Android官方推荐使用DialogFragment替换AlertDialog
2016-09-07 21:38
459 查看
DialogFragment是在Android3.0(API level 11)中引入的,它代替了已经不建议使用的AlertDialog。
DialogFragment高效地封装和管理对话框的生命周期,并让Fragment和它包含的对话框的状态保持一致。那么,已经有了AlertDialog为什么要引入DialogFragment呢?
为什么android系统有AlertDialog,PopupWindow,这些完全可以满足基本客户需求,为什么还要跑出一个DialogFragment对话框呢?这就要从DialogFragment的优点说起了:
它和Fragment基本一致的生命周期,因此便于Activity更好的控制管理DialogFragment。
随屏幕旋转(横竖屏幕切换)DialogFragment对话框随之自动调整对话框大小。而AlertDialog和PopupWindow随屏幕切换而消失,并且如果处理不当很可能引发异常。
DialogFragment的出现完美的解决了横竖屏幕切换Dialog消失的问题。
那么怎么使用DialogFragment呢?
有两种方法:
一、通过继承DialogFragment并且实现它的onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState)方法来创建一个DialogFragment,这个方法返回的是一个Dialog,意味着我们需要创建一个AlertDialog,并返回。
二、 通过继承DialogFragment并且实现它的onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup, Bundle) 这个方法来加载一个我们指定的xml布局从而提供对话框内容。
【注】以上两种方法创建对话框时候只能使用其中一种,不能两个同时使用。
首先讲第一个方法:onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState)
先看看效果图吧:
上面这个效果就充分说明了DialogFragment可以很好的解决屏幕旋转的问题。
代码也非常简单:
首先继承DialogFragment实现onCreateDialog方法:
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public class AlertDialogFragment2 extends DialogFragment {
@Override
public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()).setTitle("Title").setMessage("are you ok?")
.setPositiveButton("Sure", new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dismiss();
}
}).setNegativeButton("cancel", null)
.create();
}
}
然后在Activity中使用它:
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public void showDialogFragment(){
FragmentTransaction mFragTransaction = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
Fragment fragment = getFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag("dialogFragment");
