Android Telephony分析(七) ---- 接口扩展(异步转同步)
2016-08-12 10:15
513 查看
本文是基于上一篇《Android Telephony分析(六) —- 接口扩展(实践篇)》来写的。
上一篇介绍的接口扩展的方法需要实现两部分代码:
1. 从APP至RIL,发送请求;
2. 从RIL至APP,上报结果。
Created with Raphaël 2.1.0APPAPPTelephonyManagerTelephonyManagerPhonePhoneRILRIL发送Requestmodem处理返回结果返回结果
由于这是一个异步请求,所以两部分流程都不能少,导致流程过于复杂。
而本文的目的就是为了将异步请求转换成同步请求,节省第二部分“上报结果”的流程,从而简化整个接口扩展的流程和代码量。(当然,虽然《Android Telephony分析(六) —- 接口扩展(实践篇)》代码流程复杂了些,但是它综合较多的知识点,其自身的价值还是有的。)
本文来自http://blog.csdn.net/linyongan ,转载请务必注明出处。
假如现在Phone.java (frameworks\opt\telephony\src\java\com\android\internal\telephony)中已有两个可用的接口:
请注意,此时接口的返回值已不再是void。
在PhoneInterfaceManager.java (packages\services\telephony\src\com\android\phone)中实现该接口:
同时需要定义四个消息:
以及在内部类MainThreadHandler的handleMessage()方法中添加对这四个消息的处理:
在PhoneInterfaceManager.java中的代码是本文的核心。在sendRequest()方法中会进入死循环,调用object.wait()强行阻塞线程,直到modem返回结果上来后,object的notifyAll()才停止,最后直接把结果返回给APP,所以这就是将异步请求强行转换成同步的解决方案。
sendRequest()方法是android原生的,不用我们添加代码:
接着在TelephonyManager.java (frameworks\base\telephony\java\android\telephony)中封装Phone Service的方法:
整个过程的时序图如下:
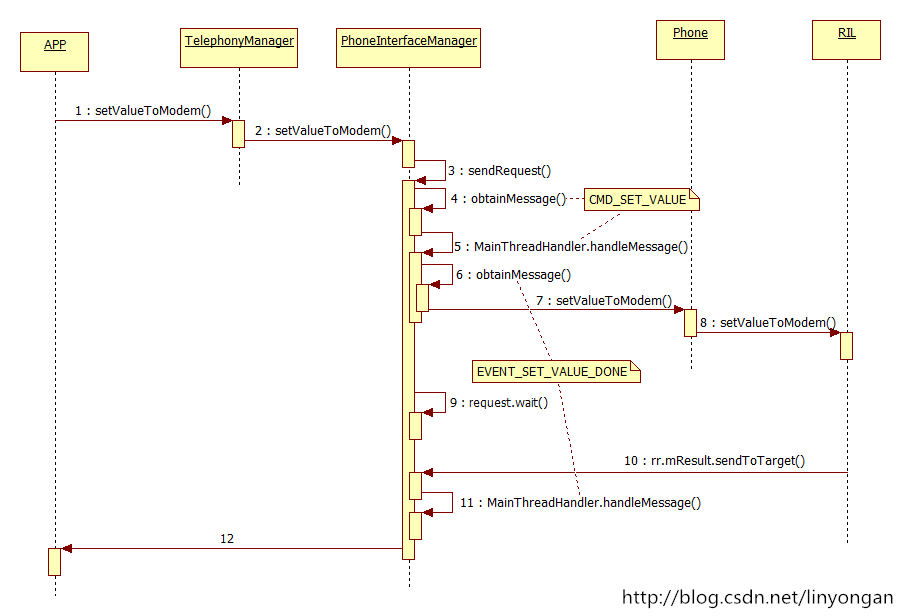
在APP侧来看,确实简单省事了很多,调用接口就可以马上得到返回值,但是有点需要注意的是,为了防止这种接口阻塞主线程,所以最好在子线程中调用这类接口。
void wait() :
导致线程进入等待状态,直到它被其他线程通过notify()或者notifyAll唤醒。该方法只能在同步方法中调用。如果当前线程不是锁的持有者,该方法抛出一个IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
void notifyAll() :
解除所有那些在该对象上调用wait方法的线程的阻塞状态。该方法只能在同步方法或同步块内部调用。如果当前线程不是锁的持有者,该方法抛出一个IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
上一篇介绍的接口扩展的方法需要实现两部分代码:
1. 从APP至RIL,发送请求;
2. 从RIL至APP,上报结果。
Created with Raphaël 2.1.0APPAPPTelephonyManagerTelephonyManagerPhonePhoneRILRIL发送Requestmodem处理返回结果返回结果
由于这是一个异步请求,所以两部分流程都不能少,导致流程过于复杂。
而本文的目的就是为了将异步请求转换成同步请求,节省第二部分“上报结果”的流程,从而简化整个接口扩展的流程和代码量。(当然,虽然《Android Telephony分析(六) —- 接口扩展(实践篇)》代码流程复杂了些,但是它综合较多的知识点,其自身的价值还是有的。)
本文来自http://blog.csdn.net/linyongan ,转载请务必注明出处。
1. 具体的代码实现
1.1 扩展CommandsInterface接口
同《Android Telephony分析(六) —- 接口扩展(实践篇)》1.1小节。1.2 扩展PhoneInternalInterface接口
同《Android Telephony分析(六) —- 接口扩展(实践篇)》1.2小节。假如现在Phone.java (frameworks\opt\telephony\src\java\com\android\internal\telephony)中已有两个可用的接口:
@Override
public void setValueToModem(int input,Message resp){
mCi.setValueToModem(input,resp);
}
@Override
public void getValueFromModem(Message resp){
mCi.getValueFromModem(resp);
}1.3 扩展ITelephony接口
先在ITelephony.aidl(frameworks\base\telephony\java\com\android\internal\telephony)中新增接口:boolean setValueToModem (int input); String getValueFromModem();
