Android中AsyncTask的使用与源码分析
2016-07-28 11:08
507 查看
本文参考Mr.Simple的:Android中AsyncTask的使用与源码分析
在Android中实现异步任务机制有两种方式,Handler和AsyncTask。
Handler模式需要为每一个任务创建一个新的线程,任务完成后通过Handler实例向UI线程发送消息,完成界面的更新,这种方式对于整个过程的控制比较精细,但也是有缺点的,例如代码相对臃肿,在多个任务同时执行时,不易对线程进行精确的控制。
为了简化操作,Android1.5提供了工具类android.os.AsyncTask,它使创建异步任务变得更加简单,不再需要编写任务线程和Handler实例即可完成相同的任务,但其内部也是使用Handler来传递消息,而且基于线程池。因此明显的AsyncTask比Handler要重量级。
先来看看AsyncTask的定义:
三种泛型类型分别代表“启动任务执行的输入参数”、“后台任务执行的进度”、“后台计算结果的类型”。在特定场合下,并不是所有类型都被使用,如果没有被使用,可以用java.lang.Void类型代替。
一个异步任务的执行一般包括以下几个步骤:
1.execute(Params... params),执行一个异步任务,需要我们在代码中调用此方法,触发异步任务的执行。
2.onPreExecute(),在execute(Params... params)被调用后立即执行,一般用来在执行后台任务前对UI做一些标记。
3.doInBackground(Params... params),在onPreExecute()完成后立即执行,用于执行较为费时的操作,此方法将接收输入参数和返回计算结果。在执行过程中可以调用publishProgress(Progress... values)来更新进度信息。
4.onProgressUpdate(Progress... values),在调用publishProgress(Progress... values)时,此方法被执行,直接将进度信息更新到UI组件上。
5.onPostExecute(Result result),当后台操作结束时,此方法将会被调用,计算结果将做为参数传递到此方法中,直接将结果显示到UI组件上。
在使用的时候,有几点需要格外注意:
1.异步任务的实例必须在UI线程中创建。
2.execute(Params... params)方法必须在UI线程中调用。
3.不能在doInBackground(Params... params)中更改UI组件的信息。
4.一个任务实例只能执行一次,如果执行第二次将会抛出异常。
一 、 AsyncTask的使用示例
接下来,我们来看看如何使用AsyncTask执行异步任务操作,我们先建立一个项目,结构如下:
结构相对简单一些,让我们先看看MainActivity.java的代码:
布局文件activity_main.xml:
因为需要访问网络,所以我们还需要在AndroidManifest.xml中加入访问网络的权限:
我们来看一下运行时的界面:
以上几个截图分别是初始界面、执行异步任务时界面、执行成功后界面、取消任务后界面。执行成功后,整个过程日志打印如下:
如果我们在执行任务时按下了"cancel"按钮,日志打印如下:
可以看到onCancelled()方法将会被调用,onPostExecute(Result result)方法将不再被调用。
二、 AsyncTask的实现基本原理
上面介绍了AsyncTask的基本应用,有些朋友也许会有疑惑,AsyncTask内部是怎么执行的呢,它执行的过程跟我们使用Handler又有什么区别呢?答案是:AsyncTask是对Thread+Handler良好的封装,在android.os.AsyncTask代码里仍然可以看到Thread和Handler的踪迹。下面就向大家详细介绍一下AsyncTask的执行原理。
我们先看一下AsyncTask的大纲视图:
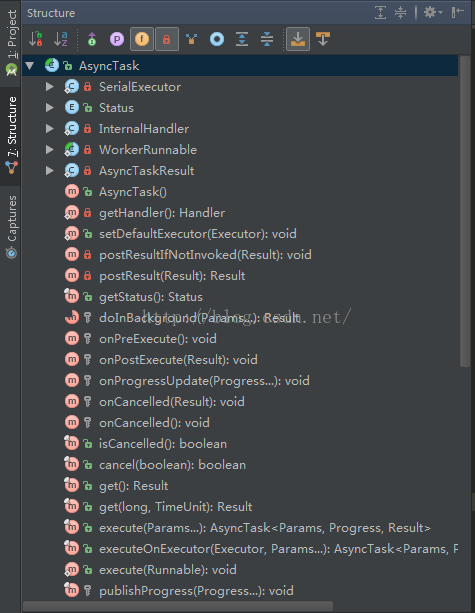
源代码如下:
我们可以看到关键几个步骤的方法都在其中。
1、doInBackground(Params... params)是一个抽象方法,我们继承AsyncTask时必须覆写此方法;
2、onPreExecute()、onProgressUpdate(Progress... values)、onPostExecute(Result result)、onCancelled()这几个方法体都是空的,我们需要的时候可以选择性的覆写它们;
3、publishProgress(Progress... values)是final修饰的,不能覆写,只能去调用,我们一般会在doInBackground(Params... params)中调用此方法来更新进度条;
4、另外,我们可以看到有一个Status的枚举类和getStatus()方法,Status枚举类代码段如下:
可以看到,AsyncTask的初始状态为PENDING,代表待定状态,RUNNING代表执行状态,FINISHED代表结束状态,这几种状态在AsyncTask一次生命周期内的很多地方被使用,非常重要。
执行任务execute(Params... params)
其实是调用executeOnExecutor(sDefaultExecutor, params)
这里涉及到三个变量:mWorker(保存了参数)、mFeature、exec(即传进来的sDefaultExecutor),我们先看一下他们的庐山真面目:
关于sDefaultExecutor, 它的初始值是AsyncTask的一个内部类SerialExecutor的实例,但如果是HONEYCOMB_MR1之前的版本,会重新设置为java.util.concurrent.ThradPoolExecutor的实例,用于管理线程的执行。代码如下:
mWorker实际上是AsyncTask的一个的抽象内部类的实现对象实例,它实现了Callable<Result>接口中的call()方法,代码如下:
而mFuture实际上是java.util.concurrent.FutureTask的实例,代码如下:
下面是它的FutureTask类的相关信息:
可以看到FutureTask是一个可以中途取消的用于异步计算的类。
回到exec.execute(mFeture),
进入到SerialExecutor的execute函数,如下:
r.run执行后,进入到FutureTask的run, 如下:
回调mWorker的call()方法以及调用在AsyncTask构造方法中创建的mFuture对象覆写了的done()方法。
现在再回过头看一下mWorker的call()方法和mFuture的done()方法:
/**
* Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.