if(fragment!=null){
//为了不重复显示dialog,在显示对话框之前移除正在显示的对话框
mFragTransaction.remove(fragment);
}
AlertDialogFragment2 dialogFragment = new AlertDialogFragment2();
dialogFragment.show(mFragTransaction, "dialogFragment");//显示一个Fragment并且给该Fragment添加一个Tag,可通过findFragmentByTag找到该Fragment
}
是不是很简单啊?
那么问题来了,既然是用Fragment显示对话框,那么它怎么和Activity进行通信呢?答案是使用fragment interface pattern方式。
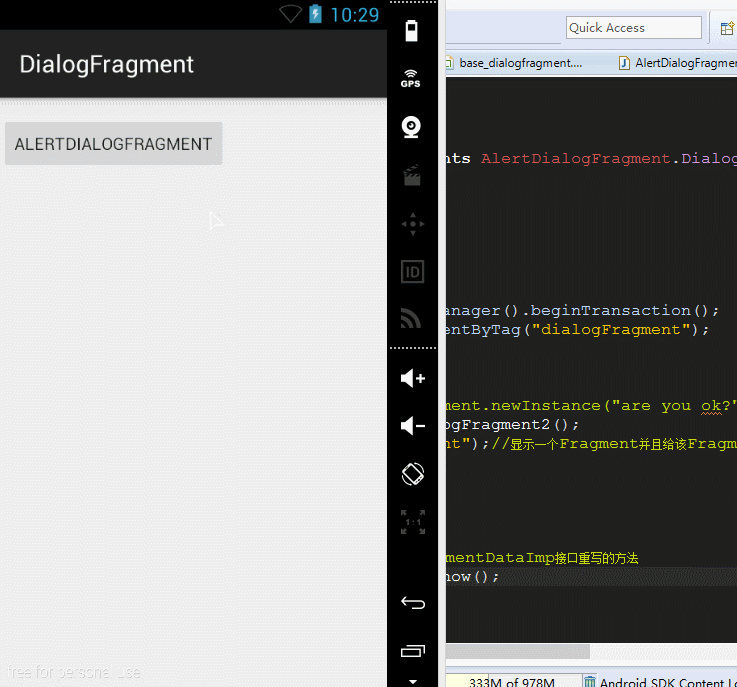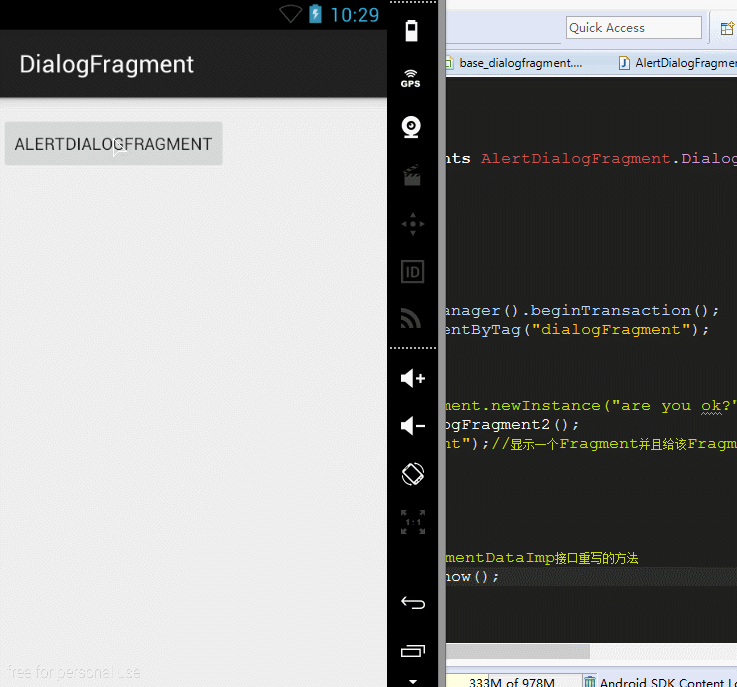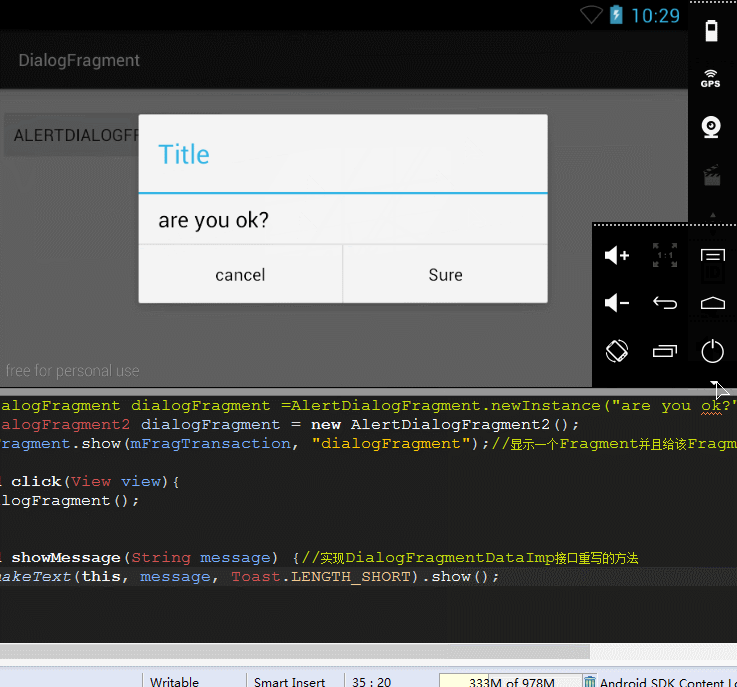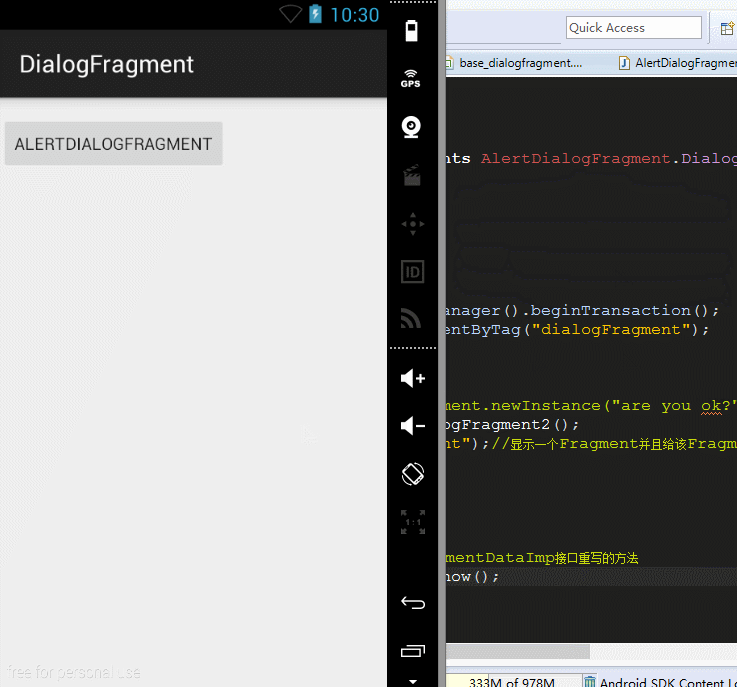
上面的对话框好像太丑了,那么我们就像自定义AlertDialog一样使用自定义的布局,然后来说明它怎么与Activity之间的通信:
还是先看看效果图吧:
中间那段message是通过传参而改变的,然后获取到该message在Activity中显示。

效果很明显,看看代码怎么实现的吧:
AlertDialogFragment.java
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public class AlertDialogFragment extends DialogFragment {
public interface DialogFragmentDataImp{//定义一个与Activity通信的接口,使用该DialogFragment的Activity须实现该接口
void showMessage(String message);
}
public static AlertDialogFragment newInstance(String message){
//创建一个带有参数的Fragment实例
AlertDialogFragment fragment = new AlertDialogFragment();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("message", message);
fragment.setArguments(bundle);//把参数传递给该DialogFragment
return fragment;
}
@Override
public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View customView = LayoutInflater.from(getActivity()).inflate(
R.layout.base_dialogfragment, null);
Button mBtnSure = (Button) customView.findViewById(R.id.yes);
Button mBtnCancel = (Button) customView.findViewById(R.id.no);
TextView mTvMsg = (TextView) customView.findViewById(R.id.message);
mTvMsg.setText(getArguments().getString("message"));//把传递过来的数据设置给TextView
