【Java集合源码剖析】LinkedList源码剖析
2017-03-19 17:21
435 查看
LinkedList简介
LinkedList是基于双向循环链表(从源码中可以很容易看出)实现的,除了可以当做链表来操作外,它还可以当做栈、队列和双端队列来使用。LinkedList同样是非线程安全的,只在单线程下适合使用。
LinkedList实现了Serializable接口,因此它支持序列化,能够通过序列化传输,实现了Cloneable接口,能被克隆。
LinkedList源码剖析
LinkedList的源码如下(加入了比较详细的注释):[java] view
plain copy

package java.util;
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
&
4000
nbsp; // 链表的表头,表头不包含任何数据。Entry是个链表类数据结构。
private transient Entry<E> header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);
// LinkedList中元素个数
private transient int size = 0;
// 默认构造函数:创建一个空的链表
public LinkedList() {
header.next = header.previous = header;
}
// 包含“集合”的构造函数:创建一个包含“集合”的LinkedList
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
// 获取LinkedList的第一个元素
public E getFirst() {
if (size==0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 链表的表头header中不包含数据。
// 这里返回header所指下一个节点所包含的数据。
return header.next.element;
}
// 获取LinkedList的最后一个元素
public E getLast() {
if (size==0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 由于LinkedList是双向链表;而表头header不包含数据。
// 因而,这里返回表头header的前一个节点所包含的数据。
return header.previous.element;
}
// 删除LinkedList的第一个元素
public E removeFirst() {
return remove(header.next);
}
// 删除LinkedList的最后一个元素
public E removeLast() {
return remove(header.previous);
}
// 将元素添加到LinkedList的起始位置
public void addFirst(E e) {
addBefore(e, header.next);
}
// 将元素添加到LinkedList的结束位置
public void addLast(E e) {
addBefore(e, header);
}
// 判断LinkedList是否包含元素(o)
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
// 返回LinkedList的大小
public int size() {
return size;
}
// 将元素(E)添加到LinkedList中
public boolean add(E e) {
// 将节点(节点数据是e)添加到表头(header)之前。
// 即,将节点添加到双向链表的末端。
addBefore(e, header);
return true;
}
// 从LinkedList中删除元素(o)
// 从链表开始查找,如存在元素(o)则删除该元素并返回true;
// 否则,返回false。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o==null) {
// 若o为null的删除情况
for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {
if (e.element==null) {
remove(e);
return true;
}
}
} else {
// 若o不为null的删除情况
for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {
if (o.equals(e.element)) {
remove(e);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// 将“集合(c)”添加到LinkedList中。
// 实际上,是从双向链表的末尾开始,将“集合(c)”添加到双向链表中。
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
// 从双向链表的index开始,将“集合(c)”添加到双向链表中。
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+
", Size: "+size);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
// 获取集合的长度
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew==0)
return false;
modCount++;
// 设置“当前要插入节点的后一个节点”
Entry<E> successor = (index==size ? header : entry(index));
// 设置“当前要插入节点的前一个节点”
Entry<E> predecessor = successor.previous;
// 将集合(c)全部插入双向链表中
for (int i=0; i<numNew; i++) {
Entry<E> e = new Entry<E>((E)a[i], successor, predecessor);
predecessor.next = e;
predecessor = e;
}
successor.previous = predecessor;
// 调整LinkedList的实际大小
size += numNew;
return true;
}
// 清空双向链表
public void clear() {
Entry<E> e = header.next;
// 从表头开始,逐个向后遍历;对遍历到的节点执行一下操作:
// (01) 设置前一个节点为null
// (02) 设置当前节点的内容为null
// (03) 设置后一个节点为“新的当前节点”
while (e != header) {
Entry<E> next = e.next;
e.next = e.previous = null;
e.element = null;
e = next;
}
header.next = header.previous = header;
// 设置大小为0
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
// 返回LinkedList指定位置的元素
public E get(int index) {
return entry(index).element;
}
// 设置index位置对应的节点的值为element
public E set(int index, E element) {
Entry<E> e = entry(index);
E oldVal = e.element;
e.element = element;
return oldVal;
}
// 在index前添加节点,且节点的值为element
public void add(int index, E element) {
addBefore(element, (index==size ? header : entry(index)));
