ffmpeg 函数简单分析 : av_read_frame()
2017-06-26 09:30
736 查看
ffmpeg中的av_read_frame()的作用是读取码流中的音频若干帧或者视频一帧。例如,解码视频的时候,每解码一个视频帧,需要先调用 av_read_frame()获得一帧视频的压缩数据,然后才能对该数据进行解码(例如H.264中一帧压缩数据通常对应一个NAL)。
对该函数源代码的分析是很久之前做的了,现在翻出来,用博客记录一下。
上代码之前,先参考了其他人对av_read_frame()的解释,在此做一个参考:
通过av_read_packet(***),读取一个包,需要说明的是此函数必须是包含整数帧的,不存在半帧的情况,以ts流为例,是读取一个完整的PES包(一个完整pes包包含若干视频或音频es包),读取完毕后,通过av_parser_parse2(***)分析出视频一帧(或音频若干帧),返回,下次进入循环的时候,如果上次的数据没有完全取完,则st = s->cur_st;不会是NULL,即再此进入av_parser_parse2(***)流程,而不是下面的av_read_packet(**)流程,这样就保证了,如果读取一次包含了N帧视频数据(以视频为例),则调用av_read_frame(***)N次都不会去读数据,而是返回第一次读取的数据,直到全部解析完毕。
av_read_frame()的声明位于libavformat\avformat.h,如下所示。
[cpp] view
plain copy
/**
* Return the next frame of a stream.
* This function returns what is stored in the file, and does not validate
* that what is there are valid frames for the decoder. It will split what is
* stored in the file into frames and return one for each call. It will not
* omit invalid data between valid frames so as to give the decoder the maximum
* information possible for decoding.
*
* If pkt->buf is NULL, then the packet is valid until the next
* av_read_frame() or until avformat_close_input(). Otherwise the packet
* is valid indefinitely. In both cases the packet must be freed with
* av_free_packet when it is no longer needed. For video, the packet contains
* exactly one frame. For audio, it contains an integer number of frames if each
* frame has a known fixed size (e.g. PCM or ADPCM data). If the audio frames
* have a variable size (e.g. MPEG audio), then it contains one frame.
*
* pkt->pts, pkt->dts and pkt->duration are always set to correct
* values in AVStream.time_base units (and guessed if the format cannot
* provide them). pkt->pts can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if the video format
* has B-frames, so it is better to rely on pkt->dts if you do not
* decompress the payload.
*
* @return 0 if OK, < 0 on error or end of file
*/
int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);
av_read_frame()使用方法在注释中写得很详细,用中文简单描述一下它的两个参数:
s:输入的AVFormatContext
pkt:输出的AVPacket
如果返回0则说明读取正常。
函数调用结构图如下所示。
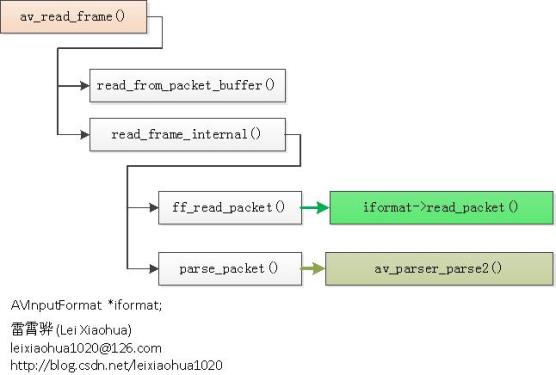
av_read_frame()的定义位于libavformat\utils.c,如下所示:
[cpp] view
plain copy
//获取一个AVPacket
/*
* av_read_frame - 新版本的ffmpeg用的是av_read_frame,而老版本的是av_read_packet
* 。区别是av_read_packet读出的是包,它可能是半帧或多帧,不保证帧的完整性。av_read_frame对
* av_read_packet进行了封装,使读出的数据总是完整的帧
*/
int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
const int genpts = s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_GENPTS;
int eof = 0;
if (!genpts)
/**
* This buffer is only needed when packets were already buffered but
* not decoded, for example to get the codec parameters in MPEG
* streams.
* 一般情况下会调用read_frame_internal(s, pkt)
* 直接返回
*/
return s->packet_buffer ? read_from_packet_buffer(s, pkt) :
read_frame_internal(s, pkt);
for (;;) {
int ret;
AVPacketList *pktl = s->packet_buffer;
if (pktl) {
AVPacket *next_pkt = &pktl->pkt;
if (next_pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
int wrap_bits = s->streams[next_pkt->stream_index]->pts_wrap_bits;
while (pktl && next_pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
if (pktl->pkt.stream_index == next_pkt->stream_index &&
(av_compare_mod(next_pkt->dts, pktl->pkt.dts, 2LL << (wrap_bits - 1)) < 0) &&
av_compare_mod(pktl->pkt.pts, pktl->pkt.dts, 2LL << (wrap_bits - 1))) { //not b frame
next_pkt->pts = pktl->pkt.dts;
}
pktl = pktl->next;
}
pktl = s->packet_buffer;
}
/* read packet from packet buffer, if there is data */
if (!(next_pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE &&
next_pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE && !eof))
return read_from_packet_buffer(s, pkt);
}
ret = read_frame_internal(s, pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
if (pktl && ret != AVERROR(EAGAIN)) {
eof = 1;
continue;
} else
return ret;
}
if (av_dup_packet(add_to_pktbuf(&s->packet_buffer, pkt,
&s->packet_buffer_end)) < 0)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
}
可以从源代码中看出,av_read_frame()调用了read_frame_internal()。
read_frame_internal()代码如下所示:
[cpp] view
plain copy
//av_read_frame对他进行了封装
static int read_frame_internal(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
int ret = 0, i, got_packet = 0;
AVDictionary *metadata = NULL;
//初始化
av_init_packet(pkt);
while (!got_packet && !s->parse_queue) {
AVStream *st;
AVPacket cur_pkt;
/* read next packet */
ret = ff_read_packet(s, &cur_pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN))
return ret;
/* flush the parsers */
for (i = 0; i < s->nb_streams; i++) {
st = s->streams[i];
//需要解析
if (st->parser && st->need_parsing)
parse_packet(s, NULL, st->index);
}
/* all remaining packets are now in parse_queue =>
* really terminate parsing */
break;
}
ret = 0;
st = s->streams[cur_pkt.stream_index];
if (cur_pkt.pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE &&
cur_pkt.dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE &&
cur_pkt.pts < cur_pkt.dts) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Invalid timestamps stream=%d, pts=%s, dts=%s, size=%d\n",
cur_pkt.stream_index,
av_ts2str(cur_pkt.pts),
av_ts2str(cur_pkt.dts),
cur_pkt.size);
}
if (s->debug & FF_FDEBUG_TS)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG,
"ff_read_packet stream=%d, pts=%s, dts=%s, size=%d, duration=%d, flags=%d\n",
cur_pkt.stream_index,
av_ts2str(cur_pkt.pts),
av_ts2str(cur_pkt.dts),
cur_pkt.size, cur_pkt.duration, cur_pkt.flags);
if (st->need_parsing && !st->parser && !(s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_NOPARSE)) {
st->parser = av_parser_init(st->codec->codec_id);
if (!st->parser) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_VERBOSE, "parser not found for codec "
"%s, packets or times may be invalid.\n",
avcodec_get_name(st->codec->codec_id));
/* no parser available: just output the raw packets */
st->need_parsing = AVSTREAM_PARSE_NONE;
} else if (st->need_parsing == AVSTREAM_PARSE_HEADERS)
st->parser->flags |= PARSER_FLAG_COMPLETE_FRAMES;
else if (st->need_parsing == AVSTREAM_PARSE_FULL_ONCE)
st->parser->flags |= PARSER_FLAG_ONCE;
else if (st->need_parsing == AVSTREAM_PARSE_FULL_RAW)