*/
public AsyncTask() {
mWorker = new WorkerRunnable<Params, Result>() {
public Result call() throws Exception {
mTaskInvoked.set(true);
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND); //设置线程为后台线程
//noinspection unchecked
Result result = doInBackground(mParams); //调用doInBackground
Binder.flushPendingCommands();
return postResult(result); //发送处理结果消息
}
};
mFuture = new FutureTask<Result>(mWorker) {
@Override
protected void done() {
try {
postResultIfNotInvoked(get()); //如果还没发送处理结果消息,则发送
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("An error occurred while executing doInBackground()",
e.getCause());
} catch (CancellationException e) {
postResultIfNotInvoked(null);
}
}
};
}
在mWorker的call()中将线程设为后台线程,调用doInBackground并通过postResult(result)发送处理结果消息。
如果没有执行mWorker的postResult, 则在mFuture的done()方法里会通过postResultIfNotInvoked(get())发送处理结果消息。
再来看一下AsyncTask是如何处理消息的,代码如下:
private static Handler getHandler() {
synchronized (AsyncTask.class) {
if (sHandler == null) {
sHandler = new InternalHandler(); //AsyncTask内部类InternalHandler的实例
}
return sHandler;
}
}
private Result postResult(Result result) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Message message = getHandler().obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_RESULT,
new AsyncTaskResult<Result>(this, result));
message.sendToTarget();
return result;
}
处理消息的sHandler是AsyncTask内部类InternalHandler的实例,继承了Handler, 看一下代码:
private static class InternalHandler extends Handler {
public InternalHandler() {
super(Looper.getMainLooper());
}
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "RawUseOfParameterizedType"})
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
AsyncTaskResult<?> result = (AsyncTaskResult<?>) msg.obj;
switch (msg.what) {
case MESSAGE_POST_RESULT:
// There is only one result
result.mTask.finish(result.mData[0]); //onCancelled或者onPosstExecute
break;
case MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS:
result.mTask.onProgressUpdate(result.mData); //调用onProgressUpdate更新UI
break;
}
}
}
根据传进来的Message,如果是MESSAGE_POST_RESULT, 调用finish,如果是MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS, 调用onProgressUpdate更新UI。
是取消还是执行完成AsyncTask,就要看finish()方法了
private void finish(Result result) {
if (isCancelled()) {
onCancelled(result); //调用onCancelled取消AsyncTask
} else {
onPostExecute(result); //调用onPostExecute将结果传递回去
}
mStatus = Status.FINISHED;
}
概括来说,当我们调用execute(Params... params)方法后,execute方法会调用onPreExecute()方法,然后由ThreadPoolExecutor实例sExecutor执行一个FutureTask任务,这个过程中doInBackground(Params... params)将被调用,如果被开发者覆写的doInBackground(Params... params)方法中调用了publishProgress(Progress... values)方法,则通过InternalHandler实例sHandler发送一条MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS消息,更新进度,sHandler处理消息时onProgressUpdate(Progress...
values)方法将被调用;如果遇到异常,则发送一条MESSAGE_POST_CANCEL的消息,取消任务,sHandler处理消息时onCancelled()方法将被调用;如果执行成功,则发送一条MESSAGE_POST_RESULT的消息,显示结果,sHandler处理消息时onPostExecute(Result result)方法被调用。
经过上面的介绍,相信朋友们都已经认识到AsyncTask的本质了,它对Thread+Handler的良好封装,减少了开发者处理问题的复杂度,提高了开发效率,希望朋友们能多多体会一下。
在Android中实现异步任务机制有两种方式,Handler和AsyncTask。
Handler模式需要为每一个任务创建一个新的线程,任务完成后通过Handler实例向UI线程发送消息,完成界面的更新,这种方式对于整个过程的控制比较精细,但也是有缺点的,例如代码相对臃肿,在多个任务同时执行时,不易对线程进行精确的控制。
为了简化操作,Android1.5提供了工具类android.os.AsyncTask,它使创建异步任务变得更加简单,不再需要编写任务线程和Handler实例即可完成相同的任务,但其内部也是使用Handler来传递消息,而且基于线程池。因此明显的AsyncTask比Handler要重量级。
先来看看AsyncTask的定义:
public abstract class AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> {三种泛型类型分别代表“启动任务执行的输入参数”、“后台任务执行的进度”、“后台计算结果的类型”。在特定场合下,并不是所有类型都被使用,如果没有被使用,可以用java.lang.Void类型代替。
一个异步任务的执行一般包括以下几个步骤:
1.execute(Params... params),执行一个异步任务,需要我们在代码中调用此方法,触发异步任务的执行。
2.onPreExecute(),在execute(Params... params)被调用后立即执行,一般用来在执行后台任务前对UI做一些标记。
3.doInBackground(Params... params),在onPreExecute()完成后立即执行,用于执行较为费时的操作,此方法将接收输入参数和返回计算结果。在执行过程中可以调用publishProgress(Progress... values)来更新进度信息。
4.onProgressUpdate(Progress... values),在调用publishProgress(Progress... values)时,此方法被执行,直接将进度信息更新到UI组件上。
5.onPostExecute(Result result),当后台操作结束时,此方法将会被调用,计算结果将做为参数传递到此方法中,直接将结果显示到UI组件上。
在使用的时候,有几点需要格外注意:
1.异步任务的实例必须在UI线程中创建。
2.execute(Params... params)方法必须在UI线程中调用。
3.不能在doInBackground(Params... params)中更改UI组件的信息。
4.一个任务实例只能执行一次,如果执行第二次将会抛出异常。
一 、 AsyncTask的使用示例
接下来,我们来看看如何使用AsyncTask执行异步任务操作,我们先建立一个项目,结构如下:

结构相对简单一些,让我们先看看MainActivity.java的代码:
package com.silion.asynctaskdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import okhttp3.OkHttpClient;
import okhttp3.Request;
import okhttp3.Response;
import okhttp3.ResponseBody;
/**
* Created by silion on 2016/7/7.