}
// 删除index位置的节点
public E remove(int index) {
return remove(entry(index));
}
// 获取双向链表中指定位置的节点
private Entry<E> entry(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+
", Size: "+size);
Entry<E> e = header;
// 获取index处的节点。
// 若index < 双向链表长度的1/2,则从前先后查找;
// 否则,从后向前查找。
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++)
e = e.next;
} else {
for (int i = size; i > index; i--)
e = e.previous;
}
return e;
}
// 从前向后查找,返回“值为对象(o)的节点对应的索引”
// 不存在就返回-1
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o==null) {
for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {
if (e.element==null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {
if (o.equals(e.element))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 从后向前查找,返回“值为对象(o)的节点对应的索引”
// 不存在就返回-1
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o==null) {
for (Entry e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {
index--;
if (e.element==null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Entry e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {
index--;
if (o.equals(e.element))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 返回第一个节点
// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null
public E peek() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return getFirst();
}
// 返回第一个节点
// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则抛出异常
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
// 删除并返回第一个节点
// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null
public E poll() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return removeFirst();
}
// 将e添加双向链表末尾
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
// 将e添加双向链表开头
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
// 将e添加双向链表末尾
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
// 返回第一个节点
// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null
public E peekFirst() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return getFirst();
}
// 返回最后一个节点
// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null
public E peekLast() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return getLast();
}
// 删除并返回第一个节点
// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null
public E pollFirst() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return removeFirst();
}
// 删除并返回最后一个节点
// 若LinkedList的大小为0,则返回null
public E pollLast() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return removeLast();
}
// 将e插入到双向链表开头
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
// 删除并返回第一个节点
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
// 从LinkedList开始向后查找,删除第一个值为元素(o)的节点
// 从链表开始查找,如存在节点的值为元素(o)的节点,则删除该节点
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
return remove(o);
}
// 从LinkedList末尾向前查找,删除第一个值为元素(o)的节点
// 从链表开始查找,如存在节点的值为元素(o)的节点,则删除该节点
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o==null) {
for (Entry<E> e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {
if (e.element==null) {
remove(e);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Entry<E> e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {
if (o.equals(e.element)) {
remove(e);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// 返回“index到末尾的全部节点”对应的ListIterator对象(List迭代器)
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
return new ListItr(index);
}
// List迭代器
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
// 上一次返回的节点
private Entry<E> lastReturned = header;
// 下一个节点
private Entry<E> next;
// 下一个节点对应的索引值
private int nextIndex;
// 期望的改变计数。用来实现fail-fast机制。
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
// 构造函数。
// 从index位置开始进行迭代
