【原码笔记】-- protobuf.js 与 Long.js
2017-07-10 18:19
302 查看
protobuf.js的结构和webpack的加载之后的结构很相似。这样的模块化组合是个不错的结构方式。1个是适应了不同的加载方式,2个模块直接很独立。webpack的功能更全一点。但如果自己封装js库这样够用了。而且模块对外统一接口 module.exports。这和node很像。
在处理超过16位的整形就得使用Long.js了。 主要是fromString和toString。
fromstring的思路是把字符串8位一个截取。然后转成Long型(高位,地位,符号位) 加起来。最后是一个Long型。 4294967296 是2的32次方。每次操作之前都会有一个基数的操作 mul(radixToPower)或者mul(power)这两者都是保证result的位数是正确的。
比如{low:123} 和{low:1} 相加之前,先要让{low:123}乘以10,得到{low:1230}再与{low:1}进行位操作。因为第一个是高位,不能直接相加。
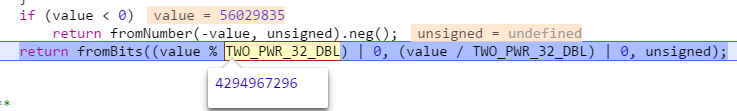
fromBits 即转为Long对象。value%4294967296 得到低位。/得到高位。结果通过位移合并起来。mul是bit的乘法,add是bit的加法。 原理是讲一个64位的拆成四段。分别16位。this.low左移16位 就得到 low的32-17位是啥。 然后和addend对象的同位相加
最后的合并是通过|运算。位移之后再还原确实很巧妙。一时看上去都不大理解。
>>>和>>有什么区别??。
toString
也是sub之后拼出来的。也就是fromstring的反向操作。
(function(global, undefined) {
"use strict";
(function prelude(modules, cache, entries) {
function $require(name) {
var $module = cache[name];
//没有就去加载
if (!$module)
modules[name][0].call($module = cache[name] = { exports: {} }, $require, $module, $module.exports);
return $module.exports;
}
//曝光成全局
var proto = global.proto = $require(entries[0]);
// AMD
if (typeof define === "function" && define.amd) {
define(["long"], function(Long) {
if (Long && Long.isLong) {
proto.util.Long = Long;
proto.configure();
}
});
return proto;
}
//CommonJS
if (typeof module === "object" && module && module.exports)
module.exports = proto;
})
//传参
({
1: [function (require, module, exports) {
function first() {
console.log("first");
}
module.exports = first;
}, {}],
2: [function(require, module, exports) {
function second() {
console.log("second");
}
module.exports = second;
}],
3: [function (require, module, exports) {
var proto = {};
proto.first = require(1);
proto.second = require(2);
proto.build = "full";
module.exports = proto;
}]
}, {}, [3]);
})(typeof window==="object"&&window||typeof self==="object"&&self||this)在处理超过16位的整形就得使用Long.js了。 主要是fromString和toString。
function fromString(str, unsigned, radix) {
if (str.length === 0)
throw Error('empty string');
if (str === "NaN" || str === "Infinity" || str === "+Infinity" || str === "-Infinity")
return ZERO;
if (typeof unsigned === 'number') {
// For goog.math.long compatibility
radix = unsigned,
unsigned = false;
} else {
unsigned = !!unsigned;
}
radix = radix || 10;
if (radix < 2 || 36 < radix)
throw RangeError('radix');
var p;
if ((p = str.indexOf('-')) > 0)
throw Error('interior hyphen');
else if (p === 0) {
return fromString(str.substring(1), unsigned, radix).neg();
}
// Do several (8) digits each time through the loop, so as to
// minimize the calls to the very expensive emulated div.
