Mysql快速导出导入数据的实验
2017-08-11 08:02
381 查看
一、创建测试数据库
二、使用Python3.6产生测试数据
1、ChangePipSource.py 作用:加快PIP的安装速度,原理:使用豆瓣的镜像
2、生成测试数据的脚本
(1)Util/Config.py
(2)Util/MySQLHelper.py
(3)generate_user_data.py
3、将生成的100W条测试数据导出生成CSV

4、测试导入
5、测试一下系统中的大表
对比发下PSC的t_resource_info的备份时间:
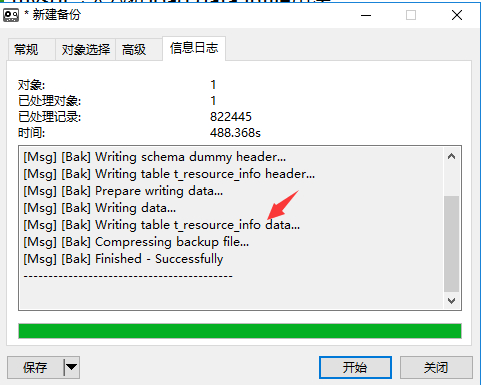
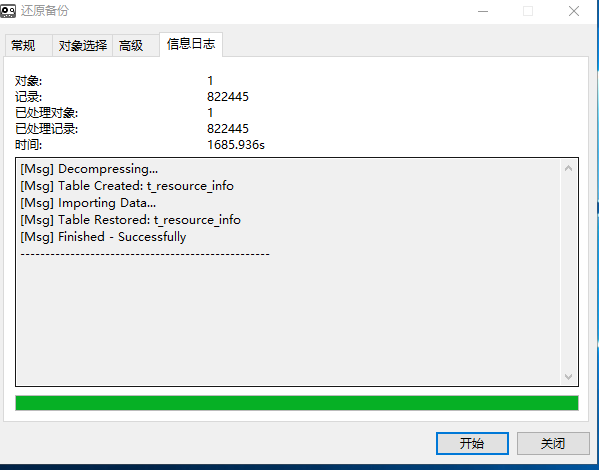
6、下一步的思考 思路
http://www.cnblogs.com/obullxl/archive/2012/06/11/jdbc-mysql-load-data-infile.html
CREATE database example;
use example;
create TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`last_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`first_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` set('M','F') DEFAULT NULL,
`age` tinyint(1) DEFAULT NULL,
`phone` varchar(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`address` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_last_first_name_age` (`last_name`,`first_name`,`age`) USING BTREE,
KEY `idx_phone` (`phone`) USING BTREE,
KEY `idx_create_time` (`create_time`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;二、使用Python3.6产生测试数据
1、ChangePipSource.py 作用:加快PIP的安装速度,原理:使用豆瓣的镜像
import os ini = """[global] index-url = https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple/ [install] trusted-host=pypi.doubanio.com disable-pip-version-check = true timeout = 600 """ pippath = os.environ["USERPROFILE"] + "\\pip\\" if not os.path.exists(pippath): os.mkdir(pippath) with open(pippath + "pip.ini", "w+") as f: f.write(ini)
2、生成测试数据的脚本
(1)Util/Config.py
class InitConfig: DataBaseHost = '127.0.0.1' DataBasePort = 22066 DataBaseUser = 'root' DataBasePassword = 'dsideal' DataBaseName = "example"
(2)Util/MySQLHelper.py
# --encoding:utf-8--
# pip install pymysql
import pymysql.cursors
from Util.Config import *
class MySQLHelper:
myVersion = 0.1
def __init__(self, host=InitConfig.DataBaseHost, port=InitConfig.DataBasePort, user=InitConfig.DataBaseUser,
password=InitConfig.DataBasePassword, db=InitConfig.DataBaseName, charset="utf8"):
self.host = host
self.user = user
self.port = port
self.password = password
self.charset = charset
self.db = db
try:
self.conn = pymysql.connect(host=self.host, port=self.port, user=self.user, passwd=self.password,
db=self.db, charset=self.charset, cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
except Exception as e:
print('MySql Error : %d %s' % (e.args[0], e.args[1]))
def query(self, sql):
try:
self.cursor.execute(sql)
result = self.cursor.fetchall()
return result
except Exception as e:
print('MySql Error: %s SQL: %s' % (e, sql))
def execute(self, sql):
try:
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
print('MySql Error: %s SQL: %s' % (e, sql))
def executemany(self, sql, data):
try:
self.cursor.executemany(sql, data)
self.conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
print('MySql Error: %s SQL: %s' % (e, sql))
def close(self):
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close()(3)generate_user_data.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import random
import string
import time
from Util.MySQLHelper import *
#批量插的次数
loop_count = 1000000
#每次批量查的数据量
batch_size = 100
success_count = 0
fails_count = 0
#数据库的连接
chars = 'AaBbCcDdEeFfGgHhIiJjKkLlMmNnOoPpQqRrSsTtUuVvWwXxYyZz'
digits = '0123456789'
def random_generate_string(length):
return ''.join(random.sample(chars, length))
def random_generate_number(length):
if length > len(digits):
digit_list = random.sample(digits, len(digits))
digit_list.append(random.choice(digits))
return ''.join(digit_list)
return ''.join(random.sample(digits, length))
def random_generate_data(num):
c = [num]
phone_num_seed = 13100000000
def _random_generate_data():
c[0] += 1
return (
c[0],
"last_name_" + str(random.randrange(100000)),
"first_name_" + str(random.randrange(100000)),
random.choice('MF'),
random.randint(1, 120),
phone_num_seed + c[0],
random_generate_string(20),
random_generate_string(10),
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
)
return _random_generate_data
def execute_many(insert_sql, batch_data):
db = MySQLHelper()
db.executemany(insert_sql, batch_data)
db.close()
try:
#user表列的数量
column_count = 9
#插入的SQL
insert_sql = "replace into user(id, last_name, first_name, sex, age, phone, address, password, create_time) values (" + ",".join([ "%s" for x in range(column_count)]) + ")"
batch_count = 0
begin_time = time.time()
for x in range(loop_count):
batch_count = x * batch_size
gen_fun = random_generate_data(batch_count)
batch_data = [gen_fun() for x in range(batch_size)]
execute_many(insert_sql, batch_data)
success_count=success_count+batch_size
print("Running..."+str(success_count))
end_time = time.time()
total_sec = end_time - begin_time
qps = success_count / total_sec
print("总共生成数据: " + str(success_count))
print("总共耗时(s): " + str(total_sec))
print("QPS: " + str(qps))
except Exception as e:
print(e)
raise
else:
pass
finally:
pass3、将生成的100W条测试数据导出生成CSV
select id,last_name,first_name,sex,age,phone,address,password,create_time from user into outfile 'd://user.csv' fields terminated by ',' optionally enclosed by '"' escaped by '"' lines terminated by '\r\n';

