JavaScript学习之Date对象和Math对象
2017-06-14 17:41
483 查看
一、Date对象
1、Date对象作用
日期对象可以储存任意一个日期,并且可以精确到毫秒数(1/1000 秒)。
语法:var Udate=new Date();
2.Date对象常用方法:
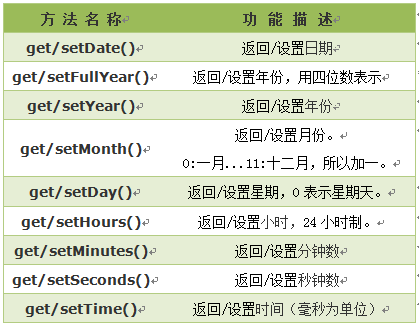
3.Date方法实例之2018春节倒计时
二、Math对象
1.什么是Math对象?
Math对象,提供对数据的数学计算。
注意:Math 对象是一个固有的对象,无需创建它,直接把 Math 作为对象使用就可以调用其所有属性和方法。这是它与Date,String对象的区别。
2.Math对象的属性和方法
Math对象属性
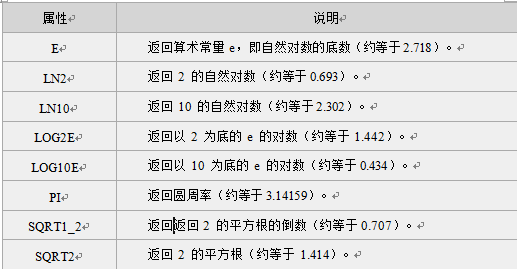
Math对象方法
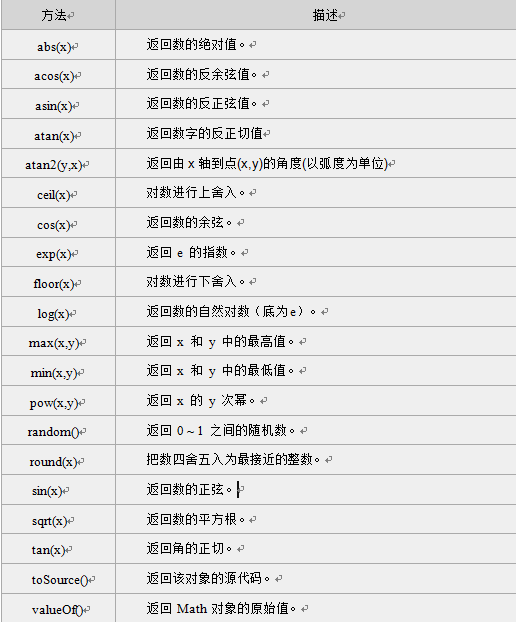
3.Math对象Math.random()方法实现验证码小项目
练习小项目之选项卡
多个选项卡(使用闭包回调函数方法简化代码)
1、Date对象作用
日期对象可以储存任意一个日期,并且可以精确到毫秒数(1/1000 秒)。
语法:var Udate=new Date();
2.Date对象常用方法:

3.Date方法实例之2018春节倒计时
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>倒计时</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
</div>
<script>
var oBox=document.getElementById("box");
function go(){
var nowT=new Date();
var fultureT=new Date(2018,1,16,0,0,0);
var T=Math.floor((fultureT.getTime()-nowT.getTime())/1000);
var d=Math.floor(T/84600);
var h=Math.floor(T%84600/3600);
var m=Math.floor(T%84600%3600/60);
var s=Math.floor(T%60);
time=d+"天"+h+"时"+m+"分"+s+"秒";
oBox.innerHTML=time;
}
go();
setInterval(go,1000);
</script>
</body>
</html>二、Math对象
1.什么是Math对象?
Math对象,提供对数据的数学计算。
注意:Math 对象是一个固有的对象,无需创建它,直接把 Math 作为对象使用就可以调用其所有属性和方法。这是它与Date,String对象的区别。
2.Math对象的属性和方法
Math对象属性

