Android:layout_weight
2016-07-16 13:05
363 查看
The weight value is a number that specifies the amount of remaining space each view should consume, relative to the amount consumed by sibling views. This works kind of like the amount of ingredients in a drink recipe: "2 parts soda, 1 part syrup" means two-thirds
of the drink is soda. For example, if you give one view a weight of 2 and another one a weight of 1, the sum is 3, so the first view fills 2/3 of the remaining space and the second view fills the rest. If you add a third view and give it a weight of 1, then
the first view (with weight of 2) now gets 1/2 the remaining space, while the remaining two each get 1/4.
The default weight for all views is 0, so if you specify any weight value greater than 0 to only one view, then that view fills whatever space remains after all views are given the space they require
首先先按照控件声明的尺寸进行分配,然后将剩下的尺寸按照weight分配。
首先声明只有在Linearlayout中,该属性才有效。之所以Android:layout_weight会引起争议,是因为在设置该属性的同时,设置android:layout_width为wrap_content和match_parent会造成两种截然相反的效果。如下所示:
[html] view
plain copy
print?


<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@android:color/black"
android:text="111"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:text="222"
android:textSize="20sp" />
上面的布局将两个TextView的宽度均设为match_parent,一个权重为1,一个权重为2.得到效果如下:
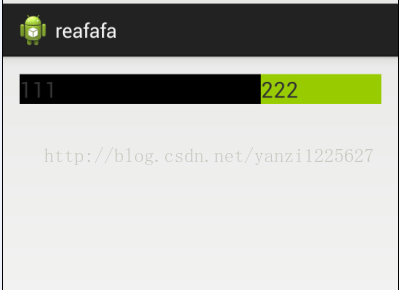
可以看到权重为1的反而占了三分之二!
再看如下布局:
[html] view
plain copy
print?


<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@android:color/black"
android:text="111"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:text="222"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</LinearLayout>
即宽度为wrap_content,得到视图如下:
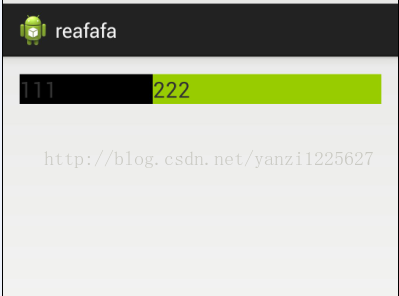
左边 TextView占比三分之一,又正常了。
android:layout_weight的真实含义是:一旦View设置了该属性(假设有效的情况下),那么该 View的宽度等于原有宽度(android:layout_width)加上剩余空间的占比!
设屏幕宽度为L,在两个view的宽度都为match_parent的情况下,原有宽度为L,两个的View的宽度都为L,那么剩余宽度为L-(L+L) = -L, 左边的View占比三分之一,所以总宽度是L+(-L)*1/3 = (2/3)L.事实上默认的View的weight这个值为0,一旦设置了这个值,那么所在view在绘制的时候执行onMeasure两次的原因就在这。
Google官方推荐,当使用weight属性时,将width设为0dip即可,效果跟设成wrap_content是一样的。这样weight就可以理解为占比了!
of the drink is soda. For example, if you give one view a weight of 2 and another one a weight of 1, the sum is 3, so the first view fills 2/3 of the remaining space and the second view fills the rest. If you add a third view and give it a weight of 1, then
the first view (with weight of 2) now gets 1/2 the remaining space, while the remaining two each get 1/4.
The default weight for all views is 0, so if you specify any weight value greater than 0 to only one view, then that view fills whatever space remains after all views are given the space they require
首先先按照控件声明的尺寸进行分配,然后将剩下的尺寸按照weight分配。
首先声明只有在Linearlayout中,该属性才有效。之所以Android:layout_weight会引起争议,是因为在设置该属性的同时,设置android:layout_width为wrap_content和match_parent会造成两种截然相反的效果。如下所示:
[html] view
plain copy
print?

<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@android:color/black"
android:text="111"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:text="222"
android:textSize="20sp" />
上面的布局将两个TextView的宽度均设为match_parent,一个权重为1,一个权重为2.得到效果如下:

可以看到权重为1的反而占了三分之二!
再看如下布局:
[html] view
plain copy
print?

<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@android:color/black"
android:text="111"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"
android:text="222"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</LinearLayout>
即宽度为wrap_content,得到视图如下:

左边 TextView占比三分之一,又正常了。
android:layout_weight的真实含义是:一旦View设置了该属性(假设有效的情况下),那么该 View的宽度等于原有宽度(android:layout_width)加上剩余空间的占比!
设屏幕宽度为L,在两个view的宽度都为match_parent的情况下,原有宽度为L,两个的View的宽度都为L,那么剩余宽度为L-(L+L) = -L, 左边的View占比三分之一,所以总宽度是L+(-L)*1/3 = (2/3)L.事实上默认的View的weight这个值为0,一旦设置了这个值,那么所在view在绘制的时候执行onMeasure两次的原因就在这。
Google官方推荐,当使用weight属性时,将width设为0dip即可,效果跟设成wrap_content是一样的。这样weight就可以理解为占比了!
相关文章推荐
- Android ServiceConnection
- Android ServiceConnection类的onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name)在什么时候执行
- RxAndroid用法
- Android RxJava 自定义操作符基础和Subject介绍
- Android Service
- Android Activity各启动模式的差异
- Android Animation学习 实现 IOS 滤镜退出动画
- Android Camera 流程梳理
- 加速Android Studio的Gradle构建速度
- ubuntu下,Android Studio 卡在 Scanning project directories
- Android图片添加阴影效果的两种方式
- Android本地文件点击视频播放器vitamio版
- [译]FaceBook出品:基于Android的内存优化
- android.os.NetworkOnMainThreadException
- Android自定义Dialog类,并在Activity中实现按钮监听
- Android Volley完全解析(一),初识Volley的基本用法
- [Android Tips] 22. Available Java 7 Features in Android
- android 通知提醒
- android学习路线:如何成长为高级工程师
- 新建android项目时总是出错“The import android.support.v7 cannot be resolved”
