Android省市区三级联动滚轮选择(真实项目中提取出来的组件)
2016-08-16 10:30
531 查看
from : http://blog.csdn.net/wulianghuan/article/details/41549189/
最近项目要做一个,类似淘宝手机客户端的,选择收货地址的三级联动滚动选择组件,下面是它的大致界面截图:
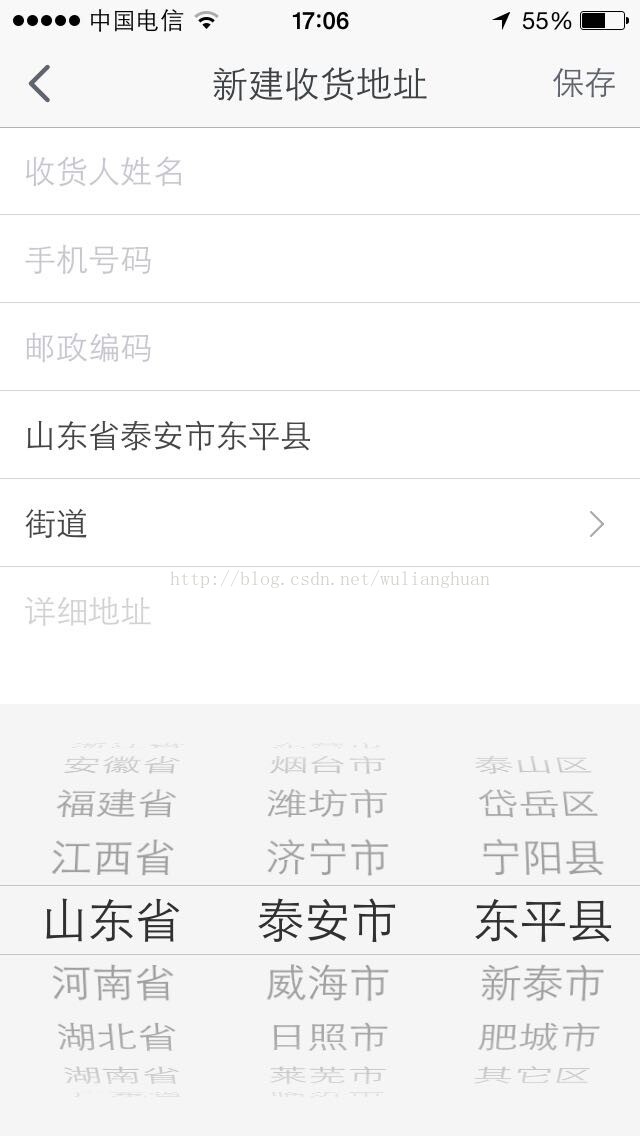
在IOS中有个叫UIPickerView的选择器,并且在dataSource中定义了UIPickerView的数据源和定制内容,所以用只要熟悉它的基本用法,要实现这么个三级联动滑动选择是挺简单的。
言归正传,今天讨论的是在Android里面如何来实现这么个效果,那么如何实现呢??? 相信部分童鞋首先想到的是android.widget.DatePicker和android.widget.TimePicker,因为它们的样子长得很像,事实就是它们仅仅是长得相而已,Google在设计这个两个widget的时候,并没有提供对外的数据源适配接口,带来的问题就是,我们只能通过它们来选择日期和时间,至于为什么这样设计,如果有童鞋知道,请给我留言,Thanks~
DatePicker.class包含的方法截图:
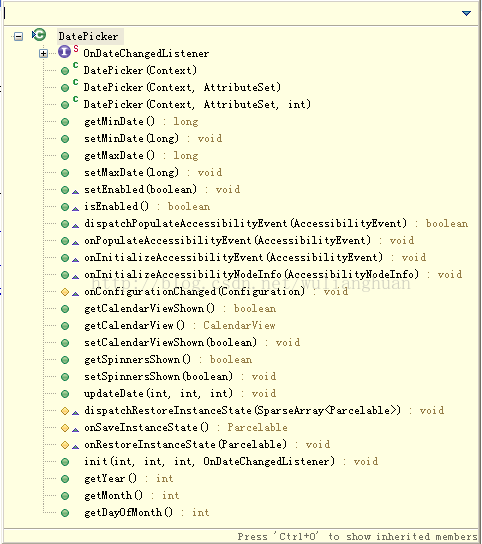
全都是关于时间获取用的方法.
好了,既然在Android中没办法偷懒的用一个系统widget搞定,那么只能自己来自定义view来实现了,这篇就围绕这个来展开分享一下,我在项目中实现这个的全过程。首先是做了下开源代码调研,在github上面有一个叫做 android-wheel 的开源控件,
代码地址https://github.com/maarek/android-wheel
是一个非常好用的组件,对于数据适配接口的抽取和事件的回调都做了抽取,代码的耦合度低,唯一不足就是在界面的定制这块,如果你需要做更改,需要去动源代码的。我这里在界面的代码做了改动,放在我的项目src目录下了:
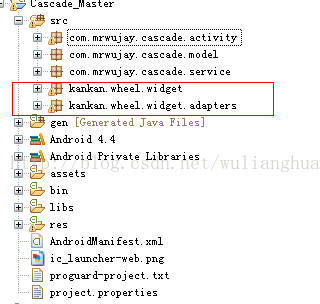
在此次项目中,省市区及邮编的数据是放在了assets/province_data.xml里面,是产品经理花了好几天时间整理的,绝对是最齐全和完善了,辛苦辛苦!!!
关于XML的解析,一共有SAX、PULL、DOM三种解析方式,这里就不讲了,可以看我的前面的几篇学习的文章:
Android解析XML方式(一)使用SAX解析
Android解析XML方式(二)使用PULL解析XML
Android解析XML方式(三)使用DOM解析XML
此次项目中使用的是SAX解析方式,因为它占用内存少,并且速度快,数据解析代码写在了 com.mrwujay.cascade.service/XmlParserHandler.java中,代码如下:
[java] view
plain copy
print?