mBtnSure.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
DialogFragmentDataImp imp = (DialogFragmentDataImp) getActivity();
imp.showMessage(getArguments().getString("message"));//对话框与Activity间通信,传递数据给实现了DialogFragmentDataImp接口的Activity
dismiss();
}
});
mBtnCancel.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
dismiss();
}
});
return new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()).setView(customView)
.create();
}
}
再看看MainActivity.java
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity implements AlertDialogFragment.DialogFragmentDataImp{
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
public void showDialogFragment(){
FragmentTransaction mFragTransaction = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
Fragment fragment = getFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag("dialogFragment");
if(fragment!=null){
//为了不重复显示dialog,在显示对话框之前移除正在显示的对话框
mFragTransaction.remove(fragment);
}
AlertDialogFragment dialogFragment =AlertDialogFragment.newInstance("are you ok?");
dialogFragment.show(mFragTransaction, "dialogFragment");//显示一个Fragment并且给该Fragment添加一个Tag,可通过findFragmentByTag找到该Fragment
}
public void click(View view){
showDialogFragment();
}
@Override
public void showMessage(String message) {//实现DialogFragmentDataImp接口重写的方法
Toast.makeText(this, message, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
最后看看自定义AlertDialog的布局文件:
base_dialogfragment.xml
[html] view
plain copy
print?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:text="提示" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/message"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:textSize="15sp"