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button btExecute;
private Button btCancel;
private ProgressBar pb;
private TextView tvContent;
private DownloadTask mTask;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btExecute = (Button) findViewById(R.id.execute);
btExecute.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
mTask = new DownloadTask();
mTask.execute("http://www.baidu.com");
btExecute.setEnabled(false);
btCancel.setEnabled(true);
}
});
btCancel = (Button
4000
) findViewById(R.id.cancel);
btCancel.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (mTask.getStatus() == AsyncTask.Status.RUNNING) {
mTask.cancel(true);
}
}
});
pb = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.progress_bar);
tvContent = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text_view);
}
public class DownloadTask extends AsyncTask<String, Integer, String> {
private OkHttpClient mClient;
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
Log.i("silion", "onPreExecute called");
tvContent.setText("loading...");
super.onPreExecute();
}
@Override
protected String doInBackground(String... params) {
Log.i("silion", "doInBackground called");
mClient = new OkHttpClient();
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
ResponseBody body = run(params[0]);
long total = body.contentLength();
is = body.byteStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int count = 0;
int length;
while ((length = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
baos.write(buf, 0, length);
count += length;
//调用publishProgress公布进度,最后onProgressUpdate方法将被执行
publishProgress((int) ((count / (float) total) * 100));
//为了演示进度,休眠500毫秒
Thread.sleep(100);
}
return new String(baos.toByteArray(), "utf-8");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (baos != null) {
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... progresses) {
Log.i("silion", "onProgressUpdate called");
pb.setProgress(progresses[0]);
tvContent.setText("longding..." + progresses[0] + "%");
super.onProgressUpdate(progresses);
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String result) {
Log.i("silion", "onPostExecute called");
tvContent.setText(result);
btExecute.setEnabled(true);
btCancel.setEnabled(false);
super.onPostExecute(result);
}
@Override
protected void onCancelled() {
Log.i("silion", "onCancelled called");
tvContent.setText("cancelled");
pb.setProgress(0);
btExecute.setEnabled(true);
btCancel.setEnabled(false);
super.onCancelled();
}
ResponseBody run(String url) throws IOException {
/**
* 把HttpClient替换成OKHttp之后,有时会获取不到content-length
* 经常抓包分析,发现服务器会随机的对下发的资源做GZip操作,而此时就没有相应的content-length
* 在Header中加入”Accept-Encoding”, “identity”,这样强迫服务器不走压缩。问题就得到了解决
*/
Request request = new Request.Builder().url(url).header("Accept-Encoding", "identity").build();
Response response = mClient.newCall(request).execute();
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
return response.body();
} else {
throw new IOException("Unexpected code" + response);
}
}
}
}布局文件activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <Button android:id="@+id/execute" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="execute"/> <Button android:id="@+id/cancel" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:enabled="false" android:text="cancel"/> <ProgressBar android:id="@+id/progress_bar" style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:max="100" android:progress="0"/> <ScrollView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/text_view" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </ScrollView> </LinearLayout>
因为需要访问网络,所以我们还需要在AndroidManifest.xml中加入访问网络的权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
我们来看一下运行时的界面:
以上几个截图分别是初始界面、执行异步任务时界面、执行成功后界面、取消任务后界面。执行成功后,整个过程日志打印如下:
07-27 15:36:40.941 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onPreExecute called 07-27 15:36:40.941 17249-3258/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ doInBackground called 07-27 15:36:43.341 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called ... 07-27 15:36:53.231 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:36:53.341 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onPostExecute called
如果我们在执行任务时按下了"cancel"按钮,日志打印如下:
07-27 15:38:29.861 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo D/ViewRootImpl﹕ ViewPostImeInputStage ACTION_DOWN 07-27 15:38:29.931 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onPreExecute called 07-27 15:38:29.931 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ doInBackground called 07-27 15:38:30.591 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:30.691 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:30.791 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:30.891 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:30.991 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:31.091 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:31.201 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:31.301 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:31.401 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:31.501 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:31.601 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:31.701 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:31.741 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo D/ViewRootImpl﹕ ViewPostImeInputStage ACTION_DOWN 07-27 15:38:31.801 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onProgressUpdate called 07-27 15:38:31.821 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ java.lang.InterruptedException 07-27 15:38:31.831 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ at java.lang.Thread.sleep(Native Method) 07-27 15:38:31.831 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ at java.lang.Thread.sleep(Thread.java:1031) 07-27 15:38:31.831 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ at java.lang.Thread.sleep(Thread.java:985) 07-27 15:38:31.831 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ at com.silion.asynctaskdemo.MainActivity$DownloadTask.doInBackground(MainActivity.java:90) 07-27 15:38:31.831 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ at com.silion.asynctaskdemo.MainActivity$DownloadTask.doInBackground(MainActivity.java:60) 07-27 15:38:31.831 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ at android.os.AsyncTask$2.call(AsyncTask.java:292) 07-27 15:38:31.831 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:237) 07-27 15:38:31.831 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ at android.os.AsyncTask$SerialExecutor$1.run(AsyncTask.java:231) 07-27 15:38:31.831 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1112) 07-27 15:38:31.831 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:587) 07-27 15:38:31.831 17249-4130/com.silion.asynctaskdemo W/System.err﹕ at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:818) 07-27 15:38:31.841 17249-17249/com.silion.asynctaskdemo I/silion﹕ onCancelled called
可以看到onCancelled()方法将会被调用,onPostExecute(Result result)方法将不再被调用。
二、 AsyncTask的实现基本原理
上面介绍了AsyncTask的基本应用,有些朋友也许会有疑惑,AsyncTask内部是怎么执行的呢,它执行的过程跟我们使用Handler又有什么区别呢?答案是:AsyncTask是对Thread+Handler良好的封装,在android.os.AsyncTask代码里仍然可以看到Thread和Handler的踪迹。下面就向大家详细介绍一下AsyncTask的执行原理。
我们先看一下AsyncTask的大纲视图:

源代码如下:
/* * Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package android.os; import android.annotation.MainThread; import android.annotation.WorkerThread; import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.CancellationException; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; /** * <p>AsyncTask enables proper and easy use of the UI thread. This class allows to * perform background operations and publish results on the UI thread without * having to manipulate threads and/or handlers.</p> * * <p>AsyncTask is designed to be a helper class around {@link Thread} and {@link Handler} * and does not constitute a generic threading framework. AsyncTasks should ideally be * used for short operations (a few seconds at the most.) If you need to keep threads * running for long periods of time, it is highly recommended you use the various APIs * provided by the <code>java.util.concurrent</code> package such as {@link Executor}, * {@link ThreadPoolExecutor} and {@link FutureTask}.</p> * * <p>An asynchronous task is defined by a computation that runs on a background thread and * whose result is published on the UI thread. An asynchronous task is defined by 3 generic * types, called <code>Params</code>, <code>Progress</code> and <code>Result</code>, * and 4 steps, called <code>onPreExecute</code>, <code>doInBackground</code>, * <code>onProgressUpdate</code> and <code>onPostExecute</code>.</p> * * <div class="special reference"> * <h3>Developer Guides</h3> * <p>For more information about using tasks and threads, read the * <a href="{@docRoot}guide/topics/fundamentals/processes-and-threads.html">Processes and * Threads</a> developer guide.</p> * </div> * * <h2>Usage</h2> * <p>AsyncTask must be subclassed to be used. The subclass will override at least * one method ({@link #doInBackground}), and most often will override a * second one ({@link #onPostExecute}.)</p> * * <p>Here is an example of subclassing:</p> * <pre class="prettyprint"> * private class DownloadFilesTask extends AsyncTask<URL, Integer, Long> { * protected Long doInBackground(URL... urls) { * int count = urls.length; * long totalSize = 0; * for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { * totalSize += Downloader.downloadFile(urls[i]); * publishProgress((int) ((i / (float) count) * 100)); * // Escape early if cancel() is called * if (isCancelled()) break; * } * return totalSize; * } * * protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... progress) { * setProgressPercent(progress[0]); * } * * protected void onPostExecute(Long result) { * showDialog("Downloaded " + result + " bytes"); * } * } * </pre> * * <p>Once created, a task is executed very simply:</p> * <pre class="prettyprint"> * new DownloadFilesTask().execute(url1, url2, url3); * </pre> * * <h2>AsyncTask's generic types</h2> * <p>The three types used by an asynchronous task are the following:</p> * <ol> * <li><code>Params</code>, the type of the parameters sent to the task upon * execution.</li> * <li><code>Progress</code>, the type of the progress units published during * the background computation.</li> * <li><code>Result</code>, the type of the result of the background * computation.</li> * </ol> * <p>Not all types are always used by an asynchronous task. To mark a type as unused, * simply use the type {@link Void}:</p> * &l 16531 t;pre> * private class MyTask extends AsyncTask<Void, Void, Void> { ... } * </pre> * * <h2>The 4 steps</h2> * <p>When an asynchronous task is executed, the task goes through 4 steps:</p> * <ol> * <li>{@link #onPreExecute()}, invoked on the UI thread before the task * is executed. This step is normally used to setup the task, for instance by * showing a progress bar in the user interface.</li> * <li>{@link #doInBackground}, invoked on the background thread * immediately after {@link #onPreExecute()} finishes executing. This step is used * to perform background computation that can take a long time. The parameters * of the asynchronous task are passed to this step. The result of the computation must * be returned by this step and will be passed back to the last step. This step * can also use {@link #publishProgress} to publish one or more units * of progress. These values are published on the UI thread, in the * {@link #onProgressUpdate} step.</li> * <li>{@link #onProgressUpdate}, invoked on the UI thread after a * call to {@link #publishProgress}. The timing of the execution is * undefined. This method is used to display any form of progress in the user * interface while the background computation is still executing. For instance, * it can be used to animate a progress bar or show logs in a text field.</li> * <li>{@link #onPostExecute}, invoked on the UI thread after the background * computation finishes. The result of the background computation is passed to * this step as a parameter.</li> * </ol> * * <h2>Cancelling a task</h2> * <p>A task can be cancelled at any time by invoking {@link #cancel(boolean)}. Invoking * this method will cause subsequent calls to {@link #isCancelled()} to return true. * After invoking this method, {@link #onCancelled(Object)}, instead of * {@link #onPostExecute(Object)} will be invoked after {@link #doInBackground(Object[])} * returns. To ensure that a task is cancelled as quickly as possible, you should always * check the return value of {@link #isCancelled()} periodically from * {@link #doInBackground(Object[])}, if possible (inside a loop for instance.)</p> * * <h2>Threading rules</h2> * <p>There are a few threading rules that must be followed for this class to * work properly:</p> * <ul> * <li>The AsyncTask class must be loaded on the UI thread. This is done * automatically as of {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#JELLY_BEAN}.</li> * <li>The task instance must be created on the UI thread.</li> * <li>{@link #execute} must be invoked on the UI thread.</li> * <li>Do not call {@link #onPreExecute()}, {@link #onPostExecute}, * {@link #doInBackground}, {@link #onProgressUpdate} manually.</li> * <li>The task can be executed only once (an exception will be thrown if * a second execution is attempted.)</li> * </ul> * * <h2>Memory observability</h2> * <p>AsyncTask guarantees that all callback calls are synchronized in such a way that the following * operations are safe without explicit synchronizations.</p> * <ul> * <li>Set member fields in the constructor or {@link #onPreExecute}, and refer to them * in {@link #doInBackground}. * <li>Set member fields in {@link #doInBackground}, and refer to them in * {@link #onProgressUpdate} and {@link #onPostExecute}. * </ul> * * <h2>Order of execution</h2> * <p>When first introduced, AsyncTasks were executed serially on a single background * thread. Starting with {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#DONUT}, this was changed * to a pool of threads allowing multiple tasks to operate in parallel. Starting with * {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#HONEYCOMB}, tasks are executed on a single * thread to avoid common application errors caused by parallel execution.</p> * <p>If you truly want parallel execution, you can invoke * {@link #executeOnExecutor(java.util.concurrent.Executor, Object[])} with * {@link #THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR}.