st->parser->flags |= PARSER_FLAG_USE_CODEC_TS;
}
if (!st->need_parsing || !st->parser) {
/* no parsing needed: we just output the packet as is */
*pkt = cur_pkt;
compute_pkt_fields(s, st, NULL, pkt);
if ((s->iformat->flags & AVFMT_GENERIC_INDEX) &&
(pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY) && pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
ff_reduce_index(s, st->index);
av_add_index_entry(st, pkt->pos, pkt->dts,
0, 0, AVINDEX_KEYFRAME);
}
got_packet = 1;
} else if (st->discard < AVDISCARD_ALL) {
if ((ret = parse_packet(s, &cur_pkt, cur_pkt.stream_index)) < 0)
return ret;
} else {
/* free packet */
av_free_packet(&cur_pkt);
}
if (pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY)
st->skip_to_keyframe = 0;
if (st->skip_to_keyframe) {
av_free_packet(&cur_pkt);
if (got_packet) {
*pkt = cur_pkt;
}
got_packet = 0;
}
}
if (!got_packet && s->parse_queue)
ret = read_from_packet_buffer(&s->parse_queue, &s->parse_queue_end, pkt);
if (ret >= 0) {
AVStream *st = s->streams[pkt->stream_index];
int discard_padding = 0;
if (st->first_discard_sample && pkt->pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
int64_t pts = pkt->pts - (is_relative(pkt->pts) ? RELATIVE_TS_BASE : 0);
int64_t sample = ts_to_samples(st, pts);
int duration = ts_to_samples(st, pkt->duration);
int64_t end_sample = sample + duration;
if (duration > 0 && end_sample >= st->first_discard_sample &&
sample < st->last_discard_sample)
discard_padding = FFMIN(end_sample - st->first_discard_sample, duration);
}
if (st->skip_samples || discard_padding) {
uint8_t *p = av_packet_new_side_data(pkt, AV_PKT_DATA_SKIP_SAMPLES, 10);
if (p) {
AV_WL32(p, st->skip_samples);
AV_WL32(p + 4, discard_padding);
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "demuxer injecting skip %d\n", st->skip_samples);
}
st->skip_samples = 0;
}
if (st->inject_global_side_data) {
for (i = 0; i < st->nb_side_data; i++) {
AVPacketSideData *src_sd = &st->side_data[i];
uint8_t *dst_data;
if (av_packet_get_side_data(pkt, src_sd->type, NULL))
continue;
dst_data = av_packet_new_side_data(pkt, src_sd->type, src_sd->size);
if (!dst_data) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Could not inject global side data\n");
continue;
}
memcpy(dst_data, src_sd->data, src_sd->size);
}
st->inject_global_side_data = 0;
}
if (!(s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_KEEP_SIDE_DATA))
av_packet_merge_side_data(pkt);
}
av_opt_get_dict_val(s, "metadata", AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN, &metadata);
if (metadata) {
s->event_flags |= AVFMT_EVENT_FLAG_METADATA_UPDATED;
av_dict_copy(&s->metadata, metadata, 0);
av_dict_free(&metadata);
av_opt_set_dict_val(s, "metadata", NULL, AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN);
}
if (s->debug & FF_FDEBUG_TS)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG,
"read_frame_internal stre
20000
am=%d, pts=%s, dts=%s, "
"size=%d, duration=%d, flags=%d\n",
pkt->stream_index,
av_ts2str(pkt->pts),
av_ts2str(pkt->dts),
pkt->size, pkt->duration, pkt->flags);
return ret;
}
read_frame_internal()代码比较长,这里只简单看一下它前面的部分。它前面部分有2步是十分关键的:
(1)调用了ff_read_packet()从相应的AVInputFormat读取数据。
(2)如果媒体频流需要使用AVCodecParser,则调用parse_packet()解析相应的AVPacket。
下面我们分成分别看一下ff_read_packet()和parse_packet()的源代码。
ff_read_packet()的代码比较长,如下所示。
[cpp] view
plain copy
int ff_read_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
int ret, i, err;
AVStream *st;
for (;;) {
AVPacketList *pktl = s->raw_packet_buffer;
if (pktl) {
*pkt = pktl->pkt;
st = s->streams[pkt->stream_index];
if (s->raw_packet_buffer_remaining_size <= 0)
if ((err = probe_codec(s, st, NULL)) < 0)
return err;
if (st->request_probe <= 0) {
s->raw_packet_buffer = pktl->next;
s->raw_packet_buffer_remaining_size += pkt->size;
av_free(pktl);
return 0;
}
}
pkt->data = NULL;
pkt->size = 0;
av_init_packet(pkt);
//关键:读取Packet
ret = s->iformat->read_packet(s, pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
if (!pktl || ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN))
return ret;
for (i = 0; i < s->nb_streams; i++) {
st = s->streams[i];
if (st->probe_packets)
if ((err = probe_codec(s, st, NULL)) < 0)
return err;
av_assert0(st->request_probe <= 0);
}
continue;
}
if ((s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_DISCARD_CORRUPT) &&
(pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_CORRUPT)) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Dropped corrupted packet (stream = %d)\n",
pkt->stream_index);
av_free_packet(pkt);
continue;
}
if (pkt->stream_index >= (unsigned)s->nb_streams) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Invalid stream index %d\n", pkt->stream_index);
continue;
}
st = s->streams[pkt->stream_index];
if (update_wrap_reference(s, st, pkt->stream_index, pkt) && st->pts_wrap_behavior == AV_PTS_WRAP_SUB_OFFSET) {
// correct first time stamps to negative values
if (!is_relative(st->first_dts))
st->first_dts = wrap_timestamp(st, st->first_dts);
if (!is_relative(st->start_time))
st->start_time = wrap_timestamp(st, st->start_time);
if (!is_relative(st->cur_dts))
st->cur_dts = wrap_timestamp(st, st->cur_dts);
}
pkt->dts = wrap_timestamp(st, pkt->dts);
pkt->pts = wrap_timestamp(st, pkt->pts);
force_codec_ids(s, st);
/* TODO: audio: time filter; video: frame reordering (pts != dts) */
if (s->use_wallclock_as_timestamps)
pkt->dts = pkt->pts = av_rescale_q(av_gettime(), AV_TIME_BASE_Q, st->time_base);
if (!pktl && st->request_probe <= 0)
return ret;
add_to_pktbuf(&s->raw_packet_buffer, pkt, &s->raw_packet_buffer_end);
s->raw_packet_buffer_remaining_size -= pkt->size;
if ((err = probe_codec(s, st, pkt)) < 0)
return err;
}
}
ff_read_packet()中最关键的地方就是调用了AVInputFormat的read_packet()方法。AVInputFormat的read_packet()是一个函数指针,指向当前的AVInputFormat的读取数据的函数。在这里我们以FLV封装格式对应的AVInputFormat为例,看看read_packet()的实现函数是什么样子的。
FLV封装格式对应的AVInputFormat的定义位于libavformat\flvdec.c,如下所示。
[cpp] view
plain copy
AVInputFormat ff_flv_demuxer = {
.name = "flv",
.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("FLV (Flash Video)"),
.priv_data_size = sizeof(FLVContext),
.read_probe = flv_probe,
.read_header = flv_read_header,
.read_packet = flv_read_packet,
.read_seek = flv_read_seek,