android:text="确定要退出么?" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:gravity="right"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/no"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@null"
android:text="Cancel"
android:textColor="#ff009688"
android:textSize="12sp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/yes"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginRight="5dp"
android:background="@null"
android:text="Sure"
android:textColor="#ff009688"
android:textSize="12sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
总结:
一、我们通过定义一个DialogFragmentDataImp接口,并把activity强转为我们定义的DialogFragmentDataImp接口,然后将参数信息返回,最后让Activity实现接口里面的方法,从而得到返回而来的message,这就是和Activity之间的通信。
二、我们定义了一个newInstance(String message)方法,目地是解决DialogFragment需要使用从Activity传过来的信息的情况,通过fragment.setArguments(bundle)将信息传递给DialogFragment,通过getArguments().getString("message")从DialogFragment中取出信息以便使用。
三、
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public void showDialogFragment(){
FragmentTransaction mFragTransaction = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
Fragment fragment = getFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag("dialogFragment");
if(fragment!=null){
//为了不重复显示dialog,在显示对话框之前移除正在显示的对话框
mFragTransaction.remove(fragment);
}
AlertDialogFragment dialogFragment =AlertDialogFragment.newInstance("are you ok?");
dialogFragment.show(mFragTransaction, "dialogFragment");//显示一个Fragment并且给该Fragment添加一个Tag,可通过findFragmentByTag找到该Fragment
}
这段代码中,可以保证每次只弹出一个对话框。
好了,第一个方法就说到这里了。
现在讲第二个方法:onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup, Bundle)
我相信这个方法大家并不陌生,因为用过Fragment的都知道,这是为Fragment绑定UI的方法,那么就很容易了,还是按原样的使用,加载一个布局xml文件,然后返回即ok。
