My First SLAM Implementation EKF-SLAM
2016-09-29 00:36
525 查看
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/c602273091/article/details/52695612
ABSTRACT
PRINCIPLE
IMPLEMENTATION
RESULT
To do it with EKF-SLAM, you can have better comprehensive understanding of SLAM.
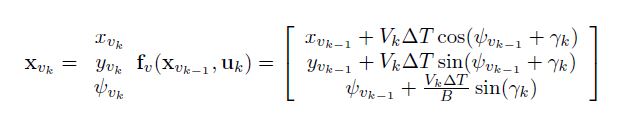
Calculate Predict Covariance:
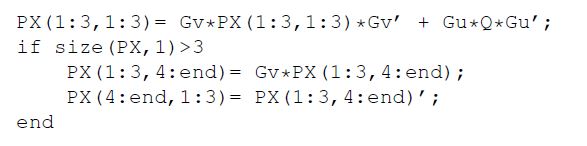
The Jacobian Gv and Gu are calculated by:
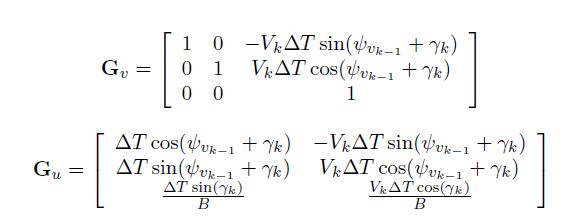
The sensor model is update by:
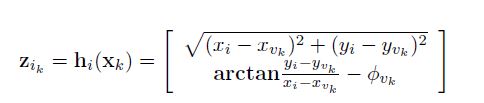
And the Jacobian for robot state is:
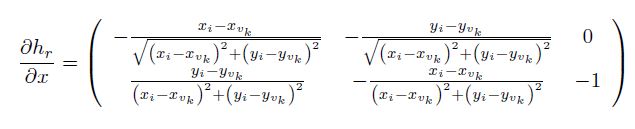
the Jacobian for land mark is:
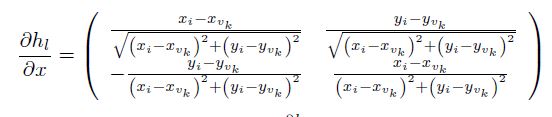
For more details for EKF, search WiKi with EKF.
ABSTRACT
PRINCIPLE
IMPLEMENTATION
RESULT
ABSTRACT
Learn by doing !To do it with EKF-SLAM, you can have better comprehensive understanding of SLAM.
PRINCIPLE
State update by control:(here the control is applied with noise)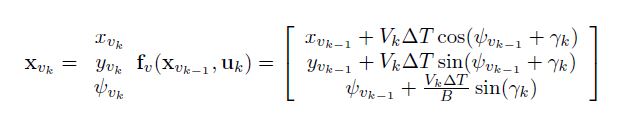
Calculate Predict Covariance:
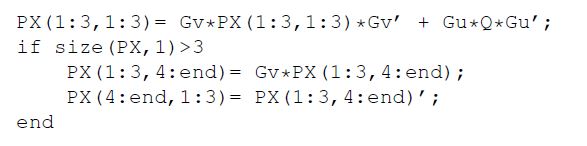
The Jacobian Gv and Gu are calculated by:
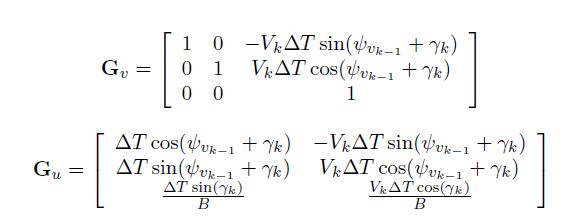
The sensor model is update by:
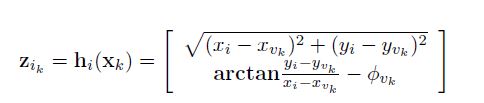
And the Jacobian for robot state is:
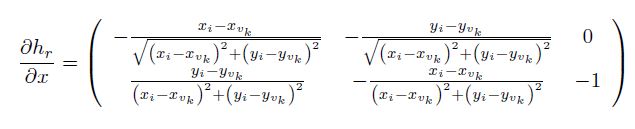
the Jacobian for land mark is:
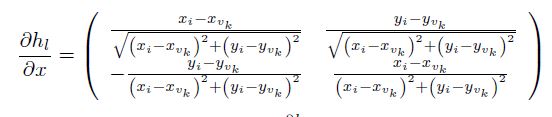
For more details for EKF, search WiKi with EKF.