.read_close = flv_read_close,
.extensions = "flv",
.priv_class = &flv_class,
};
从ff_flv_demuxer的定义可以看出,read_packet()对应的是flv_read_packet()函数。在看flv_read_packet()函数之前,我们先回顾一下FLV封装格式的结构,如下图所示。

从图中可以看出,FLV文件体部分是由一个一个的Tag连接起来的(中间间隔着Previous Tag Size)。每个Tag包含了Tag Header和Tag Data两个部分。Tag Data根据Tag的Type不同而不同:可以分为音频Tag Data,视频Tag Data以及Script Tag Data。下面简述一下音频Tag Data和视频Tag Data。
Audio Tag在官方标准中定义如下。

Audio Tag开始的第1个字节包含了音频数据的参数信息,从第2个字节开始为音频流数据。
第1个字节的前4位的数值表示了音频数据格式:
0 = Linear PCM, platform endian
1 = ADPCM
2 = MP3
3 = Linear PCM, little endian
4 = Nellymoser 16-kHz mono
5 = Nellymoser 8-kHz mono
6 = Nellymoser
7 = G.711 A-law logarithmic PCM
8 = G.711 mu-law logarithmic PCM
9 = reserved
10 = AAC
14 = MP3 8-Khz
15 = Device-specific sound
第1个字节的第5-6位的数值表示采样率:0 = 5.5kHz,1 = 11KHz,2 = 22 kHz,3 = 44 kHz。
第1个字节的第7位表示采样精度:0 = 8bits,1 = 16bits。
第1个字节的第8位表示音频类型:0 = sndMono,1 = sndStereo。
其中,当音频编码为AAC的时候,第一个字节后面存储的是AACAUDIODATA,格式如下所示。

Video Tag在官方标准中的定义如下。

Video Tag也用开始的第1个字节包含视频数据的参数信息,从第2个字节为视频流数据。
第1个字节的前4位的数值表示帧类型(FrameType):
1: keyframe (for AVC, a seekableframe)(关键帧)
2: inter frame (for AVC, a nonseekableframe)
3: disposable inter frame (H.263only)
4: generated keyframe (reservedfor server use only)
5: video info/command frame
第1个字节的后4位的数值表示视频编码ID(CodecID):
1: JPEG (currently unused)
2: Sorenson H.263
3: Screen video
4: On2 VP6
5: On2 VP6 with alpha channel
6: Screen video version 2
7: AVC
其中,当音频编码为AVC(H.264)的时候,第一个字节后面存储的是AVCVIDEOPACKET,格式如下所示。

了解了FLV的基本格式之后,就可以看一下FLV解析Tag的函数flv_read_packet()了。
flv_read_packet()的定义位于libavformat\flvdec.c,如下所示。
[cpp] view
plain copy
static int flv_read_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
FLVContext *flv = s->priv_data;
int ret, i, type, size, flags;
int stream_type=-1;
int64_t next, pos, meta_pos;
int64_t dts, pts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
int av_uninit(channels);
int av_uninit(sample_rate);
AVStream *st = NULL;
/* pkt size is repeated at end. skip it */
for (;; avio_skip(s->pb, 4)) {
pos = avio_tell(s->pb);
//解析Tag Header==========
//Tag类型
type = (avio_r8(s->pb) & 0x1F);
//Datasize数据大小
size = avio_rb24(s->pb);
//Timstamp时间戳
dts = avio_rb24(s->pb);
dts |= avio_r8(s->pb) << 24;
av_dlog(s, "type:%d, size:%d, dts:%"PRId64" pos:%"PRId64"\n", type, size, dts, avio_tell(s->pb));
if (avio_feof(s->pb))
return AVERROR_EOF;
//StreamID
avio_skip(s->pb, 3); /* stream id, always 0 */
flags = 0;
//========================
if (flv->validate_next < flv->validate_count) {
int64_t validate_pos = flv->validate_index[flv->validate_next].pos;
if (pos == validate_pos) {
if (FFABS(dts - flv->validate_index[flv->validate_next].dts) <=
VALIDATE_INDEX_TS_THRESH) {
flv->validate_next++;
} else {
clear_index_entries(s, validate_pos);
flv->validate_count = 0;
}
} else if (pos > validate_pos) {
clear_index_entries(s, validate_pos);
flv->validate_count = 0;
}
}
if (size == 0)
continue;
next = size + avio_tell(s->pb);
if (type == FLV_TAG_TYPE_AUDIO) {
//Type是音频
stream_type = FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO;
//Tag Data的第一个字节
flags = avio_r8(s->pb);
size--;
} else if (type == FLV_TAG_TYPE_VIDEO) {
//Type是音频
stream_type = FLV_STREAM_TYPE_VIDEO;
//Tag Data的第一个字节
flags = avio_r8(s->pb);
size--;
if ((flags & FLV_VIDEO_FRAMETYPE_MASK) == FLV_FRAME_VIDEO_INFO_CMD)
goto skip;
} else if (type == FLV_TAG_TYPE_META) {
stream_type=FLV_STREAM_TYPE_DATA;
if (size > 13 + 1 + 4 && dts == 0) { // Header-type metadata stuff
meta_pos = avio_tell(s->pb);
if (flv_read_metabody(s, next) <= 0) {
goto skip;
}
avio_seek(s->pb, meta_pos, SEEK_SET);
}
} else {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG,
"Skipping flv packet: type %d, size %d, flags %d.\n",
type, size, flags);
skip:
avio_seek(s->pb, next, SEEK_SET);
continue;
}
/* skip empty data packets */
if (!size)
continue;
/* now find stream */
for (i = 0; i < s->nb_streams; i++) {
st = s->streams[i];
if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO) {
if (st->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO &&
(s->audio_codec_id || flv_same_audio_codec(st->codec, flags)))
break;
} else if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_VIDEO) {
if (st->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO &&
(s->video_codec_id || flv_same_video_codec(st->codec, flags)))
break;
} else if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_DATA) {
if (st->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA)
break;
}
}
if (i == s->nb_streams) {
static const enum AVMediaType stream_types[] = {AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO, AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA};
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Stream discovered after head already parsed\n");
st = create_stream(s, stream_types[stream_type]);
if (!st)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
av_dlog(s, "%d %X %d \n", stream_type, flags, st->discard);
if ((flags & FLV_VIDEO_FRAMETYPE_MASK) == FLV_FRAME_KEY ||
stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO)
av_add_index_entry(st, pos, dts, size, 0, AVINDEX_KEYFRAME);
if ( (st->discard >= AVDISCARD_NONKEY && !((flags & FLV_VIDEO_FRAMETYPE_MASK) == FLV_FRAME_KEY || (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO)))
||(st->discard >= AVDISCARD_BIDIR && ((flags & FLV_VIDEO_FRAMETYPE_MASK) == FLV_FRAME_DISP_INTER && (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_VIDEO)))
|| st->discard >= AVDISCARD_ALL
) {
avio_seek(s->pb, next, SEEK_SET);
continue;
}
break;
}
// if not streamed and no duration from metadata then seek to end to find
// the duration from the timestamps
if (s->pb->seekable && (!s->duration || s->duration == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) && !flv->searched_for_end) {
int size;
const int64_t pos = avio_tell(s->pb);
// Read the last 4 bytes of the file, this should be the size of the
// previous FLV tag. Use the timestamp of its payload as duration.
int64_t fsize = avio_size(s->pb);
retry_duration:
avio_seek(s->pb, fsize - 4, SEEK_SET);
size = avio_rb32(s->pb);
// Seek to the start of the last FLV tag at position (fsize - 4 - size)
// but skip the byte indicating the type.