还是使用刚刚的布局base_dialogfragment.xml,好,我们先贴代码:
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public class BaseDialogFragment extends DialogFragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.base_dialogfragment, container);
//view.findViewById(...)
return view;
}
}
就是如此简单,然后在MainActivity中显示和前面的方法一样,就不贴了。好,我们来看看效果图:
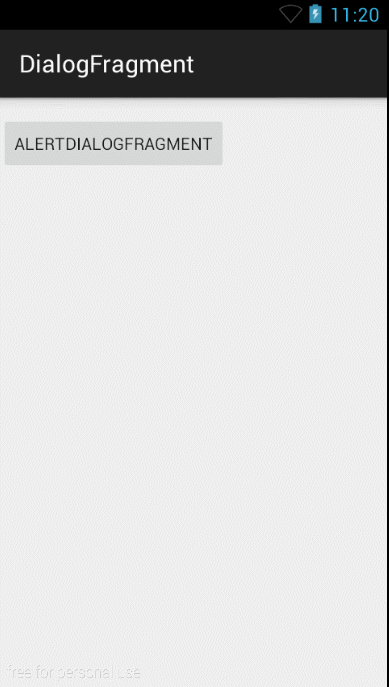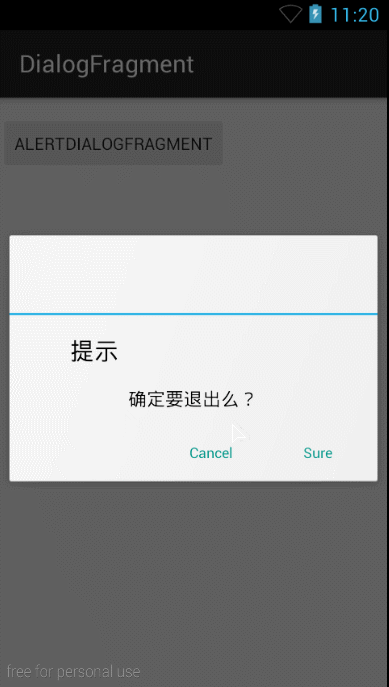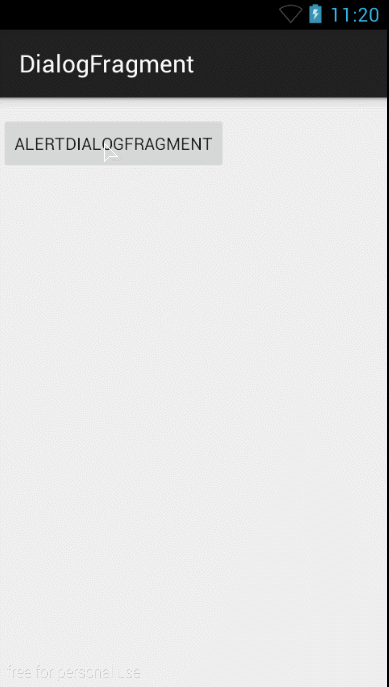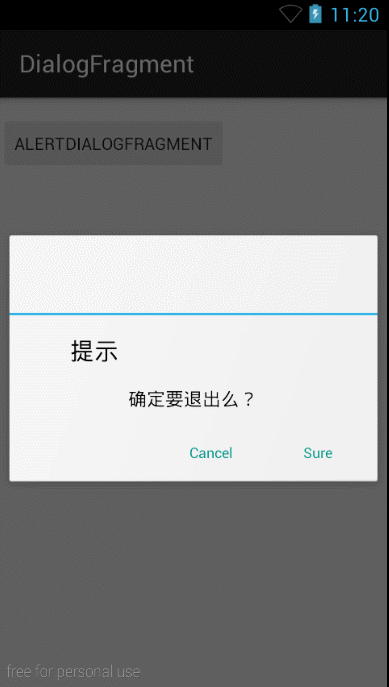
我擦,对话框怎么多了一个标题部分啊,好丑啊,明明自定义的布局文件中没有啊?别忘了,我们继承的可是一个DialogFragment啊,那么去看看它的源码吧,发现它内部是通过mDialog.setContentView(view);意思就是把我们自定义好的布局xml文件加载到Dialog的Content内容区域了,那么它的标题当然还是有啊,而刚刚的第一种方法恰是通过mDialog,setView()自定义整个布局就没有标题那部分了。那么为了用户体验好点,就需要去标题了,方法是:在onCreateView(......)内使用getDialog().requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);从而去除标题,或许你不想去除标题,反而想要在标题区域显示你设置的标题,那么可以使用:getDialog().setTitle("这是标题");。
好了,这时候我们看看去除标题后的效果:

好了,DialogFragment使用就是这些了。
个人建议使用onCreateDialog()来使用DialogFragment,因为它也可以自定义布局适合很多情况下的需求。而setCreateView它的显示大小会随你的布局的大小改变而改变。假如你的弹出的对话框提示的信息很短的话,比如只有几个字,那么它将会显示的很小,体验比较差。
源码下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/u010687392/8737841
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/u010687392
DialogFragment高效地封装和管理对话框的生命周期,并让Fragment和它包含的对话框的状态保持一致。那么,已经有了AlertDialog为什么要引入DialogFragment呢?
DialogFragment对话框出现的意义
为什么android系统有AlertDialog,PopupWindow,这些完全可以满足基本客户需求,为什么还要跑出一个DialogFragment对话框呢?这就要从DialogFragment的优点说起了:它和Fragment基本一致的生命周期,因此便于Activity更好的控制管理DialogFragment。
随屏幕旋转(横竖屏幕切换)DialogFragment对话框随之自动调整对话框大小。而AlertDialog和PopupWindow随屏幕切换而消失,并且如果处理不当很可能引发异常。
DialogFragment的出现完美的解决了横竖屏幕切换Dialog消失的问题。
那么怎么使用DialogFragment呢?