IMPLEMENTATION
% function my_efk_slam
function my_ekf_2d_slam
%% load data
format compact;
load('example_webmap'); % store in lm, wp
fig = figure;
plot(lm(1,:), lm(2,:), 'b*');
hold on;
axis equal;
plot(wp(1,:), wp(2,:), 'g', wp(1,:), wp(2,:), 'g.');
xlabel('meters'), ylabel('meters');
set(fig, 'name', 'My 2D EKF-SLAM');
%% load parameter
V = 3;% m/s
MAXG = 30*pi/180.0; % maximum steering angles
RATEG = 20*pi/180.0; % maximum rate of change steering angles
WHEELBASE = 4; % vihecle base
DT_CONTROLS = 0.025; % seconds between control signals
sigmaV = 0.3; % m/s
sigmaG = (3.0*pi/180); %radians
Q = [sigmaV^2 0; 0 sigmaG^2];
MAX_RANGE = 30.0; % meters.
DT_OBSERVE = 8*DT_CONTROLS; % time between observation
sigmaR = 0.1;
sigmaB = (1.0*pi/180);
R = [sigmaR^2 0; 0 sigmaB^2];
GATE_REJECT = 4.0; % maximum dis for creation of new feature.
GATE_AUGMENT = 25.0; % minimum dis for creation new feature.
AT_WAYPOINT = 1.0;
NUMBER_LOOPS = 2; % number of loops through the waypoint list.
SWITCH_CONTROL_NOISE= 1; % if 0, velocity and gamma are perfect
SWITCH_SENSOR_NOISE = 1; % if 0, measurements are perfect
SWITCH_INFLATE_NOISE= 0; % if 1, the estimated Q and R are inflated (ie, add stabilising noise)
SWITCH_HEADING_KNOWN= 0; % if 1, the vehicle heading is observed directly at each iteration
SWITCH_ASSOCIATION_KNOWN= 0; % if 1, associations are given, if 0, they are estimated using gates
SWITCH_BATCH_UPDATE= 1; % if 1, process scan in batch, if 0, process sequentially
SWITCH_SEED_RANDOM= 0; % if not 0, seed the randn() with its value at beginning of simulation (for repeatability)
SWITCH_USE_IEKF= 0; % if 1, use iterated EKF for updates, if 0, use normal EKF
if SWITCH_INFLATE_NOISE, QE= 2*Q; RE= 8*R; end % inflate estimated noises (ie, add stabilising noise)
if SWITCH_SEED_RANDOM, randn('state',SWITCH_SEED_RANDOM), end
%% set up animations
h.xt = patch(0, 0, 'b', 'erasemode', 'xor');
h.xv = patch(0, 0, 'r', 'erasemode', 'xor'); % vehicle
h.pth= plot(0,0,'k.','markersize',2,'erasemode','background'); % vehicle path estimate
h.obs= plot(0,0,'r','erasemode','xor'); % observations
h.xf = plot(0,0,'r+','erasemode','xor'); % estimated features
h.cov= plot(0,0,'r','erasemode','xor'); % covariance ellipses
veh = [0 -WHEELBASE -WHEELBASE;0 -2 2];
pcount = 0;
%% initialization
xtrue = zeros(3, 1);
