Nginx源码分析之ngx_array_t
2016-12-20 20:27
579 查看
ngx_array_t是一个顺序容器,类似于STL中的
源码位置:
根据图中所示
打印结果如下:
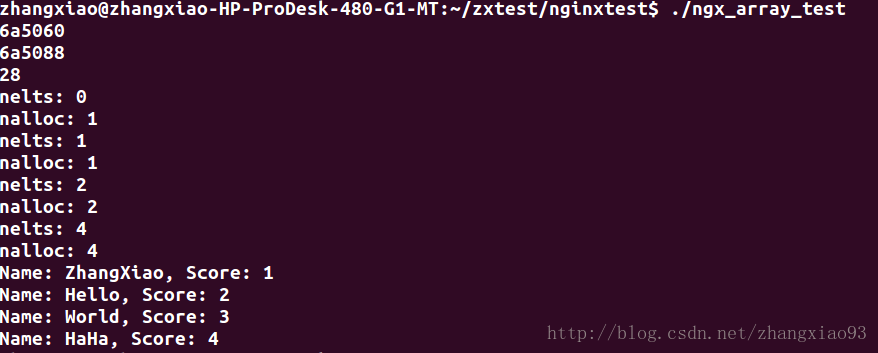
根据结果,可以知道:
1.验证了(三)中
2.当pool不重新分配的时候,nelts跟nalloc共同增长,这一点跟vector有一点区别,如果把nelts元素个数比作vector中的size,把nalloc比作capability,那么在vector中,一旦size>capability就会扩容。这一点从源码中很容易验证。
vector可以动态扩容。
源码位置:
nginx/src/core/ngx_array.h
nginx/src/core/ngx_array.c
(一)数据结构
typedef struct ngx_array_s ngx_array_t;
struct ngx_array_s {
//数组首地址
void *elts;
//数组中已经使用的元素个数
ngx_uint_t nelts;
//每个元素占用的内存大小
size_t size;
//当前数组中能容纳元素个数的总大小
ngx_uint_t nalloc;
//内存池对象
ngx_pool_t *pool;
};(二)使用方法
//创建动态数组,分配n个大小为size的空间
ngx_array_t *
ngx_array_create(ngx_pool_t *p, ngx_uint_t n, size_t size)
{
ngx_array_t *a;
a = ngx_palloc(p, sizeof(ngx_array_t));
if (a == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
a->elts = ngx_palloc(p, n * size);
if (a->elts == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
a->nelts = 0;
a->size = size;
a->nalloc = n;
a->pool = p;
return a;
}
//销毁已经分配的数组元素空间和动态数组对象
void
ngx_array_destroy(ngx_array_t *a)
{
ngx_pool_t *p;
p = a->pool;
if ((u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nalloc == p->d.last) {
p->d.last -= a->size * a->nalloc;
}
if ((u_char *) a + sizeof(ngx_array_t) == p->d.last) {
p->d.last = (u_char *) a;
}
}
//向当前动态数组a中添加一个元素,返回新添加元素的地址
void *
ngx_array_push(ngx_array_t *a)
{
void *elt, *new;
size_t size;
ngx_pool_t *p;
if (a->nelts == a->nalloc) {
/* the array is full */
size = a->size * a->nalloc;
p = a->pool;
if ((u_char *) a->elts + size == p->d.last
&& p->d.last + a->size <= p->d.end)
{
//内存池仍有空间,直接将新插入的元素往后挪一个
/*
* the array allocation is the last in the pool
* and there is space for new allocation
*/
p->d.last += a->size;
a->nalloc++;
} else {
//内存池不够了,重新分配
/* allocate a new array */
new = ngx_palloc(p, 2 * size);
if (new == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ngx_memcpy(new, a->elts, size);
a->elts = new;
a->nalloc *= 2;
}
}
elt = (u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nelts;
a->nelts++;
return elt;
}
//要添加n个元素,返回新添加这一批元素的首地址
void *
ngx_array_push_n(ngx_array_t *a, ngx_uint_t n)
{
void *elt, *new;
size_t size;
ngx_uint_t nalloc;
ngx_pool_t *p;
size = n * a->size;
if (a->nelts + n > a->nalloc) {
/* the array is full */
p = a->pool;
if ((u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nalloc == p->d.last
&& p->d.last + size <= p->d.end)
{
/*
* the array allocation is the last in the pool
* and there is space for new allocation
*/
p->d.last += size;
a->nalloc += n;
} else {
/* allocate a new array */
nalloc = 2 * ((n >= a->nalloc) ? n : a->nalloc);
new = ngx_palloc(p, nalloc * a->size);
if (new == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ngx_memcpy(new, a->elts, a->nelts * a->size);
a->elts = new;
a->nalloc = nalloc;
}
}
elt = (u_char *) a->elts + a->size * a->nelts;
a->nelts += n;
return elt;
}(三)内存结构
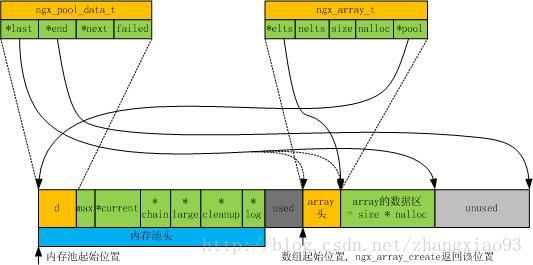
一个直观的图来看ngx_array_t数据结构内存分布。

根据图中所示
ngx_array_create返回的地址跟
elts的地址还有一个array头的差距,一会测试代码可以测试验证。
(四)测试代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "ngx_config.h"
#include "nginx.h"
#include "ngx_conf_file.h"
#include "ngx_core.h"
#include "ngx_string.h"
#include "ngx_palloc.h"
#include "ngx_list.h"
#include "ngx_queue.h"
#include "ngx_array.h"
volatile ngx_cycle_t *ngx_cycle;
void ngx_log_error_core(ngx_uint_t level, ngx_log_t *log,
ngx_err_t err, const char *fmt, ...)
