Android四大组件Service启动源码分析
2016-11-30 12:02
555 查看
1 用法
启动状态
Intent intent=new Intent(this,MyService.class);
startService(intent);
绑定状态
Intent intent=new Intent(this,MyService.class);
bindService(intent,mServiceConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
private ServiceConnection
mServiceConnection= new ServiceConnection() {
// 当与service的连接建立后被调用
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
//TODO
}
// 当与service的连接意外断开时被调用
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
//TODO
}
};
2 源码分析
(1)先看启动状态
service启动状态时序图如下
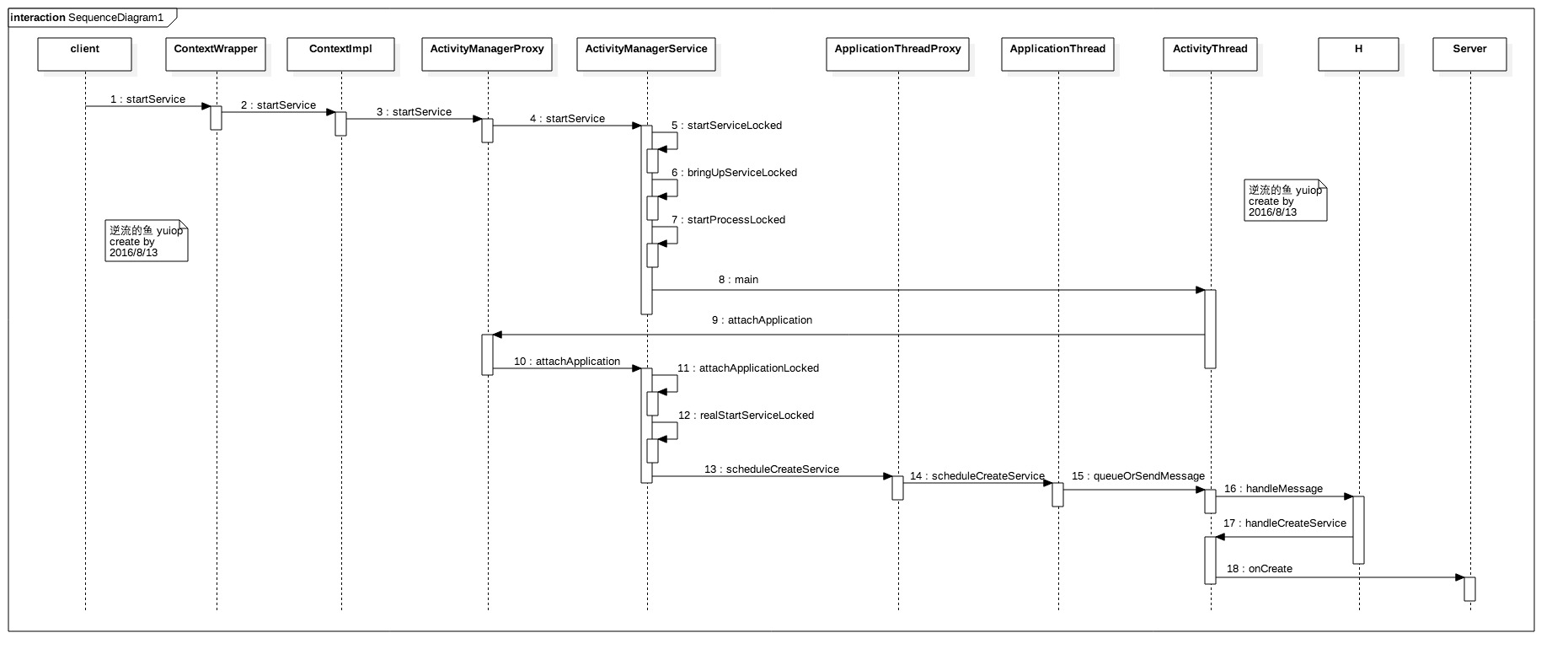
1 ContextWrapper
2 ContextImpl
3 ActivityManagerProxy
4 ActivityManagerService
ActivityManagerService的startService方法中,mServices是一个ActiveServices类,用于辅助AMS管理Service,类似于管理Activity的ActivityStakSupervisor。
5 ActiveServices
6 ApplicationThreadProxy(ApplicationThreadNative内部类)
7 ApplicationThread(ActivityThread内部类)
8 ActivityThread
这里涉及到LoadedApk ,ClassLoader ,ContextImpl,mServices
final ArrayMap<IBinder, Service> mServices
= new ArrayMap<IBinder, Service>();
这里Service的启动状态就分析完了
(2)绑定状态
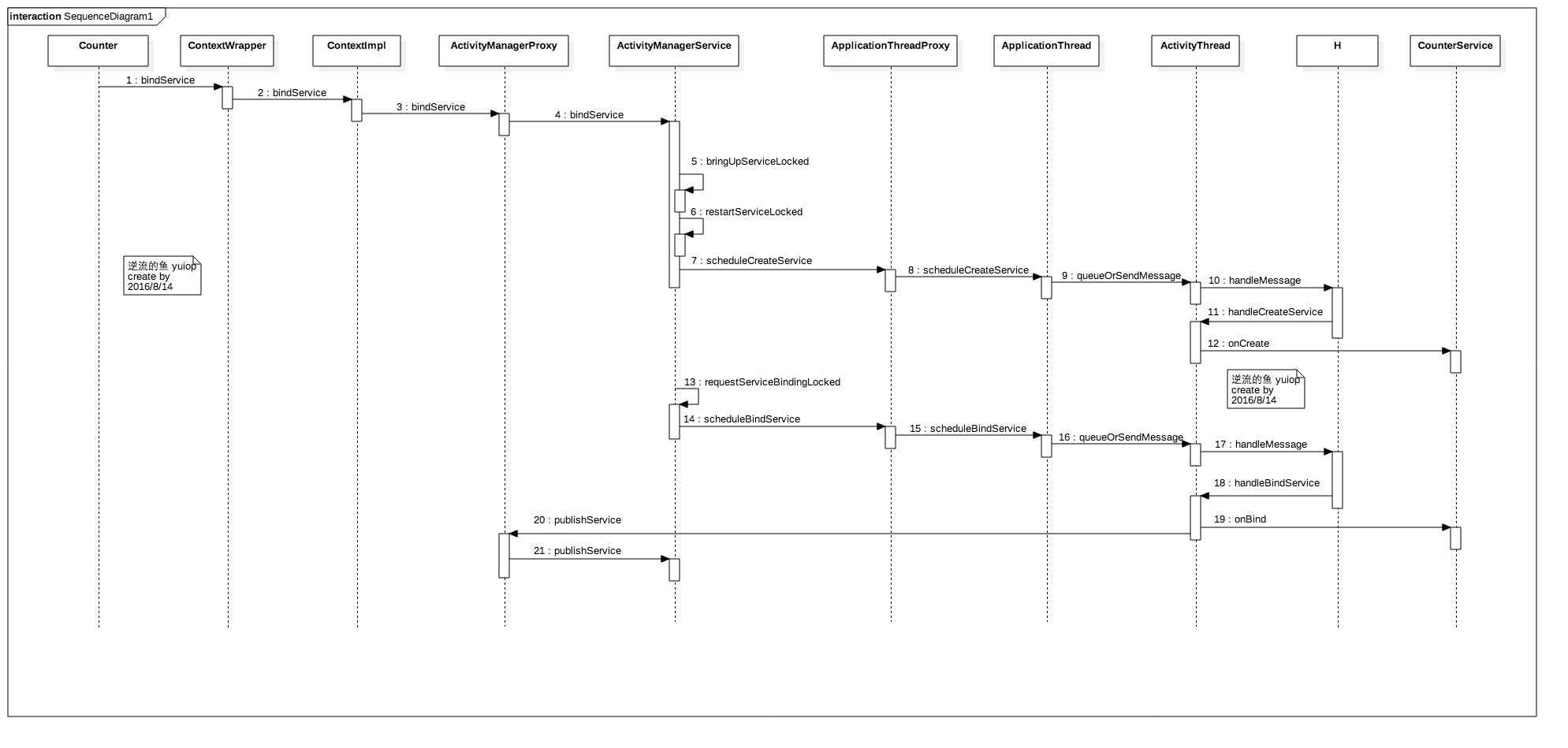
和Service启动状态一样,绑定状态也是从ContextWrapper开始
1 ContextWrapper
2 ContextImpl
ContextImpl的bindService最终会调用到自己的bindServiceCommon
3 LoadedApk
这里,mPackageInfo是个LoadedApk类,从getServiceDispatcher方法可看出,map中保存了客户端conn和LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher的一份映射,首先在map查找是否有相应的conn,没有就创建一个ServiceDispatcher,并放入mServices中
mServices的类型
private final ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>> mServices
= new ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>>();
这里涉及到ServiceConnection,LoadedApk,ServiceDispatcher,InnerConnection,详细讲解下他们的关系
4 ServiceDispatcher(LoadedApk内部类)
getServiceDispatcher方法中,如果mServices不存在客户端conn,就创建ServiceDispatcher,sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
ServiceDispatcher构造函数中会创建一个InnerConnection实例,从IServiceConnection.Stub可以看出,InnerConnection是一个binder
6 ActivityManagerProxy
回到ContextImpl,3-4-5步只是将客户端ServiceConnection转化为InnerConnection(binder),接下来是重点,ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService
7 ActivityManagerService
按部就班,从ActivityManagerProxy的bindService 到 ActivityManagerService的bindService