</p> */ public abstract class AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> { private static final String LOG_TAG = "AsyncTask"; private static final int CPU_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = CPU_COUNT + 1; private static final int MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE = CPU_COUNT * 2 + 1; private static final int KEEP_ALIVE = 1; private static final ThreadFactory sThreadFactory = new ThreadFactory() { private final AtomicInteger mCount = new AtomicInteger(1); public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { return new Thread(r, "AsyncTask #" + mCount.getAndIncrement()); } }; private static final BlockingQueue<Runnable> sPoolWorkQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(128); /** * An {@link Executor} that can be used to execute tasks in parallel. */ public static final Executor THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR = new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE, TimeUnit.SECONDS, sPoolWorkQueue, sThreadFactory); /** * An {@link Executor} that executes tasks one at a time in serial * order. This serialization is global to a particular process. */ public static final Executor SERIAL_EXECUTOR = new SerialExecutor(); private static final int MESSAGE_POST_RESULT = 0x1; private static final int MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS = 0x2; private static volatile Executor sDefaultExecutor = SERIAL_EXECUTOR; private static InternalHandler sHandler; private final WorkerRunnable<Params, Result> mWorker; private final FutureTask<Result> mFuture; private volatile Status mStatus = Status.PENDING; private final AtomicBoolean mCancelled = new AtomicBoolean(); private final AtomicBoolean mTaskInvoked = new AtomicBoolean(); private static class SerialExecutor implements Executor { final ArrayDeque<Runnable> mTasks = new ArrayDeque<Runnable>(); Runnable mActive; public synchronized void execute(final Runnable r) { mTasks.offer(new Runnable() { public void run() { try { r.run(); } finally { scheduleNext(); } } }); if (mActive == null) { scheduleNext(); } } protected synchronized void scheduleNext() { if ((mActive = mTasks.poll()) != null) { THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR.execute(mActive); } } } /** * Indicates the current status of the task. Each status will be set only once * during the lifetime of a task. */ public enum Status { /** * Indicates that the task has not been executed yet. */ PENDING, /** * Indicates that the task is running. */ RUNNING, /** * Indicates that {@link AsyncTask#onPostExecute} has finished. */ FINISHED, } private static Handler getHandler() { synchronized (AsyncTask.class) { if (sHandler == null) { sHandler = new InternalHandler(); } return sHandler; } } /** @hide */ public static void setDefaultExecutor(Executor exec) { sDefaultExecutor = exec; } /** * Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread. */ public AsyncTask() { mWorker = new WorkerRunnable<Params, Result>() { public Result call() throws Exception { mTaskInvoked.set(true); Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND); //noinspection unchecked Result result = doInBackground(mParams); Binder.flushPendingCommands(); return postResult(result); } }; mFuture = new FutureTask<Result>(mWorker) { @Override protected void done() { try { postResultIfNotInvoked(get()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e); } catch (ExecutionException e) { throw new RuntimeException("An error occurred while executing doInBackground()", e.getCause()); } catch (CancellationException e) { postResultIfNotInvoked(null); } } }; } private void postResultIfNotInvoked(Result result) { final boolean wasTaskInvoked = mTaskInvoked.get(); if (!wasTaskInvoked) { postResult(result); } } private Result postResult(Result result) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Message message = getHandler().obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_RESULT, new AsyncTaskResult<Result>(this, result)); message.sendToTarget(); return result; } /** * Returns the current status of this task. * * @return The current status. */ public final Status getStatus() { return mStatus; } /** * Override this method to perform a computation on a background thread. The * specified parameters are the parameters passed to {@link #execute} * by the caller of this task. * * This method can call {@link #publishProgress} to publish updates * on the UI thread. * * @param params The parameters of the task. * * @return A result, defined by the subclass of this task. * * @see #onPreExecute() * @see #onPostExecute * @see #publishProgress */ @WorkerThread protected abstract Result doInBackground(Params... params); /** * Runs on the UI thread before {@link #doInBackground}. * * @see #onPostExecute * @see #doInBackground */ @MainThread protected void onPreExecute() { } /** * <p>Runs on the UI thread after {@link #doInBackground}. The * specified result is the value returned by {@link #doInBackground}.</p> * * <p>This method won't be invoked if the task was cancelled.</p> * * @param result The result of the operation computed by {@link #doInBackground}. * * @see #onPreExecute * @see #doInBackground * @see #onCancelled(Object) */ @SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"}) @MainThread protected void onPostExecute(Result result) { } /** * Runs on the UI thread after {@link #publishProgress} is invoked. * The specified values are the values passed to {@link #publishProgress}. * * @param values The values indicating progress. * * @see #publishProgress * @see #doInBackground */ @SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"}) @MainThread protected void onProgressUpdate(Progress... values) { } /** * <p>Runs on the UI thread after {@link #cancel(boolean)} is invoked and * {@link #doInBackground(Object[])} has finished.</p> * * <p>The default implementation simply invokes {@link #onCancelled()} and * ignores the result. If you write your own implementation, do not call * <code>super.onCancelled(result)</code>.</p> * * @param result The result, if any, computed in * {@link #doInBackground(Object[])}, can be null * * @see #cancel(boolean) * @see #isCancelled() */ @SuppressWarnings({"UnusedParameters"}) @MainThread protected void onCancelled(Result result) { onCancelled(); } /** * <p>Applications should preferably override {@link #onCancelled(Object)}. * This method is invoked by the default implementation of * {@link #onCancelled(Object)}.</p> * * <p>Runs on the UI thread after {@link #cancel(boolean)} is invoked and * {@link #doInBackground(Object[])} has finished.</p> * * @see #onCancelled(Object) * @see #cancel(boolean) * @see #isCancelled() */ @MainThread protected void onCancelled() { } /** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this task was cancelled before it completed * normally. If you are calling {@link #cancel(boolean)} on the task, * the value returned by this method should be checked periodically from * {@link #doInBackground(Object[])} to end the task as soon as possible. * * @return <tt>true</tt> if task was cancelled before it completed * * @see #cancel(boolean) */ public final boolean isCancelled() { return mCancelled.get(); } /** * <p>Attempts to cancel execution of this task. This attempt will * fail if the task has already completed, already been cancelled, * or could not be cancelled for some other reason. If successful, * and this task has not started when <tt>cancel</tt> is called, * this task should never run. If the task has already started, * then the <tt>mayInterruptIfRunning</tt> parameter determines * whether the thread executing this task should be interrupted in * an attempt to stop the task.</p> * * <p>Calling this method will result in {@link #onCancelled(Object)} being * invoked on the UI thread after {@link #doInBackground(Object[])} * returns. Calling this method guarantees that {@link #onPostExecute(Object)} * is never invoked. After invoking this method, you should check the * value returned by {@link #isCancelled()} periodically from * {@link #doInBackground(Object[])} to finish the task as early as * possible.