请注意,此时接口的返回值已不再是void。
在PhoneInterfaceManager.java (packages\services\telephony\src\com\android\phone)中实现该接口:
@Override
public String getValueFromModem() {
//本小节的最后会讲解sendRequest()方法
String value = (String)sendRequest(CMD_GET_VALUE,null);
return value;
}
@Override
public boolean setValueToModem(int input) {
Boolean success = (Boolean)sendRequest(CMD_SET_VALUE,input);
return success;
}同时需要定义四个消息:
private static final int CMD_GET_VALUE = 100; private static final int EVENT_GET_VALUE_DONE = 101; private static final int CMD_SET_VALUE = 102; private static final int EVENT_SET_VALUE_DONE = 103;
以及在内部类MainThreadHandler的handleMessage()方法中添加对这四个消息的处理:
//发送get请求时的处理
case CMD_GET_VALUE:
request = (MainThreadRequest) msg.obj;
//将在sendRequest()方法中创建的MainThreadRequest对象封装进新的Message中。
onCompleted = obtainMessage(EVENT_GET_VALUE_DONE, request);
//在这里调用Phone中的接口
mPhone.getValueFromModem(onCompleted);
break;
//对于get请求modem返回结果的处理
case EVENT_GET_VALUE_DONE:
ar = (AsyncResult) msg.obj;
//取出发送请求时创建的MainThreadRequest对象
request = (MainThreadRequest) ar.userObj;
//如果没有出现异常且返回的结果不为空
if (ar.exception == null && ar.result != null) {
request.result = ar.result;// String
} else {
//get请求出现异常,返回默认值
request.result = "";
if (ar.result == null) {
loge("getValueFromModem: Empty response");
} else if (ar.exception instanceof CommandException) {
loge("getValueFromModem: CommandException: " +
ar.exception);
} else {
loge("getValueFromModem: Unknown exception");
}
}
synchronized (request) {
//唤醒所有正在等待该对象的线程,退出wait的状态
request.notifyAll();
}
break;
//get请求,同理
case CMD_SET_VALUE:
request = (MainThreadRequest) msg.obj;
onCompleted = obtainMessage(EVENT_SET_VALUE_DONE, request);
mPhone.setValueToModem((Integer) request.argument, onCompleted);
break;
case EVENT_SET_VALUE_DONE:
ar = (AsyncResult) msg.obj;
request = (MainThreadRequest) ar.userObj;
if (ar.exception == null) {
request.result = true;
} else {
request.result = false;
if (ar.exception instanceof CommandException) {
loge("setValueToModem: CommandException: " + ar.exception);
} else {
loge("setValueToModem: Unknown exception");
}
}
synchronized (request) {
request.notifyAll();
}
break;在PhoneInterfaceManager.java中的代码是本文的核心。在sendRequest()方法中会进入死循环,调用object.wait()强行阻塞线程,直到modem返回结果上来后,object的notifyAll()才停止,最后直接把结果返回给APP,所以这就是将异步请求强行转换成同步的解决方案。
sendRequest()方法是android原生的,不用我们添加代码:
/**
* Posts the specified command to be executed on the main thread,
* waits for the request to complete, and returns the result.