var radixToPower = fromNumber(pow_dbl(radix, 8));
var result = ZERO;
for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i += 8) {
var size = Math.min(8, str.length - i),
value = parseInt(str.substring(i, i + size), radix);
if (size < 8) {
var power = fromNumber(pow_dbl(radix, size));
result = result.mul(power).add(fromNumber(value));
} else {
result = result.mul(radixToPower);
result = result.add(fromNumber(value));
}
}
result.unsigned = unsigned;
return result;
}fromstring的思路是把字符串8位一个截取。然后转成Long型(高位,地位,符号位) 加起来。最后是一个Long型。 4294967296 是2的32次方。每次操作之前都会有一个基数的操作 mul(radixToPower)或者mul(power)这两者都是保证result的位数是正确的。
比如{low:123} 和{low:1} 相加之前,先要让{low:123}乘以10,得到{low:1230}再与{low:1}进行位操作。因为第一个是高位,不能直接相加。

function fromBits(lowBits, highBits, unsigned) {
return new Long(lowBits, highBits, unsigned);
}fromBits 即转为Long对象。value%4294967296 得到低位。/得到高位。结果通过位移合并起来。mul是bit的乘法,add是bit的加法。 原理是讲一个64位的拆成四段。分别16位。this.low左移16位 就得到 low的32-17位是啥。 然后和addend对象的同位相加
最后的合并是通过|运算。位移之后再还原确实很巧妙。一时看上去都不大理解。
LongPrototype.add = function add(addend) {
if (!isLong(addend))
addend = fromValue(addend);
// Divide each number into 4 chunks of 16 bits, and then sum the chunks.
var a48 = this.high >>> 16;
var a32 = this.high & 0xFFFF;
var a16 = this.low >>> 16;
var a00 = this.low & 0xFFFF;
var b48 = addend.high >>> 16;
var b32 = addend.high & 0xFFFF;
var b16 = addend.low >>> 16;
var b00 = addend.low & 0xFFFF;
var c48 = 0, c32 = 0, c16 = 0, c00 = 0;
c00 += a00 + b00;
c16 += c00 >>> 16;
c00 &= 0xFFFF;
c16 += a16 + b16;
c32 += c16 >>> 16;
c16 &= 0xFFFF;
c32 += a32 + b32;
c48 += c32 >>> 16;
c32 &= 0xFFFF;
c48 += a48 + b48;
c48 &= 0xFFFF;
return fromBits((c16 << 16) | c00, (c48 << 16) | c32, this.unsigned);
};>>>和>>有什么区别??。
toString
LongPrototype.toString = function toString(radix) {
radix = radix || 10;
if (radix < 2 || 36 < radix)
throw RangeError('radix');
if (this.isZero())
return '0';
if (this.isNegative()) { // Unsigned Longs are never negative
if (this.eq(MIN_VALUE)) {
// We need to change the Long value before it can be negated, so we remove
// the bottom-most digit in this base and then recurse to do the rest.
var radixLong = fromNumber(radix),
div = this.div(radixLong),
rem1 = div.mul(radixLong).sub(this);
return div.toString(radix) + rem1.toInt().toString(radix);
} else
return '-' + this.neg().toString(radix);
}
// Do several (6) digits each time through the loop, so as to
// minimize the calls to the very expensive emulated div.
var radixToPower = fromNumber(pow_dbl(radix, 6), this.unsigned),
rem = this;
var result = '';
while (true) {
var remDiv = rem.div(radixToPower),
intval = rem.sub(remDiv.mul(radixToPower)).toInt() >>> 0,
digits = intval.toString(radix);
rem = remDiv;
if (rem.isZero())
return digits + result;
else {
while (digits.length < 6)
digits = '0' + digits;
result = '' + digits + result;
}
}
};也是sub之后拼出来的。也就是fromstring的反向操作。
相关文章推荐
- Protobuf笔记以及Java Js 示例
- linux下Google的Protobuf安装及使用笔记
- linux下Google的Protobuf安装及使用笔记
- js protobuf int64 解决方案
- google protobuf学习笔记一:windows下环境配置
- google protobuf 使用过程笔记
- ProtoBuf 笔记
- Cocos2d-JS/Ajax用Protobuf与NodeJS/Java通信
- libevent&&protobuf交叉编译笔记
- 基于Netty5.0高级案例二之WebSocket中关于使用ProtoBuf传输数据介绍js部分
- 笔记-js将long日期格式转换为标准日期格式
- ios下使用protobuf的笔记
- Android Protobuf 初探笔记
- protobuf学习笔记
- cocos creator: js中实现protobuf的打包和解析
- protobuf学习笔记
- netty与protobuf与node.js
- Protobuf C/C++实战笔记(1)
- protobuf实现js与java间的http通信