avio_seek(s->pb, fsize - 3 - size, SEEK_SET);
if (size == avio_rb24(s->pb) + 11) {
uint32_t ts = avio_rb24(s->pb);
ts |= avio_r8(s->pb) << 24;
if (ts)
s->duration = ts * (int64_t)AV_TIME_BASE / 1000;
else if (fsize >= 8 && fsize - 8 >= size) {
fsize -= size+4;
goto retry_duration;
}
}
avio_seek(s->pb, pos, SEEK_SET);
flv->searched_for_end = 1;
}
if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO) {
int bits_per_coded_sample;
channels = (flags & FLV_AUDIO_CHANNEL_MASK) == FLV_STEREO ? 2 : 1;
sample_rate = 44100 << ((flags & FLV_AUDIO_SAMPLERATE_MASK) >>
FLV_AUDIO_SAMPLERATE_OFFSET) >> 3;
bits_per_coded_sample = (flags & FLV_AUDIO_SAMPLESIZE_MASK) ? 16 : 8;
if (!st->codec->channels || !st->codec->sample_rate ||
!st->codec->bits_per_coded_sample) {
st->codec->channels = channels;
st->codec->channel_layout = channels == 1
? AV_CH_LAYOUT_MONO
: AV_CH_LAYOUT_STEREO;
st->codec->sample_rate = sample_rate;
st->codec->bits_per_coded_sample = bits_per_coded_sample;
}
if (!st->codec->codec_id) {
flv_set_audio_codec(s, st, st->codec,
flags & FLV_AUDIO_CODECID_MASK);
flv->last_sample_rate =
sample_rate = st->codec->sample_rate;
flv->last_channels =
channels = st->codec->channels;
} else {
AVCodecContext ctx = {0};
ctx.sample_rate = sample_rate;
ctx.bits_per_coded_sample = bits_per_coded_sample;
flv_set_audio_codec(s, st, &ctx, flags & FLV_AUDIO_CODECID_MASK);
sample_rate = ctx.sample_rate;
}
} else if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_VIDEO) {
size -= flv_set_video_codec(s, st, flags & FLV_VIDEO_CODECID_MASK, 1);
}
//几种特殊的格式
if (st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC ||
st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264 ||
st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4) {
//对应AACPacketType或者AVCPacketType
int type = avio_r8(s->pb);
size--;
//H.264
if (st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264 || st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4) {
// sign extension
//对应CompositionTime
int32_t cts = (avio_rb24(s->pb) + 0xff800000) ^ 0xff800000;
//计算PTS
pts = dts + cts;
if (cts < 0) { // dts might be wrong
if (!flv->wrong_dts)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Negative cts, previous timestamps might be wrong.\n");
flv->wrong_dts = 1;
} else if (FFABS(dts - pts) > 1000*60*15) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"invalid timestamps %"PRId64" %"PRId64"\n", dts, pts);
dts = pts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
}
}
//如果编码器是AAC或者H.264
if (type == 0 && (!st->codec->extradata || st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC ||
st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264)) {
AVDictionaryEntry *t;
if (st->codec->extradata) {
if ((ret = flv_queue_extradata(flv, s->pb, stream_type, size)) < 0)
return ret;
ret = AVERROR(EAGAIN);
goto leave;
}
if ((ret = flv_get_extradata(s, st, size)) < 0)
return ret;
/* Workaround for buggy Omnia A/XE encoder */
t = av_dict_get(s->metadata, "Encoder", NULL, 0);
if (st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC && t && !strcmp(t->value, "Omnia A/XE"))
st->codec->extradata_size = 2;
//AAC
if (st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC && 0) {
MPEG4AudioConfig cfg;
if (avpriv_mpeg4audio_get_config(&cfg, st->codec->extradata,
st->codec->extradata_size * 8, 1) >= 0) {
st->codec->channels = cfg.channels;
st->codec->channel_layout = 0;
if (cfg.ext_sample_rate)
st->codec->sample_rate = cfg.ext_sample_rate;
else
st->codec->sample_rate = cfg.sample_rate;
av_dlog(s, "mp4a config channels %d sample rate %d\n",
st->codec->channels, st->codec->sample_rate);
}
}
ret = AVERROR(EAGAIN);
goto leave;
}
}
/* skip empty data packets */
if (!size) {
ret = AVERROR(EAGAIN);
goto leave;
}
ret = av_get_packet(s->pb, pkt, size);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
//设置PTS、DTS等等
pkt->dts = dts;
pkt->pts = pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE ? dts : pts;
pkt->stream_index = st->index;
if (flv->new_extradata[stream_type]) {
uint8_t *side = av_packet_new_side_data(pkt, AV_PKT_DATA_NEW_EXTRADATA,
flv->new_extradata_size[stream_type]);
if (side) {
memcpy(side, flv->new_extradata[stream_type],
flv->new_extradata_size[stream_type]);
av_freep(&flv->new_extradata[stream_type]);
flv->new_extradata_size[stream_type] = 0;
}
}
if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO &&
(sample_rate != flv->last_sample_rate ||
channels != flv->last_channels)) {
flv->last_sample_rate = sample_rate;
flv->last_channels = channels;
ff_add_param_change(pkt, channels, 0, sample_rate, 0, 0);
}
//标记上Keyframe
if ( stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO ||
((flags & FLV_VIDEO_FRAMETYPE_MASK) == FLV_FRAME_KEY) ||
stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_DATA)
pkt->flags |= AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY;
leave:
avio_skip(s->pb, 4);
return ret;
}
flv_read_packet()的代码比较长,但是逻辑比较简单。它的主要功能就是根据FLV文件格式的规范,逐层解析Tag以及TagData,获取Tag以及TagData中的信息。比较关键的地方已经写上了注释,不再详细叙述。
parse_packet()给需要AVCodecParser的媒体流提供解析AVPacket的功能。它的代码如下所示:
[cpp] view
plain copy
/**
* Parse a packet, add all split parts to parse_queue.
*
* @param pkt Packet to parse, NULL when flushing the parser at end of stream.
*/
static int parse_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt, int stream_index)
{
AVPacket out_pkt = { 0 }, flush_pkt = { 0 };
AVStream *st = s->streams[stream_index];
uint8_t *data = pkt ? pkt->data : NULL;
int size = pkt ? pkt->size : 0;
int ret = 0, got_output = 0;
if (!pkt) {
av_init_packet(&flush_pkt);
pkt = &flush_pkt;
got_output = 1;
} else if (!size && st->parser->flags & PARSER_FLAG_COMPLETE_FRAMES) {
// preserve 0-size sync packets
compute_pkt_fields(s, st, st->parser, pkt);
}
while (size > 0 || (pkt == &flush_pkt && got_output)) {
int len;
av_init_packet(&out_pkt);
//解析
len = av_parser_parse2(st->parser, st->codec,
&out_pkt.data, &out_pkt.size, data, size,
pkt->pts, pkt->dts, pkt->pos);
pkt->pts = pkt->dts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
pkt->pos = -1;
/* increment read pointer */
data += len;
size -= len;
got_output = !!out_pkt.size;
//继续
if (!out_pkt.size)
continue;
if (pkt->side_data) {
out_pkt.side_data = pkt->side_data;
out_pkt.side_data_elems = pkt->side_data_elems;
pkt->side_data = NULL;
pkt->side_data_elems = 0;
}
/* set the duration */
out_pkt.duration = 0;
if (st->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO) {
if (st->codec->sample_rate > 0) {
out_pkt.duration =
av_rescale_q_rnd(st->parser->duration,
(AVRational) { 1, st->codec->sample_rate },
st->time_base,
AV_ROUND_DOWN);
}
}
//设置属性值
out_pkt.stream_index = st->index;
out_pkt.pts = st->parser->pts;
out_pkt.dts = st->parser->dts;
out_pkt.pos = st->parser->pos;
if (st->need_parsing == AVSTREAM_PARSE_FULL_RAW)
out_pkt.pos = st->parser->frame_offset;
if (st->parser->key_frame == 1 ||
(st->parser->key_frame == -1 &&
st->parser->pict_type == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I))
out_pkt.flags |= AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY;
if (st->parser->key_frame == -1 && st->parser->pict_type ==AV_PICTURE_TYPE_NONE && (pkt->flags&AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY))
out_pkt.flags |= AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY;
compute_pkt_fields(s, st, st->parser, &out_pkt);
if (out_pkt.data == pkt->data && out_pkt.size == pkt->size) {
out_pkt.buf = pkt->buf;
pkt->buf = NULL;
#if FF_API_DESTRUCT_PACKET
FF_DISABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
out_pkt.destruct = pkt->destruct;
pkt->destruct = NULL;
FF_ENABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
#endif
}
if ((ret = av_dup_packet(&out_pkt)) < 0)
goto fail;
if (!add_to_pktbuf(&s->parse_queue, &out_pkt, &s->parse_queue_end)) {
av_free_packet(&out_pkt);
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto fail;
}
}
/* end of the stream => close and free the parser */
if (pkt == &flush_pkt) {
av_parser_close(st->parser);
st->parser = NULL;
}
fail:
av_free_packet(pkt);
return ret;
}
从代码中可以看出,最终调用了相应AVCodecParser的av_parser_parse2()函数,解析出来AVPacket。此后根据解析的信息还进行了一系列的赋值工作,不再详细叙述
对该函数源代码的分析是很久之前做的了,现在翻出来,用博客记录一下。
上代码之前,先参考了其他人对av_read_frame()的解释,在此做一个参考:
通过av_read_packet(***),读取一个包,需要说明的是此函数必须是包含整数帧的,不存在半帧的情况,以ts流为例,是读取一个完整的PES包(一个完整pes包包含若干视频或音频es包),读取完毕后,通过av_parser_parse2(***)分析出视频一帧(或音频若干帧),返回,下次进入循环的时候,如果上次的数据没有完全取完,则st = s->cur_st;不会是NULL,即再此进入av_parser_parse2(***)流程,而不是下面的av_read_packet(**)流程,这样就保证了,如果读取一次包含了N帧视频数据(以视频为例),则调用av_read_frame(***)N次都不会去读数据,而是返回第一次读取的数据,直到全部解析完毕。
av_read_frame()的声明位于libavformat\avformat.h,如下所示。
[cpp] view
plain copy
/**
* Return the next frame of a stream.