8 ActiveServices
mServices是ActiveServices类型,mServices.bindServiceLocked执行经过一系列方法,最后又到了realStartServiceLocked方法
9 ApplicationThreadProxy(ApplicationThreadNative内部类)
10 ApplicationThread
11 ActivityThread
又到了我们最熟悉的地方了,贴代码,不想说
在第8步realStartServiceLocked方法中app.thread.scheduleCreateService会创建service,这个在启动模式中已经分析过了。还记得创建service时会把service放入mServices中吗?再次回顾下ActivityThread的方法handleCreateService
到这里为止,已经创建了service实例,并且调用了service的方法onBind(),但是此时客户端(通常是Activity)还没有连接到service,所以还要调用客户端的serviceConnection中的onServiceConnected,这个过程是由ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService来完成,ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()就是ActivityManagerProxy! ActivityManagerProxy!
ActivityManagerProxy!,重要的事说三遍!
12 ActivityManagerProxy
真正的执行过程在AMS中
13 ActivityManagerService
14 ActiveServices
15 InnerConnection (LoadedApk内部类ServiceDispathcer中的内部类)
ConnectionRecord 就是记录客户端(Activity)中connection的数据结构,客户端的connection经过3->4->5转化为InnerConnection,即一个binder,用于跨进程通信。
16 ServiceDispatcher
mActivityThread就是ActivityThread中的Handler H,new RunConnection(name, service, 0)方法经过mActivityThread.post就运行在主线程中
3 总结
启动状态
Intent intent=new Intent(this,MyService.class);
startService(intent);
绑定状态
Intent intent=new Intent(this,MyService.class);
bindService(intent,mServiceConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
private ServiceConnection
mServiceConnection= new ServiceConnection() {
// 当与service的连接建立后被调用
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
//TODO
}
// 当与service的连接意外断开时被调用
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
//TODO
}
};
2 源码分析
(1)先看启动状态
service启动状态时序图如下

1 ContextWrapper
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
return mBase.startService(service);
}Service的启动从ContextWrapper的startService开始,mBase是ContextImpl类,Activity通过attach方法和ContextImpl关联起来。以后会详细讲解Context族谱的关系。所以重点在ContextImpl中的startService方法中。2 ContextImpl
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, mUser);
}
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, UserHandle user) {
.....
ComponentName cn = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(
getContentResolver()), getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
.....
return cn;
