OpenCV图像数据访问,查询表和时间消耗测试
2016-11-01 22:45
393 查看
OpenCV图像数据访问, 查询表和时间消耗测试
代码示例
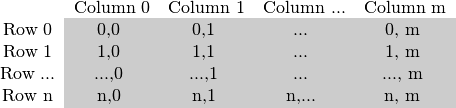
1 灰度图像的存储方式
2 RGB模式的存储方式
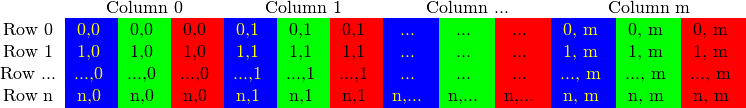
RGB模式像素的颜色值存储方式BGR。内存存储的方式在计算机内存足够大的情况下是连续的,也许是不连续的判断方式: cv::Mat::isContinuous()
代码示例
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/utility.hpp>
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
static void help()
{
cout
<< "\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------" << endl
<< "This program shows how to scan image objects in OpenCV (cv::Mat). As use case"
<< " we take an input image and divide the native color palette (255) with the " << endl
<< "input. Shows C operator[] method, iterators and at function for on-the-fly item address calculation."<< endl
<< "Usage:" << endl
<< "./how_to_scan_images <imageNameToUse> <divideWith> [G]" << endl
<< "if you add a G parameter the image is processed in gray scale" << endl
<< "--------------------------------------------------------------------------" << endl
<< endl;
}
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceC(Mat& I, const uchar* table);
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceIterator(Mat& I, const uchar* table);
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceRandomAccess(Mat& I, const uchar * table);
int main( int argc, char* argv[])
{
help();
if (argc < 3)
{
cout << "Not enough parameters" << endl;
return -1;
}
Mat I, J;
if( argc == 4 && !strcmp(argv[3],"G") )
I = imread(argv[1], IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);//灰度模式打开图像
else
I = imread(argv[1], IMREAD_COLOR);//RGB模式打开图像
if (I.empty())
{
cout << "The image" << argv[1] << " could not be loaded." << endl;
return -1;
}
//! [dividewith]
int divideWith = 0; // convert our input string to number - C++ style
stringstream s;
s << argv[2];
s >> divideWith;
if (!s || !divideWith)
{
cout << "Invalid number entered for dividing. " << endl;
return -1;
}
uchar table[256];
for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i)
table[i] = (uchar)(divideWith * (i/divideWith));
//! [dividewith]
const int times = 100;
double t;
t = (double)getTickCount();
for (int i = 0; i < times; ++i)
{
cv::Mat clone_i = I.clone();
J = ScanImageAndReduceC(clone_i, table);
}
t = 1000*((double)getTickCount() - t)/getTickFrequency();
t /= times;
cout << "Time of reducing with the C operator [] (averaged for "
<< times << " runs): " << t << " milliseconds."<< endl;
t = (double)getTickCount();
for (int i = 0; i < times; ++i)
{
cv::Mat clone_i = I.clone();
J = ScanImageAndReduceIterator(clone_i, table);
}
t = 1000*((double)getTickCount() - t)/getTickFrequency();
t /= times;
cout << "Time of reducing with the iterator (averaged for "
<< times << " runs): " << t << " milliseconds."<< endl;
t = (double)getTickCount();
for (int i = 0; i < times; ++i)
{
cv::Mat clone_i = I.clone();
ScanImageAndReduceRandomAccess(clone_i, table);
}
t = 1000*((double)getTickCount() - t)/getTickFrequency();
t /= times;
cout << "Time of reducing with the on-the-fly address generation - at function (averaged for "
<< times << " runs): " << t << " milliseconds."<< endl;
//! [查询表初始化]
Mat lookUpTable(1, 256, CV_8U);
uchar* p = lookUpTable.ptr();
for( int i = 0; i < 256; ++i)
p[i] = table[i];
//! [table-init]
t = (double)getTickCount();
for (int i = 0; i < times; ++i)
//! [查询表使用]
LUT(I, lookUpTable, J);
//! [查询表使用]
t = 1000*((double)getTickCount() - t)/getTickFrequency();
t /= times;
cout << "Time of reducing with the LUT function (averaged for "
<< times << " runs): " << t << " milliseconds."<< endl;
return 0;
}
//! [C风格[]方式访问]
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceC(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() == CV_8U);
int channels = I.channels();
int nRows = I.rows;
int nCols = I.cols * channels;
if (I.isContinuous())
{
nCols *= nRows;
nRows = 1;
}
int i,j;
uchar* p;
for( i = 0; i < nRows; ++i)
{
p = I.ptr<uchar>(i);
for ( j = 0; j < nCols; ++j)
{
p[j] = table[p[j]];
}
}
return I;
}
//! [迭代器安全方式访问]
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceIterator(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() == CV_8U);
const int channels = I.channels();
switch(channels)
{
case 1:
{
MatIterator_<uchar> it, end;
for( it = I.begin<uchar>(), end = I.end<uchar>(); it != end; ++it)
*it = table[*it];
break;
}
case 3:
{
MatIterator_<Vec3b> it, end;
for( it = I.begin<Vec3b>(), end = I.end<Vec3b>(); it != end; ++it)
{
(*it)[0] = table[(*it)[0]];
(*it)[1] = table[(*it)[1]];
(*it)[2] = table[(*it)[2]];
}
}
}
return I;
}
//! [数组寻址随机访问方式]
Mat& ScanImageAndReduceRandomAccess(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() == CV_8U);
const int channels = I.channels();
switch(channels)
{
case 1:
{
for( int i = 0; i < I.rows; ++i)
for( int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j )
I.at<uchar>(i,j) = table[I.at<uchar>(i,j)];//灰度图像cv::at()
break;
}
case 3:
{
Mat_<Vec3b> _I = I;
for( int i = 0; i < I.rows; ++i)
for( int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j )
{
_I(i,j)[0] = table[_I(i,j)[0]];
_I(i,j)[1] = table[_I(i,j)[1]];
_I(i,j)[2] = table[_I(i,j)[2]];
}
I = _I;
break;
}
}
return I;
}1 灰度图像的存储方式

2 RGB模式的存储方式

RGB模式像素的颜色值存储方式BGR。内存存储的方式在计算机内存足够大的情况下是连续的,也许是不连续的判断方式: cv::Mat::isContinuous()
相关文章推荐
- OpenCV学习笔记——使用OpenCV访问图像数据
- opencv-从图像旋转学习Mat数据访问
- opencv学习笔记-入门(7)单通道的图像数据访问
- opencv访问图像数据
- OpenCV中double和float类型图像数据的访问
- Opencv中访问图像数据类型
- 第四篇 学习OpenCV之访问图像数据
- MySQL在插入90万条数据消耗的时间以及查询90万条数据时的性能优化
- 第四篇 学习OpenCV之访问图像数据
- OpenCV--用读取矩阵,访问图像数据
- 重温OpenCV图像数据访问
- opencv里常用的访问图像像素数据方法
- oracle跨库访问查询、数据获取、打印(测试【已通】)
- OpenCV自学笔记2:访问图像数据
- OpenCV访问图像数据并设定灰度值
- opencv学习笔记-入门(7)单通道的图像数据访问
- OpenCV使用不同方式访问图像数据
- 访问opencv的Mat中的图像数据
- OleDb与Access数据访问中日期时间参数类型错误和命名参数的用法
- [转自microsoft]NET 数据访问架构指南",-数据库连接的测试.即监视链接池化
