View的绘制流程分析之二 -- measure
2017-05-23 00:07
357 查看
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/crazy1235/article/details/72633385
上面说到 performTraversals() 函数的时候,内部调用了 performMeasure()
又调用了View中的 measure() 函数!
来看 onMeasure() 函数
setMeasureDimension() 函数倒是很简单!目的就是存储计算出来的测量宽高~
现在来主要关注 getDefaultSize()
当specMode 是 UNSPECIFIED 的时候,View的宽/高为getDefaultSize()的第一个参数,也就是 getSuggestedMinimumWidth() 或者 getSuggestedMinimumHeight()
当View没有背景时,返回mMinWidth,该变量默认值是0,对应android:minWidth这个属性。所以,如果不指定该属性的话,就是0。
如果View有背景,则返回背景的原始宽度。
getSuggestedMinimumHeight()的内部逻辑与getSuggestedMinimumWidth()类似。
所以,当SpecMode是UNSPECIFIED的时候,View的测量宽/高 就是 getSuggestedMinimumWidth() 和 getSuggestedMinimumHeight() 两个方法的返回值!
当SpecMode是AT_MOST 或者 EXACTLY 时,View的测量 宽/高 就是 measureSpec 中的SpecSize ,也就是测量后的大小~
分析到这里,View的measure过程也就分析完了~
那么ViewGroup的measure是什么时候开始的呢???
还得从DecorView来说起!
在 Activity.attach() 函数中创建了PhoneWindow对象!
在PhoneWindow的构造函数中,创建了DecorView对象!
DecorView继承FrameLayout,所以它是一个ViewGroup!
所以整个window的绘制是从DecorView这个ViewGroup开始的!
这里的mView就是DecorView
其实ViewGroup 是一个抽象类,并没有重写onMeasure()函数!ViewGroup的子类们重写了onMeasure()函数!
既然DecorView继承了FrameLayout,那就拿FrameLayout来分析一下它的 measure过程。
从上面FrameLayout的onMeasure()方法体可以看出来,对子view进行了两次测量,准确的来说不是所有的子view都进行了二次测量~
这是为什么呢?
来往下看~
mMatchParentChildren 是一个集合,是用来存储需要二次测量的子view的!
那么都有哪些子view需要放到这个集合里面进行二次测量呢?
当 measureMatchParentChildren == true 的时候!
那么什么情况下 FrameLayout这个ViewGroup 的宽或者高的SpecMode不为EXACTLY呢?
我在 View的绘制流程分析之一 已经进行了分析!
再来一张图(转载~):
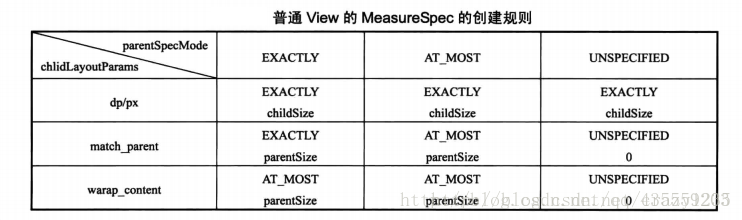
抛去UNSPECIFIED 这个mode不管,当前FrameLayout这个ViewGroup的测量模式不为EXACTLY有三种情况!
FrameLayout的父容器的SpecMode为AT_MOST,并且这个FrameLayout的 宽 / 高 属性是match_parent
FrameLayout的 宽 / 高 属性是wrap_content
总而言之,就是FrameLayout这个ViewGroup的宽或高不是一个固定的值,也就是不是EXACTLY模式!
这种情况下,再去判断子view(FrameLayout的子view)的宽高属性是否是match_parent,如果是则把这个子view添加到集合中去!
其实很容易理解!通过第一次遍历所有(不是GONE)的子view之后,就把父布局,也就是这个FrameLayout的宽高给测量出来了。
但是对于那些宽高设置为match_parent,它们的宽高依赖于父容器的大小,所以需要再次遍历它们设置它们的宽高~
直接调用的父类ViewGroup中的方法
在计算子view的宽度或高度的测量规格时,把父容器的padding值,和子view的margin值 加了上去!
关于getChildMeasureSpec() 这个函数的分析,在上一篇blog已经说过了! getChildMeasureSpec()
那么得到了宽高的测量规格之后,就可以调用measure进行测量了!
child.measure() 调用了View中的measure() 函数,此函数是final类型!不允许子类重写!
