Educational Codeforces Round 21总结
2017-05-23 22:34
661 查看
A. Lucky Year
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Apart from having lots of holidays throughout the year, residents of Berland also have whole lucky years. Year is considered lucky if
it has no more than 1 non-zero digit in its number. So years 100, 40000, 5 are lucky and 12, 3001 and 12345
are not.
You are given current year in Berland. Your task is to find how long will residents of Berland wait till the next lucky year.
Input
The first line contains integer number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 109)
— current year in Berland.
Output
Output amount of years from the current year to the next lucky one.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
In the first example next lucky year is 5. In the second one — 300. In the third — 5000.
题意:数字中最多有一个不是0的数字就叫做幸运数字。求给定数字的下一个幸运数字
解:求数字最前面的那个数字temp,temp是10的cnt次方?,答案就是(temp+1)*(temp*pow(10,cnt));
B. Average Sleep Time
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
It's been almost a week since Polycarp couldn't get rid of insomnia. And as you may already know, one week in Berland lasts k days!
When Polycarp went to a doctor with his problem, the doctor asked him about his sleeping schedule (more specifically, the average amount of hours of sleep per week). Luckily, Polycarp kept records of sleep times for the last n days.
So now he has a sequencea1, a2, ..., an,
where ai is the sleep time
on the i-th day.
The number of records is so large that Polycarp is unable to calculate the average value by himself. Thus he is asking you to help him with the calculations. To get the average Polycarp is going to consider k consecutive
days as a week. So there will be n - k + 1 weeks to take into consideration. For example, if k = 2, n = 3 and a = [3, 4, 7],
then the result is
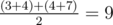
.
You should write a program which will calculate average sleep times of Polycarp over all weeks.
Input
The first line contains two integer numbers n and k (1 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 2·105).
The second line contains n integer numbers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 105).
Output
Output average sleeping time over all weeks.
The answer is considered to be correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
In particular, it is enough to output real number with at least 6 digits after the decimal point.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
In the third example there are n - k + 1 = 7 weeks, so the answer is sums of all weeks divided by 7.
题意:求平均,用前缀和求
C. Tea Party
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Polycarp invited all his friends to the tea party to celebrate the holiday. He has n cups, one for each of his n friends,
with volumesa1, a2, ..., an.
His teapot stores w milliliters of tea (w ≤ a1 + a2 + ... + an).
Polycarp wants to pour tea in cups in such a way that:
Every cup will contain tea for at least half of its volume
Every cup will contain integer number of milliliters of tea
All the tea from the teapot will be poured into cups
All friends will be satisfied.
Friend with cup i won't be satisfied, if there exists such
cup j that cup i contains less tea than
cup j but ai > aj.
For each cup output how many milliliters of tea should be poured in it. If it's impossible to pour all the tea and satisfy all conditions then output -1.
Input
The first line contains two integer numbers n and w (1 ≤ n ≤ 100,
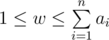
).
The second line contains n numbers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 100).
Output
Output how many milliliters of tea every cup should contain. If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
If it's impossible to pour all the tea and satisfy all conditions then output -1.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
In the third example you should pour to the first cup at least 5 milliliters, to the second one at least 4, to the third one at least 5. It sums up to 14, which is greater than 10 milliliters available.
题意:有 n 个茶杯,茶壶里有 m 毫升茶,每个茶杯大小不等,我们要满足以下三个条件 :1. 每个茶杯中的茶要超过茶杯容量的一半 2. 每个茶杯中倒的茶必须是整数毫升 3. 大茶杯中的茶的容量不能少于任意一个小茶杯中的茶的容量,若 n
,m 不满足条件,输出 -1 ,否则输出一种满足条件的情况
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Apart from having lots of holidays throughout the year, residents of Berland also have whole lucky years. Year is considered lucky if
it has no more than 1 non-zero digit in its number. So years 100, 40000, 5 are lucky and 12, 3001 and 12345
are not.