* This function returns what is stored in the file, and does not validate
* that what is there are valid frames for the decoder. It will split what is
* stored in the file into frames and return one for each call. It will not
* omit invalid data between valid frames so as to give the decoder the maximum
* information possible for decoding.
*
* If pkt->buf is NULL, then the packet is valid until the next
* av_read_frame() or until avformat_close_input(). Otherwise the packet
* is valid indefinitely. In both cases the packet must be freed with
* av_free_packet when it is no longer needed. For video, the packet contains
* exactly one frame. For audio, it contains an integer number of frames if each
* frame has a known fixed size (e.g. PCM or ADPCM data). If the audio frames
* have a variable size (e.g. MPEG audio), then it contains one frame.
*
* pkt->pts, pkt->dts and pkt->duration are always set to correct
* values in AVStream.time_base units (and guessed if the format cannot
* provide them). pkt->pts can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if the video format
* has B-frames, so it is better to rely on pkt->dts if you do not
* decompress the payload.
*
* @return 0 if OK, < 0 on error or end of file
*/
int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);
av_read_frame()使用方法在注释中写得很详细,用中文简单描述一下它的两个参数:
s:输入的AVFormatContext
pkt:输出的AVPacket
如果返回0则说明读取正常。
函数调用结构图
函数调用结构图如下所示。
av_read_frame()
av_read_frame()的定义位于libavformat\utils.c,如下所示:[cpp] view
plain copy
//获取一个AVPacket
/*
* av_read_frame - 新版本的ffmpeg用的是av_read_frame,而老版本的是av_read_packet
* 。区别是av_read_packet读出的是包,它可能是半帧或多帧,不保证帧的完整性。av_read_frame对
* av_read_packet进行了封装,使读出的数据总是完整的帧
*/
int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
const int genpts = s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_GENPTS;
int eof = 0;
if (!genpts)
/**
* This buffer is only needed when packets were already buffered but
* not decoded, for example to get the codec parameters in MPEG
* streams.
* 一般情况下会调用read_frame_internal(s, pkt)
* 直接返回
*/
return s->packet_buffer ? read_from_packet_buffer(s, pkt) :
read_frame_internal(s, pkt);
for (;;) {
int ret;
AVPacketList *pktl = s->packet_buffer;
if (pktl) {
AVPacket *next_pkt = &pktl->pkt;
if (next_pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
int wrap_bits = s->streams[next_pkt->stream_index]->pts_wrap_bits;
while (pktl && next_pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
if (pktl->pkt.stream_index == next_pkt->stream_index &&
(av_compare_mod(next_pkt->dts, pktl->pkt.dts, 2LL << (wrap_bits - 1)) < 0) &&
av_compare_mod(pktl->pkt.pts, pktl->pkt.dts, 2LL << (wrap_bits - 1))) { //not b frame
next_pkt->pts = pktl->pkt.dts;
}
pktl = pktl->next;
}
pktl = s->packet_buffer;
}
/* read packet from packet buffer, if there is data */
if (!(next_pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE &&
next_pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE && !eof))
return read_from_packet_buffer(s, pkt);
}
ret = read_frame_internal(s, pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
if (pktl && ret != AVERROR(EAGAIN)) {
eof = 1;
continue;
} else
return ret;
}
if (av_dup_packet(add_to_pktbuf(&s->packet_buffer, pkt,
&s->packet_buffer_end)) < 0)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
}
可以从源代码中看出,av_read_frame()调用了read_frame_internal()。
read_frame_internal()
read_frame_internal()代码如下所示:[cpp] view
plain copy
//av_read_frame对他进行了封装
static int read_frame_internal(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
int ret = 0, i, got_packet = 0;
AVDictionary *metadata = NULL;
//初始化
av_init_packet(pkt);
while (!got_packet && !s->parse_queue) {
AVStream *st;
AVPacket cur_pkt;
/* read next packet */
ret = ff_read_packet(s, &cur_pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN))
return ret;
/* flush the parsers */
for (i = 0; i < s->nb_streams; i++) {
st = s->streams[i];
//需要解析
if (st->parser && st->need_parsing)
parse_packet(s, NULL, st->index);
}
/* all remaining packets are now in parse_queue =>
* really terminate parsing */
break;
}
ret = 0;
st = s->streams[cur_pkt.stream_index];
if (cur_pkt.pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE &&
cur_pkt.dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE &&
cur_pkt.pts < cur_pkt.dts) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Invalid timestamps stream=%d, pts=%s, dts=%s, size=%d\n",
cur_pkt.stream_index,
av_ts2str(cur_pkt.pts),
av_ts2str(cur_pkt.dts),
cur_pkt.size);
}
if (s->debug & FF_FDEBUG_TS)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG,
"ff_read_packet stream=%d, pts=%s, dts=%s, size=%d, duration=%d, flags=%d\n",
cur_pkt.stream_index,
av_ts2str(cur_pkt.pts),
av_ts2str(cur_pkt.dts),
cur_pkt.size, cur_pkt.duration, cur_pkt.flags);
if (st->need_parsing && !st->parser && !(s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_NOPARSE)) {
st->parser = av_parser_init(st->codec->codec_id);
if (!st->parser) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_VERBOSE, "parser not found for codec "
"%s, packets or times may be invalid.\n",
avcodec_get_name(st->codec->codec_id));
/* no parser available: just output the raw packets */
st->need_parsing = AVSTREAM_PARSE_NONE;
} else if (st->need_parsing == AVSTREAM_PARSE_HEADERS)
st->parser->flags |= PARSER_FLAG_COMPLETE_FRAMES;
else if (st->need_parsing == AVSTREAM_PARSE_FULL_ONCE)
st->parser->flags |= PARSER_FLAG_ONCE;
else if (st->need_parsing == AVSTREAM_PARSE_FULL_RAW)
st->parser->flags |= PARSER_FLAG_USE_CODEC_TS;
}
if (!st->need_parsing || !st->parser) {
/* no parsing needed: we just output the packet as is */
*pkt = cur_pkt;
compute_pkt_fields(s, st, NULL, pkt);
if ((s->iformat->flags & AVFMT_GENERIC_INDEX) &&
(pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY) && pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
ff_reduce_index(s, st->index);
av_add_index_entry(st, pkt->pos, pkt->dts,
0, 0, AVINDEX_KEYFRAME);
}
got_packet = 1;
} else if (st->discard < AVDISCARD_ALL) {
if ((ret = parse_packet(s, &cur_pkt, cur_pkt.stream_index)) < 0)
return ret;
} else {
/* free packet */
av_free_packet(&cur_pkt);
}
if (pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY)
st->skip_to_keyframe = 0;
if (st->skip_to_keyframe) {
av_free_packet(&cur_pkt);
if (got_packet) {
*pkt = cur_pkt;
}
got_packet = 0;
}
}
if (!got_packet && s->parse_queue)
ret = read_from_packet_buffer(&s->parse_queue, &s->parse_queue_end, pkt);
if (ret >= 0) {
AVStream *st = s->streams[pkt->stream_index];
int discard_padding = 0;
if (st->first_discard_sample && pkt->pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
int64_t pts = pkt->pts - (is_relative(pkt->pts) ? RELATIVE_TS_BASE : 0);