</p> * * @param mayInterruptIfRunning <tt>true</tt> if the thread executing this * task should be interrupted; otherwise, in-progress tasks are allowed * to complete. * * @return <tt>false</tt> if the task could not be cancelled, * typically because it has already completed normally; * <tt>true</tt> otherwise * * @see #isCancelled() * @see #onCancelled(Object) */ public final boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { mCancelled.set(true); return mFuture.cancel(mayInterruptIfRunning); } /** * Waits if necessary for the computation to complete, and then * retrieves its result. * * @return The computed result. * * @throws CancellationException If the computation was cancelled. * @throws ExecutionException If the computation threw an exception. * @throws InterruptedException If the current thread was interrupted * while waiting. */ public final Result get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { return mFuture.get(); } /** * Waits if necessary for at most the given time for the computation * to complete, and then retrieves its result. * * @param timeout Time to wait before cancelling the operation. * @param unit The time unit for the timeout. * * @return The computed result. * * @throws CancellationException If the computation was cancelled. * @throws ExecutionException If the computation threw an exception. * @throws InterruptedException If the current thread was interrupted * while waiting. * @throws TimeoutException If the wait timed out. */ public final Result get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException { return mFuture.get(timeout, unit); } /** * Executes the task with the specified parameters. The task returns * itself (this) so that the caller can keep a reference to it. * * <p>Note: this function schedules the task on a queue for a single background * thread or pool of threads depending on the platform version. When first * introduced, AsyncTasks were executed serially on a single background thread. * Starting with {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#DONUT}, this was changed * to a pool of threads allowing multiple tasks to operate in parallel. Starting * {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#HONEYCOMB}, tasks are back to being * executed on a single thread to avoid common application errors caused * by parallel execution. If you truly want parallel execution, you can use * the {@link #executeOnExecutor} version of this method * with {@link #THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR}; however, see commentary there for warnings * on its use. * * <p>This method must be invoked on the UI thread. * * @param params The parameters of the task. * * @return This instance of AsyncTask. * * @throws IllegalStateException If {@link #getStatus()} returns either * {@link AsyncTask.Status#RUNNING} or {@link AsyncTask.Status#FINISHED}. * * @see #executeOnExecutor(java.util.concurrent.Executor, Object[]) * @see #execute(Runnable) */ @MainThread public final AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> execute(Params... params) { return executeOnExecutor(sDefaultExecutor, params); } /** * Executes the task with the specified parameters. The task returns * itself (this) so that the caller can keep a reference to it. * * <p>This method is typically used with {@link #THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR} to * allow multiple tasks to run in parallel on a pool of threads managed by * AsyncTask, however you can also use your own {@link Executor} for custom * behavior. * * <p><em>Warning:</em> Allowing multiple tasks to run in parallel from * a thread pool is generally <em>not</em> what one wants, because the order * of their operation is not defined. For example, if these tasks are used * to modify any state in common (such as writing a file due to a button click), * there are no guarantees on the order of the modifications. * Without careful work it is possible in rare cases for the newer version * of the data to be over-written by an older one, leading to obscure data * loss and stability issues. Such changes are best * executed in serial; to guarantee such work is serialized regardless of * platform version you can use this function with {@link #SERIAL_EXECUTOR}. * * <p>This method must be invoked on the UI thread. * * @param exec The executor to use. {@link #THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR} is available as a * convenient process-wide thread pool for tasks that are loosely coupled. * @param params The parameters of the task. * * @return This instance of AsyncTask. * * @throws IllegalStateException If {@link #getStatus()} returns either * {@link AsyncTask.Status#RUNNING} or {@link AsyncTask.Status#FINISHED}. * * @see #execute(Object[]) */ @MainThread public final AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> executeOnExecutor(Executor exec, Params... params) { if (mStatus != Status.PENDING) { switch (mStatus) { case RUNNING: throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:" + " the task is already running."); case FINISHED: throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:" + " the task has already been executed " + "(a task can be executed only once)"); } } mStatus = Status.RUNNING; onPreExecute(); mWorker.mParams = params; exec.execute(mFuture); return this; } /** * Convenience version of {@link #execute(Object...)} for use with * a simple Runnable object. See {@link #execute(Object[])} for more * information on the order of execution. * * @see #execute(Object[]) * @see #executeOnExecutor(java.util.concurrent.Executor, Object[]) */ @MainThread public static void execute(Runnable runnable) { sDefaultExecutor.execute(runnable); } /** * This method can be invoked from {@link #doInBackground} to * publish updates on the UI thread while the background computation is * still running. Each call to this method will trigger the execution of * {@link #onProgressUpdate} on the UI thread. * * {@link #onProgressUpdate} will not be called if the task has been * canceled. * * @param values The progress values to update the UI with. * * @see #onProgressUpdate * @see #doInBackground */ @WorkerThread protected final void publishProgress(Progress... values) { if (!isCancelled()) { getHandler().obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS, new AsyncTaskResult<Progress>(this, values)).sendToTarget(); } } private void finish(Result result) { if (isCancelled()) { onCancelled(result); } else { onPostExecute(result); } mStatus = Status.FINISHED; } private static class InternalHandler extends Handler { public InternalHandler() { super(Looper.getMainLooper()); } @SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "RawUseOfParameterizedType"}) @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { AsyncTaskResult<?> result = (AsyncTaskResult<?>) msg.obj; switch (msg.what) { case MESSAGE_POST_RESULT: // There is only one result result.mTask.finish(result.mData[0]); break; case MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS: result.mTask.onProgressUpdate(result.mData); break; } } } private static abstract class WorkerRunnable<Params, Result> implements Callable<Result> { Params[] mParams; } @SuppressWarnings({"RawUseOfParameterizedType"}) private static class AsyncTaskResult<Data> { final AsyncTask mTask; final Data[] mData; AsyncTaskResult(AsyncTask task, Data... data) { mTask = task; mData = data; } } }
我们可以看到关键几个步骤的方法都在其中。
1、doInBackground(Params... params)是一个抽象方法,我们继承AsyncTask时必须覆写此方法;
2、onPreExecute()、onProgressUpdate(Progress... values)、onPostExecute(Result result)、onCancelled()这几个方法体都是空的,我们需要的时候可以选择性的覆写它们;
3、publishProgress(Progress... values)是final修饰的,不能覆写,只能去调用,我们一般会在doInBackground(Params... params)中调用此方法来更新进度条;
4、另外,我们可以看到有一个Status的枚举类和getStatus()方法,Status枚举类代码段如下:
private volatile Status mStatus = Status.PENDING; //初始状态
/**
* Indicates the current status of the task. Each status will be set only once
* during the lifetime of a task.
*/
public enum Status {
/**
* Indicates that the task has not been executed yet.