You are given current year in Berland. Your task is to find how long will residents of Berland wait till the next lucky year.
Input
The first line contains integer number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 109)
— current year in Berland.
Output
Output amount of years from the current year to the next lucky one.
Examples
input
4
output
1
input
201
output
99
input
4000
output
1000
Note
In the first example next lucky year is 5. In the second one — 300. In the third — 5000.
题意:数字中最多有一个不是0的数字就叫做幸运数字。求给定数字的下一个幸运数字
解:求数字最前面的那个数字temp,temp是10的cnt次方?,答案就是(temp+1)*(temp*pow(10,cnt));
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
private static final int Max=(int) (1e5+10);
private static long n;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
InitData();
GetAns();
}
private static void InitData() throws Exception{
SC cin=new SC(System.in);
n=cin.nextLong();
}
private static void GetAns(){
if(n<10){
System.out.println(1);
}else{
long x=n;
long temp=0;
long ans=1;
while(n>0){
temp=n%10;
n/=10;
ans*=10;
}
System.out.println((temp+1)*(ans/10)-x);
}
}
static class SC
{
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
SC(InputStream s)
{
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s));
}
String next() throws IOException
{
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreTokens())
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() throws NumberFormatException, IOException
{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
long nextLong() throws NumberFormatException, IOException
{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
}
}B. Average Sleep Time
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
It's been almost a week since Polycarp couldn't get rid of insomnia. And as you may already know, one week in Berland lasts k days!
When Polycarp went to a doctor with his problem, the doctor asked him about his sleeping schedule (more specifically, the average amount of hours of sleep per week). Luckily, Polycarp kept records of sleep times for the last n days.
So now he has a sequencea1, a2, ..., an,
where ai is the sleep time
on the i-th day.
The number of records is so large that Polycarp is unable to calculate the average value by himself. Thus he is asking you to help him with the calculations. To get the average Polycarp is going to consider k consecutive
days as a week. So there will be n - k + 1 weeks to take into consideration. For example, if k = 2, n = 3 and a = [3, 4, 7],
then the result is
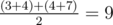
.
You should write a program which will calculate average sleep times of Polycarp over all weeks.
Input
The first line contains two integer numbers n and k (1 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 2·105).
The second line contains n integer numbers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 105).
Output
Output average sleeping time over all weeks.
The answer is considered to be correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
In particular, it is enough to output real number with at least 6 digits after the decimal point.
Examples
input
3 2 3 4 7
output
9.0000000000
input
1 110
output
10.0000000000
input
8 2
1 2 4 100000 123 456 789 1
output
28964.2857142857
Note
In the third example there are n - k + 1 = 7 weeks, so the answer is sums of all weeks divided by 7.
题意:求平均,用前缀和求
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
private static final int Max=(int) (1e6+10);
private static int n,k;
private static int a[];
private static double dp[];
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
InitData();
GetAns();
}
private static void InitData() throws Exception{
SC cin=new SC(System.in);
n=cin.nextInt();
k=cin.nextInt();
a=new int[Max];
dp=new double[Max];
dp[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
a[i]=cin.nextInt();
if(i==1){
dp[i]=a[i];
}else{
dp[i]=dp[i-1]+a[i];
}
}
}
private static void GetAns(){
double ans=0;
for(int i=k;i<=n;i++){
ans+=(dp[i]-dp[i-k]);
}
System.out.println(ans/((n-k+1)));
}
static class SC
{
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
SC(InputStream s)
{
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s));
}
String next() throws IOException
{
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreTokens())
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() throws NumberFormatException, IOException
{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
long nextLong() throws NumberFormatException, IOException
{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
}
}C. Tea Party
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Polycarp invited all his friends to the tea party to celebrate the holiday. He has n cups, one for each of his n friends,
with volumesa1, a2, ..., an.
His teapot stores w milliliters of tea (w ≤ a1 + a2 + ... + an).
