实例讲解Android中ContentProvider组件的使用方法
ContentProvider基本使用
为了在应用程序之间交换数据,android提供了ContentProvider,ContentProvider是不同应用程序之间进行数据交换的标准API,当一个应用程序需要把自己的数据暴露给其他程序使用时,该应用程序就可以通过提供ContentPRovider来实现,其他应用程序就可以通过ContentResolver来操作ContentProvider暴露的数据。
实现ContentProvider的步骤:
1)编写一个类,继承ContentProvider,并且重写里面的CRUD方法。
2)在androidmanifest.xml文件中注册provider。
在androidmanifest.xml中注册provider需要以下3个属性:
android:name provider的实现类。
android:authorities provider的uri。
android:exported provider是否暴露给其他程序。
ContentResovler操作ContentProvider:
1)获取ContentResolver,getContentResovler()方法来自于ContextWrapper,所以activity和service中都可以使用。
2)调用CURD方法,通过参数url,调用指定的ContentProvider的方法。
下面是一个demo,向contentProvider中插入一条数据,并且返回到listview中。
main.xml:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".Main" > <ListView android:id="@+id/listview" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </RelativeLayout>
MySQLiteOpenHelper类
package com.app.dao;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
public class MySQLiteOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
public MySQLiteOpenHelper(Context context, String name,
CursorFactory factory, int version) {
super(context, name, factory, version);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
String create_sql = "create table tb_test(_id integer primary key autoincrement,name,gender,age)";
db.execSQL(create_sql);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
}
}
MyContentProvider类
package com.app.dao;
import android.content.ContentProvider;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
public class MyContentProvider extends ContentProvider{
MySQLiteOpenHelper helper=null;
@Override
public int delete(Uri arg0, String arg1, String[] arg2) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public String getType(Uri arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri arg0, ContentValues values) {
String insert_sql="insert into tb_test values(null,'wx','boy',17)";
helper.getReadableDatabase().execSQL(insert_sql);
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
helper=new MySQLiteOpenHelper(this.getContext(),"test.db3",null,1);
return true;
}
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri arg0, String[] arg1, String arg2, String[] arg3,
String arg4) {
String query_sql="select * from tb_test";
Cursor cursor=helper.getReadableDatabase().rawQuery(query_sql, null);
return cursor;
}
@Override
public int update(Uri arg0, ContentValues arg1, String arg2, String[] arg3) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
}
listview的显示界面show.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" > <TextView android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/gender" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginLeft="60dp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/age" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginLeft="60dp" /> </LinearLayout>
Main.java
package com.app.main;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ContentResolver;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.widget.CursorAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
public class Main extends Activity {
ContentResolver resolver = null;
ListView lv = null;
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
lv = (ListView) this.findViewById(R.id.listview);
resolver = this.getContentResolver();
String str = "content://com.app.test.db/";
Uri uri = Uri.parse(str);
resolver.insert(uri, null);
Cursor cursor = resolver.query(uri, null, null, null, null);
SimpleCursorAdapter adapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(this,
R.layout.show, cursor,
new String[] { "name", "gender", "age" }, new int[] {
R.id.name, R.id.gender, R.id.age },
CursorAdapter.FLAG_REGISTER_CONTENT_OBSERVER);
lv.setAdapter(adapter);
}
}
实现效果:(执行了3次插入后的效果)

ContentProvider的单元测试
ContentProvider是android的四大组件之一,在编写代码的时候最好是加上单元测试,这样可以确定对数据的CRUD的正确。本篇文章主要介绍ContentProvider中两个主要辅助类的使用还有单元测试的在ContentProvider中的使用。
需要用到的两个辅助类:UriMatcher类和ContentUris类。
UriMatcher类:能够对输入的uri参数就行匹配,以确定对什么表执行什么样的操作。
ContentUris类:有些方法需要返回uri,运用此类可以方便的生成uri类。
对于单元测试,个人觉得非常有必要在今后写代码的时候使用,这样可以非常准确的确定代码的正确性。
使用单元测试的步骤:
1)加入instrumentation,这个部分的代码是固定,也可以完全在ADT提供的向导中导入。
<instrumentation android:name="android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner" android:targetPackage="com.example.android_contentprovider" > </instrumentation>
2)添加<uses-library>,这个部分的代码也是固定的写法。
<uses-library android:name="android.test.runner" />
好了,必备的知识已经讲完了,现在上代码:
1)生成一个SQLiteDatabase类,这个是必需的类MySQLiteOpenHelper类
package com.app.db;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
public class MySQLiteOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private static String DB_NAME = "test.db3";
private static int VERSION = 1;
public MySQLiteOpenHelper(Context context) {
super(context, DB_NAME, null, VERSION);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
//建表语句
String create_student = "create table student(_id integer primary key autoincrement,name varchar(10),age integer,gender vachar(10))";