Math对象方法

3.Math对象Math.random()方法实现验证码小项目
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>验证码</title>
<style>
div {
width: 310px;
height: 180px;
background: #ccc;
border-radius: 5px;
padding: 20px;
}
#in {
width: 130px;
height: 74px;
float: left;
font: "微软雅黑";
font-size: 28px;
line-height: 74px;
padding-left: 16px;
}
#span1 {
display: block;
float: right;
width: 150px;
height: 80px;
background: #fff;
color: orange;
font: "微软雅黑";
font-size: 30px;
line-height: 80px;
font-style: initial;
}
#a {
text-decoration: none;
text-align: center;
width: 310px;
height: 70px;
margin-top: 10px;
color: #000;
font: "微软雅黑";
font-size: 30px;
display: block;
background: orange;
float: left;
line-height: 70px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<input id="in" type="text" />
<span id="span1"></span>
<a id="a" href="#">提交</a>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var oin = document.getElementById("in");
var osp = document.getElementById("span1");
var oa = document.getElementById("a");
var arr = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z'];
var str="";
function yz(){
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
var n =Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length);
str=str+arr
}
console.log(str)
osp.innerHTML=str;
}
yz();
oa.onclick=function(){
if(oin.value==""){
alert("请输入验证码!");
str="";
yz();
}else if(oin.value.toUpperCase()!=osp.innerHTML.toUpperCase()){
alert("输入错误,请重新输入!");
str="";
yz();
}else{
alert("验证码正确!");
str="";
yz();
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>练习小项目之选项卡
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>选项卡</title>
<style>
#a1 {
width: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
#u0{
width: 100%;overflow: hidden;
}
#u0>.c {
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
background: #CCCCCC;
font-size: 25px;
color: #FFFFFF;
text-align: center;
line-height: 60px;
float: left;
display: block;
list-style: none;
margin-left: 10px;
}
#u1>li {
list-style: none;
font-size: 18px;
color: #000;
}
#u2>li {
list-style: none;
font-size: 18px;
color: #000;
}
#u3>li {
list-style: none;
font-size: 18px;
color: #000;
}
#a2{clear: both;}
.bs {
background: #FFB6C1;color: #FFFFFF;
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
font-size: 25px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 60px;
float: left;
display: block;
list-style: none;
margin-left: 10px;
}
#a2 div:nth-child(2),#a2 div:last-child{display: none;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="a1">
<ul id="u0">
<li class="bs">
no.1
</li>
<li class="c">
no.2
</li>
<li class="c">
no.3
</li>
</ul>
<div id="a2">
<div>
<ul id="u1">
<li>内容1</li>
<li>内容2</li>
<li>内容3</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<ul id="u2">
<li>内容4</li>
<li>内容5</li>
<li>内容6</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<ul id="u3">
<li>内容7</li>
<li>内容8</li>
<li>内容9</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var oli = document.getElementById("u0").getElementsByTagName("li");
var odiv = document.getElementById("a2").getElementsByTagName("div");
for(var i = 0; i < oli.length; i++) {
oli[i]._index = i;
oli[i].onclick = function() {
for(var i = 0; i < oli.length; i++) {
oli[i].className = "c";
odiv[i].style.display = "none"
}
this.className = "bs";
odiv[this._index].style.display = "block";
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>多个选项卡(使用闭包回调函数方法简化代码)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>多个tab选项卡</title>
<script>
window.onload = function() {
tab("tabMain", "click");
tab("tabMain1", "click");
tab("tabMain2", "click");
tab("tabMain4", "click");
function tab(id, event) {
var oDiv = document.getElementById(id);
var oBtn = oDiv.getElementsByTagName("li");
var oBox = oDiv.getElementsByTagName("div");
for(var i = 0; i < oBtn.length; i++) {
//console.log(i)
(function(index) {//自执行函数
oBtn[index].addEventListener(event, function() {
for(var i = 0; i < oBtn.length; i++) {
oBtn[i].className = '';
oBox[i].className = 'tabSide';
}
this.className = 'active';
oBox[index].className = 'active';
});//添加事件监听
})(i)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
list-style: none;
}
.tabMenu {
width: 300px;
margin: 50px auto 0 auto;
}
.tabMenu ul {
display: block;
相关文章推荐
- JavaScript中Date(日期对象),Math对象--学习笔记
- javascript 学习总结(四)Date对象
- 浅谈JavaScript中Date(日期对象),Math对象
- Javascript数组,String对象,Math对象,Date对象,正则表达式
- Javascript学习之Date对象详解
- JavaScript---对象学习(三)Math对象和Global对象,自定义对象学习
- Javascript学习------内部对象 String Date event(重要)
- 跟我学习javascript的Date对象
- javascript学习(十四)JS Function对象和Math对象
- 轻松学习JavaScript十:JavaScript的Date对象制作一个简易钟表
- javascript中的Date对象和Math对象
- 每天一篇javascript学习小结(Date对象)
- javascript学习之Date对象
- JavaScript Date 对象学习
- 【Javascript】javascript学习 二十四 JavaScript Date(日期)对象
- 跟我学习javascript的Date对象
- javascript Date 对象学习
- W3Cschool——学习二:JavaScript对象,String,Date,Array
- JavaScript学习之Date对象
- JavaScript---对象学习(二)Array对象、Date对象及其重要函数学习