package com.mrwujay.cascade.service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.xml.sax.Attributes;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler;
import com.mrwujay.cascade.model.CityModel;
import com.mrwujay.cascade.model.DistrictModel;
import com.mrwujay.cascade.model.ProvinceModel;
public class XmlParserHandler extends DefaultHandler {
/**
* 存储所有的解析对象
*/
private List<ProvinceModel> provinceList = new ArrayList<ProvinceModel>();
public XmlParserHandler() {
}
public List<ProvinceModel> getDataList() {
return provinceList;
}
@Override
public void startDocument() throws SAXException {
// 当读到第一个开始标签的时候,会触发这个方法
}
ProvinceModel provinceModel = new ProvinceModel();
CityModel cityModel = new CityModel();
DistrictModel districtModel = new DistrictModel();
@Override
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String qName,
Attributes attributes) throws SAXException {
// 当遇到开始标记的时候,调用这个方法
if (qName.equals("province")) {
provinceModel = new ProvinceModel();
provinceModel.setName(attributes.getValue(0));
provinceModel.setCityList(new ArrayList<CityModel>());
} else if (qName.equals("city")) {
cityModel = new CityModel();
cityModel.setName(attributes.getValue(0));
cityModel.setDistrictList(new ArrayList<DistrictModel>());
} else if (qName.equals("district")) {
districtModel = new DistrictModel();
districtModel.setName(attributes.getValue(0));
districtModel.setZipcode(attributes.getValue(1));
}
}
@Override
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String qName)
throws SAXException {
// 遇到结束标记的时候,会调用这个方法
if (qName.equals("district")) {
cityModel.getDistrictList().add(districtModel);
} else if (qName.equals("city")) {
provinceModel.getCityList().add(cityModel);
} else if (qName.equals("province")) {
provinceList.add(provinceModel);
}
}
@Override
public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length)
throws SAXException {
}
}
通过XmlParserHandler.java提供的getDataList()方法获取得到,之后再进行拆分放到省、市、区不同的HashMap里面方便做数据适配。
这里是它的具体实现代码:
[java] view
plain copy
print?