}Activity篇分析过,ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()获得了ActivityManagerProxy(ActivityManagerNative的内部类),ActivityManagerProxy的startService真正是在AMS中执行3 ActivityManagerProxy
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, int userId) throws RemoteException
{
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
service.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeInt(userId);
mRemote.transact(START_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
ComponentName res = ComponentName.readFromParcel(reply);
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
return res;
}4 ActivityManagerService
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, int userId) {
......
ComponentName res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid, userId);
......
return res;
}
}ActivityManagerService的startService方法中,mServices是一个ActiveServices类,用于辅助AMS管理Service,类似于管理Activity的ActivityStakSupervisor。
5 ActiveServices
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
......
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
......
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
......
}mServices.startServiceLocked执行一系列方法后,最后在realStartServiceLocked真正创建了service实例。类似Activity篇,app.thread是ApplicationThreadProxy,ServiceRecord是记录Service的数据结构。6 ApplicationThreadProxy(ApplicationThreadNative内部类)
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token, ServiceInfo info,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
info.writeToParcel(data, 0);
compatInfo.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeInt(processState);
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_CREATE_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, null,
IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
data.recycle();
}和Activity篇一样,这里是一个binder通信,ApplicationThreadProxy和ApplicationThread的通信,所以真正的执行在ApplicationThread的scheduleCreateService中7 ApplicationThread(ActivityThread内部类)
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}8 ActivityThread
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2, boolean async) {
......
mH.sendMessage(msg);
}很显然,这个过程和Activity的启动过程类似,都是通过发送消息给Handler H来完成。private class H extends Handler {
......