4、测试导入
truncate table user; load data infile 'd://user.csv' into table `user` fields terminated by ',' optionally enclosed by '"' escaped by '"' lines terminated by '\r\n';
5、测试一下系统中的大表
load data infile '/usr/local/t_resource_info.csv' into table `t_resource_info` fields terminated by ',' optionally enclosed by '"' escaped by '"' lines terminated by '\r\n'; /* 1、导出 受影响的行: 822445 时间: 26.410s 985.91MB 2、导入 受影响的行: 822445 时间: 257.772s */
对比发下PSC的t_resource_info的备份时间:


6、下一步的思考 思路
http://www.cnblogs.com/obullxl/archive/2012/06/11/jdbc-mysql-load-data-infile.html
相关文章推荐
- mysql下的快速导入导出数据以及索引禁用
- 快速的mysql导入导出数据(load data和outfile)
- Mysql 大量数据快速导入导出
- Mysql 大量数据快速导入导出
- Mysql 大量数据快速导入导出
- Mysql大量数据快速导入导出
- MySQL快速远程导入导出数据库数据
- MySQL杂项(索引注意事项 快速导入导出数据 锁 字符集 慢查询)
- MySQL数据文件的导入、导出
- MySQL数据的导出和导入工具:mysqldump(备份数据库的命令)
- ASP.NET中使用开源组件NPOI快速导入导出Execl数据
- Oracle中用exp/imp命令快速导入导出数据
- Mysql正确的导入、导出数据的方法
- php将mysql数据表(含中文数据)导出生成excel表,快速生成且解决中文乱码问题。
- 怎么样使用Navicat for MySQL 导出mysql中的数据和将sql数据库文件导入到mysql数据库中
- linux系统下,MySQL导入导出数据 ErrCode(13)(permission denied)解决方案
- oracle如何快速导入导出文本格式数据
- mysql命令导入导出数据
- 八、mysql数据导入、导出
- MYSQL数据导入导出大全