ListItr(int index) {
// index的有效性处理
<
4000
span style="margin:0px; padding:0px; border:none; color:black; background-color:inherit"> if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+ ", Size: "+size);
// 若 “index 小于 ‘双向链表长度的一半’”,则从第一个元素开始往后查找;
// 否则,从最后一个元素往前查找。
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
next = header.next;
for (nextIndex=0; nextIndex<index; nextIndex++)
next = next.next;
} else {
next = header;
for (nextIndex=size; nextIndex>index; nextIndex--)
next = next.previous;
}
}
// 是否存在下一个元素
public boolean hasNext() {
// 通过元素索引是否等于“双向链表大小”来判断是否达到最后。
return nextIndex != size;
}
// 获取下一个元素
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (nextIndex == size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
// next指向链表的下一个元素
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.element;
}
// 是否存在上一个元素
public boolean hasPrevious() {
// 通过元素索引是否等于0,来判断是否达到开头。
return nextIndex != 0;
}
// 获取上一个元素
public E previous() {
if (nextIndex == 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// next指向链表的上一个元素
lastReturned = next = next.previous;
nextIndex--;
checkForComodification();
return lastReturned.element;
}
// 获取下一个元素的索引
public int nextIndex() {
return nextIndex;
}
// 获取上一个元素的索引
public int previousIndex() {
return nextIndex-1;
}
// 删除当前元素。
// 删除双向链表中的当前节点
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
Entry<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;
try {
LinkedList.this.remove(lastReturned);
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
if (next==lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = header;
expectedModCount++;
}
// 设置当前节点为e
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == header)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.element = e;
}
// 将e添加到当前节点的前面
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = header;
addBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;
}
// 判断 “modCount和expectedModCount是否相等”,依次来实现fail-fast机制。
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// 双向链表的节点所对应的数据结构。
// 包含3部分:上一节点,下一节点,当前节点值。
private static class Entry<E> {
// 当前节点所包含的值
E element;
// 下一个节点
Entry<E> next;
// 上一个节点
Entry<E> previous;
/**
* 链表节点的构造函数。
* 参数说明:
* element —— 节点所包含的数据
* next —— 下一个节点
* previous —— 上一个节点
*/
Entry(E element, Entry<E> next, Entry<E> previous) {
this.element = element;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
}
// 将节点(节点数据是e)添加到entry节点之前。
private Entry<E> addBefore(E e, Entry<E> entry) {
// 新建节点newEntry,将newEntry插入到节点e之前;并且设置newEntry的数据是e
Entry<E> newEntry = new Entry<E>(e, entry, entry.previous);
newEntry.previous.next = newEntry;
newEntry.next.previous = newEntry;
// 修改LinkedList大小
size++;
// 修改LinkedList的修改统计数:用来实现fail-fast机制。
modCount++;
return newEntry;
}
// 将节点从链表中删除
private E remove(Entry<E> e) {
if (e == header)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
E result = e.element;
e.previous.next = e.next;
e.next.previous = e.previous;
e.next = e.previous = null;
e.element = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return result;
}
// 反向迭代器
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingIterator();
}
// 反向迭代器实现类。
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator {
final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
// 反向迭代器是否下一个元素。
// 实际上是判断双向链表的当前节点是否达到开头
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
// 反向迭代器获取下一个元素。
// 实际上是获取双向链表的前一个节点
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
// 删除当前节点
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}
// 返回LinkedList的Object[]数组
public Object[] toArray() {
// 新建Object[]数组
Object[] result = new Object[size];