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord)msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
......
case CREATE_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceCreate");
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case BIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceBind");
handleBindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case UNBIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceUnbind");
handleUnbindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case SERVICE_ARGS:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceStart");
handleServiceArgs((ServiceArgsData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case STOP_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceStop");
handleStopService((IBinder)msg.obj);
maybeSnapshot();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
......
}
}这里进入CREATE_SERVICE分支,执行了handleCreateService方法,所以重点在handleCreateService方法中private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
//首先通过类加载器创建了Service的实例
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
.....
//接着创建了ContextImpl对象,并通过Service的attach方法建立了二者的关系
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl();
context.init(packageInfo, null, this);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
context.setOuterContext(service);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());//最后调用Service的onCreate方法并将Service对象存储到mServices中 service.onCreate(); mServices.put(data.token, service)这里涉及到LoadedApk ,ClassLoader ,ContextImpl,mServices
final ArrayMap<IBinder, Service> mServices
= new ArrayMap<IBinder, Service>();
这里Service的启动状态就分析完了
(2)绑定状态

和Service启动状态一样,绑定状态也是从ContextWrapper开始
1 ContextWrapper
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}mBase是ContextImpl,上面已经说过了。2 ContextImpl
ContextImpl的bindService最终会调用到自己的bindServiceCommon
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
//这里将客户端的ServiceConnection转化为ServiceDispatcher。InnerConnection对象
//之所以要转化,因为这里可能涉及到跨进程
if (mPackageInfo != null) { sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags); }
......
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService( mMainThread.getApplicationThread(),
getActivityToken(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()
), sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
......
}3 LoadedApk
这里,mPackageInfo是个LoadedApk类,从getServiceDispatcher方法可看出,map中保存了客户端conn和LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher的一份映射,首先在map查找是否有相应的conn,没有就创建一个ServiceDispatcher,并放入mServices中
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> map = mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler);
}
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}sd.getIServiceConnection得到ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection实例。InnerConnection是一个binder,是一个IServiceConnection类型(这里的InnerConnection不是代理,是真正的binder)mServices的类型
private final ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>> mServices
= new ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>>();
这里涉及到ServiceConnection,LoadedApk,ServiceDispatcher,InnerConnection,详细讲解下他们的关系
4 ServiceDispatcher(LoadedApk内部类)
getServiceDispatcher方法中,如果mServices不存在客户端conn,就创建ServiceDispatcher,sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,
Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mLocation = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
mFlags = flags;
}
IServiceConnection getIServiceConnection() {
return mIServiceConnection;
}5 InnerConnection(ServiceDispatcher内部类)ServiceDispatcher构造函数中会创建一个InnerConnection实例,从IServiceConnection.Stub可以看出,InnerConnection是一个binder
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}6 ActivityManagerProxy
回到ContextImpl,3-4-5步只是将客户端ServiceConnection转化为InnerConnection(binder),接下来是重点,ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection,
int flags, int userId) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
service.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeStrongBinder(connection.asBinder());
data.writeInt(flags);
data.writeInt(userId);
mRemote.transact(BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int res = reply.readInt();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
return res;
}7 ActivityManagerService
按部就班,从ActivityManagerProxy的bindService 到 ActivityManagerService的bindService
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType,
IServiceConnection connection, int flags, int userId) {
......
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service, resolvedType,
connection, flags, userId);
}
}8 ActiveServices
mServices是ActiveServices类型,mServices.bindServiceLocked执行经过一系列方法,最后又到了realStartServiceLocked方法
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
.......
//startService启动方式
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
......
//bindService启动方式
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
......
//onStartCommand
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
......
}和启动service是通过app.thread.scheduleCreateService不同,绑定service是通过requestServiceBindingsLocked执行private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r,
IntentBindRecord i, boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) {
......
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
......
return true;
}app.thread出现多次了,ApplicationThreadProxy! ApplicationThreadProxy! ApplicationThreadProxy!重要的事说三遍。9 ApplicationThreadProxy(ApplicationThreadNative内部类)
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent, boolean rebind,
int processState) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeInt(rebind ? 1 : 0);
data.writeInt(processState);
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, null,
IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
data.recycle();
}10 ApplicationThread
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "scheduleBindService token=" + token + " intent=" + intent + " uid="
+ Binder.getCallingUid() + " pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid());
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}11 ActivityThread
又到了我们最熟悉的地方了,贴代码,不想说
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2, boolean async) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(
TAG, "SCHEDULE " + what + " " + mH.codeToString(what)
+ ": " + arg1 + " / " + obj);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = what;
msg.obj = obj;
msg.arg1 = arg1;
msg.arg2 = arg2;
if (async) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
mH.sendMessage(msg);
}private class H extends Handler {
......