int64_t sample = ts_to_samples(st, pts);
int duration = ts_to_samples(st, pkt->duration);
int64_t end_sample = sample + duration;
if (duration > 0 && end_sample >= st->first_discard_sample &&
sample < st->last_discard_sample)
discard_padding = FFMIN(end_sample - st->first_discard_sample, duration);
}
if (st->skip_samples || discard_padding) {
uint8_t *p = av_packet_new_side_data(pkt, AV_PKT_DATA_SKIP_SAMPLES, 10);
if (p) {
AV_WL32(p, st->skip_samples);
AV_WL32(p + 4, discard_padding);
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "demuxer injecting skip %d\n", st->skip_samples);
}
st->skip_samples = 0;
}
if (st->inject_global_side_data) {
for (i = 0; i < st->nb_side_data; i++) {
AVPacketSideData *src_sd = &st->side_data[i];
uint8_t *dst_data;
if (av_packet_get_side_data(pkt, src_sd->type, NULL))
continue;
dst_data = av_packet_new_side_data(pkt, src_sd->type, src_sd->size);
if (!dst_data) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Could not inject global side data\n");
continue;
}
memcpy(dst_data, src_sd->data, src_sd->size);
}
st->inject_global_side_data = 0;
}
if (!(s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_KEEP_SIDE_DATA))
av_packet_merge_side_data(pkt);
}
av_opt_get_dict_val(s, "metadata", AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN, &metadata);
if (metadata) {
s->event_flags |= AVFMT_EVENT_FLAG_METADATA_UPDATED;
av_dict_copy(&s->metadata, metadata, 0);
av_dict_free(&metadata);
av_opt_set_dict_val(s, "metadata", NULL, AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN);
}
if (s->debug & FF_FDEBUG_TS)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG,
"read_frame_internal stre
20000
am=%d, pts=%s, dts=%s, "
"size=%d, duration=%d, flags=%d\n",
pkt->stream_index,
av_ts2str(pkt->pts),
av_ts2str(pkt->dts),
pkt->size, pkt->duration, pkt->flags);
return ret;
}
read_frame_internal()代码比较长,这里只简单看一下它前面的部分。它前面部分有2步是十分关键的:
(1)调用了ff_read_packet()从相应的AVInputFormat读取数据。
(2)如果媒体频流需要使用AVCodecParser,则调用parse_packet()解析相应的AVPacket。
下面我们分成分别看一下ff_read_packet()和parse_packet()的源代码。
ff_read_packet()
ff_read_packet()的代码比较长,如下所示。[cpp] view
plain copy
int ff_read_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
int ret, i, err;
AVStream *st;
for (;;) {
AVPacketList *pktl = s->raw_packet_buffer;
if (pktl) {
*pkt = pktl->pkt;
st = s->streams[pkt->stream_index];
if (s->raw_packet_buffer_remaining_size <= 0)
if ((err = probe_codec(s, st, NULL)) < 0)
return err;
if (st->request_probe <= 0) {
s->raw_packet_buffer = pktl->next;
s->raw_packet_buffer_remaining_size += pkt->size;
av_free(pktl);
return 0;
}
}
pkt->data = NULL;
pkt->size = 0;
av_init_packet(pkt);
//关键:读取Packet
ret = s->iformat->read_packet(s, pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
if (!pktl || ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN))
return ret;
for (i = 0; i < s->nb_streams; i++) {
st = s->streams[i];
if (st->probe_packets)
if ((err = probe_codec(s, st, NULL)) < 0)
return err;
av_assert0(st->request_probe <= 0);
}
continue;
}
if ((s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_DISCARD_CORRUPT) &&
(pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_CORRUPT)) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Dropped corrupted packet (stream = %d)\n",
pkt->stream_index);
av_free_packet(pkt);
continue;
}
if (pkt->stream_index >= (unsigned)s->nb_streams) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Invalid stream index %d\n", pkt->stream_index);
continue;
}
st = s->streams[pkt->stream_index];
if (update_wrap_reference(s, st, pkt->stream_index, pkt) && st->pts_wrap_behavior == AV_PTS_WRAP_SUB_OFFSET) {
// correct first time stamps to negative values
if (!is_relative(st->first_dts))
st->first_dts = wrap_timestamp(st, st->first_dts);
if (!is_relative(st->start_time))
st->start_time = wrap_timestamp(st, st->start_time);
if (!is_relative(st->cur_dts))
st->cur_dts = wrap_timestamp(st, st->cur_dts);
}
pkt->dts = wrap_timestamp(st, pkt->dts);
pkt->pts = wrap_timestamp(st, pkt->pts);
force_codec_ids(s, st);
/* TODO: audio: time filter; video: frame reordering (pts != dts) */
if (s->use_wallclock_as_timestamps)
pkt->dts = pkt->pts = av_rescale_q(av_gettime(), AV_TIME_BASE_Q, st->time_base);
if (!pktl && st->request_probe <= 0)
return ret;
add_to_pktbuf(&s->raw_packet_buffer, pkt, &s->raw_packet_buffer_end);
s->raw_packet_buffer_remaining_size -= pkt->size;
if ((err = probe_codec(s, st, pkt)) < 0)
return err;
}
}
ff_read_packet()中最关键的地方就是调用了AVInputFormat的read_packet()方法。AVInputFormat的read_packet()是一个函数指针,指向当前的AVInputFormat的读取数据的函数。在这里我们以FLV封装格式对应的AVInputFormat为例,看看read_packet()的实现函数是什么样子的。
FLV封装格式对应的AVInputFormat的定义位于libavformat\flvdec.c,如下所示。
[cpp] view
plain copy
AVInputFormat ff_flv_demuxer = {
.name = "flv",
.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("FLV (Flash Video)"),
.priv_data_size = sizeof(FLVContext),
.read_probe = flv_probe,
.read_header = flv_read_header,
.read_packet = flv_read_packet,
.read_seek = flv_read_seek,
.read_close = flv_read_close,
.extensions = "flv",
.priv_class = &flv_class,
};
从ff_flv_demuxer的定义可以看出,read_packet()对应的是flv_read_packet()函数。在看flv_read_packet()函数之前,我们先回顾一下FLV封装格式的结构,如下图所示。

从图中可以看出,FLV文件体部分是由一个一个的Tag连接起来的(中间间隔着Previous Tag Size)。每个Tag包含了Tag Header和Tag Data两个部分。Tag Data根据Tag的Type不同而不同:可以分为音频Tag Data,视频Tag Data以及Script Tag Data。下面简述一下音频Tag Data和视频Tag Data。
Audio Tag Data
Audio Tag在官方标准中定义如下。
Audio Tag开始的第1个字节包含了音频数据的参数信息,从第2个字节开始为音频流数据。
第1个字节的前4位的数值表示了音频数据格式:
0 = Linear PCM, platform endian
1 = ADPCM
2 = MP3
3 = Linear PCM, little endian
4 = Nellymoser 16-kHz mono
5 = Nellymoser 8-kHz mono
6 = Nellymoser
7 = G.711 A-law logarithmic PCM
8 = G.711 mu-law logarithmic PCM
9 = reserved
10 = AAC
14 = MP3 8-Khz
15 = Device-specific sound
第1个字节的第5-6位的数值表示采样率:0 = 5.5kHz,1 = 11KHz,2 = 22 kHz,3 = 44 kHz。
第1个字节的第7位表示采样精度:0 = 8bits,1 = 16bits。
第1个字节的第8位表示音频类型:0 = sndMono,1 = sndStereo。
其中,当音频编码为AAC的时候,第一个字节后面存储的是AACAUDIODATA,格式如下所示。

Video Tag Data
Video Tag在官方标准中的定义如下。
Video Tag也用开始的第1个字节包含视频数据的参数信息,从第2个字节为视频流数据。
第1个字节的前4位的数值表示帧类型(FrameType):
1: keyframe (for AVC, a seekableframe)(关键帧)
2: inter frame (for AVC, a nonseekableframe)
3: disposable inter frame (H.263only)
4: generated keyframe (reservedfor server use only)
5: video info/command frame
第1个字节的后4位的数值表示视频编码ID(CodecID):
1: JPEG (currently unused)
2: Sorenson H.263
3: Screen video
4: On2 VP6
5: On2 VP6 with alpha channel
6: Screen video version 2
7: AVC
其中,当音频编码为AVC(H.264)的时候,第一个字节后面存储的是AVCVIDEOPACKET,格式如下所示。

了解了FLV的基本格式之后,就可以看一下FLV解析Tag的函数flv_read_packet()了。
flv_read_packet()
flv_read_packet()的定义位于libavformat\flvdec.c,如下所示。[cpp] view
plain copy
static int flv_read_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