其实也很容易理解, 所有的容器测量都要先遍历子view进行测量,然后在确定容器的大小,所以最终实际的任务大多在一个个子view的测量上,容器的大小只需要针对这些子view的测量大小加加减减而已 !
view的measure过程在本篇blog上面已经进行了分析!本质上还是调用onMeasure() 函数!
如果这个View是一个ViewGroup,则会回调具体的容器类的onMeasure() 函数,如果不是则调用View或者它的子类(如果重写了)的onMeasure() 函数!
此时回过头来再看FrameLayout.onMeasure() 方法体下面这一句
当对所有的子view测量完毕之后,调用这个函数把计算得来的父容器的测量结果进行保存!
重点在 resolveSizeAndState() 函数!
计算出来size之后,就通过 setMeasuredDimension() 函数保存测量宽高!
这样从ViewGroup到一个个子View的测量,保存每个view/viewGroup的测量宽高!
分析到这里,performTraversals() 函数里面 performMeasure() 也就执行完毕了!
measure - 测量
确定View的测量宽高上面说到 performTraversals() 函数的时候,内部调用了 performMeasure()
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}又调用了View中的 measure() 函数!
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 计算key值
long key = (long) widthMeasureSpec << 32 | (long) heightMeasureSpec & 0xffffffffL;
// 初始化mMeasureCache对象,用来缓存测量结果
if (mMeasureCache == null) mMeasureCache = new LongSparseLongArray(2);
final boolean forceLayout = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
// ...
if (forceLayout || needsLayout) {
// ...
// 尝试去查找缓存
int cacheIndex = forceLayout ? -1 : mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
//没有读取到缓存或者忽略缓存时
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// 测量自己
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else { // 读取缓存
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
// Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
// ...
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
// 缓存
mMeasureCache.put(key, ((long) mMeasuredWidth) << 32 |
(long) mMeasuredHeight & 0xffffffffL); // suppress sign extension
}来看 onMeasure() 函数
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec), getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}setMeasureDimension() 函数倒是很简单!目的就是存储计算出来的测量宽高~
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}现在来主要关注 getDefaultSize()
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}当specMode 是 UNSPECIFIED 的时候,View的宽/高为getDefaultSize()的第一个参数,也就是 getSuggestedMinimumWidth() 或者 getSuggestedMinimumHeight()
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}当View没有背景时,返回mMinWidth,该变量默认值是0,对应android:minWidth这个属性。所以,如果不指定该属性的话,就是0。
如果View有背景,则返回背景的原始宽度。
getSuggestedMinimumHeight()的内部逻辑与getSuggestedMinimumWidth()类似。
所以,当SpecMode是UNSPECIFIED的时候,View的测量宽/高 就是 getSuggestedMinimumWidth() 和 getSuggestedMinimumHeight() 两个方法的返回值!
当SpecMode是AT_MOST 或者 EXACTLY 时,View的测量 宽/高 就是 measureSpec 中的SpecSize ,也就是测量后的大小~
分析到这里,View的measure过程也就分析完了~
那么ViewGroup的measure是什么时候开始的呢???
还得从DecorView来说起!
在 Activity.attach() 函数中创建了PhoneWindow对象!
public PhoneWindow(Context context, Window preservedWindow) {
this(context);
// ...
if (preservedWindow != null) {
mDecor = (DecorView) preservedWindow.getDecorView();
// ...
}在PhoneWindow的构造函数中,创建了DecorView对象!
public class DecorView extends FrameLayout implements RootViewSurfaceTaker, WindowCallbacks
DecorView继承FrameLayout,所以它是一个ViewGroup!
所以整个window的绘制是从DecorView这个ViewGroup开始的!
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
这里的mView就是DecorView
其实ViewGroup 是一个抽象类,并没有重写onMeasure()函数!ViewGroup的子类们重写了onMeasure()函数!