protected void initProvinceDatas()
{
List<ProvinceModel> provinceList = null;
AssetManager asset = getAssets();
try {
InputStream input = asset.open("province_data.xml");
// 创建一个解析xml的工厂对象
SAXParserFactory spf = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
// 解析xml
SAXParser parser = spf.newSAXParser();
XmlParserHandler handler = new XmlParserHandler();
parser.parse(input, handler);
input.close();
// 获取解析出来的数据
provinceList = handler.getDataList();
//*/ 初始化默认选中的省、市、区
if (provinceList!= null && !provinceList.isEmpty()) {
mCurrentProviceName = provinceList.get(0).getName();
List<CityModel> cityList = provinceList.get(0).getCityList();
if (cityList!= null && !cityList.isEmpty()) {
mCurrentCityName = cityList.get(0).getName();
List<DistrictModel> districtList = cityList.get(0).getDistrictList();
mCurrentDistrictName = districtList.get(0).getName();
mCurrentZipCode = districtList.get(0).getZipcode();
}
}
//*/
mProvinceDatas = new String[provinceList.size()];
for (int i=0; i< provinceList.size(); i++) {
mProvinceDatas[i] = provinceList.get(i).getName();
List<CityModel> cityList = provinceList.get(i).getCityList();
String[] cityNames = new String[cityList.size()];
for (int j=0; j< cityList.size(); j++) {
cityNames[j] = cityList.get(j).getName();
List<DistrictModel> districtList = cityList.get(j).getDistrictList();
String[] distrinctNameArray = new String[districtList.size()];
DistrictModel[] distrinctArray = new DistrictModel[districtList.size()];
for (int k=0; k<districtList.size(); k++) {
DistrictModel districtModel = new DistrictModel(districtList.get(k).getName(), districtList.get(k).getZipcode());
mZipcodeDatasMap.put(districtList.get(k).getName(), districtList.get(k).getZipcode());
distrinctArray[k] = districtModel;
distrinctNameArray[k] = districtModel.getName();
}
mDistrictDatasMap.put(cityNames[j], distrinctNameArray);
}
mCitisDatasMap.put(provinceList.get(i).getName(), cityNames);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
}
}
在使用wheel组件时,数据适配起来也很方便,只需要做些数据、显示数量的配置即可,我这边设置了一行显示7条数据
[java] view
plain copy
print?


initProvinceDatas();
mViewProvince.setViewAdapter(new ArrayWheelAdapter<String>(MainActivity.this, mProvinceDatas));
// 设置可见条目数量
mViewProvince.setVisibleItems(7);
mViewCity.setVisibleItems(7);
mViewDistrict.setVisibleItems(7);
updateCities();
updateAreas();
要监听wheel组件的滑动、点击、选中改变事件,可以通过实现它的三个事件监听接口来实现,分别是:
1、OnWheelScrollListener 滑动事件:
[java] view
plain copy
print?


/**
* Wheel scrolled listener interface.
*/
public interface OnWheelScrollListener {
/**
* Callback method to be invoked when scrolling started.
* @param wheel the wheel view whose state has changed.
*/
void onScrollingStarted(WheelView wheel);
/**
* Callback method to be invoked when scrolling ended.
* @param wheel the wheel view whose state has changed.
*/
void onScrollingFinished(WheelView wheel);
}
2、OnWheelClickedListener 条目点击事件:
[java] view
plain copy
print?


/**
* Wheel clicked listener interface.
* <p>The onItemClicked() method is called whenever a wheel item is clicked
* <li> New Wheel position is set
* <li> Wheel view is scrolled
*/
public interface OnWheelClickedListener {
/**
* Callback method to be invoked when current item clicked
* @param wheel the wheel view
* @param itemIndex the index of clicked item
*/
void onItemClicked(WheelView wheel, int itemIndex);
}
3、OnWheelChangedListener 被选中项的positon变化事件:
[java] view
plain copy
print?


