Python多线程经典问题之乘客做公交车算法实例
2017-03-22 11:49
791 查看
本文实例讲述了Python多线程经典问题之乘客做公交车算法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
问题描述:
乘客乘坐公交车问题,司机,乘客,售票员协同工作,通过多线程模拟三者的工作。
司机:开车,停车
售票员:打开车门,关闭车门
乘客:上车,下车
用Python的Event做线程同步通信,代码如下:
# *-* coding:gb2312 *-*
import threading
import time
stationName=("车站0","车站1","车站2","车站3","车站4","车站5","车站6")
currentStationIndex = -1
eventBusStop = threading.Event()
eventClosedDoor = threading.Event()
eventOpenedDoor = threading.Event()
stationCount = len(stationName)
class Passenger(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self,no,getonStation,getoffStation):
self.no =no
self.getonStation=getonStation
self.getoffStation=getoffStation
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
def run(self):
bExit= False
global currentStationIndex
global stationCount
bAlreadyGetOnStation = False
while not bExit:
eventOpenedDoor.wait()
if self.getonStation == currentStationIndex and bAlreadyGetOnStation == False:
print "乘客%d在%s上车" %(self.no,stationName[currentStationIndex])
bAlreadyGetOnStation =True
elif self.getoffStation == currentStationIndex:
print "乘客%d在%s下车" %(self.no,stationName[currentStationIndex])
bExit = True
time.sleep(1)
class Driver(threading.Thread):
def run(self):
bExit= False
global currentStationIndex
global stationCount
while not bExit:
print "司机: 公交车开始行驶....."
time.sleep(5)
currentStationIndex += 1
print "司机: 到站 ",stationName[currentStationIndex]
eventBusStop.set()
eventClosedDoor.wait()
eventClosedDoor.clear()
if currentStationIndex == stationCount-1:
bExit= True
class Conductor(threading.Thread):
def run(self):
bExit= False
global currentStationIndex
global stationCount
while not bExit:
eventBusStop.wait()
eventBusStop.clear()
print "售票员打开车门:%s到了" %(stationName[currentStationIndex])
eventOpenedDoor.set()
time.sleep(5)
print "售票员关闭车门"
eventOpenedDoor.clear()
eventClosedDoor.set()
if currentStationIndex == stationCount-1:
bExit = True
def test():
passPool=[]
passPool.append(Passenger(0,0,3))
passPool.append(Passenger(1,1,3))
passPool.append(Passenger(2,2,4))
passPool.append(Passenger(3,0,5))
passPool.append(Passenger(4,1,3))
passPool.append(Passenger(5,2,4))
passPool.append(Passenger(6,4,5))
passPool.append(Passenger(7,0,2))
passPool.append(Passenger(8,1,3))
passPool.append(Conductor())
passPool.append(Driver())
leng = len(passPool)
for i in range(leng):
passPool[i].start()
if __name__=='__main__':
test()
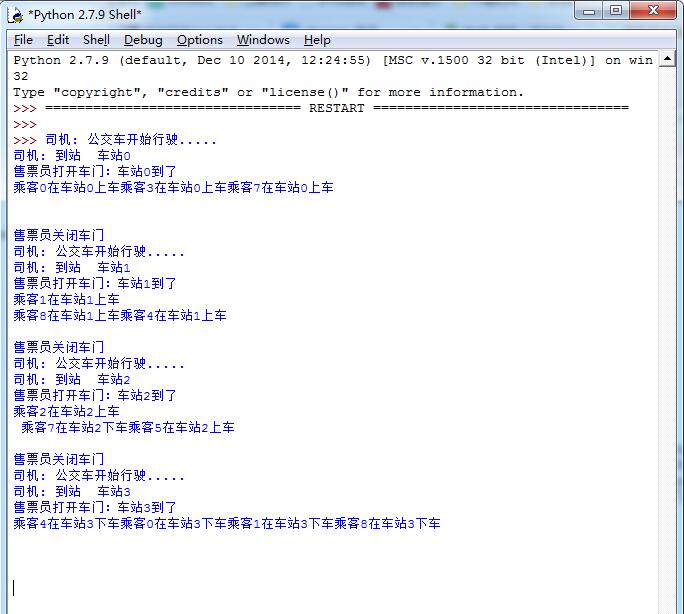
输出结果如下:
更多关于Python相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:《Python进程与线程操作技巧总结》、《Python Socket编程技巧总结》、《Python图片操作技巧总结》、《Python数据结构与算法教程》、《Python函数使用技巧总结》、《Python字符串操作技巧汇总》、《Python入门与进阶经典教程》及《Python文件与目录操作技巧汇总》
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。
您可能感兴趣的文章:
相关文章推荐
- 多线程经典问题-----乘客做公交车问题解答2
- 多线程经典问题-----乘客做公交车问题解答3
- 多线程经典问题-----乘客做公交车问题解答1
- 多线程经典问题-----乘客做公交车问题解答3
- 黑马程序员——多线程操作经典实例:生产者消费者问题
- 《面试-回溯法》 ---五种经典的算法问题之回溯法python
- 经典多线程实例:生产者消费者问题
- 经典算法问题:“this is a test” 逆序输出为“test a is this”.使用Python实现
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(源码)
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(文档)
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(源码)
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(源码)
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(文档)
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(源码)
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(源码)
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(文档)
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(文档)
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(文档)
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(源码)
- 经典面试问题:12小球问题算法(源码)
