tensorflow入门实践例子—MNIST手写数字识别
2017-08-18 19:07
671 查看
MNIST是手写数字图像数据集,是一个用于图像识别基础数据集。
这里用tensorflow实现MNIST手写数据集,用两种方法:一种是普通的BP神经网络;另一种是卷积神经网络。
这里的Python版本是2.7,tensorflow版本是1.0。
BP神经网络实现
执行结果:
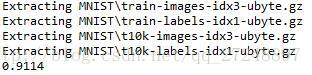
执行结果:

这里用tensorflow实现MNIST手写数据集,用两种方法:一种是普通的BP神经网络;另一种是卷积神经网络。
这里的Python版本是2.7,tensorflow版本是1.0。
1、BP神经网络
读取MNIST数据集文件mnist_input.py"""Functions for downloading and reading MNIST data."""
from __future__ import print_function
import gzip
import os
import urllib
import numpy
SOURCE_URL = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/'
def maybe_download(filename, work_directory):
"""Download the data from Yann's website, unless it's already here."""
if not os.path.exists(work_directory):
os.mkdir(work_directory)
filepath = os.path.join(work_directory, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
filepath, _ = urllib.urlretrieve(SOURCE_URL + filename, filepath)
statinfo = os.stat(filepath)
print('Succesfully downloaded', filename, statinfo.st_size, 'bytes.')
return filepath
def _read32(bytestream):
dt = numpy.dtype(numpy.uint32).newbyteorder('>')
return numpy.frombuffer(bytestream.read(4), dtype=dt)
def extract_images(filename):
"""Extract the images into a 4D uint8 numpy array [index, y, x, depth]."""
print('Extracting', filename)
with gzip.open(filename) as bytestream:
magic = _read32(bytestream)
if magic != 2051:
raise ValueError(
'Invalid magic number %d in MNIST image file: %s' %
(magic, filename))
num_images = _read32(bytestream)
rows = _read32(bytestream)
cols = _read32(bytestream)
buf = bytestream.read(rows * cols * num_images)
data = numpy.frombuffer(buf, dtype=numpy.uint8)
data = data.reshape(num_images, rows, cols, 1)
return data
def dense_to_one_hot(labels_dense, num_classes=10):
"""Convert class labels from scalars to one-hot vectors."""
num_labels = labels_dense.shape[0]
index_offset = numpy.arange(num_labels) * num_classes
labels_one_hot = numpy.zeros((num_labels, num_classes))
labels_one_hot.flat[index_offset + labels_dense.ravel()] = 1
return labels_one_hot
def extract_labels(filename, one_hot=False):
"""Extract the labels into a 1D uint8 numpy array [index]."""
print('Extracting', filename)
with gzip.open(filename) as bytestream:
magic = _read32(bytestream)
if magic != 2049:
raise ValueError(
'Invalid magic number %d in MNIST label file: %s' %
(magic, filename))
num_items = _read32(bytestream)
buf = bytestream.read(num_items)
labels = numpy.frombuffer(buf, dtype=numpy.uint8)
if one_hot:
return dense_to_one_hot(labels)
return labels
class DataSet(object):
def __init__(self, images, labels, fake_data=False):
if fake_data:
self._num_examples = 10000
else:
assert images.shape[0] == labels.shape[0], (
"images.shape: %s labels.shape: %s" % (images.shape,
labels.shape))
self._num_examples = images.shape[0]
# Convert shape from [num examples, rows, columns, depth]
# to [num examples, rows*columns] (assuming depth == 1)
assert images.shape[3] == 1
images = images.reshape(images.shape[0],
images.shape[1] * images.shape[2])
# Convert from [0, 255] -> [0.0, 1.0].
images = images.astype(numpy.float32)
images = numpy.multiply(images, 1.0 / 255.0)
self._images = images
self._labels = labels
self._epochs_completed = 0
self._index_in_epoch = 0
@property
def images(self):
return self._images
@property
def labels(self):
return self._labels
@property
def num_examples(self):
return self._num_examples
@property
def epochs_completed(self):
return self._epochs_completed
def next_batch(self, batch_size, fake_data=False):
"""Return the next `batch_size` examples from this data set."""
if fake_data:
fake_image = [1.0 for _ in xrange(784)]
fake_label = 0
return [fake_image for _ in xrange(batch_size)], [
fake_label for _ in xrange(batch_size)]
start = self._index_in_epoch
self._index_in_epoch += batch_size
if self._index_in_epoch > self._num_examples:
# Finished epoch
self._epochs_completed += 1
# Shuffle the data
perm = numpy.arange(self._num_examples)
numpy.random.shuffle(perm)
self._images = self._images[perm]
self._labels = self._labels[perm]
# Start next epoch
start = 0
self._index_in_epoch = batch_size
assert batch_size <= self._num_examples
end = self._index_in_epoch
return self._images[start:end], self._labels[start:end]
def read_data_sets(train_dir, fake_data=False, one_hot=False):
class DataSets(object):
pass
data_sets = DataSets()
if fake_data:
data_sets.train = DataSet([], [], fake_data=True)
data_sets.validation = DataSet([], [], fake_data=True)
data_sets.test = DataSet([], [], fake_data=True)
return data_sets
TRAIN_IMAGES = 'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
TRAIN_LABELS = 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
TEST_IMAGES = 't10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
TEST_LABELS = 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
VALIDATION_SIZE = 5000
local_file = maybe_download(TRAIN_IMAGES, train_dir)
train_images = extract_images(local_file)
local_file = maybe_download(TRAIN_LABELS, train_dir)
train_labels = extract_labels(local_file, one_hot=one_hot)
local_file = maybe_download(TEST_IMAGES, train_dir)
test_images = extract_images(local_file)
local_file = maybe_download(TEST_LABELS, train_dir)
test_labels = extract_labels(local_file, one_hot=one_hot)
validation_images = train_images[:VALIDATION_SIZE]
validation_labels = train_labels[:VALIDATION_SIZE]
train_images = train_images[VALIDATION_SIZE:]
train_labels = train_labels[VALIDATION_SIZE:]
data_sets.train = DataSet(train_images, train_labels)
data_sets.validation = DataSet(validation_images, validation_labels)
data_sets.test = DataSet(test_images, test_labels)
return data_setsBP神经网络实现
# simple MNIST
import tensorflow as tf
import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST', one_hot=True)
# input data
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
# W:weights b:biases
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
# predictions
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W)+b)
# label
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(cross_entropy)
# init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
for i in range(1000):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x:batch_xs, y_:batch_ys})
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
print (sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict = {x:mnist.test.images, y_:mnist.test.labels}))执行结果:

2、卷积神经网络
卷积神经网络实现# load tensorflow model
import tensorflow as tf
# load get data file
import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot = True)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# x: input data y_: label
x = tf.placeholder("float", shape = [None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", shape = [None, 10])
# convolutional layer
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev = 0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape = shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides = [1, 1, 1, 1], padding = 'SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize = [1, 2, 2, 1], strides = [1, 2, 2, 1], padding = 'SAME')
# conv1
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
# conv2
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
# flat
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64, 1024])
b_fc1 = weight_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
# Dropout
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
# oupout layer
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
# train and evaluate
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y_conv))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
for i in range(20000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i%100 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict = {x:batch[0], y_:batch[1], keep_prob:1.0})
print ("step %d, training accuracy %g"%(i, train_accuracy))
train_step.run(feed_dict = {x:batch[0], y_:batch[1], keep_prob:0.5})
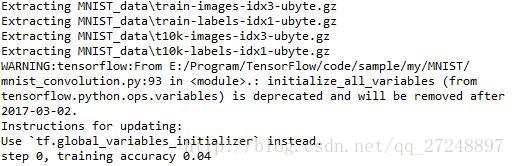
print ("test accuracy %g"%accuracy.eval(feed_dict = {x:mnist.test.images, y_:mnist.test.labels, keep_prob:1.0}))执行结果:


相关文章推荐
- tensorflow 入门小例子(mnist手写数字识别)
- 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识别(二)--入门篇
- 30分钟手把手带你入门TensorFlow——Mnist手写数字识别实战教程
- pycharm下tensorflow的调试,并实现mnist手写数字识别的例子
- 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识别--入门篇
- 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识别(二)--入门篇
- tensorflow入门-mnist手写数字识别(一)
- tensorflow的入门--手写数字识别mnist的傻瓜教程
- Keras入门课2 -- 使用CNN识别mnist手写数字
- TensorFlow用MNIST训练的模型来识别手写数字
- tensorflow实战之四:MNIST手写数字识别的优化3-过拟合
- 深度学习入门实践_十行搭建手写数字识别神经网络
- 深度学习-传统神经网络使用TensorFlow框架实现MNIST手写数字识别
- TensorFlow 入门之手写识别(MNIST) softmax算法
- tensorflow中MLP识别mnist手写数字
- TensorFlow在MNIST中的应用 识别手写数字(OpenCV+TensorFlow+CNN)
- tensorflow进行MNIST手写数字识别-简单版
- 使用tensorflow利用神经网络分类识别MNIST手写数字数据集,转自随心1993
- 入门深度学习mxnet框架——运行mnist手写数字例子
- 深度学习-CNN卷积神经网络使用TensorFlow框架实现MNIST手写数字识别