/**
* Wheel changed listener interface.
* <p>The onChanged() method is called whenever current wheel positions is changed:
* <li> New Wheel position is set
* <li> Wheel view is scrolled
*/
public interface OnWheelChangedListener {
/**
* Callback method to be invoked when current item changed
* @param wheel the wheel view whose state has changed
* @param oldValue the old value of current item
* @param newValue the new value of current item
*/
void onChanged(WheelView wheel, int oldValue, int newValue);
}
这里只要知道哪个省、市、区被选中了,实现第三个接口就行,在方法回调时去作同步和更新数据,比如省级条目滑动的时候,市级和县级数据都要做对应的适配、市级滑动时需要去改变县级(区)的数据,这样才能实现级联的效果,至于如何改变,需要三个HashMap来分别保存他们的对应关系:
[java] view
plain copy
print?


/**
* key - 省 value - 市
*/
protected Map<String, String[]> mCitisDatasMap = new HashMap<String, String[]>();
/**
* key - 市 values - 区
*/
protected Map<String, String[]> mDistrictDatasMap = new HashMap<String, String[]>();
/**
* key - 区 values - 邮编
*/
protected Map<String, String> mZipcodeDatasMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
在onChanged()回调方法中,对于省、市、区/县的滑动,分别做数据的适配,代码如下:
[java] view
plain copy
print?


@Override
public void onChanged(WheelView wheel, int oldValue, int newValue) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (wheel == mViewProvince) {
updateCities();
} else if (wheel == mViewCity) {
updateAreas();
} else if (wheel == mViewDistrict) {
mCurrentDistrictName = mDistrictDatasMap.get(mCurrentCityName)[newValue];
mCurrentZipCode = mZipcodeDatasMap.get(mCurrentDistrictName);
}
}
/**
* 根据当前的市,更新区WheelView的信息
*/
private void updateAreas() {
int pCurrent = mViewCity.getCurrentItem();
mCurrentCityName = mCitisDatasMap.get(mCurrentProviceName)[pCurrent];
String[] areas = mDistrictDatasMap.get(mCurrentCityName);
if (areas == null) {
areas = new String[] { "" };
}
mViewDistrict.setViewAdapter(new ArrayWheelAdapter<String>(this, areas));
mViewDistrict.setCurrentItem(0);
}
/**
* 根据当前的省,更新市WheelView的信息
*/
private void updateCities() {
int pCurrent = mViewProvince.getCurrentItem();
mCurrentProviceName = mProvinceDatas[pCurrent];
String[] cities = mCitisDatasMap.get(mCurrentProviceName);
if (cities == null) {
cities = new String[] { "" };
}
mViewCity.setViewAdapter(new ArrayWheelAdapter<String>(this, cities));
mViewCity.setCurrentItem(0);
updateAreas();
}
综上代码,最终实现的界面截图:

源码下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/wulianghuan/8205211
最近项目要做一个,类似淘宝手机客户端的,选择收货地址的三级联动滚动选择组件,下面是它的大致界面截图:

在IOS中有个叫UIPickerView的选择器,并且在dataSource中定义了UIPickerView的数据源和定制内容,所以用只要熟悉它的基本用法,要实现这么个三级联动滑动选择是挺简单的。
言归正传,今天讨论的是在Android里面如何来实现这么个效果,那么如何实现呢??? 相信部分童鞋首先想到的是android.widget.DatePicker和android.widget.TimePicker,因为它们的样子长得很像,事实就是它们仅仅是长得相而已,Google在设计这个两个widget的时候,并没有提供对外的数据源适配接口,带来的问题就是,我们只能通过它们来选择日期和时间,至于为什么这样设计,如果有童鞋知道,请给我留言,Thanks~
DatePicker.class包含的方法截图:

全都是关于时间获取用的方法.
好了,既然在Android中没办法偷懒的用一个系统widget搞定,那么只能自己来自定义view来实现了,这篇就围绕这个来展开分享一下,我在项目中实现这个的全过程。首先是做了下开源代码调研,在github上面有一个叫做 android-wheel 的开源控件,
代码地址https://github.com/maarek/android-wheel
是一个非常好用的组件,对于数据适配接口的抽取和事件的回调都做了抽取,代码的耦合度低,唯一不足就是在界面的定制这块,如果你需要做更改,需要去动源代码的。我这里在界面的代码做了改动,放在我的项目src目录下了:

在此次项目中,省市区及邮编的数据是放在了assets/province_data.xml里面,是产品经理花了好几天时间整理的,绝对是最齐全和完善了,辛苦辛苦!!!
关于XML的解析,一共有SAX、PULL、DOM三种解析方式,这里就不讲了,可以看我的前面的几篇学习的文章:
Android解析XML方式(一)使用SAX解析
Android解析XML方式(二)使用PULL解析XML
Android解析XML方式(三)使用DOM解析XML
此次项目中使用的是SAX解析方式,因为它占用内存少,并且速度快,数据解析代码写在了 com.mrwujay.cascade.service/XmlParserHandler.java中,代码如下:
[java] view
plain copy
print?

package com.mrwujay.cascade.service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.xml.sax.Attributes;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler;
import com.mrwujay.cascade.model.CityModel;
import com.mrwujay.cascade.model.DistrictModel;
import com.mrwujay.cascade.model.ProvinceModel;
public class XmlParserHandler extends DefaultHandler {
/**
* 存储所有的解析对象
*/
private List<ProvinceModel> provinceList = new ArrayList<ProvinceModel>();
public XmlParserHandler() {
}
public List<ProvinceModel> getDataList() {
return provinceList;
}
@Override
public void startDocument() throws SAXException {
// 当读到第一个开始标签的时候,会触发这个方法
}
ProvinceModel provinceModel = new ProvinceModel();
CityModel cityModel = new CityModel();
DistrictModel districtModel = new DistrictModel();
@Override
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String qName,
Attributes attributes) throws SAXException {
// 当遇到开始标记的时候,调用这个方法
if (qName.equals("province")) {
provinceModel = new ProvinceModel();
provinceModel.setName(attributes.getValue(0));
provinceModel.setCityList(new ArrayList<CityModel>());
} else if (qName.equals("city")) {
cityModel = new CityModel();
cityModel.setName(attributes.getValue(0));
cityModel.setDistrictList(new ArrayList<DistrictModel>());
} else if (qName.equals("district")) {
districtModel = new DistrictModel();
districtModel.setName(attributes.getValue(0));
districtModel.setZipcode(attributes.getValue(1));
}
}
@Override
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String qName)
throws SAXException {
// 遇到结束标记的时候,会调用这个方法
if (qName.equals("district")) {
cityModel.getDistrictList().add(districtModel);
} else if (qName.equals("city")) {
provinceModel.getCityList().add(cityModel);
} else if (qName.equals("province")) {
provinceList.add(provinceModel);
}
}
@Override
public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length)
throws SAXException {
}
}
通过XmlParserHandler.java提供的getDataList()方法获取得到,之后再进行拆分放到省、市、区不同的HashMap里面方便做数据适配。
这里是它的具体实现代码:
[java] view
plain copy
print?

