7
#该层设定1024个神经元
layer_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(layer_pool2,[-1,7*7*64])
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(layer_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
#droput网络
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
#输出层
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop,W_fc2)+b_fc2)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
#loss-function
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_lable*tf.log(y_conv))
#梯度下降
train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(cross_entropy)
#tf.argmax(x,1)表示从x的第二维度选取最大值
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv,1), tf.argmax(y_lable,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
#训练train
#训练3000次
for i in range(3000)
#每次选取50训练集
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i%100 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:batch[0], y_labe: batch[1], keep_prob: 1.0})
print ("step %d, training accuracy %g"%(i, train_accuracy))
train.run(feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_label: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
print ("test accuracy %g"%accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y_label: mnist.test.labels, keep_prob: 1.0}))详细代码
相关文章推荐
- Deep Learning-TensorFlow (10) CNN卷积神经网络_ TFLearn 快速搭建深度学习模型
- tensorflow之简单卷积神经网络(CNN)搭建
- TensorFlow基础教程:搭建卷积神经网络CNN
- 用Tensorflow搭建CNN卷积神经网络,实现MNIST手写数字识别
- TensorFlow (2) CNN卷积神经网络_ TFLearn 快速搭建深度学习模型
- 03:一文全解:使用Tensorflow搭建卷积神经网络CNN识别手写数字图片
- tensorflow 学习笔记(五) - mnist实例--卷积神经网络(CNN)
- (四)Tensorflow学习之旅——MNIST分类的卷积神经网络CNN示例
- 深度学习之卷积神经网络CNN及tensorflow代码实现示例
- 用tensorflow搭建CNN
- 深度学习之卷积神经网络CNN及tensorflow代码实现示例
- 深度学习之卷积神经网络CNN及tensorflow代码实现
- 深度学习-CNN卷积神经网络使用TensorFlow框架实现MNIST手写数字识别
- 深度学习之卷积神经网络CNN及tensorflow代码实现示例
- 【Tensorflow】实现简单的卷积神经网络CNN实际代码
- TensorFlow实例(5.2)--MNIST手写数字进阶算法(卷积神经网络CNN) 之 卷积tf.nn.conv2d
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)在TensorFlow文本分类中的应用Implementing a CNN for Text Classification in TensorFlow
- Tensorflow之 CNN卷积神经网络的MNIST手写数字识别
- Deep Learning-TensorFlow (1) CNN卷积神经网络_MNIST手写数字识别代码实现
- 【TensorFlow-windows】(四) CNN(卷积神经网络)进行手写数字识别(mnist)