{
}
typedef struct{
ngx_str_t name;
unsigned int score;
}StuInfo;
void printArray(ngx_array_t *);
void dumpArrayInfo(ngx_array_t *);
int main(int argc,char**argv)
{
ngx_pool_t * pool;
pool=ngx_create_pool(1024,NULL);
ngx_array_t* dynamicArray=ngx_array_create(pool,1,sizeof(StuInfo));
///
printf("%x\r\n",(u_char*)(dynamicArray));
printf("%x\r\n",(u_char*)(dynamicArray->elts));
printf("%x\r\n",sizeof(ngx_array_t));
dumpArrayInfo(dynamicArray);
#if 1
StuInfo* a = ngx_array_push(dynamicArray);
dumpArrayInfo(dynamicArray);
ngx_str_set(&(a->name),"ZhangXiao");
a->score=1;
a = ngx_array_push(dynamicArray);
dumpArrayInfo(dynamicArray);
ngx_str_set(&(a->name),"Hello");
a->score=2;
StuInfo* b = ngx_array_push_n(dynamicArray,2);
dumpArrayInfo(dynamicArray);
ngx_str_set(&(b->name),"World");
b->score=3;
ngx_str_set(&((b+1)->name),"HaHa");
(b+1)->score=4;
printArray(dynamicArray);
#endif
ngx_array_destroy(dynamicArray);
return 0;
}
void dumpArrayInfo(ngx_array_t *a)
{
printf("nelts: %d\r\n",a->nelts);
printf("nalloc: %d\r\n",a->nalloc);
}
void printArray(ngx_array_t *a)
{
ngx_uint_t seq=0;
#if 0
//两种方式都可以
do
{
StuInfo * it = (StuInfo*)a->elts+seq;
printf("Name: %s, Score: %d\r\n",it->name.data,it->score);
++seq;
}while(seq<a->nelts);
#endif
do
{
StuInfo * it = a->elts;
printf("Name: %s, Score: %d\r\n",it[seq].name.data,it[seq].score);
++seq;
}while(seq<a->nelts);
}打印结果如下:

根据结果,可以知道:
1.验证了(三)中
ngx_array_create返回的地址跟
elts的地址还有一个array头的差距
2.当pool不重新分配的时候,nelts跟nalloc共同增长,这一点跟vector有一点区别,如果把nelts元素个数比作vector中的size,把nalloc比作capability,那么在vector中,一旦size>capability就会扩容。这一点从源码中很容易验证。
相关文章推荐
- Nginx源码分析—数组结构ngx_array_t
- nginx源码分析—数组结构ngx_array_t
- Nginx 源码分析-- ngx_array、ngx_list基本数据结构
- nginx源码分析—数组结构ngx_array_t
- nginx源码分析—数组结构ngx_array_t
- nginx源码分析之ngx_array_t
- Nginx源码分析---数组结构ngx_array_t
- Nginx源码分析 - 基础数据结构篇 - 数组结构 ngx_array.c
- nginx源码分析—数组结构ngx_array_t
- nginx源码分析—数组结构ngx_array_t
- 文章2:Nginx源码分析-ngx_array_t动态数组
- nginx数组代码分析[ngx_array.c]
- nginx源码分析—链表结构ngx_list_t
- nginx源码分析—队列结构ngx_queue_t
- Nginx 源码分析-- ngx_string 的一些简单分析
- nginx源码分析-ngx_cycle_s结构说明
- Nginx源码分析---内存池结构ngx_pool_t及内存管理
- Nginx源码学习-双向链表(ngx_queue_t)实现及实例分析
- nginx 源码学习(六) 基本数据结构 ngx_array_t
- Nginx源码分析---hash结构ngx_hash_t(v1.0.4)