x = zeros(3, 1);
P = zeros(3);
dt = DT_CONTROLS;
dtsum = 0;
ftag = 1:size(lm,2);
da_table = zeros(1,size(lm,2));
iwp = 1;
G = 0;
%% stored data for off-line
data.i = 1;
data.path = x;
data.true = xtrue;
data.state(1).x = x;
data.state(1).P = diag(P);
QE = Q;
RE = R;
% main loop
while iwp ~= 0
%% compute steering [G,iwp]= compute_steering(xtrue, wp, iwp, AT_WAYPOINT, G, RATEG, MAXG, dt);
cwp = wp(:, iwp);
d2 = (cwp(1) - xtrue(1))^2 + (cwp(2) - xtrue(2))^2;
if d2 < AT_WAYPOINT^2
iwp = iwp + 1;
if iwp > size(wp, 2)
iwp = 0;
end
if iwp ~= 0
cwp = wp(:, iwp);
end
end
if iwp ~= 0
deltaG = pi_to_pi(atan2(cwp(2) - xtrue(2), cwp(1) - xtrue(1)) - xtrue(3) - G);
maxDelta = RATEG*dt;
if abs(deltaG) > maxDelta
deltaG = sign(deltaG)*maxDelta;
end
G = G + deltaG;
if abs(G) > MAXG
G = sign(G)*MAXG;
end
end
%[G,iwp]= compute_steering(xtrue, wp, iwp, AT_WAYPOINT, G, RATEG, MAXG, dt);
if iwp == 0 && NUMBER_LOOPS > 1, iwp = 1; NUMBER_LOOPS = NUMBER_LOOPS - 1; disp(NUMBER_LOOPS); end;
%% xtrue= vehicle_model(xtrue, V,G, WHEELBASE,dt);
xtrue = [xtrue(1) + V * dt * cos(G + xtrue(3,:));
xtrue(2) + V * dt * sin(G + xtrue(3,:));
pi_to_pi(xtrue(3) + V*dt*sin(G)/WHEELBASE)];
%% [Vn,Gn]= add_control_noise(V,G,Q, SWITCH_CONTROL_NOISE);
if SWITCH_CONTROL_NOISE == 1
Vn= V + randn(1)*sqrt(Q(1,1));
Gn= G + randn(1)*sqrt(Q(2,2));
end
%% EKF Predict Step [x,P]= predict (x,P, Vn,Gn,QE, WHEELBASE,dt);
arrAngle = [x(3) Gn];
arrAngle(1) = pi_to_pi(arrAngle(1));
arrAngle(2) = pi_to_pi(arrAngle(2));
nAngle = pi_to_pi(arrAngle(1) + arrAngle(2));
Gv = [1 0 -Vn*dt*sin(nAngle); 0 1 Vn*dt*cos(nAngle); 0 0 1];%% Fill in
Gu = [dt*cos(nAngle) -Vn*dt*sin(nAngle);...
dt*sin(nAngle) Vn*dt*cos(nAngle); ...
dt*sin(arrAngle(2))/WHEELBASE Vn*dt*cos(arrAngle(2))/WHEELBASE];%% Fill in
% predict covariance
P(1:3,1:3)= Gv*P(1:3,1:3)*Gv' + Gu*QE*Gu';
if size(P,1)>3
P(1:3,4:end)= Gv*P(1:3,4:end);
P(4:end,1:3)= P(1:3,4:end)';
end
% predict state
x(1:3)= [x(1) + Vn*dt*cos(nAngle);...
x(2) + Vn*dt*sin(nAngle);...
arrAngle(1) + Vn*dt*sin(arrAngle(2))/WHEELBASE];
%% EKF update step
dtsum = dtsum + dt;
if dtsum >= DT_OBSERVE
dtsum = 0;
%% [z,ftag_visible]= get_observations(xtrue, lm, ftag, MAX_RANGE);
dx = lm(1,:) - xtrue(1);
dy = lm(2,:) - xtrue(2);
phi = xtrue(3);
ii = find(abs(dx)<MAX_RANGE & abs(dy) <MAX_RANGE ...
