Web---演示Servlet的相关类、表单多参数接收、文件上传简单入门
2016-07-22 13:23
585 查看
说明:
Servlet的其他相关类:ServletConfig – 代表Servlet的初始化配置参数。
ServletContext – 代表整个Web项目。
ServletRequest – 代表用户的请求。
ServletResponse – 代表用户的响应。
本篇博客讲解:
ServletRequest – 代表用户的请求。
ServletResponse – 代表用户的响应。
表单中的多选框参数接收。
文件的上传技术。
ServletRequest :
ServletRequest 和 ServletResponse 差不多。一个代表用户的请求,一个代表用户的响应!service方法中的两个重要参数。
ServletRequest – 用接收用户的请求。它的作用是:
可获取请求头信息。
可设置请请求的字符编码。
可获得用户传递的参数。Post或get。
可获取远程(即访问者)的IP地址。
可获取输入流,如用户上传文件、相片等。
它的一个子接口:javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest
ServletResponse – 用于向用户返回数据。
设置响应类型- contentType
设置编码-setCharacterEncoding
获取输出流。
它的一个子接口:javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse
index.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> </head> <body> <h1>Request和Response的用法演示</h1> <!-- 通过requset.getContextPath()可以把项目的根目录(也就是项目名)写活 --> <form action="<%= request.getContextPath() %>/requestDemo" method="get" > name:<input type="text" name="name"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form> </body> </html>
web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app version="3.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"> <display-name></display-name> <servlet> <description>Request和Response的用法演示</description> <servlet-name>RequestDemo</servlet-name> <servlet-class>cn.hncu.servlets.RequestDemo</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>RequestDemo</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/requestDemo</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> </web-app>
RequestDemo.java
package cn.hncu.servlets;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Random;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* @author 陈浩翔
*
* 2016-7-22
*/
public class RequestDemo extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//告诉浏览器我响应的是什么类型的文件,编码是什么
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\">");
out.println("<HTML>");
out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>A Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>");
out.println(" <BODY>");
out.print("request:"+request+"<br/>");
Random r = new Random(new Date().getTime());
int a = r.nextInt(200);//获取一个[0,200)的随机整数
//每一次请求,request对象是新的(之前放进去的属性是属于另一个request对象),因此这里读取的属性是null.这个只能在web内部传递!
//如果是转发,那么request对象的共享的,也就是同一个,在这种情况下,里面的属性可以共用
if(request.getAttribute("name")==null){
System.out.println("放入:"+a);
request.setAttribute("name", a);
}
out.print("<br/>"+request.getAttribute("name"));
//注意:setCharacterEncoding()--该方法只对post方式有效,因为它只设置请求体(正文)中内容的读取编码
//以下演示setCharacterEncoding()和getCharacterEncoding()
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");//设置用request对象中读取信息的编码格式--即下面的是按照什么编码格式把数据读取出来
//有时,我们使用转发,就需要在别的处理类中读取之前所设的编码
//String charset = request.getCharacterEncoding();//这里肯定是utf-8了,刚刚我们设了。
//我们如果没有设编码,则默认(Toncat)是(ISO8859-1),返回的是null.
//System.out.println("charset:"+charset);
//以下演示getContentType()---如果是get提交方式则返回null.
//如果是post方式提交则返回:application/x-www-form-urlencoded
String contentType = request.getContentType();
out.print("<br/>contentType="+contentType);
//接收用户名--如果要接收中文,必须先设置编码 request.setCharacterEncoding()
String name = request.getParameter("name");
out.print("<br/>name="+name);
//以下演示通过getMethod()判断请求方式,同时演示Get方式下的中文乱码解决!!
//但是注意!这个并不可靠!有的浏览器会不兼容的!-如果一定要用get方式,而且还要解决中文乱码,那么久明确告诉用户,用什么浏览器访问!
if(request.getMethod().equals("GET")){
System.out.println("get...");
//该读取中文的方式在360浏览器和火狐浏览器都可以!但是IE不行。总之,在get方式下最好不要传递中文!不可靠的。
name = new String(name.getBytes("iso8859-1"), "utf-8");//如果是中文。Tomcat直接就用iso8859-1解码了,属于解码错误,如果要显示中文,我们就把它再还原!
System.out.println(name);
out.print("<br/>GET-name:"+name);
}
//获取客户端的国际化信息---浏览器Internet选项中设置的语言环境!
Locale loc = request.getLocale();//Locale 对象表示了特定的地理、政治和文化地区。需要 Locale 来执行其任务的操作称为语言环境敏感的 操作,它使用 Locale 为用户量身定制信息。
out.print("<br/>Country:"+loc.getCountry());
out.print("<br/>DisplayCountry:"+loc.getDisplayCountry());
out.print("<br/>DisplayLanguage:"+loc.getDisplayLanguage());
out.print("<br/>DisplayName:"+loc.getDisplayName());
/*我的客户端环境
Country:CN
DisplayCountry:中国
DisplayLanguage:中文
DisplayName:中文 (中国)
*/
out.println(" </BODY>");
out.println("</HTML>");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}里面很多知识点,我都在RequestDemo.java文件的注释中写了!注意看就行,演示结果就不贴了。
中间讲了一下客户端的国际化信息!其实就是你电脑环境是什么语言,在什么地区。我们写这个,就可以在网页中支持多国的语言!