db.execSQL(create_student);
//千万不能执行这句 // db.close();
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase arg0, int arg1, int arg2) {
}
}
然后添加我们需要的MyContentProvider类:
package com.app.contentprovider;
import com.app.db.MySQLiteOpenHelper;
import android.content.ContentProvider;
import android.content.ContentUris;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.UriMatcher;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyContentProvider extends ContentProvider {
MySQLiteOpenHelper helper = null;
private static UriMatcher matcher = new UriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH);
// 匹配单条记录
private static final int student = 1;
// 匹配多条记录
private static final int students = 2;
static {
matcher.addURI("com.app.wx", "student/#", student);
matcher.addURI("com.app.wx", "student", students);
}
@Override
public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
int action = matcher.match(uri);
switch (action) {
// 匹配单条记录
case student:
long id = ContentUris.parseId(uri);
//获取单条记录的id号
String delete_id = "_id=" + id;
if (selection != null) {
delete_id += delete_id + " and " + selection;
}
db.delete("student", delete_id, selectionArgs);
break;
// 匹配多条记录
case students:
db.delete("student", selection, selectionArgs);
break;
}
return 0;
}
//必需实现这个方法,这个方法与intent有关系,以后再讲
@Override
public String getType(Uri uri) {
int code = matcher.match(uri);
switch (code) {
case student:
return "vnd.android.cursor.item/student_item";
case students:
return "vnd.android.cursor.dir/students";
default:
return null;
}
}
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
int action = matcher.match(uri);
switch (action) {
case students:
long id1 = db.insert("student", "_id", values);
Log.i("--------", ContentUris.withAppendedId(uri, id1).toString());
return ContentUris.withAppendedId(uri, id1);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
helper = new MySQLiteOpenHelper(this.getContext());
return true;
}
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection,
String[] selectionArgs, String orderBy) {
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = null;
int action = matcher.match(uri);
switch (action) {
case students:
cursor = db.query("student", projection, selection, selectionArgs,
null, null, orderBy);
break;
}
System.out.println("-----------count:" + cursor.getCount());
return cursor;
}
@Override
public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection,
String[] arg3) {
int count = -1;
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
int action = matcher.match(uri);
switch (action) {
case student:
// 以id来处理更新
long id = ContentUris.parseId(uri);
String id_selection = "_id=" + id;
if (selection != null && !selection.equals("")) {
id_selection = id_selection + " and " + values;
}
count = db.update("student", values, id_selection, arg3);
System.out.println("----------count:" + count);
break;
}
return count;
}
}
这个类很长,但是执行的方法都是比较常见的CURD的方法,重要的是UriMatcher和ContentUris类的使用。
接着执行单元测试类:Test
package com.app.contentprovider;
import android.content.ContentResolver;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.test.AndroidTestCase;
import android.util.Log;
public class Test extends AndroidTestCase {
public void insert() {
ContentResolver resolver = this.getContext().getContentResolver();
String str = "content://com.app.wx/student";
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("name", "wzq");
values.put("age", 18);
values.put("gender", "boy");
resolver.insert(Uri.parse(str), values);
}
public void update() {
ContentResolver resolver = this.getContext().getContentResolver();
String str = "content://com.app.wx/student/2";
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("name", "哈哈");
resolver.update(Uri.parse(str), values, null, null);
}
public void query() {
ContentResolver resolver = this.getContext().getContentResolver();
String str = "content://com.app.wx/student";
Uri uri = Uri.parse(str);
Cursor cursor = resolver.query(uri, new String[] { "_id",
"name,age,gender" }, null, null, "_id desc");
Log.d("------count",cursor.getCount()+"");
}
public void delete() {
ContentResolver resolver = this.getContext().getContentResolver();
String str = "content://com.app.wx/student/2";
Uri uri = Uri.parse(str);
long id=resolver.delete(uri, null, null);
}
}
执行insert方法之后(执行了三次):
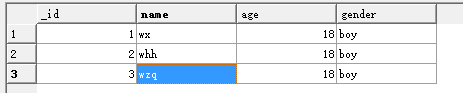
执行了update方法之后:
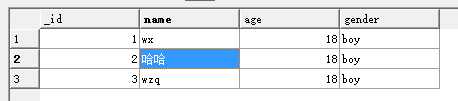
执行了query方法之后:

执行了delete方法之后:
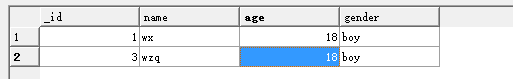
您可能感兴趣的文章:
- 使用C++实现JNI接口需要注意的事项
- Android IPC进程间通讯机制
- Android Manifest 用法
- [转载]Activity中ConfigChanges属性的用法
- Android之获取手机上的图片和视频缩略图thumbnails
- Android之使用Http协议实现文件上传功能
- Android学习笔记(二九):嵌入浏览器
- android string.xml文件中的整型和string型代替
- i-jetty环境搭配与编译
- android之定时器AlarmManager
- android wifi 无线调试
- Android Native 绘图方法
- Android java 与 javascript互访(相互调用)的方法例子
- android 代码实现控件之间的间距
- android FragmentPagerAdapter的“标准”配置
- Android"解决"onTouch和onClick的冲突问题
- android:installLocation简析
- android searchView的关闭事件
- SourceProvider.getJniDirectories