FLVContext *flv = s->priv_data;
int ret, i, type, size, flags;
int stream_type=-1;
int64_t next, pos, meta_pos;
int64_t dts, pts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
int av_uninit(channels);
int av_uninit(sample_rate);
AVStream *st = NULL;
/* pkt size is repeated at end. skip it */
for (;; avio_skip(s->pb, 4)) {
pos = avio_tell(s->pb);
//解析Tag Header==========
//Tag类型
type = (avio_r8(s->pb) & 0x1F);
//Datasize数据大小
size = avio_rb24(s->pb);
//Timstamp时间戳
dts = avio_rb24(s->pb);
dts |= avio_r8(s->pb) << 24;
av_dlog(s, "type:%d, size:%d, dts:%"PRId64" pos:%"PRId64"\n", type, size, dts, avio_tell(s->pb));
if (avio_feof(s->pb))
return AVERROR_EOF;
//StreamID
avio_skip(s->pb, 3); /* stream id, always 0 */
flags = 0;
//========================
if (flv->validate_next < flv->validate_count) {
int64_t validate_pos = flv->validate_index[flv->validate_next].pos;
if (pos == validate_pos) {
if (FFABS(dts - flv->validate_index[flv->validate_next].dts) <=
VALIDATE_INDEX_TS_THRESH) {
flv->validate_next++;
} else {
clear_index_entries(s, validate_pos);
flv->validate_count = 0;
}
} else if (pos > validate_pos) {
clear_index_entries(s, validate_pos);
flv->validate_count = 0;
}
}
if (size == 0)
continue;
next = size + avio_tell(s->pb);
if (type == FLV_TAG_TYPE_AUDIO) {
//Type是音频
stream_type = FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO;
//Tag Data的第一个字节
flags = avio_r8(s->pb);
size--;
} else if (type == FLV_TAG_TYPE_VIDEO) {
//Type是音频
stream_type = FLV_STREAM_TYPE_VIDEO;
//Tag Data的第一个字节
flags = avio_r8(s->pb);
size--;
if ((flags & FLV_VIDEO_FRAMETYPE_MASK) == FLV_FRAME_VIDEO_INFO_CMD)
goto skip;
} else if (type == FLV_TAG_TYPE_META) {
stream_type=FLV_STREAM_TYPE_DATA;
if (size > 13 + 1 + 4 && dts == 0) { // Header-type metadata stuff
meta_pos = avio_tell(s->pb);
if (flv_read_metabody(s, next) <= 0) {
goto skip;
}
avio_seek(s->pb, meta_pos, SEEK_SET);
}
} else {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG,
"Skipping flv packet: type %d, size %d, flags %d.\n",
type, size, flags);
skip:
avio_seek(s->pb, next, SEEK_SET);
continue;
}
/* skip empty data packets */
if (!size)
continue;
/* now find stream */
for (i = 0; i < s->nb_streams; i++) {
st = s->streams[i];
if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO) {
if (st->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO &&
(s->audio_codec_id || flv_same_audio_codec(st->codec, flags)))
break;
} else if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_VIDEO) {
if (st->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO &&
(s->video_codec_id || flv_same_video_codec(st->codec, flags)))
break;
} else if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_DATA) {
if (st->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA)
break;
}
}
if (i == s->nb_streams) {
static const enum AVMediaType stream_types[] = {AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO, AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA};
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Stream discovered after head already parsed\n");
st = create_stream(s, stream_types[stream_type]);
if (!st)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
av_dlog(s, "%d %X %d \n", stream_type, flags, st->discard);
if ((flags & FLV_VIDEO_FRAMETYPE_MASK) == FLV_FRAME_KEY ||
stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO)
av_add_index_entry(st, pos, dts, size, 0, AVINDEX_KEYFRAME);
if ( (st->discard >= AVDISCARD_NONKEY && !((flags & FLV_VIDEO_FRAMETYPE_MASK) == FLV_FRAME_KEY || (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO)))
||(st->discard >= AVDISCARD_BIDIR && ((flags & FLV_VIDEO_FRAMETYPE_MASK) == FLV_FRAME_DISP_INTER && (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_VIDEO)))
|| st->discard >= AVDISCARD_ALL
) {
avio_seek(s->pb, next, SEEK_SET);
continue;
}
break;
}
// if not streamed and no duration from metadata then seek to end to find
// the duration from the timestamps
if (s->pb->seekable && (!s->duration || s->duration == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) && !flv->searched_for_end) {
int size;
const int64_t pos = avio_tell(s->pb);
// Read the last 4 bytes of the file, this should be the size of the
// previous FLV tag. Use the timestamp of its payload as duration.
int64_t fsize = avio_size(s->pb);
retry_duration:
avio_seek(s->pb, fsize - 4, SEEK_SET);
size = avio_rb32(s->pb);
// Seek to the start of the last FLV tag at position (fsize - 4 - size)
// but skip the byte indicating the type.
avio_seek(s->pb, fsize - 3 - size, SEEK_SET);
if (size == avio_rb24(s->pb) + 11) {
uint32_t ts = avio_rb24(s->pb);
ts |= avio_r8(s->pb) << 24;
if (ts)
s->duration = ts * (int64_t)AV_TIME_BASE / 1000;
else if (fsize >= 8 && fsize - 8 >= size) {
fsize -= size+4;
goto retry_duration;
}
}
avio_seek(s->pb, pos, SEEK_SET);
flv->searched_for_end = 1;
}
if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO) {
int bits_per_coded_sample;
channels = (flags & FLV_AUDIO_CHANNEL_MASK) == FLV_STEREO ? 2 : 1;
sample_rate = 44100 << ((flags & FLV_AUDIO_SAMPLERATE_MASK) >>
FLV_AUDIO_SAMPLERATE_OFFSET) >> 3;
bits_per_coded_sample = (flags & FLV_AUDIO_SAMPLESIZE_MASK) ? 16 : 8;
if (!st->codec->channels || !st->codec->sample_rate ||
!st->codec->bits_per_coded_sample) {
st->codec->channels = channels;
st->codec->channel_layout = channels == 1
? AV_CH_LAYOUT_MONO
: AV_CH_LAYOUT_STEREO;
st->codec->sample_rate = sample_rate;
st->codec->bits_per_coded_sample = bits_per_coded_sample;
}
if (!st->codec->codec_id) {
flv_set_audio_codec(s, st, st->codec,
flags & FLV_AUDIO_CODECID_MASK);
flv->last_sample_rate =
sample_rate = st->codec->sample_rate;
flv->last_channels =
channels = st->codec->channels;
} else {
AVCodecContext ctx = {0};
ctx.sample_rate = sample_rate;
ctx.bits_per_coded_sample = bits_per_coded_sample;
flv_set_audio_codec(s, st, &ctx, flags & FLV_AUDIO_CODECID_MASK);
sample_rate = ctx.sample_rate;
}
} else if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_VIDEO) {
size -= flv_set_video_codec(s, st, flags & FLV_VIDEO_CODECID_MASK, 1);
}
//几种特殊的格式
if (st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC ||
st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264 ||
st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4) {
//对应AACPacketType或者AVCPacketType
int type = avio_r8(s->pb);
size--;
//H.264
if (st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264 || st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4) {
// sign extension
//对应CompositionTime
int32_t cts = (avio_rb24(s->pb) + 0xff800000) ^ 0xff800000;
//计算PTS
pts = dts + cts;
if (cts < 0) { // dts might be wrong
if (!flv->wrong_dts)