自带网站的显示语言。
演示一下简单的原理:
首先配置好2个文件:
a_zh_CN.properties:
name=张三
a_en_US.properties:
name=Jcak
文件名格式:
取名格式: 自定义名国家语言.properties
LocDemo.java:
package testLoc;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class LocDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("a");//把文件按_拆分,文件的第一个名(自己取的)
String name = rb.getString("name");
System.out.println(name);//显而易见,这里的输出是:张三
}
//因为我的客户端是中文的
//它会自动去 a_zh_CN.properties 文件中找name属性匹配。
// 取名格式: 自定义名_国家_语言.properties
}我们在做网站的时候,就可以先配置好所有的属性,动态生成网页,如果语言环境换了,就可以自动换成对应的语言环境!!!
其实不这样也是可以的。有些网站偷懒,就是用多套网页!哪个客户处于什么语言环境,我们就给他显示哪个语言的网页!只是这样就是有多少种语言,你就得准备多少套对应的网页了。而用读取参数,再动态写进去,只要一套就可以实现所有本站的语言翻译!只是多配几个properties而已!
表单多参数接收:
index.jsp:
<!-- 以下专门演示表单参数接收 checkbox-多选框--> <form action="<%= request.getContextPath() %>/param" method="post"> Name:<input type="text" name="name" /><br/> Age:<input type="text" name="age" /><br/> 爱好: <input type="checkbox" name="hody" value="music"/>音乐 <input type="checkbox" name="hody" value="tv"/>电视 <input type="checkbox" name="hody" value="driver"/>开车 <br/> 性别: <input type="radio" name="sex" value="1" checked="checked"/>男 <input type="radio" name="sex" value="0" checked="checked"/>女<br/> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form>
web.xml:
<servlet> <description>表单提交技术</description> <servlet-name>ParamServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>cn.hncu.servlets.ParamServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>ParamServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/param</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
ParamServlet.java:
package cn.hncu.servlets;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class ParamServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//读取单个参数
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
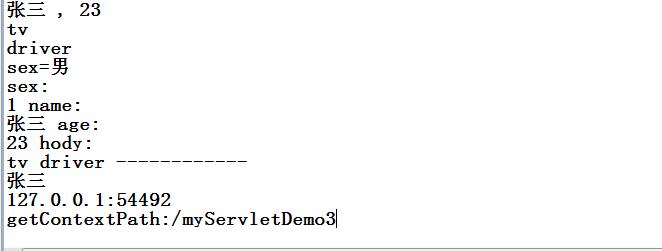
System.out.println(name+" , "+age);
//读取多个参数-用getParameterValues()方法
String hody[] = request.getParameterValues("hody");
//防范以下:
if(hody!=null){
for(String s:hody){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
//读取单选框,和读取单个参数是一样的
String sex = request.getParameter("sex");
if(sex.equals("0")){
System.out.println("sex=女");
}else{
System.out.println("sex=男");
}
//再演示另外一种方式-演示getParameterMap()
Map<String, String[]> map = request.getParameterMap();
//遍历出所有参数:(用迭代器)
Iterator<Entry<String, String[]>> it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){//如果还有下一个
