Android Service两种启动方式
2016-09-20 16:32
429 查看
1.Context.startService()方式启动
①Context.startService()方式的生命周期: 启动时,startService –> onCreate() –> onStart()(可多次调用) ,Service
running,停止时,stopService –> onDestroy()
note:
在Service未被创建并运行时,则android先调用onCreate(),然后调用onStart()。
如果调用startService()方法前服务已经被创建,多次调用startService()方法并不会导致多次创建服务,但会导致多次调用onStart()方法。
同上,如果Service已经运行,则只调用onStart(),所以一个Service的onStart方法可能会重复调用多次。
采用startService()方法启动的服务,只能调用Context.stopService()方法结束服务,服务结束时会调用onDestroy()。如果是调用者自己(即启动服务的应用或活动)直接退出而没有调用stopService的话,Service会一直在后台运行 Context.startService()方法启动服务,该Service的调用者再启动起来后可以通过stopService关闭Service。
服务可以通过Service.stopSelf()方法或者Service.stopSelfResult()方法来停止自己,只要调用一次stopService()方法便可以停止服务,无论调用了多少次的启动服务方法。
2.Context.bindService()方式启动:
①Context.bindService()方式的生命周期: 绑定时,bindService -> onCreate() –> onBind()(只一次,不可多次绑定)->onServiceConnected,Service
running, 调用者退出了,即解绑定时,Srevice就会unbindService –>onUnbind() –> onDestory()
note:
Context.bindService()方式启动 Service的方法:绑定Service需要三个参数:bindService(intent, conn, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);第一个:Intent对象第二个:ServiceConnection对象,创建该对象要实现它的onServiceConnected()和 onServiceDisconnected()来判断连接成功或者是断开连接第三个:如何创建Service,一般指定绑定的时候自动创建。
onBind()将返回给客户端一个IBind接口实例,IBind允许客户端回调服务的方法,比如得到Service的实例、运行状态或其他操作。这个时候把调用者(Context,例如Activity)会和Service绑定在一起,Context退出了,Srevice就会调用onUnbind->onDestroy相应退出。
两种启动方式,在Service每一次的开启关闭过程中,只有onStart可被多次调用(通过多次startService调用),其他onCreate,onBind,onUnbind,onDestory在一个生命周期中只能被调用一次。

下面的应用,分别使用startService和bindService来启动本地的服务。
1.Context.startService()方式启动
简单的音乐播放
Activity
[java] view
plain copy
print?


public class PlayMusicService extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private Button playBtn;
private Button stopBtn;
private Button pauseBtn;
private Button exitBtn;
private Button closeBtn;
private Intent intent;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.music_service);
playBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.play);
stopBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.stop);
pauseBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.pause);
exitBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.exit);
closeBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.close);
playBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
stopBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
pauseBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
exitBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
closeBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int op = -1;
intent = new Intent("com.homer.service.musicService");
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.play: // play music
op = 1;
break;
case R.id.stop: // stop music
op = 2;
break;
case R.id.pause: // pause music
op = 3;
break;
case R.id.close: // close activity
this.finish();
break;
case R.id.exit: // stopService
op = 4;
stopService(intent);
this.finish();
break;
}
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt("op", op);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
startService(intent); // startService
}
@Override
public void onDestroy(){
super.onDestroy();
if(intent != null){
stopService(intent);
}
}
}

Service
[java] view
plain copy
print?


public class MusicService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
private MediaPlayer mediaPlayer;
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.v(TAG, "onCreate");
Toast.makeText(this, "show media player", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
if (mediaPlayer == null) {
mediaPlayer = MediaPlayer.create(this, R.raw.tmp);
mediaPlayer.setLooping(false);
}
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.v(TAG, "onDestroy");
Toast.makeText(this, "stop media player", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
if (mediaPlayer != null) {
mediaPlayer.stop();
mediaPlayer.release();
}
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.v(TAG, "onStart");
if (intent != null) {
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
if (bundle != null) {
int op = bundle.getInt("op");
switch (op) {
case 1:
play();
break;
case 2:
stop();
break;
case 3:
pause();
break;
}
}
}
}
public void play() {
if (!mediaPlayer.isPlaying()) {
mediaPlayer.start();
}
}
public void pause() {
if (mediaPlayer != null && mediaPlayer.isPlaying()) {
mediaPlayer.pause();
}
}
public void stop() {
if (mediaPlayer != null) {
mediaPlayer.stop();
try {
mediaPlayer.prepare(); // 在调用stop后如果需要再次通过start进行播放,需要之前调用prepare函数
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
AndroidManifest.xml
注册activity
[css] view
plain copy
print?


<activity
android:name=".service.PlayMusicService"
android:label="@string/app_name" />
注册service
[css] view
plain copy
print?