protected void initProvinceDatas()
{
List<ProvinceModel> provinceList = null;
AssetManager asset = getAssets();
try {
InputStream input = asset.open("province_data.xml");
// 创建一个解析xml的工厂对象
SAXParserFactory spf = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
// 解析xml
SAXParser parser = spf.newSAXParser();
XmlParserHandler handler = new XmlParserHandler();
parser.parse(input, handler);
input.close();
// 获取解析出来的数据
provinceList = handler.getDataList();
//*/ 初始化默认选中的省、市、区
if (provinceList!= null && !provinceList.isEmpty()) {
mCurrentProviceName = provinceList.get(0).getName();
List<CityModel> cityList = provinceList.get(0).getCityList();
if (cityList!= null && !cityList.isEmpty()) {
mCurrentCityName = cityList.get(0).getName();
List<DistrictModel> districtList = cityList.get(0).getDistrictList();
mCurrentDistrictName = districtList.get(0).getName();
mCurrentZipCode = districtList.get(0).getZipcode();
}
}
//*/
mProvinceDatas = new String[provinceList.size()];
for (int i=0; i< provinceList.size(); i++) {
mProvinceDatas[i] = provinceList.get(i).getName();
List<CityModel> cityList = provinceList.get(i).getCityList();
String[] cityNames = new String[cityList.size()];
for (int j=0; j< cityList.size(); j++) {
cityNames[j] = cityList.get(j).getName();
List<DistrictModel> districtList = cityList.get(j).getDistrictList();
String[] distrinctNameArray = new String[districtList.size()];
DistrictModel[] distrinctArray = new DistrictModel[districtList.size()];
for (int k=0; k<districtList.size(); k++) {
DistrictModel districtModel = new DistrictModel(districtList.get(k).getName(), districtList.get(k).getZipcode());
mZipcodeDatasMap.put(districtList.get(k).getName(), districtList.get(k).getZipcode());
distrinctArray[k] = districtModel;
distrinctNameArray[k] = districtModel.getName();
}
mDistrictDatasMap.put(cityNames[j], distrinctNameArray);
}
mCitisDatasMap.put(provinceList.get(i).getName(), cityNames);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
}
}
在使用wheel组件时,数据适配起来也很方便,只需要做些数据、显示数量的配置即可,我这边设置了一行显示7条数据
[java] view
plain copy
print?

initProvinceDatas();
mViewProvince.setViewAdapter(new ArrayWheelAdapter<String>(MainActivity.this, mProvinceDatas));
// 设置可见条目数量
mViewProvince.setVisibleItems(7);
mViewCity.setVisibleItems(7);
mViewDistrict.setVisibleItems(7);
updateCities();
updateAreas();
要监听wheel组件的滑动、点击、选中改变事件,可以通过实现它的三个事件监听接口来实现,分别是:
1、OnWheelScrollListener 滑动事件:
[java] view
plain copy
print?

/**
* Wheel scrolled listener interface.
*/
public interface OnWheelScrollListener {
/**
* Callback method to be invoked when scrolling started.
* @param wheel the wheel view whose state has changed.
*/
void onScrollingStarted(WheelView wheel);
/**
* Callback method to be invoked when scrolling ended.
* @param wheel the wheel view whose state has changed.
*/
void onScrollingFinished(WheelView wheel);
}
2、OnWheelClickedListener 条目点击事件:
[java] view
plain copy
print?

/**
* Wheel clicked listener interface.
* <p>The onItemClicked() method is called whenever a wheel item is clicked
* <li> New Wheel position is set
* <li> Wheel view is scrolled
*/
public interface OnWheelClickedListener {
/**
* Callback method to be invoked when current item clicked
* @param wheel the wheel view
* @param itemIndex the index of clicked item
*/
void onItemClicked(WheelView wheel, int itemIndex);
}
3、OnWheelChangedListener 被选中项的positon变化事件:
[java] view
plain copy
print?

/**
* Wheel changed listener interface.
* <p>The onChanged() method is called whenever current wheel positions is changed:
* <li> New Wheel position is set
* <li> Wheel view is scrolled
*/
public interface OnWheelChangedListener {
/**
* Callback method to be invoked when current item changed
* @param wheel the wheel view whose state has changed
* @param oldValue the old value of current item
* @param newValue the new value of current item
*/
void onChanged(WheelView wheel, int oldValue, int newValue);
}
这里只要知道哪个省、市、区被选中了,实现第三个接口就行,在方法回调时去作同步和更新数据,比如省级条目滑动的时候,市级和县级数据都要做对应的适配、市级滑动时需要去改变县级(区)的数据,这样才能实现级联的效果,至于如何改变,需要三个HashMap来分别保存他们的对应关系:
[java] view
plain copy
print?