Polycarp wants to pour tea in cups in such a way that:
Every cup will contain tea for at least half of its volume
Every cup will contain integer number of milliliters of tea
All the tea from the teapot will be poured into cups
All friends will be satisfied.
Friend with cup i won't be satisfied, if there exists such
cup j that cup i contains less tea than
cup j but ai > aj.
For each cup output how many milliliters of tea should be poured in it. If it's impossible to pour all the tea and satisfy all conditions then output -1.
Input
The first line contains two integer numbers n and w (1 ≤ n ≤ 100,
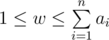
).
The second line contains n numbers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 100).
Output
Output how many milliliters of tea every cup should contain. If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
If it's impossible to pour all the tea and satisfy all conditions then output -1.
Examples
input
2 10 8 7
output
6 4
input
4 41 1 1 1
output
1 1 1 1
input
3 10 9 8 10
output
-1
Note
In the third example you should pour to the first cup at least 5 milliliters, to the second one at least 4, to the third one at least 5. It sums up to 14, which is greater than 10 milliliters available.
题意:有 n 个茶杯,茶壶里有 m 毫升茶,每个茶杯大小不等,我们要满足以下三个条件 :1. 每个茶杯中的茶要超过茶杯容量的一半 2. 每个茶杯中倒的茶必须是整数毫升 3. 大茶杯中的茶的容量不能少于任意一个小茶杯中的茶的容量,若 n
,m 不满足条件,输出 -1 ,否则输出一种满足条件的情况
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
private static final int Max = (int) (1e3 + 10);
private static int n, w;
private static LinkedList<node> list;
private static int []A;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InitData();
}
private static void InitData() throws Exception {
SC cin = new SC(System.in);
n = cin.nextInt();
w = cin.nextInt();
list=new LinkedList<>();
A=new int[Max];
int sum1=0,sum2=0;
int ans=w;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int x=cin.nextInt();
node node=new node(x,i);
list.add(node);
if(( x&1)==1){
sum1+=((x>>1)+1);
A[i]=((node.a>>1)+1);
}else{
sum1+=(x>>1);
A[i]=(node.a>>1);
}
ans-=A[i];
sum2+=x;
}
if(sum1<=w){
if(w>sum2){
System.out.println(-1);
}else{
if(ans>0){
Collections.sort(list,new Comparator<node>() {
@Override
public int compare(node o1, node o2) {
return o1.a-o2.a;
}
});
for(int i=n-1;i>=0&&ans>0;i--){
node node=list.get(i);
int temp=node.a-A[node.b];
if(temp>ans){
A[node.b]+=ans;
ans=0;
}else{
A[node.b]+=temp;
ans-=temp;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(i==0){
System.out.print(A[i]);
}else{
System.out.print(" "+A[i]);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}else{
System.out.println(-1);
}
}
public static class node{
int a;
int b;
public node(){
}
public node(int a,int b){
this.a=a;
this.b=b;
}
}
static class SC {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
SC(InputStream s) {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s));
}
String next() throws IOException {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreTokens())
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
long nextLong() throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
}
}
/**
3 100
37 26 37
50 1113
25 21 23 37 28 23 19 25 5 12 3 11 46 50 13 50 7 1 8 40 4 6 34 27 11 39 45 31 10 12 48 2 19 37 47 45 30 24 21 42 36 14 31 30 31 50 6 3 33 49
**/
相关文章推荐
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 A. Lucky Year
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 808A Lucky Year
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 C. Tea Party
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 C. Tea Party
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 C. Tea Party
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 B. Average Sleep Time
- Educational Codeforces Round 8 总结
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 C. Tea Party
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 C. Tea Party
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 C. Tea Party
- Educational Codeforces Round 6 总结
- Educational Codeforces Round 5 总结
- codeforces Educational Codeforces Round 21 A - Lucky Year
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 C. Tea Party
- Educational Codeforces Round 9 总结
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 B. Average Sleep Time
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 808B Average Sleep Time
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 C. Tea Party
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 D ( 二分 )
- Educational Codeforces Round 21 A