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Negative cts, previous timestamps might be wrong.\n");
flv->wrong_dts = 1;
} else if (FFABS(dts - pts) > 1000*60*15) {
av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"invalid timestamps %"PRId64" %"PRId64"\n", dts, pts);
dts = pts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
}
}
//如果编码器是AAC或者H.264
if (type == 0 && (!st->codec->extradata || st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC ||
st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264)) {
AVDictionaryEntry *t;
if (st->codec->extradata) {
if ((ret = flv_queue_extradata(flv, s->pb, stream_type, size)) < 0)
return ret;
ret = AVERROR(EAGAIN);
goto leave;
}
if ((ret = flv_get_extradata(s, st, size)) < 0)
return ret;
/* Workaround for buggy Omnia A/XE encoder */
t = av_dict_get(s->metadata, "Encoder", NULL, 0);
if (st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC && t && !strcmp(t->value, "Omnia A/XE"))
st->codec->extradata_size = 2;
//AAC
if (st->codec->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_AAC && 0) {
MPEG4AudioConfig cfg;
if (avpriv_mpeg4audio_get_config(&cfg, st->codec->extradata,
st->codec->extradata_size * 8, 1) >= 0) {
st->codec->channels = cfg.channels;
st->codec->channel_layout = 0;
if (cfg.ext_sample_rate)
st->codec->sample_rate = cfg.ext_sample_rate;
else
st->codec->sample_rate = cfg.sample_rate;
av_dlog(s, "mp4a config channels %d sample rate %d\n",
st->codec->channels, st->codec->sample_rate);
}
}
ret = AVERROR(EAGAIN);
goto leave;
}
}
/* skip empty data packets */
if (!size) {
ret = AVERROR(EAGAIN);
goto leave;
}
ret = av_get_packet(s->pb, pkt, size);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
//设置PTS、DTS等等
pkt->dts = dts;
pkt->pts = pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE ? dts : pts;
pkt->stream_index = st->index;
if (flv->new_extradata[stream_type]) {
uint8_t *side = av_packet_new_side_data(pkt, AV_PKT_DATA_NEW_EXTRADATA,
flv->new_extradata_size[stream_type]);
if (side) {
memcpy(side, flv->new_extradata[stream_type],
flv->new_extradata_size[stream_type]);
av_freep(&flv->new_extradata[stream_type]);
flv->new_extradata_size[stream_type] = 0;
}
}
if (stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO &&
(sample_rate != flv->last_sample_rate ||
channels != flv->last_channels)) {
flv->last_sample_rate = sample_rate;
flv->last_channels = channels;
ff_add_param_change(pkt, channels, 0, sample_rate, 0, 0);
}
//标记上Keyframe
if ( stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_AUDIO ||
((flags & FLV_VIDEO_FRAMETYPE_MASK) == FLV_FRAME_KEY) ||
stream_type == FLV_STREAM_TYPE_DATA)
pkt->flags |= AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY;
leave:
avio_skip(s->pb, 4);
return ret;
}
flv_read_packet()的代码比较长,但是逻辑比较简单。它的主要功能就是根据FLV文件格式的规范,逐层解析Tag以及TagData,获取Tag以及TagData中的信息。比较关键的地方已经写上了注释,不再详细叙述。
parse_packet()
parse_packet()给需要AVCodecParser的媒体流提供解析AVPacket的功能。它的代码如下所示:[cpp] view
plain copy
/**
* Parse a packet, add all split parts to parse_queue.
*
* @param pkt Packet to parse, NULL when flushing the parser at end of stream.
*/
static int parse_packet(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt, int stream_index)
{
AVPacket out_pkt = { 0 }, flush_pkt = { 0 };
AVStream *st = s->streams[stream_index];
uint8_t *data = pkt ? pkt->data : NULL;
int size = pkt ? pkt->size : 0;
int ret = 0, got_output = 0;
if (!pkt) {
av_init_packet(&flush_pkt);
pkt = &flush_pkt;
got_output = 1;
} else if (!size && st->parser->flags & PARSER_FLAG_COMPLETE_FRAMES) {
// preserve 0-size sync packets
compute_pkt_fields(s, st, st->parser, pkt);
}
while (size > 0 || (pkt == &flush_pkt && got_output)) {
int len;
av_init_packet(&out_pkt);
//解析
len = av_parser_parse2(st->parser, st->codec,
&out_pkt.data, &out_pkt.size, data, size,
pkt->pts, pkt->dts, pkt->pos);
pkt->pts = pkt->dts = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;
pkt->pos = -1;
/* increment read pointer */
data += len;
size -= len;
got_output = !!out_pkt.size;
//继续
if (!out_pkt.size)
continue;
if (pkt->side_data) {
out_pkt.side_data = pkt->side_data;
out_pkt.side_data_elems = pkt->side_data_elems;
pkt->side_data = NULL;
pkt->side_data_elems = 0;
}
/* set the duration */
out_pkt.duration = 0;
if (st->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO) {
if (st->codec->sample_rate > 0) {
out_pkt.duration =
av_rescale_q_rnd(st->parser->duration,
(AVRational) { 1, st->codec->sample_rate },
st->time_base,
AV_ROUND_DOWN);
}
}
//设置属性值
out_pkt.stream_index = st->index;
out_pkt.pts = st->parser->pts;
out_pkt.dts = st->parser->dts;
out_pkt.pos = st->parser->pos;
if (st->need_parsing == AVSTREAM_PARSE_FULL_RAW)
out_pkt.pos = st->parser->frame_offset;
if (st->parser->key_frame == 1 ||
(st->parser->key_frame == -1 &&
st->parser->pict_type == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I))
out_pkt.flags |= AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY;
if (st->parser->key_frame == -1 && st->parser->pict_type ==AV_PICTURE_TYPE_NONE && (pkt->flags&AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY))
out_pkt.flags |= AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY;
compute_pkt_fields(s, st, st->parser, &out_pkt);
if (out_pkt.data == pkt->data && out_pkt.size == pkt->size) {
out_pkt.buf = pkt->buf;
pkt->buf = NULL;
#if FF_API_DESTRUCT_PACKET
FF_DISABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
out_pkt.destruct = pkt->destruct;
pkt->destruct = NULL;
FF_ENABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
#endif
}
if ((ret = av_dup_packet(&out_pkt)) < 0)
goto fail;
if (!add_to_pktbuf(&s->parse_queue, &out_pkt, &s->parse_queue_end)) {
av_free_packet(&out_pkt);
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto fail;
}
}
/* end of the stream => close and free the parser */
if (pkt == &flush_pkt) {
av_parser_close(st->parser);
st->parser = NULL;
}
fail:
av_free_packet(pkt);
return ret;
}
从代码中可以看出,最终调用了相应AVCodecParser的av_parser_parse2()函数,解析出来AVPacket。此后根据解析的信息还进行了一系列的赋值工作,不再详细叙述
相关文章推荐
- ffmpeg 源代码简单分析 : av_read_frame()
- FFMPeg代码分析:av_read_frame()函数的内部构造
- ffmpeg 源代码简单分析 : av_read_frame()
- Ffmpeg解析media容器过程/ ffmpeg 源代码简单分析 : av_read_frame()
- ffmpeg 源代码简单分析 : av_read_frame()
- ffmpeg 源代码简单分析 : av_read_frame()
- ffmpeg 源代码简单分析 :av_read_frame()
- ffmpeg 源代码简单分析 : av_read_frame()
- ffmpeg 源代码简单分析 : av_read_frame()
- ffmpeg 源代码简单分析 : av_read_frame()
- FFmpeg源代码简单分析:av_write_frame()
- ffmpeg av_read_frame源码分析
- FFmpeg函数简单分析:av_find_decoder()和av_find_encoder()
- FFmpeg的av_read_frame()的分析
- ffmpeg 函数简单分析 : av_register_all()
- FFmpeg函数简单分析:内存的分配和释放(av_malloc()、av_free()等)
- FFmpeg源代码简单分析:av_write_frame()
- FFmpeg源代码简单分析:av_write_frame()
- (转)ffmpeg 中 av_read_frame_internal分析
- FFmpeg-av_read_frame