& (dx*cos(phi)+dy*sin(phi))>0 ...
& (dx.^2 + dy.^2) < MAX_RANGE^2);
lm_one = lm(:, ii);
ftag_visible = ftag(ii);
%% z= compute_range_bearing(x,lm);
dx = lm_one(1,:) - xtrue(1);
dy = lm_one(2,:) - xtrue(2);
z = [sqrt(dx.^2 + dy.^2); atan2(dy,dx) - phi];
%% z= add_observation_noise(z,R, SWITCH_SENSOR_NOISE);
if SWITCH_SENSOR_NOISE
len = size(z, 2);
if len > 0
z(1,:) = z(1,:) + randn(1, len)*sqrt(R(1, 1));
z(2,:) = z(2,:) + randn(1, len)*sqrt(R(2, 2));
end
end
%% [zf,idf,zn, da_table]= data_associate_known(x,z,ftag_visible, da_table);
zf = [];
zn = [];
idf = [];
idn = [];
for i = 1:length(ftag_visible)
ii = ftag_visible(i);
if da_table(ii) == 0
zn = [zn z(:, i)];
idn = [idn ii];
else
zf = [zf z(:,i)];
idf = [idf da_table(ii)];
end
end
Nxv = 3;
Nf = (length(x) - Nxv)/2;
da_table(idn) = Nf + (1:size(zn,2));
%% [x,P]= single_update(x,P,zf,RE,idf);
lenz = size(zf, 2);
for i = 1:lenz
%% [zp,H]= observe_model(x, idf(i));
fpos= Nxv + idf(i)*2 - 1; % position of xf in state
H= zeros(2, length(x));
xDis = -x(1) + x(fpos);
yDis = -x(2) + x(fpos+1);
anDis = x(3);
SquareDis = xDis^2 + yDis^2;
EnDis = sqrt(SquareDis);
% predict z
zp = [EnDis; atan2(yDis,xDis)-anDis]; %%Fill in
% calculate H
H(:,1:3) = [-(xDis/EnDis) -yDis/EnDis 0; ...
yDis/SquareDis -xDis/SquareDis -1];%%Fillin observation jacobian
H(:,fpos:fpos+1)= [xDis/EnDis yDis/EnDis; ...
-yDis/SquareDis xDis/SquareDis];
v = [zf(1,i) - zp(1);pi_to_pi(zf(2,i)-zp(2))];
%% [x,P]= KF_simple_update(x,P,v,R,H);
PHt = P*H';
S = H*PHt + R;
Si = inv(S);
Si = (Si + Si')*0.5;
W = PHt*Si;
x = x + W*v;
P = P - ((W*S*W') + (W*S*W')')*0.5;
end
[x,P]= augment(x,P, zn,RE);
end
% offline data store
data= store_data(data, x, P, xtrue);
% plots
xt= transformtoglobal(veh,xtrue);
xv= transformtoglobal(veh,x(1:3));
set(h.xt, 'xdata', xt(1,:), 'ydata', xt(2,:))
set(h.xv, 'xdata', xv(1,:), 'ydata', xv(2,:))
set(h.xf, 'xdata', x(4:2:end), 'ydata', x(5:2:end))
ptmp= make_covariance_ellipses(x(1:3),P(1:3,1:3));
pcov(:,1:size(ptmp,2))= ptmp;
if dtsum==0
set(h.cov, 'xdata', pcov(1,:), 'ydata', pcov(2,:))
pcount= pcount+1;
if pcount == 15
set(h.pth, 'xdata', data.path(1,1:data.i), 'ydata', data.path(2,1:data.i))
pcount=0;
end
if ~isempty(z)
plines= make_laser_lines (z,x(1:3));
set(h.obs, 'xdata', plines(1,:), 'ydata', plines(2,:))
pcov= make_covariance_ellipses(x,P);
end
end
drawnow
end