*/
PENDING,
/**
* Indicates that the task is running.
*/
RUNNING,
/**
* Indicates that {@link AsyncTask#onPostExecute} has finished.
*/
FINISHED,
}
/**
* Returns the current status of this task.
*
* @return The current status.
*/
public final Status getStatus() {
return mStatus;
}可以看到,AsyncTask的初始状态为PENDING,代表待定状态,RUNNING代表执行状态,FINISHED代表结束状态,这几种状态在AsyncTask一次生命周期内的很多地方被使用,非常重要。
执行任务execute(Params... params)
/**
* Executes the task with the specified parameters. The task returns
* itself (this) so that the caller can keep a reference to it.
*
* <p>Note: this function schedules the task on a queue for a single background
* thread or pool of threads depending on the platform version. When first
* introduced, AsyncTasks were executed serially on a single background thread.
* Starting with {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#DONUT}, this was changed
* to a pool of threads allowing multiple tasks to operate in parallel. Starting
* {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#HONEYCOMB}, tasks are back to being
* executed on a single thread to avoid common application errors caused
* by parallel execution. If you truly want parallel execution, you can use
* the {@link #executeOnExecutor} version of this method
* with {@link #THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR}; however, see commentary there for warnings
* on its use.
*
* <p>This method must be invoked on the UI thread.
*
* @param params The parameters of the task.
*
* @return This instance of AsyncTask.
*
* @throws IllegalStateException If {@link #getStatus()} returns either
* {@link AsyncTask.Status#RUNNING} or {@link AsyncTask.Status#FINISHED}.
*
* @see #executeOnExecutor(java.util.concurrent.Executor, Object[])
* @see #execute(Runnable)
*/
@MainThread
public final AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> execute(Params... params) {
return executeOnExecutor(sDefaultExecutor, params);
}其实是调用executeOnExecutor(sDefaultExecutor, params)
/**
* Executes the task with the specified parameters. The task returns
* itself (this) so that the caller can keep a reference to it.
*
* <p>This method is typically used with {@link #THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR} to
* allow multiple tasks to run in parallel on a pool of threads managed by
* AsyncTask, however you can also use your own {@link Executor} for custom
* behavior.
*
* <p><em>Warning:</em> Allowing multiple tasks to run in parallel from
* a thread pool is generally <em>not</em> what one wants, because the order
* of their operation is not defined. For example, if these tasks are used
* to modify any state in common (such as writing a file due to a button click),
* there are no guarantees on the order of the modifications.
* Without careful work it is possible in rare cases for the newer version
* of the data to be over-written by an older one, leading to obscure data
* loss and stability issues. Such changes are best
* executed in serial; to guarantee such work is serialized regardless of
* platform version you can use this function with {@link #SERIAL_EXECUTOR}.
*
* <p>This method must be invoked on the UI thread.
*
* @param exec The executor to use. {@link #THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR} is available as a
* convenient process-wide thread pool for tasks that are loosely coupled.
* @param params The parameters of the task.
*
* @return This instance of AsyncTask.
*
* @throws IllegalStateException If {@link #getStatus()} returns either
* {@link AsyncTask.Status#RUNNING} or {@link AsyncTask.Status#FINISHED}.
*
* @see #execute(Object[])
*/
@MainThread
public final AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> executeOnExecutor(Executor exec,
Params... params) {
if (mStatus != Status.PENDING) {
switch (mStatus) {
case RUNNING:
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
+ " the task is already running.");
case FINISHED:
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"
+ " the task has already been executed "
+ "(a task can be executed only once)");
}
}
mStatus = Status.RUNNING;
onPreExecute(); //调用onPreExecute,<span style="font-family: Arial; font-size: 14px; line-height: 26px;">在执行后台任务前对UI做一些初始化或标记</span>
mWorker.mParams = params;
exec.execute(mFuture);
return this;
}这里涉及到三个变量:mWorker(保存了参数)、mFeature、exec(即传进来的sDefaultExecutor),我们先看一下他们的庐山真面目:
关于sDefaultExecutor, 它的初始值是AsyncTask的一个内部类SerialExecutor的实例,但如果是HONEYCOMB_MR1之前的版本,会重新设置为java.util.concurrent.ThradPoolExecutor的实例,用于管理线程的执行。代码如下:
/**
* An {@link Executor} that executes tasks one at a time in serial
* order. This serialization is global to a particular process.
*/
public static final Executor SERIAL_EXECUTOR = new SerialExecutor();
private static volatile Executor sDefaultExecutor = SERIAL_EXECUTOR;
private static class SerialExecutor implements Executor {
final ArrayDeque<Runnable> mTasks = new ArrayDeque<Runnable>();
Runnable mActive;
public synchronized void execute(final Runnable r) {
mTasks.offer(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
r.run();
} finally {
scheduleNext();
}
}
});
if (mActive == null) {
scheduleNext();
}
}
protected synchronized void scheduleNext() {
if ((mActive = mTasks.poll()) != null) {
THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR.execute(mActive);
}
}
}
// If the app is Honeycomb MR1 or earlier, switch its AsyncTask
// implementation to use the pool executor. Normally, we use the
// serialized executor as the default. This has to happen in the
// main thread so the main looper is set right.
if (data.appInfo.targetSdkVersion <= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB_MR1) {
AsyncTask.setDefaultExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR);
}mWorker实际上是AsyncTask的一个的抽象内部类的实现对象实例,它实现了Callable<Result>接口中的call()方法,代码如下:
private static abstract class WorkerRunnable<Params, Result> implements Callable<Result> {
Params[] mParams;
}
public AsyncTask() {
mWorker = new WorkerRunnable<Params, Result>() {
public Result call() throws Exception {
mTaskInvoked.set(true);
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
//noinspection unchecked
Result result = doInBackground(mParams);
Binder.flushPendingCommands();
return postResult(result);
}
};
...
}而mFuture实际上是java.util.concurrent.FutureTask的实例,代码如下:
/**
* Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.
*/
public AsyncTask() {
...
mFuture = new FutureTask<Result>(mWorker) {
@Override
protected void done() {
try {
postResultIfNotInvoked(get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("An error occurred while executing doInBackground()",
e.getCause());
} catch (CancellationException e) {
postResultIfNotInvoked(null);
}
}
};
}下面是它的FutureTask类的相关信息:
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> {
...