/**
* key - 省 value - 市
*/
protected Map<String, String[]> mCitisDatasMap = new HashMap<String, String[]>();
/**
* key - 市 values - 区
*/
protected Map<String, String[]> mDistrictDatasMap = new HashMap<String, String[]>();
/**
* key - 区 values - 邮编
*/
protected Map<String, String> mZipcodeDatasMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
在onChanged()回调方法中,对于省、市、区/县的滑动,分别做数据的适配,代码如下:
[java] view
plain copy
print?

@Override
public void onChanged(WheelView wheel, int oldValue, int newValue) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (wheel == mViewProvince) {
updateCities();
} else if (wheel == mViewCity) {
updateAreas();
} else if (wheel == mViewDistrict) {
mCurrentDistrictName = mDistrictDatasMap.get(mCurrentCityName)[newValue];
mCurrentZipCode = mZipcodeDatasMap.get(mCurrentDistrictName);
}
}
/**
* 根据当前的市,更新区WheelView的信息
*/
private void updateAreas() {
int pCurrent = mViewCity.getCurrentItem();
mCurrentCityName = mCitisDatasMap.get(mCurrentProviceName)[pCurrent];
String[] areas = mDistrictDatasMap.get(mCurrentCityName);
if (areas == null) {
areas = new String[] { "" };
}
mViewDistrict.setViewAdapter(new ArrayWheelAdapter<String>(this, areas));
mViewDistrict.setCurrentItem(0);
}
/**
* 根据当前的省,更新市WheelView的信息
*/
private void updateCities() {
int pCurrent = mViewProvince.getCurrentItem();
mCurrentProviceName = mProvinceDatas[pCurrent];
String[] cities = mCitisDatasMap.get(mCurrentProviceName);
if (cities == null) {
cities = new String[] { "" };
}
mViewCity.setViewAdapter(new ArrayWheelAdapter<String>(this, cities));
mViewCity.setCurrentItem(0);
updateAreas();
}
综上代码,最终实现的界面截图:

源码下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/wulianghuan/8205211
相关文章推荐
- Android省市区三级联动滚轮选择(真实项目中提取出来的组件)
- Android省市区三级联动滚轮选择(真实项目中提取出来的组件)
- Android省市区三级联动滚轮选择(真实项目中提取出来的组件)
- Android省市区三级联动滚轮选择(真实项目中提取出来的组件)
- Android省市区三级联动滚轮选择(真实项目中提取出来的组件)
- Android省市区三级联动滚轮选择(真实项目中提取出来的组件)
- Android省市区三级联动滚轮选择(真实项目中提取出来的组件)
- Android省市区三级联动滚轮选择(真实项目中提取出来的组件)
- 安卓学习笔记---Android-PickerView实现 3D滚轮效果(时间选择器、省市区三级联动,单项选择效果)
- Android省市区三级联动滚轮选择
- Android省市区三级联动滚轮选择——Cascade_Master
- android 省市区选择三级联动
- Android中使用开源框架citypickerview实现省市区三级联动选择
- 史上最好用的Android省市区选择,三级联动
- Android省市县三级联动 真实项目抽出 调用只需3行代码
- 高仿iOS 滚轮实现 省市区 城市选择三级联动
- Android省市区三级联动滚轮控件,使用本地数据库数据
- Android中使用开源框架Citypickerview实现省市区三级联动选择
- Android中使用开源框架Citypickerview实现省市区三级联动选择
- 高仿iOS 滚轮实现 省市区 城市选择三级联动,无需自己配置省市区域的数据