data= finalise_data(data);
set(h.pth, 'xdata', data.path(1,:), 'ydata', data.path(2,:))
function p= make_laser_lines (rb,xv)
% compute set of line segments for laser range-bearing measurements
if isempty(rb), p=[]; return, end
len= size(rb,2);
lnes(1,:)= zeros(1,len)+ xv(1);
lnes(2,:)= zeros(1,len)+ xv(2);
lnes(3:4,:)= transformtoglobal([rb(1,:).*cos(rb(2,:)); rb(1,:).*sin(rb(2,:))], xv);
p= line_plot_conversion (lnes);
function p= make_covariance_ellipses(x,P)
% compute ellipses for plotting state covariances
N= 10;
inc= 2*pi/N;
phi= 0:inc:2*pi;
lenx= length(x);
lenf= (lenx-3)/2;
p= zeros (2,(lenf+1)*(N+2));
ii=1:N+2;
p(:,ii)= make_ellipse(x(1:2), P(1:2,1:2), 2, phi);
ctr= N+3;
for i=1:lenf
ii= ctr:(ctr+N+1);
jj= 2+2*i; jj= jj:jj+1;
p(:,ii)= make_ellipse(x(jj), P(jj,jj), 2, phi);
ctr= ctr+N+2;
end
function p= make_ellipse(x,P,s, phi)
% make a single 2-D ellipse of s-sigmas over phi angle intervals
r= sqrtm(P);
a= s*r*[cos(phi); sin(phi)];
p(2,:)= [a(2,:)+x(2) NaN];
p(1,:)= [a(1,:)+x(1) NaN];
function data= store_data(data, x, P, xtrue)
% add current data to offline storage
CHUNK= 5000;
if data.i == size(data.path,2) % grow array in chunks to amortise reallocation
data.path= [data.path zeros(3,CHUNK)];
data.true= [data.true zeros(3,CHUNK)];
end
i= data.i + 1;
data.i= i;
data.path(:,i)= x(1:3);
data.true(:,i)= xtrue;
data.state(i).x= x;
%data.state(i).P= P;
data.state(i).P= diag(P);
function data= finalise_data(data)
% offline storage finalisation
data.path= data.path(:,1:data.i);
data.true= data.true(:,1:data.i);RESULT
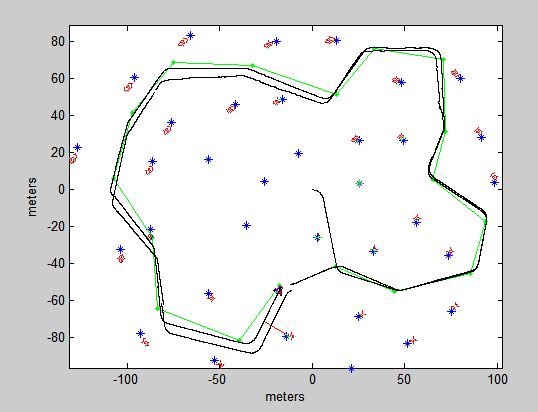
As you can see from the image below, the black path is the real path of the car, the green path is the road path. The second recursive of the road is better than the first one.
相关文章推荐
- my first blog
- 1st anniversary for my first job
- my first coq
- My first Blog in CSDN
- SLAM, in my eyes
- This is my first article in csdn.
- My First Love_Belushi 歌词
- This is my first program
- It is to celebrate my blog's first day
- [AngularJS]项目框架搭建-MyFirst Skeleton
- MY FIRst BLOG
- my first android test
- 【作品】My first special topic website
- My First Blog,It's my Start!
- My First Python code for learnning English.
- Markdown my first markdown blog
- EKF-SLAM matlab仿真(2)
- My first blog for java
- my first hhh
- My First HelloWorld-----------让圆角来美化csdn Blog