int i = 0;
// 将链表中所有节点的数据都添加到Object[]数组中
for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)
result[i++] = e.element;
return result;
}
// 返回LinkedList的模板数组。所谓模板数组,即可以将T设为任意的数据类型
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
// 若数组a的大小 < LinkedList的元素个数(意味着数组a不能容纳LinkedList中全部元素)
// 则新建一个T[]数组,T[]的大小为LinkedList大小,并将该T[]赋值给a。
if (a.length < size)
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
// 将链表中所有节点的数据都添加到数组a中
int i = 0;
Object[] result = a;
for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)
result[i++] = e.element;
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
// 克隆函数。返回LinkedList的克隆对象。
public Object clone() {
LinkedList<E> clone = null;
// 克隆一个LinkedList克隆对象
try {
clone = (LinkedList<E>) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError();
}
// 新建LinkedList表头节点
clone.header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);
clone.header.next = clone.header.previous = clone.header;
clone.size = 0;
clone.modCount = 0;
// 将链表中所有节点的数据都添加到克隆对象中
for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)
clone.add(e.element);
return clone;
}
// java.io.Serializable的写入函数
// 将LinkedList的“容量,所有的元素值”都写入到输出流中
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// 写入“容量”
s.writeInt(size);
// 将链表中所有节点的数据都写入到输出流中
for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)
s.writeObject(e.element);
}
// java.io.Serializable的读取函数:根据写入方式反向读出
// 先将LinkedList的“容量”读出,然后将“所有的元素值”读出
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// 从输入流中读取“容量”
int size = s.readInt();
// 新建链表表头节点
header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);
header.next = header.previous = header;
// 从输入流中将“所有的元素值”并逐个添加到链表中
for (int i=0; i<size; i++)
addBefore((E)s.readObject(), header);
}
}
几点总结
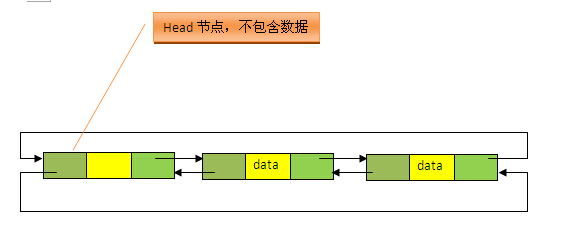
关于LinkedList的源码,给出几点比较重要的总结:1、从源码中很明显可以看出,LinkedList的实现是基于双向循环链表的,且头结点中不存放数据,如下图;
2、注意两个不同的构造方法。无参构造方法直接建立一个仅包含head节点的空链表,包含Collection的构造方法,先调用无参构造方法建立一个空链表,而后将Collection中的数据加入到链表的尾部后面。
3、在查找和删除某元素时,源码中都划分为该元素为null和不为null两种情况来处理,LinkedList中允许元素为null。
4、LinkedList是基于链表实现的,因此不存在容量不足的问题,所以这里没有扩容的方法。
5、注意源码中的Entry<E> entry(int index)方法。该方法返回双向链表中指定位置处的节点,而链表中是没有下标索引的,要指定位置出的元素,就要遍历该链表,从源码的实现中,我们看到这里有一个加速动作。源码中先将index与长度size的一半比较,如果index<size/2,就只从位置0往后遍历到位置index处,而如果index>size/2,就只从位置size往前遍历到位置index处。这样可以减少一部分不必要的遍历,从而提高一定的效率(实际上效率还是很低)。
6、注意链表类对应的数据结构Entry。如下;
[java] view
plain copy

// 双向链表的节点所对应的数据结构。
// 包含3部分:上一节点,下一节点,当前节点值。
private static class Entry<E> {
// 当前节点所包含的值
E element;
// 下一个节点
Entry<E> next;
// 上一个节点
Entry<E> previous;
/**
* 链表节点的构造函数。
* 参数说明:
* element —— 节点所包含的数据
* next —— 下一个节点
* previous —— 上一个节点
*/
Entry(E element, Entry<E> next, Entry<E> previous) {
this.element = element;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
}
7、LinkedList是基于链表实现的,因此插入删除效率高,查找效率低(虽然有一个加速动作)。
8、要注意源码中还实现了栈和队列的操作方法,因此也可以作为栈、队列和双端队列来使用。
相关文章推荐
- 【Java1.7.5集合源码剖析】LinkedList源码剖析
- 【Java集合源码剖析】LinkedList源码剖析
- 【Java集合源码剖析】LinkedList源码剖析
- 【Java集合源码剖析】LinkedList源码剖析
- 第二篇:JAVA集合之LinkedList源码剖析
- Java集合------LinkedList源码剖析
- 【Java集合源码剖析】LinkedList源码剖析
- 转:【Java集合源码剖析】LinkedList源码剖析
- 【Java集合源码剖析】LinkedList源码剖析
- 【Java集合源码剖析】LinkedList源码剖析
- 【Java集合源码剖析】LinkedList源码剖析
- 【java集合框架源码剖析系列】java源码剖析之LinkedList
- Java 集合系列05之 LinkedList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
- Java LinkedList 源码剖析
- Java类集框架之LinkedList源码剖析
- Java集合之LinkedList源码分析
- java_集合体系之:LinkedList详解、源码及示例——04
- Java集合源码学习笔记(五)ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector和Hashtable,HashMap的比较
- 【java集合框架源码剖析系列】java源码剖析之LinkedList
- Java 集合系列05之 LinkedList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