<service
android:name=".service.MusicService"
android:enabled="true" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.homer.service.musicService" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
2.Context.bindService()方式启动:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.dada.test;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import com.dada.test.BindService.MyBinder;
public class TestActivity extends Activity {
private boolean flag;
private static final String TAG = "TestActivity";
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button btnStart = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnStart);
Button btnStop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnStop);
btnStart.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//启动service 方式2
bindService();
}
});
btnStop.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//停止service 方式2
unBindService();
}
});
}
//启动service 方式2
//
private void bindService(){
Intent intent = new Intent(TestActivity.this,BindService.class);
Log.i(TAG, "bindService()");
bindService(intent, conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); //在activity 绑定服务
}
private void unBindService(){
Log.i(TAG, "unBindService() start....");
if(flag == true){
Log.i(TAG, "unBindService() flag");
unbindService(conn);
flag = false;
}
}
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.i(TAG, "onServiceDisconnected()");
}
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// 在服务成功绑定的回调方法onServiceConnected, 会传递过来一个
IBinder对象:service
Log.i(TAG, "onServiceConnected()");
/*通过向下转型得到了 MyBinder 的实例,有了这个实例,活动和服务之间的关系就变得非常紧密了*/
MyBinder binder = (MyBinder)service;
/*强制类型转化为自定义的接口类型MyBinder,调用接口里面的方法。*/
BindService bindService = binder.getService1();
bindService.MyMethod();
flag = true;
/*上面这段就实现了活动绑定并启动服务,服务通过其自建内部类MyBinder来调用服务的方法。
activity->bindService方法-》服务的onBind方法(返回自建内部类MyBinder实例)-》ServiceConnection.onServiceConnected()-》通过MyBinder实例
调用服务方法, 现在我们可以在活动中根据具体的场景来调用MyBinder中的任何 public 方法,即实现了指挥服务干什么,服务就去干什么的功能。*/
}
};
}
9.3.3 活动和服务进行通信
绑定本地服务调用方法的步骤:
在服务的内部创建一个内部binder类 并提供一个方法,可以间接调用服务的方法
实现服务的onbind方法,返回的就是这个内部binder类
在activity 绑定服务。bindService();
在服务成功绑定的回调方法onServiceConnected, 会传递过来一个 IBinder对象
强制类型转化为自定义的接口类型binder类,调用接口里面的方法。
service
[java] view
plain copy
package com.dada.test;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class BindService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "BindService";
private MyBinder myBinder = new MyBinder();
public void MyMethod(){
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->MyMethod()");
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->onBind()");
return myBinder;
}
//在服务的内部创建一个内部类MyBinder
提供一个方法getService1(),可以间接调用服务的方法MyMethod()
public class MyBinder extends Binder{
public BindService getService1(){
return BindService.this;
}
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->onCreate()");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->onStart()");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->onDestroy()");
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->onUnbind()");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
}
运行日志
点击启动
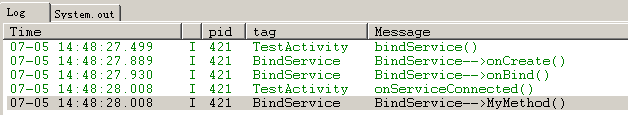
点击停止