既然DecorView继承了FrameLayout,那就拿FrameLayout来分析一下它的 measure过程。
FrameLayout的measure流程
从decorView的measure() 方法体内看出,内部调用了onMeasure()。@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 1. 获取子View的个数
int count = getChildCount();
// 2. 如果宽/高的SpecMode有一个不是EXACTLY,则为true
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
// 3. 清空集合
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
// 4. 遍历子view
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
// 5. GONE类型的view不测量
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
// 6. 测量子view的宽高
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 7. 计算最大宽度
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
// 8. 计算最大高度
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
// 9. 如果measureMatchParentChildren 为true,并且子view设置的宽/高属性是match_parent,就把这个子view添加到集合中
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// 10. 补充计算最大宽度,最大高度
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// 11. 再次比较计算最大宽度,最大高度
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// 12. 如果有背景,则需要再次与背景图的宽高相比较得出最大宽高
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
// 13. 设置当前ViewGroup的测量宽高
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState), resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec, childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
// 14. 遍历需要二次测量的子view
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) { // 子view宽度设置的是MATCH_PARENT
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else { // 子view宽度设置的不是MATCH_PARENT
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) { // 子view高度设置的是MATCH_PARENT
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else { // 子view高度设置不是MATCH_PARENT
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
// 15. 测量子view
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}从上面FrameLayout的onMeasure()方法体可以看出来,对子view进行了两次测量,准确的来说不是所有的子view都进行了二次测量~
这是为什么呢?
来往下看~
mMatchParentChildren 是一个集合,是用来存储需要二次测量的子view的!
private final ArrayList<View> mMatchParentChildren = new ArrayList<>(1);
那么都有哪些子view需要放到这个集合里面进行二次测量呢?
当 measureMatchParentChildren == true 的时候!
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY || MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
那么什么情况下 FrameLayout这个ViewGroup 的宽或者高的SpecMode不为EXACTLY呢?
我在 View的绘制流程分析之一 已经进行了分析!
再来一张图(转载~):

抛去UNSPECIFIED 这个mode不管,当前FrameLayout这个ViewGroup的测量模式不为EXACTLY有三种情况!
FrameLayout的父容器的SpecMode为AT_MOST,并且这个FrameLayout的 宽 / 高 属性是match_parent
FrameLayout的 宽 / 高 属性是wrap_content
总而言之,就是FrameLayout这个ViewGroup的宽或高不是一个固定的值,也就是不是EXACTLY模式!
这种情况下,再去判断子view(FrameLayout的子view)的宽高属性是否是match_parent,如果是则把这个子view添加到集合中去!
其实很容易理解!通过第一次遍历所有(不是GONE)的子view之后,就把父布局,也就是这个FrameLayout的宽高给测量出来了。
但是对于那些宽高设置为match_parent,它们的宽高依赖于父容器的大小,所以需要再次遍历它们设置它们的宽高~
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
先来看看第一次遍历时,对子view的测量过程直接调用的父类ViewGroup中的方法
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
// 获取布局参数
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 计算得出宽度测量规格
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
// 计算得出高度测量规格
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
// 调用子view的measure()函数进行测量
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}在计算子view的宽度或高度的测量规格时,把父容器的padding值,和子view的margin值 加了上去!
关于getChildMeasureSpec() 这个函数的分析,在上一篇blog已经说过了! getChildMeasureSpec()
那么得到了宽高的测量规格之后,就可以调用measure进行测量了!
child.measure() 调用了View中的measure() 函数,此函数是final类型!不允许子类重写!
其实也很容易理解, 所有的容器测量都要先遍历子view进行测量,然后在确定容器的大小,所以最终实际的任务大多在一个个子view的测量上,容器的大小只需要针对这些子view的测量大小加加减减而已 !
view的measure过程在本篇blog上面已经进行了分析!本质上还是调用onMeasure() 函数!
如果这个View是一个ViewGroup,则会回调具体的容器类的onMeasure() 函数,如果不是则调用View或者它的子类(如果重写了)的onMeasure() 函数!
此时回过头来再看FrameLayout.onMeasure() 方法体下面这一句
// 13. 设置当前ViewGroup的测量宽高 setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState), resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec, childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
当对所有的子view测量完毕之后,调用这个函数把计算得来的父容器的测量结果进行保存!
重点在 resolveSizeAndState() 函数!
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (specSize < size) { // 父容器给的尺寸小于测量出来的尺寸,改变result值!
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: // 精确模式下,结果就是测量的值
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
default:
result = size;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}计算出来size之后,就通过 setMeasuredDimension() 函数保存测量宽高!
这样从ViewGroup到一个个子View的测量,保存每个view/viewGroup的测量宽高!
分析到这里,performTraversals() 函数里面 performMeasure() 也就执行完毕了!
相关文章推荐
- View的绘制流程分析之二 -- measure
- View的绘制流程分析之二-Android对Window对象的管理机制分析
- 每日一学(三) android View绘制流程之onMeasure()分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析 .
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
- Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析
