高并发之 - 全局有序唯一id Snowflake 应用实战
2017-07-22 11:33
190 查看
前言
本篇主要介绍高并发算法Snowflake是怎么应用到实战项目中的。
对于怎么理解Snowflake算法,大家可以从网上搜索‘Snowflake’,大量资源可供查看,这里就不一一详诉,这里主要介绍怎么实战应用。
对于不理解的,可以看看这篇文章 Twitter-Snowflake,64位自增ID算法详解
首先它是Twitter提出来的。
前世今生
以前我们可以用UUID作为唯一标识,但是UUID是无序的,又是英文、数字、横杆的结合。当我们要生成有序的id并且按时间排序时,UUID必然不是最好的选择。
当我们需要有序的id时,可以用数据库的自增长id,但是在当今高并发系统时代下,自增长id速度太慢,满足不了需求。然而,对于有‘有序的id按时间排序’这一需求时,Twitter提出了它的算法,并且用于Twitter中。
需要注意的地方
可达并发量根据不同的配置不同,每秒上万并发量不成问题。
id可用时间:69年
使用限制
使用Snowflake其实有个限制,就是必须知道运行中是哪台机器。比如我们用Azure云,配置了10个实例(机器),要知道这10个机器是哪一台。
开始用Snowflake
首先,直接贴Snowflake算法代码,算法怎么实现就不具体说:(C#版,java版的代码也一样实现)
怎么用呢?
直接用
说明
workerId是机器id,表示分布式环境下的那台机器。datacenterId是数据库中心,表示哪个数据库中心。这里的机器id与数据库中心id最大是31。
我们看到nextId方法里面是用锁来生成id的。
然而我们怎么真正地应用到我们实际的项目中呢?
Snowflake运用到项目中
例如,我们分布式有三台机器,1个数据库。
那么workerId分别在机器A/B/C中的值为1/2/3,datacenterId都为0。
这个配置好了之后,那么我们怎么在代码里面编写呢?
比如,对于一个web应用,我们都知道,在客户端请求时,服务器都会生成一个Controller,那么怎么保证IdWorker实例只能在一台服务器中存在一个呢?
答案大家都知道,是静态属性(当然也可以单例)。下面我们用控制台程序来模仿一下controller的请求,当10个线程请求时会发生什么情况。
模仿的Controller如下:
我们看到,id会生成1000000个,并且如果有相同的时候打印出来相同的id。(这里为什么用锁来锁住HashSet,因为HashSet线程不是安全的,所以要用锁)
下面我在主程序中,开启10个线程,分别来new一次TestIdWorkerController,new一次Thread。
我们看到,每秒打印输出的集合,如何输出的集合数量=1000000(id数)*10(线程数),也侧面验证了没有重复。
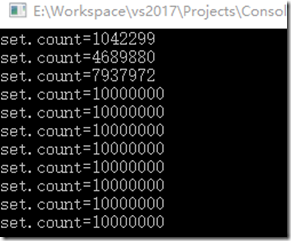
从上图看出,执行完毕,并且没打印same,结果也为1000000(id数)*10(线程数)。所以尽情的所用吧。
本篇主要介绍高并发算法Snowflake是怎么应用到实战项目中的。
对于怎么理解Snowflake算法,大家可以从网上搜索‘Snowflake’,大量资源可供查看,这里就不一一详诉,这里主要介绍怎么实战应用。
对于不理解的,可以看看这篇文章 Twitter-Snowflake,64位自增ID算法详解
为什么有Snowflake算法的出现呢?
首先它是Twitter提出来的。
前世今生
以前我们可以用UUID作为唯一标识,但是UUID是无序的,又是英文、数字、横杆的结合。当我们要生成有序的id并且按时间排序时,UUID必然不是最好的选择。
当我们需要有序的id时,可以用数据库的自增长id,但是在当今高并发系统时代下,自增长id速度太慢,满足不了需求。然而,对于有‘有序的id按时间排序’这一需求时,Twitter提出了它的算法,并且用于Twitter中。
需要注意的地方
可达并发量根据不同的配置不同,每秒上万并发量不成问题。
id可用时间:69年
使用限制
使用Snowflake其实有个限制,就是必须知道运行中是哪台机器。比如我们用Azure云,配置了10个实例(机器),要知道这10个机器是哪一台。
开始用Snowflake
首先,直接贴Snowflake算法代码,算法怎么实现就不具体说:(C#版,java版的代码也一样实现)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp6
{
/// <summary>
/// From: https://github.com/twitter/snowflake /// An object that generates IDs.