没有打出onServiceDisconnected的日志的原因:
注:SDK上是这么说的:This is called when the connection with the service has been
unexpectedly disconnected -- that is, its process crashed. Because it is running in our same
process, we should never see this happen.
所以说,只有在service因异常而断开连接的时候,这个方法才会用到
其他
由于Service 的onStart()方法只有在startService()启动Service的情况下才调用,故使用onStart()的时候要注意这点。
如果我们想保持和 Service 的通信,又不想让 Service 随着 Activity 退出而退出呢?你可以先 startService() 然后再 bindService() 。当你不需要绑定的时候就执行 unbindService() 方法,执行这个方法只会触发 Service 的 onUnbind() 而不会把这个 Service 销毁。这样就可以既保持和
Service 的通信,也不会随着 Activity 销毁而销毁了。
另外需要注意,任何一个服务在整个应用程序范围内都是通用的,即 Service 不仅可以和 MainActivity 绑定,还可以和任何一个其他的活动进行绑定,而且在绑定完成后它们都可以获取到相同的 Binder 实例。
http://blog.csdn.net/dada360778512/article/details/7720107
http://blog.csdn.net/sunboy_2050/article/details/7364024
①Context.startService()方式的生命周期: 启动时,startService –> onCreate() –> onStart()(可多次调用) ,Service
running,停止时,stopService –> onDestroy()
note:
在Service未被创建并运行时,则android先调用onCreate(),然后调用onStart()。
如果调用startService()方法前服务已经被创建,多次调用startService()方法并不会导致多次创建服务,但会导致多次调用onStart()方法。
同上,如果Service已经运行,则只调用onStart(),所以一个Service的onStart方法可能会重复调用多次。
采用startService()方法启动的服务,只能调用Context.stopService()方法结束服务,服务结束时会调用onDestroy()。如果是调用者自己(即启动服务的应用或活动)直接退出而没有调用stopService的话,Service会一直在后台运行 Context.startService()方法启动服务,该Service的调用者再启动起来后可以通过stopService关闭Service。
服务可以通过Service.stopSelf()方法或者Service.stopSelfResult()方法来停止自己,只要调用一次stopService()方法便可以停止服务,无论调用了多少次的启动服务方法。
2.Context.bindService()方式启动:
①Context.bindService()方式的生命周期: 绑定时,bindService -> onCreate() –> onBind()(只一次,不可多次绑定)->onServiceConnected,Service
running, 调用者退出了,即解绑定时,Srevice就会unbindService –>onUnbind() –> onDestory()
note:
Context.bindService()方式启动 Service的方法:绑定Service需要三个参数:bindService(intent, conn, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);第一个:Intent对象第二个:ServiceConnection对象,创建该对象要实现它的onServiceConnected()和 onServiceDisconnected()来判断连接成功或者是断开连接第三个:如何创建Service,一般指定绑定的时候自动创建。
onBind()将返回给客户端一个IBind接口实例,IBind允许客户端回调服务的方法,比如得到Service的实例、运行状态或其他操作。这个时候把调用者(Context,例如Activity)会和Service绑定在一起,Context退出了,Srevice就会调用onUnbind->onDestroy相应退出。
两种启动方式,在Service每一次的开启关闭过程中,只有onStart可被多次调用(通过多次startService调用),其他onCreate,onBind,onUnbind,onDestory在一个生命周期中只能被调用一次。

下面的应用,分别使用startService和bindService来启动本地的服务。
1.Context.startService()方式启动
简单的音乐播放
Activity
[java] view
plain copy
print?


public class PlayMusicService extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private Button playBtn;
private Button stopBtn;
private Button pauseBtn;
private Button exitBtn;
private Button closeBtn;
private Intent intent;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.music_service);
playBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.play);
stopBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.stop);
pauseBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.pause);
exitBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.exit);
closeBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.close);
playBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
stopBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
pauseBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
exitBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
closeBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int op = -1;
intent = new Intent("com.homer.service.musicService");
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.play: // play music
op = 1;
break;
case R.id.stop: // stop music
op = 2;
break;
case R.id.pause: // pause music
op = 3;
break;
case R.id.close: // close activity
this.finish();
break;
case R.id.exit: // stopService
op = 4;
stopService(intent);
this.finish();
break;
}
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt("op", op);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
startService(intent); // startService
}
@Override
public void onDestroy(){
super.onDestroy();
if(intent != null){
stopService(intent);
}
}
}

Service
[java] view
plain copy
print?


public class MusicService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
private MediaPlayer mediaPlayer;
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.v(TAG, "onCreate");
Toast.makeText(this, "show media player", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
if (mediaPlayer == null) {
mediaPlayer = MediaPlayer.create(this, R.raw.tmp);
mediaPlayer.setLooping(false);
}
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.v(TAG, "onDestroy");
Toast.makeText(this, "stop media player", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
if (mediaPlayer != null) {
mediaPlayer.stop();
mediaPlayer.release();
}
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.v(TAG, "onStart");
if (intent != null) {
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
if (bundle != null) {
int op = bundle.getInt("op");
switch (op) {
case 1:
play();
break;
case 2:
stop();
break;
case 3:
pause();
break;
}
}
}
}
public void play() {
if (!mediaPlayer.isPlaying()) {
mediaPlayer.start();
}
}
public void pause() {
if (mediaPlayer != null && mediaPlayer.isPlaying()) {
mediaPlayer.pause();
}
}
public void stop() {
if (mediaPlayer != null) {
mediaPlayer.stop();
try {
mediaPlayer.prepare(); // 在调用stop后如果需要再次通过start进行播放,需要之前调用prepare函数
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
AndroidManifest.xml
注册activity
[css] view
plain copy
print?


<activity
android:name=".service.PlayMusicService"
android:label="@string/app_name" />
注册service
[css] view
plain copy
print?