}
/**
* A {@link Future} that is {@link Runnable}. Successful execution of
* the {@code run} method causes completion of the {@code Future}
* and allows access to its results.
* @see FutureTask
* @see Executor
* @since 1.6
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> The result type returned by this Future's {@code get} method
*/
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {
/**
* Sets this Future to the result of its computation
* unless it has been cancelled.
*/
void run();
}可以看到FutureTask是一个可以中途取消的用于异步计算的类。
回到exec.execute(mFeture),
进入到SerialExecutor的execute函数,如下:
final ArrayDeque<Runnable> mTasks = new ArrayDeque<Runnable>(); //双队列列表
public synchronized void execute(final Runnable r) {
mTasks.offer(new Runnable() { //添加到队列,参考offer的注释Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque.
public void run() {
try {
r.run();
} finally {
scheduleNext();
}
}
});
if (mActive == null) {
scheduleNext();
}
}在SerialExecutor的execute主要是将异步任务mFuture(r.run)加入到将要执行的双队列列表。r.run执行后,进入到FutureTask的run, 如下:
/**
* Creates a {@code FutureTask} that will, upon running, execute the
* given {@code Callable}.
*
* @param callable the callable task
* @throws NullPointerException if the callable is null
*/
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!U.compareAndSwapObject(this, RUNNER, null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable; //就是在AsyncTask()初始化mFuture传入的mWorker
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call(); //调用mWorker的call(),并在call中才真正调用了doInBackground函数,至此线程真正启动了
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result); //最后会调用在AsyncTask构造方法中创建的mFuture对象覆写了的done()方法
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}回调mWorker的call()方法以及调用在AsyncTask构造方法中创建的mFuture对象覆写了的done()方法。
现在再回过头看一下mWorker的call()方法和mFuture的done()方法:
/**
* Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.
*/
public AsyncTask() {
mWorker = new WorkerRunnable<Params, Result>() {
public Result call() throws Exception {
mTaskInvoked.set(true);
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND); //设置线程为后台线程
//noinspection unchecked
Result result = doInBackground(mParams); //调用doInBackground
Binder.flushPendingCommands();
return postResult(result); //发送处理结果消息
}
};
mFuture = new FutureTask<Result>(mWorker) {
@Override
protected void done() {
try {
postResultIfNotInvoked(get()); //如果还没发送处理结果消息,则发送
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("An error occurred while executing doInBackground()",
e.getCause());
} catch (CancellationException e) {
postResultIfNotInvoked(null);
}
}
};
}
在mWorker的call()中将线程设为后台线程,调用doInBackground并通过postResult(result)发送处理结果消息。
如果没有执行mWorker的postResult, 则在mFuture的done()方法里会通过postResultIfNotInvoked(get())发送处理结果消息。
再来看一下AsyncTask是如何处理消息的,代码如下:
private static Handler getHandler() {
synchronized (AsyncTask.class) {
if (sHandler == null) {
sHandler = new InternalHandler(); //AsyncTask内部类InternalHandler的实例
}
return sHandler;
}
}
private Result postResult(Result result) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Message message = getHandler().obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_RESULT,
new AsyncTaskResult<Result>(this, result));
message.sendToTarget();
return result;
}
处理消息的sHandler是AsyncTask内部类InternalHandler的实例,继承了Handler, 看一下代码:
private static class InternalHandler extends Handler {
public InternalHandler() {
super(Looper.getMainLooper());
}
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "RawUseOfParameterizedType"})
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
AsyncTaskResult<?> result = (AsyncTaskResult<?>) msg.obj;
switch (msg.what) {
case MESSAGE_POST_RESULT:
// There is only one result
result.mTask.finish(result.mData[0]); //onCancelled或者onPosstExecute
break;
case MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS:
result.mTask.onProgressUpdate(result.mData); //调用onProgressUpdate更新UI
break;
}
}
}
根据传进来的Message,如果是MESSAGE_POST_RESULT, 调用finish,如果是MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS, 调用onProgressUpdate更新UI。
是取消还是执行完成AsyncTask,就要看finish()方法了
private void finish(Result result) {
if (isCancelled()) {
onCancelled(result); //调用onCancelled取消AsyncTask
} else {
onPostExecute(result); //调用onPostExecute将结果传递回去
}
mStatus = Status.FINISHED;
}
概括来说,当我们调用execute(Params... params)方法后,execute方法会调用onPreExecute()方法,然后由ThreadPoolExecutor实例sExecutor执行一个FutureTask任务,这个过程中doInBackground(Params... params)将被调用,如果被开发者覆写的doInBackground(Params... params)方法中调用了publishProgress(Progress... values)方法,则通过InternalHandler实例sHandler发送一条MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS消息,更新进度,sHandler处理消息时onProgressUpdate(Progress...
values)方法将被调用;如果遇到异常,则发送一条MESSAGE_POST_CANCEL的消息,取消任务,sHandler处理消息时onCancelled()方法将被调用;如果执行成功,则发送一条MESSAGE_POST_RESULT的消息,显示结果,sHandler处理消息时onPostExecute(Result result)方法被调用。
经过上面的介绍,相信朋友们都已经认识到AsyncTask的本质了,它对Thread+Handler的良好封装,减少了开发者处理问题的复杂度,提高了开发效率,希望朋友们能多多体会一下。
相关文章推荐
- Android AsyncTask源码分析
- Android中异步类AsyncTask用法总结
- Android中AsyncTask的用法实例分享
- Android的异步任务AsyncTask详解
- Android使用AsyncTask实现多线程下载的方法
- 简介Android 中的AsyncTask
- Android AsyncTask完全解析 带你从源码的角度彻底理解
- Android用HandlerThread模拟AsyncTask功能(ThreadTask)
- Android 中使用 AsyncTask 异步读取网络图片
- Android中通过AsyncTask类来制作炫酷进度条的实例教程
- Android中AsyncTask异步任务使用详细实例(一)
- asynctask的用法详解
- Android中AsyncTask详细介绍
- Android中AsyncTask与handler用法实例分析
- Android利用AsyncTask异步类实现网页内容放大缩小
- Android通过Handler与AsyncTask两种方式动态更新ListView(附源码)
- 详解Android App中的AsyncTask异步任务执行方式
- Android开发笔记之:AsyncTask的应用详解
- android教程之使用asynctask在后台运行耗时任务
- 详解Android中用于线程处理的AsyncTask类的用法及源码