Entry<String, String[]> en =it.next();
System.out.println(en.getKey()+":");
String values[] = en.getValue();
for(String v:values){
System.out.print(v+" ");
}
}
System.out.println("------------");
//这里的map还可以这样用:
String names[] = map.get("name");
String hobys[] = map.get("hoby");
for(String strName:names){
System.out.println(strName+" ");
}
if(hobys!=null){
for(String hoby:hobys){
System.out.println(hoby+" ");
}
}
//以后会用到的BeanUtils工具会使用到getParameterMap()方法
//获取客户端的ip和端口号
String host = request.getRemoteHost();
int port = request.getRemotePort();
System.out.println(host+":"+port);
//演示下request.getContextPath()到底是什么
//输出: /项目名
System.out.println("getContextPath:"+request.getContextPath());// /myServletDemo3
}
}演示结果(360浏览器8.1版本):
表单提交服务器端已经做好了防范,就算提交空的表单,服务器那端也不会挂!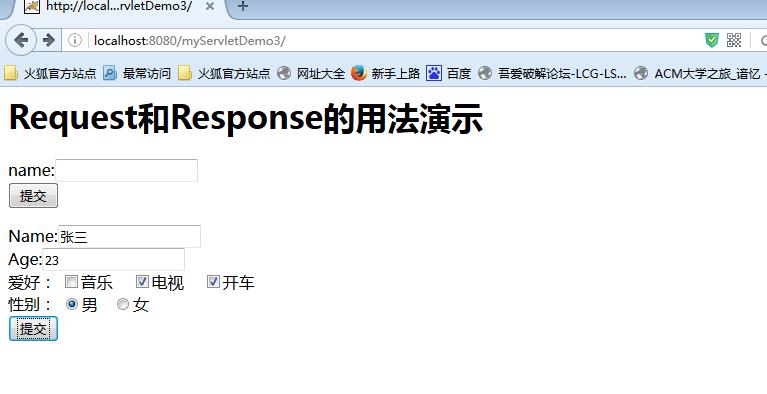
文件上传简单入门
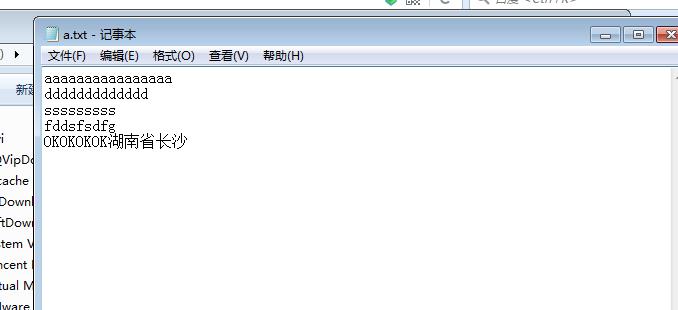
简单的对文件上传演示,具体的下节博客讲:原上传文件内容是:
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa ddddddddddddd sssssssss fddsfsdfg OKOKOKOK湖南省长沙
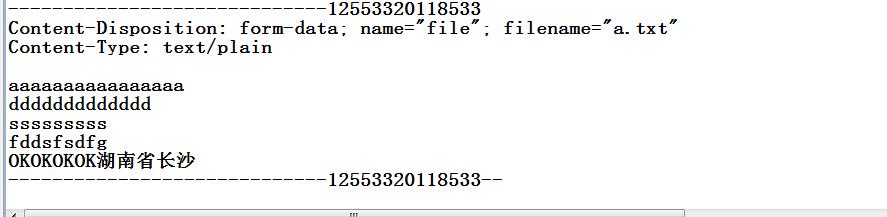
接收的到的数据是:
-----------------------------12553320118533
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file"; filename="a.txt"
Content-Type: text/plain
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa ddddddddddddd sssssssss fddsfsdfg OKOKOKOK湖南省长沙
-----------------------------12553320118533--
多了序列号还有文件内容的说明,这就需要我们的解析了!!!
对
-----------------------------12553320118533 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file"; filename="a.txt" Content-Type: text/plain
一个一个的解析~文件名,文件格式,这里都有!注意哦,这只是txt文件。
可以想想,jpg格式,MP3格式,等等~那些我们该如何解析呢,肯定不能用字符流来接收了,也就是说,用字节流来接收,接收后把序列号和文件内容说明需要转换回字符,然后再根据文件说明,进行文件解析!
不过不用担心,别人已经有给我们写好了工具类,我们可以直接拿来用就可以了。下节讲哦。

原文件:
接收到的数据:
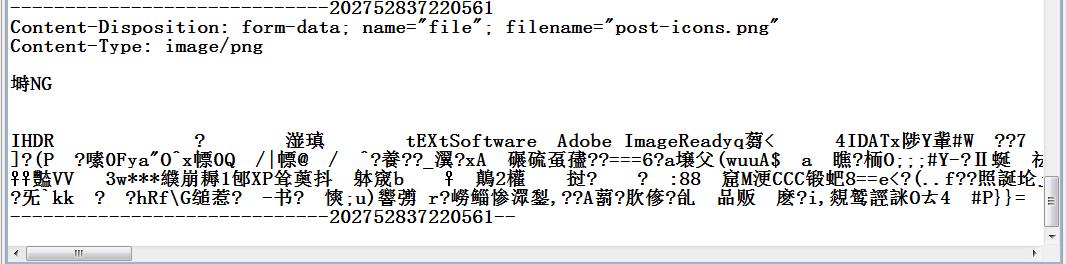
可以上传一张图片给大家看看,用字符流接收到的是什么数据了。乱码时肯定的~

然后我们看,接收到的字符~~二进制文件就出问题了吧,只能用字节流来出来的。
相关文章推荐
- Web---演示Servlet的相关类、表单多参数接收、文件上传简单入门
- 快速编写“专家级”makefile(4.打造更专业的编译环境——增进复用性)
- 关于员工的个人职业发展
- springmvc工具类封装RowMapper (未测试)
- JavaScript数组求和高效率方法
- 2016夏季练习——最小生成树
- [转]面向对象的六大原则
- 死锁相关 变量 与 PURGE 线程停止
- string::npos 含义及用途
- 快速编写“专家级”makefile(4.打造更专业的编译环境)
- 关于输出格式的一些总结——cout
- Hdu-5744 Keep On Movin(贪心)
- Android Fragment嵌套使用存在的一些BUG以及解决方法
- AngularJs实现checkbox的全选、全取消
- html5 meter
- 如何用jQuery禁用浏览器的前进后退按钮?(未测试)
- 使用CHotKeyCtrl的几点总结
- IoC原理及实现
- 实习项目——基于Qt5的银行排号叫号系统(客户端)
- 如何给Ubuntu 安装Vmware Tools_