<service
android:name=".service.MusicService"
android:enabled="true" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.homer.service.musicService" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
2.Context.bindService()方式启动:
[java] view
plain copy
package com.dada.test;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import com.dada.test.BindService.MyBinder;
public class TestActivity extends Activity {
private boolean flag;
private static final String TAG = "TestActivity";
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button btnStart = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnStart);
Button btnStop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnStop);
btnStart.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//启动service 方式2
bindService();
}
});
btnStop.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//停止service 方式2
unBindService();
}
});
}
//启动service 方式2
//
private void bindService(){
Intent intent = new Intent(TestActivity.this,BindService.class);
Log.i(TAG, "bindService()");
bindService(intent, conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); //在activity 绑定服务
}
private void unBindService(){
Log.i(TAG, "unBindService() start....");
if(flag == true){
Log.i(TAG, "unBindService() flag");
unbindService(conn);
flag = false;
}
}
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.i(TAG, "onServiceDisconnected()");
}
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// 在服务成功绑定的回调方法onServiceConnected, 会传递过来一个
IBinder对象:service
Log.i(TAG, "onServiceConnected()");
/*通过向下转型得到了 MyBinder 的实例,有了这个实例,活动和服务之间的关系就变得非常紧密了*/
MyBinder binder = (MyBinder)service;
/*强制类型转化为自定义的接口类型MyBinder,调用接口里面的方法。*/
BindService bindService = binder.getService1();
bindService.MyMethod();
flag = true;
/*上面这段就实现了活动绑定并启动服务,服务通过其自建内部类MyBinder来调用服务的方法。
activity->bindService方法-》服务的onBind方法(返回自建内部类MyBinder实例)-》ServiceConnection.onServiceConnected()-》通过MyBinder实例
调用服务方法, 现在我们可以在活动中根据具体的场景来调用MyBinder中的任何 public 方法,即实现了指挥服务干什么,服务就去干什么的功能。*/
}
};
}
9.3.3 活动和服务进行通信
绑定本地服务调用方法的步骤:
在服务的内部创建一个内部binder类 并提供一个方法,可以间接调用服务的方法
实现服务的onbind方法,返回的就是这个内部binder类
在activity 绑定服务。bindService();
在服务成功绑定的回调方法onServiceConnected, 会传递过来一个 IBinder对象
强制类型转化为自定义的接口类型binder类,调用接口里面的方法。
service
[java] view
plain copy
package com.dada.test;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class BindService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "BindService";
private MyBinder myBinder = new MyBinder();
public void MyMethod(){
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->MyMethod()");
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->onBind()");
return myBinder;
}
//在服务的内部创建一个内部类MyBinder
提供一个方法getService1(),可以间接调用服务的方法MyMethod()
public class MyBinder extends Binder{
public BindService getService1(){
return BindService.this;
}
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->onCreate()");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->onStart()");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->onDestroy()");
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.i(TAG, "BindService-->onUnbind()");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
}
运行日志
点击启动

点击停止

没有打出onServiceDisconnected的日志的原因:
注:SDK上是这么说的:This is called when the connection with the service has been
unexpectedly disconnected -- that is, its process crashed. Because it is running in our same
process, we should never see this happen.
所以说,只有在service因异常而断开连接的时候,这个方法才会用到
其他
由于Service 的onStart()方法只有在startService()启动Service的情况下才调用,故使用onStart()的时候要注意这点。
与 Service 通信并且让它持续运行
如果我们想保持和 Service 的通信,又不想让 Service 随着 Activity 退出而退出呢?你可以先 startService() 然后再 bindService() 。当你不需要绑定的时候就执行 unbindService() 方法,执行这个方法只会触发 Service 的 onUnbind() 而不会把这个 Service 销毁。这样就可以既保持和Service 的通信,也不会随着 Activity 销毁而销毁了。
另外需要注意,任何一个服务在整个应用程序范围内都是通用的,即 Service 不仅可以和 MainActivity 绑定,还可以和任何一个其他的活动进行绑定,而且在绑定完成后它们都可以获取到相同的 Binder 实例。
http://blog.csdn.net/dada360778512/article/details/7720107
http://blog.csdn.net/sunboy_2050/article/details/7364024
相关文章推荐
- android 启动service的两种方式有什么不同
- Android Service两种启动方式
- Android Service两种启动方式
- Android Service两种启动方式
- Android Service 两种启动方式的区别
- Android Service 两种启动方式的区别
- android 启动 service 的两种方式,及什么时候用哪个 android 什么时候用bindService
- Android Service两种启动方式详解(总结版)
- Android中,关于service的启动两种方式描述不正确的是
- android service的两种启动方式
- Android Service 两种启动方式
- Android Service两种启动启动方式 及 adndroid service生命周期
- Android 启动 Service(startservice和bindservice) 两种方式的区别
- Android Service两种启动方式及 生命周期
- Android Service两种启动启动方式 及 adndroid service生命周期
- Android Service的两种启动方式
- Android Service 两种启动方式的区别
- Android Service两种启动方式
- 【Android】- Android Service的两种启动方式
- Android Service的两种启动方式