/// This is broken into a separate class in case
/// we ever want to support multiple worker threads
/// per process
/// </summary>
public class IdWorker
{
private long workerId;
private long datacenterId;
private long sequence = 0L;
private static long twepoch = 1288834974657L;
/// <summary>
/// 机器标识位数
/// </summary>
private static long workerIdBits = 5L;
/// <summary>
/// //数据中心标识位数
/// </summary>
private static long datacenterIdBits = 5L;
/// <summary>
/// //机器ID最大值
/// </summary>
private static long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << (int)workerIdBits);
/// <summary>
/// //数据中心ID最大值
/// </summary>
private static long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << (int)datacenterIdBits);
/// <summary>
/// //毫秒内自增位
/// </summary>
private static long sequenceBits = 12L;
/// <summary>
/// //机器ID偏左移12位
/// </summary>
private long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;
/// <summary>
/// //数据中心ID左移17位
/// </summary>
private long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;
/// <summary>
/// //时间毫秒左移22位
/// </summary>
private long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits;
private long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << (int)sequenceBits);
private long lastTimestamp = -1L;
private static object syncRoot = new object();
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="workerId">机器id,哪台机器。最大31</param>
/// <param name="datacenterId">数据中心id,哪个数据库,最大31</param>
public IdWorker(long workerId, long datacenterId)
{
// sanity check for workerId
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentException(string.Format("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxWorkerId));
}
if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentException(string.Format("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", maxDatacenterId));
}
this.workerId = workerId;
this.datacenterId = datacenterId;
}
public long nextId()
{
lock (syncRoot)
{
long timestamp = timeGen();
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp)
{
throw new ApplicationException(string.Format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds", lastTimestamp - timestamp));
}
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp)
{
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
if (sequence == 0)
{
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);
}
}
else
{
sequence = 0L;
}
lastTimestamp = timestamp;
return ((timestamp - twepoch) << (int)timestampLeftShift) | (datacenterId << (int)datacenterIdShift) | (workerId << (int)workerIdShift) | sequence;
}
}
protected long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp)
{
long timestamp = timeGen();
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp)
{
timestamp = timeGen();
}
return timestamp;
}
protected long timeGen()
{
return (long)(DateTime.UtcNow - new DateTime(1970, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, DateTimeKind.Utc)).TotalMilliseconds;
}
}
}怎么用呢?
直接用
IdWorker idWorker = new IdWorker(1, 2); long id = idWorker.nextId();
说明
workerId是机器id,表示分布式环境下的那台机器。datacenterId是数据库中心,表示哪个数据库中心。这里的机器id与数据库中心id最大是31。
我们看到nextId方法里面是用锁来生成id的。
然而我们怎么真正地应用到我们实际的项目中呢?
Snowflake运用到项目中
例如,我们分布式有三台机器,1个数据库。
那么workerId分别在机器A/B/C中的值为1/2/3,datacenterId都为0。
这个配置好了之后,那么我们怎么在代码里面编写呢?
比如,对于一个web应用,我们都知道,在客户端请求时,服务器都会生成一个Controller,那么怎么保证IdWorker实例只能在一台服务器中存在一个呢?
答案大家都知道,是静态属性(当然也可以单例)。下面我们用控制台程序来模仿一下controller的请求,当10个线程请求时会发生什么情况。
模仿的Controller如下:
class TestIdWorkerController
{
private static readonly IdWorker _idWorker = new IdWorker(1, 2);
public void GenerateId(HashSet<long> set)
{
int i = 0;
while (true)
{
if (i++ == 1000000)
break;
long id = _idWorker.nextId();
lock (set)
{
if (!set.Add(id))
Console.WriteLine($"same id={id}");
}
}
}
}我们看到,id会生成1000000个,并且如果有相同的时候打印出来相同的id。(这里为什么用锁来锁住HashSet,因为HashSet线程不是安全的,所以要用锁)
下面我在主程序中,开启10个线程,分别来new一次TestIdWorkerController,new一次Thread。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//存放id的集合
HashSet<long> set = new HashSet<long>();
//启动10个线程
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
TestIdWorkerController testIdWorker = new TestIdWorkerController();
Thread thread = new Thread(() => testIdWorker.GenerateId(set));
thread.Start();
}
//每秒钟打印当前生成的状态
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine($"set.count={set.Count}");
Thread.Sleep(1000 * 1);
}
}我们看到,每秒打印输出的集合,如何输出的集合数量=1000000(id数)*10(线程数),也侧面验证了没有重复。

从上图看出,执行完毕,并且没打印same,结果也为1000000(id数)*10(线程数)。所以尽情的所用吧。
相关文章推荐
- Twitter的分布式自增ID算法Snowflake的PHP实现,Snowflake PHP版本,高并发唯一id,全局唯一id,不重复id
- 高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一(订单号)Id
- 全局唯一ID生成器(Snowflake ID组成)
- 高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id汇总
- 如何在高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id
- 高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id汇总
- 【转】高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id汇总
- 高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id汇总
- 【转】如何在高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id
- 如何在高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id
- 高并发分布式环境中获取全局唯一ID[分布式数据库全局唯一主键生成]
- 高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id汇总
- 如何在高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id
- 如何在高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id
- 在高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id
- Snowflake 全局唯一Id 生成
- 分布式ID生成方法-趋势有序的全局唯一ID
- 高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id汇总
- 如何在高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id
- 如何在高并发分布式系统中生成全局唯一Id
