HDU 1272 HDU 1308&&POJ 1308(树的判断)(并查集)
2016-07-08 16:36
337 查看
小希的迷宫
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 41768 Accepted Submission(s): 12880
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
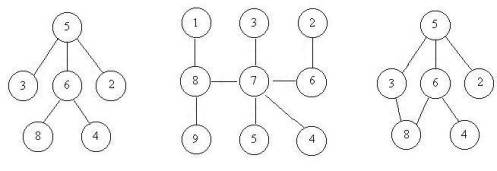
上次Gardon的迷宫城堡小希玩了很久(见Problem B),现在她也想设计一个迷宫让Gardon来走。但是她设计迷宫的思路不一样,首先她认为所有的通道都应该是双向连通的,就是说如果有一个通道连通了房间A和B,那么既可以通过它从房间A走到房间B,也可以通过它从房间B走到房间A,为了提高难度,小希希望任意两个房间有且仅有一条路径可以相通(除非走了回头路)。小希现在把她的设计图给你,让你帮忙判断她的设计图是否符合她的设计思路。比如下面的例子,前两个是符合条件的,但是最后一个却有两种方法从5到达8。
[align=left]Input[/align]
输入包含多组数据,每组数据是一个以0 0结尾的整数对列表,表示了一条通道连接的两个房间的编号。房间的编号至少为1,且不超过100000。每两组数据之间有一个空行。
整个文件以两个-1结尾。
[align=left]Output[/align]
对于输入的每一组数据,输出仅包括一行。如果该迷宫符合小希的思路,那么输出"Yes",否则输出"No"。
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4
5 6 0 0
8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5
7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0
3 8 6 8 6 4
5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0
-1 -1
这个循环输入挺不错的,第一次遇到。
注意:仅仅输入0 0的时候,结果也是Yes,没有房间的时候也满足。(wa了好久)
/*
题目要求:任意两点之间有且仅有一条路径
所以,只需要判断这个图是否是棵树就行了
1.是连通图
2.没有回路
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;
int f
,vis
,n,flag;
void Init()
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
f[i]=i;
}
int getf(int t)
{
if(f[t]==t)
return t;
else
{//路径压缩
f[t] = getf(f[t]);
return f[t];
}
}
void merge(int v,int u)
{
int t1,t2;
t1 = getf(v);
t2 = getf(u);
if(t1!=t2)
{
f[t2] = t1;//靠左原则
}
else
flag=0;//在一个集合中,再连接就成回路,不满足树
}
int main()
{
int x,y;
Init();
while(~scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)&&(x!=-1||y!=-1))
{
if(!x||!y)
{
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
continue;
}
flag =1;
merge(x,y);
vis[x]=vis[y]=1;//此数组用来标记是否有这个点
while(scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)&&(x||y))
{
merge(x,y);
vis[x]=vis[y]=1;
}
int sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)//貌似不会有超时影响
{
if(vis[i]&&f[i] == i)
sum++;
}
if(sum>1)
flag=0;
if(flag)
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else
cout<<"No"<<endl;
Init();
}
return 0;
}Is It A Tree?
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 20878 Accepted Submission(s): 4727
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
A tree is a well-known data structure that is either empty (null, void, nothing) or is a set of one or more nodes connected by directed edges between nodes satisfying the following properties.
There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point.
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.
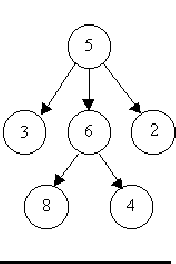
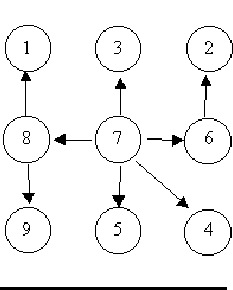
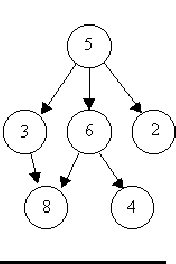
In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
[align=left]Input[/align]
The input will consist of a sequence of descriptions (test cases) followed by a pair of negative integers. Each test case will consist of a sequence of edge descriptions followed by a pair of zeroes Each edge description
will consist of a pair of integers; the first integer identifies the node from which the edge begins, and the second integer identifies the node to which the edge is directed. Node numbers will always be greater than zero.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For each test case display the line ``Case k is a tree." or the line ``Case k is not a tree.", where k corresponds to the test case number (they are sequentially numbered starting with 1).
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4
5 6 0 0
8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5
7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0
3 8 6 8 6 4
5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0
-1 -1
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
Case 1 is a tree.
Case 2 is a tree.
Case 3 is not a tree.
一样的题目,poj过了,hdu却没有过,貌似不是oi的问题,等待明天补充,补充在下面::
/*
题目要求:任意两点之间有且仅有一条路径
所以,只需要判断这个图是否是棵树就行了,有方向的
1.是连通图
2.没有回路
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;
int f
,vis
,n,flag;
void Init()
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
f[i]=i;
}
int getf(int t)
{
if(f[t]==t)
return t;
else
{//路径压缩
f[t] = getf(f[t]);
return f[t];
}
}
void merge(int v,int u)
{
int t1,t2;
t1 = getf(v);
t2 = getf(u);
if(t1!=t2)
{
f[t2] = t1;//靠左原则
}
else
flag=0;//在一个集合中,再连接就成回路,不满足树
}
int main()
{
int t=0;
int x,y;
Init();
while(~scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)&&(x>=0||y>=0))
{
t++;
if(!x||!y)
{
cout<<"Case "<<t;
cout<<" is a tree."<<endl;
continue;
}
flag =1;
merge(x,y);
vis[x]=vis[y]=1;//此数组用来标记是否有这个点
while(scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)&&(x||y))
{
merge(x,y);
vis[x]=vis[y]=1;
}
int sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)//貌似不会有超时影响
{
if(vis[i]&&f[i] == i)
sum++;
}
if(sum>1)
flag=0;
cout<<"Case "<<t;
if(flag)
cout<<" is a tree."<<endl;
else
cout<<" is not a tree."<<endl;
Init();
}
return 0;
}要将有向边这个情况加入到代码中,只需要修改一下merge函数就可以了,所以说poj过了可能是数据比较弱吧,对这类题目态度要严谨点
代码:
void merge(int v,int u)
{
int t1,t2;
t1 = getf(v);
t2 = getf(u);
if(t1!=t2)
{
f[t2] = t1;//靠左原则
}
if(t2!=u||t1==t2)
flag=0;//保证u不在另一个树中,入度不大于1,在一个集合中,再连接就成回路,不满足树
}
相关文章推荐
- 设计产品,除了用户体验,别轻视了运营
- 带有滚动监听的ScrollView
- 浅谈Java设计模式(四)建造者模式(Builder)
- svn diff 详解
- 扩展 HtmlwebpackPlugin 插入自定义的脚本
- oracle中字符串的大小比较,字符串与数字的比较和运算
- 面试题28:字符串全排列
- 依赖倒置原则
- 关于Attempted to add window with non-application token WindowToken错误的解决
- go搭建
- 或与加
- CMS-RCNN阅读小结
- js局部变量和全局变量
- php自动加载文件
- Nginx+Tomcat+SSL 识别 https还是http
- Layer3 OSPF的路由选路
- 爬虫遇到图片禁止访问(如403)
- AJAX教程系列三:get与post区别
- 设计模式——代理模式
- java生成xml格式文件的方法