有两种方法:
一、通过继承DialogFragment并且实现它的onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState)方法来创建一个DialogFragment,这个方法返回的是一个Dialog,意味着我们需要创建一个AlertDialog,并返回。
二、 通过继承DialogFragment并且实现它的onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup, Bundle) 这个方法来加载一个我们指定的xml布局从而提供对话框内容。
【注】以上两种方法创建对话框时候只能使用其中一种,不能两个同时使用。
首先讲第一个方法:onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState)
先看看效果图吧:

上面这个效果就充分说明了DialogFragment可以很好的解决屏幕旋转的问题。
代码也非常简单:
首先继承DialogFragment实现onCreateDialog方法:
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public class AlertDialogFragment2 extends DialogFragment {
@Override
public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()).setTitle("Title").setMessage("are you ok?")
.setPositiveButton("Sure", new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dismiss();
}
}).setNegativeButton("cancel", null)
.create();
}
}
然后在Activity中使用它:
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public void showDialogFragment(){
FragmentTransaction mFragTransaction = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
Fragment fragment = getFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag("dialogFragment");
if(fragment!=null){
//为了不重复显示dialog,在显示对话框之前移除正在显示的对话框
mFragTransaction.remove(fragment);
}
AlertDialogFragment2 dialogFragment = new AlertDialogFragment2();
dialogFragment.show(mFragTransaction, "dialogFragment");//显示一个Fragment并且给该Fragment添加一个Tag,可通过findFragmentByTag找到该Fragment
}
是不是很简单啊?
那么问题来了,既然是用Fragment显示对话框,那么它怎么和Activity进行通信呢?答案是使用fragment interface pattern方式。
上面的对话框好像太丑了,那么我们就像自定义AlertDialog一样使用自定义的布局,然后来说明它怎么与Activity之间的通信:
还是先看看效果图吧:
中间那段message是通过传参而改变的,然后获取到该message在Activity中显示。

效果很明显,看看代码怎么实现的吧:
AlertDialogFragment.java
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public class AlertDialogFragment extends DialogFragment {
public interface DialogFragmentDataImp{//定义一个与Activity通信的接口,使用该DialogFragment的Activity须实现该接口
void showMessage(String message);
}
public static AlertDialogFragment newInstance(String message){
//创建一个带有参数的Fragment实例
AlertDialogFragment fragment = new AlertDialogFragment();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("message", message);
fragment.setArguments(bundle);//把参数传递给该DialogFragment
return fragment;
}
@Override
public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View customView = LayoutInflater.from(getActivity()).inflate(
R.layout.base_dialogfragment, null);
Button mBtnSure = (Button) customView.findViewById(R.id.yes);
Button mBtnCancel = (Button) customView.findViewById(R.id.no);
TextView mTvMsg = (TextView) customView.findViewById(R.id.message);
mTvMsg.setText(getArguments().getString("message"));//把传递过来的数据设置给TextView
mBtnSure.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
DialogFragmentDataImp imp = (DialogFragmentDataImp) getActivity();
imp.showMessage(getArguments().getString("message"));//对话框与Activity间通信,传递数据给实现了DialogFragmentDataImp接口的Activity
dismiss();
}
});
mBtnCancel.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
dismiss();
}
});
return new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()).setView(customView)
.create();
}
}
再看看MainActivity.java
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity implements AlertDialogFragment.DialogFragmentDataImp{
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
public void showDialogFragment(){
FragmentTransaction mFragTransaction = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
Fragment fragment = getFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag("dialogFragment");
if(fragment!=null){
//为了不重复显示dialog,在显示对话框之前移除正在显示的对话框
mFragTransaction.remove(fragment);
}
AlertDialogFragment dialogFragment =AlertDialogFragment.newInstance("are you ok?");