*/
private Object sendRequest(int command, Object argument, Integer subId) {
if (Looper.myLooper() == mMainThreadHandler.getLooper()) {
throw new RuntimeException("This method will deadlock if called from the main thread.");
}
//创建Request对象
MainThreadRequest request = new MainThreadRequest(argument, subId);
Message msg = mMainThreadHandler.obtainMessage(command, request);
msg.sendToTarget();
//锁住request对象
synchronized (request) {
//进入死循环
while (request.result == null) {
try {
//让线程进入等待状态,直到它被notifyAll唤醒
request.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//就算异常也不退出,不return。
}
}
}
return request.result;
}
//其中MainThreadRequest只是一个普通的内部类,不是线程。
//所以上面request.wait()调用的时Object类wait()方法。
private static final class MainThreadRequest {
/** The argument to use for the request */
public Object argument;
/** The result of the request that is run on the main thread */
public Object result;
// The subscriber id that this request applies to. Defaults to
// SubscriptionManager.INVALID_SUBSCRIPTION_ID
public Integer subId = SubscriptionManager.INVALID_SUBSCRIPTION_ID;
public MainThreadRequest(Object argument) {
this.argument = argument;
}
public MainThreadRequest(Object argument, Integer subId) {
this.argument = argument;
if (subId != null) {
this.subId = subId;
}
}
}接着在TelephonyManager.java (frameworks\base\telephony\java\android\telephony)中封装Phone Service的方法:
/**@hide*/
public String getValueFromModem() {
try {
ITelephony telephony = getITelephony();
if (telephony != null)
return telephony.getValueFromModem();
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
Rlog.e(TAG, "getValueFromModem RemoteException", ex);
} catch (NullPointerException ex) {
Rlog.e(TAG, "getValueFromModem NPE", ex);
}
return "";
}
/**@hide*/
public boolean setValueToModem(int input) {
try {
ITelephony telephony = getITelephony();
if (telephony != null)
return telephony.setValueToModem(input);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
Rlog.e(TAG, "setValueToModem RemoteException", ex);
} catch (NullPointerException ex) {
Rlog.e(TAG, "setValueToModem NPE", ex);
}
return false;
}整个过程的时序图如下:

2. APP如何使用接口
在APP中可以这样调用并调试接口://set值 boolean setResult = TelephonyManager.getDefault().setValueToModem(1); //get值 String getResult = TelephonyManager.getDefault().getValueToModem();
在APP侧来看,确实简单省事了很多,调用接口就可以马上得到返回值,但是有点需要注意的是,为了防止这种接口阻塞主线程,所以最好在子线程中调用这类接口。
3. 总结
将异步请求转换成同步请求,紧紧依赖着Object类的wait和notifyAll方法才能实现。当然Android代码中不仅仅只有PhoneInterfaceManager.java这个地方使用了这种方法,高通也实现了类似的代码提供API给APP侧调用,进而可以动态修改某些NV的值,这里只能点到为止。最后附上wait和notifyAll方法的详解:void wait() :
导致线程进入等待状态,直到它被其他线程通过notify()或者notifyAll唤醒。该方法只能在同步方法中调用。如果当前线程不是锁的持有者,该方法抛出一个IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
void notifyAll() :
解除所有那些在该对象上调用wait方法的线程的阻塞状态。该方法只能在同步方法或同步块内部调用。如果当前线程不是锁的持有者,该方法抛出一个IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
相关文章推荐
- 使用C++实现JNI接口需要注意的事项
- Android IPC进程间通讯机制
- Android Manifest 用法
- [转载]Activity中ConfigChanges属性的用法
- Android之获取手机上的图片和视频缩略图thumbnails
- Android之使用Http协议实现文件上传功能
- Android学习笔记(二九):嵌入浏览器
- android string.xml文件中的整型和string型代替
- i-jetty环境搭配与编译
- android之定时器AlarmManager
- android wifi 无线调试
- Android Native 绘图方法
- Android java 与 javascript互访(相互调用)的方法例子
- android 代码实现控件之间的间距
- android FragmentPagerAdapter的“标准”配置
- Android"解决"onTouch和onClick的冲突问题
- android:installLocation简析
- android searchView的关闭事件
- SourceProvider.getJniDirectories