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord)msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
......
case CREATE_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceCreate");
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case BIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceBind");
handleBindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case UNBIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceUnbind");
handleUnbindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case SERVICE_ARGS:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceStart");
handleServiceArgs((ServiceArgsData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
case STOP_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceStop");
handleStopService((IBinder)msg.obj);
maybeSnapshot();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
......
}
}BIND_SERVICE对应于handleBindServiceprivate void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
......
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, 0, 0, 0);
}
ensureJitEnabled();
......
}
}在第8步realStartServiceLocked方法中app.thread.scheduleCreateService会创建service,这个在启动模式中已经分析过了。还记得创建service时会把service放入mServices中吗?再次回顾下ActivityThread的方法handleCreateService
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
......
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl();
context.init(packageInfo, null, this);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
context.setOuterContext(service);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
//mService存储创建的service
mServices.put(data.token, service);
}再次看看mServicesfinal ArrayMap<IBinder, Service> mServices = new ArrayMap<IBinder, Service>();复习完毕,现在再来看handleBindService,Service s = mServices.get(data.token);,从mServices中获取Service对象,然后调用s.onBind()。
到这里为止,已经创建了service实例,并且调用了service的方法onBind(),但是此时客户端(通常是Activity)还没有连接到service,所以还要调用客户端的serviceConnection中的onServiceConnected,这个过程是由ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService来完成,ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()就是ActivityManagerProxy! ActivityManagerProxy!
ActivityManagerProxy!,重要的事说三遍!
12 ActivityManagerProxy
public void publishService(IBinder token,
Intent intent, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeStrongBinder(service);
mRemote.transact(PUBLISH_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
}真正的执行过程在AMS中
13 ActivityManagerService
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}又见到mServices了,这个ActiveServices类是服务端AMS管理service的助手14 ActiveServices
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
......
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
......
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
......
c.conn.connected(r.name, service); ...... }15 InnerConnection (LoadedApk内部类ServiceDispathcer中的内部类)
ConnectionRecord 就是记录客户端(Activity)中connection的数据结构,客户端的connection经过3->4->5转化为InnerConnection,即一个binder,用于跨进程通信。
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}c.conn.connected中调用了sd.connected,即调用了ServiceDispatcher 的connected方法16 ServiceDispatcher
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
doConnected(name, service);
}
}这里涉及到mActivityThread(Handler),注意一下,将客户端connection转化为binder是在客户端内进行的,也就是说3->4->5步是在客户端进行的,LoadedApk相关的类的执行都是在客户端执行的。还记得第2步吗?mActivityThread就是ActivityThread中的Handler H,new RunConnection(name, service, 0)方法经过mActivityThread.post就运行在主线程中
private final class RunConnection implements Runnable {
RunConnection(ComponentName name, IBinder service, int command) {
mName = name;
mService = service;
mCommand = command;
}
public void run() {
if (mCommand == 0) {
doConnected(mName, mService);
} else if (mCommand == 1) {
doDeath(mName, mService);
}
}
final ComponentName mName;
final IBinder mService;
final int mCommand;
}public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
......
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}因为ServiceDispatcher保存了客户端的connection对象,所以可以调用onServiceConnected。在第4步就保存了。到这里客户端(Activity)就和服务端关联了。3 总结
相关文章推荐
- Android源码解析四大组件系列(一)---Service的启动过程分析
- Android四大组件Activity启动源码分析
- Android的四大组件之二--BroadcastReceiver(相关内容,开机启动Service)
- 深入剖析Android四大组件(二)——Service服务之启动与绑定
- android开发步步为营之37:四大组件之Service(上)通过startService(intent)启动
- Android 5.0 Camera系统源码分析(1):CameraService启动流程
- android四大组件值Service(2)启动方式
- Android 5.0 Camera系统源码分析(1):CameraService启动流程
- Android窗口管理服务WindowManagerService显示Activity组件的启动窗口(Starting Window)的过程分析
- Android窗口管理服务WindowManagerService显示Activity组件的启动窗口(Starting Window)的过程分析
- Android窗口管理服务WindowManagerService显示Activity组件的启动窗口(Starting Window)的过程分析
- android四大组件启动流程 - Service启动流程
- Android服务启动之StartService源码分析
- Android服务之PackageManagerService启动源码分析
- Android服务启动之StartService源码分析
- Android窗口管理服务WindowManagerService显示Activity组件的启动窗口(Starting Window)的过程分析