dialogFragment.show(mFragTransaction, "dialogFragment");//显示一个Fragment并且给该Fragment添加一个Tag,可通过findFragmentByTag找到该Fragment
}
public void click(View view){
showDialogFragment();
}
@Override
public void showMessage(String message) {//实现DialogFragmentDataImp接口重写的方法
Toast.makeText(this, message, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
最后看看自定义AlertDialog的布局文件:
base_dialogfragment.xml
[html] view
plain copy
print?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:text="提示" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/message"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:textSize="15sp"
android:text="确定要退出么?" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:gravity="right"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/no"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@null"
android:text="Cancel"
android:textColor="#ff009688"
android:textSize="12sp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/yes"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginRight="5dp"
android:background="@null"
android:text="Sure"
android:textColor="#ff009688"
android:textSize="12sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
总结:
一、我们通过定义一个DialogFragmentDataImp接口,并把activity强转为我们定义的DialogFragmentDataImp接口,然后将参数信息返回,最后让Activity实现接口里面的方法,从而得到返回而来的message,这就是和Activity之间的通信。
二、我们定义了一个newInstance(String message)方法,目地是解决DialogFragment需要使用从Activity传过来的信息的情况,通过fragment.setArguments(bundle)将信息传递给DialogFragment,通过getArguments().getString("message")从DialogFragment中取出信息以便使用。
三、
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public void showDialogFragment(){
FragmentTransaction mFragTransaction = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
Fragment fragment = getFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag("dialogFragment");
if(fragment!=null){
//为了不重复显示dialog,在显示对话框之前移除正在显示的对话框
mFragTransaction.remove(fragment);
}
AlertDialogFragment dialogFragment =AlertDialogFragment.newInstance("are you ok?");
dialogFragment.show(mFragTransaction, "dialogFragment");//显示一个Fragment并且给该Fragment添加一个Tag,可通过findFragmentByTag找到该Fragment
}
这段代码中,可以保证每次只弹出一个对话框。
好了,第一个方法就说到这里了。
现在讲第二个方法:onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup, Bundle)
我相信这个方法大家并不陌生,因为用过Fragment的都知道,这是为Fragment绑定UI的方法,那么就很容易了,还是按原样的使用,加载一个布局xml文件,然后返回即ok。
还是使用刚刚的布局base_dialogfragment.xml,好,我们先贴代码:
[java] view
plain copy
print?
public class BaseDialogFragment extends DialogFragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.base_dialogfragment, container);
//view.findViewById(...)
return view;
}
}
就是如此简单,然后在MainActivity中显示和前面的方法一样,就不贴了。好,我们来看看效果图:

我擦,对话框怎么多了一个标题部分啊,好丑啊,明明自定义的布局文件中没有啊?别忘了,我们继承的可是一个DialogFragment啊,那么去看看它的源码吧,发现它内部是通过mDialog.setContentView(view);意思就是把我们自定义好的布局xml文件加载到Dialog的Content内容区域了,那么它的标题当然还是有啊,而刚刚的第一种方法恰是通过mDialog,setView()自定义整个布局就没有标题那部分了。那么为了用户体验好点,就需要去标题了,方法是:在onCreateView(......)内使用getDialog().requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);从而去除标题,或许你不想去除标题,反而想要在标题区域显示你设置的标题,那么可以使用:getDialog().setTitle("这是标题");。
好了,这时候我们看看去除标题后的效果:

好了,DialogFragment使用就是这些了。
个人建议使用onCreateDialog()来使用DialogFragment,因为它也可以自定义布局适合很多情况下的需求。而setCreateView它的显示大小会随你的布局的大小改变而改变。假如你的弹出的对话框提示的信息很短的话,比如只有几个字,那么它将会显示的很小,体验比较差。
源码下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/u010687392/8737841
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/u010687392
相关文章推荐
- Android开发——官方推荐使用DialogFragment替换AlertDialog
- Android官方推荐使用DialogFragment替换AlertDialog
- Android开发——官方推荐使用DialogFragment替换AlertDialog
- Android官方推荐使用DialogFragment替换AlertDialog
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android官方推荐:DialogFragment创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
- Android 官方推荐 : DialogFragment 创建对话框
