C++ 栈的应用
2016-04-11 14:43
477 查看
1、栈的应用1 解决迷宫问题
问题:一个n*n的0、1矩阵,0 表示可以走通,1表示不可以走 ,假定矩阵的下边是出口,给定矩阵的入口坐标,求出走出迷宫的路径
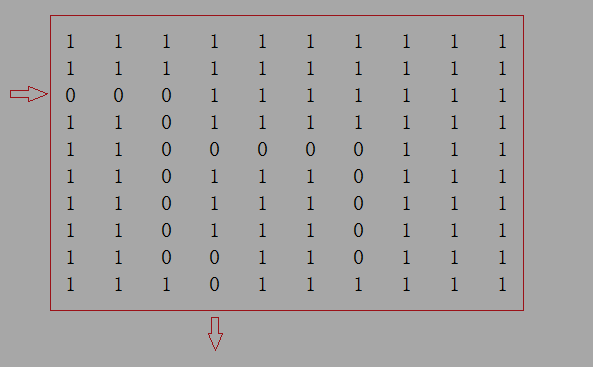
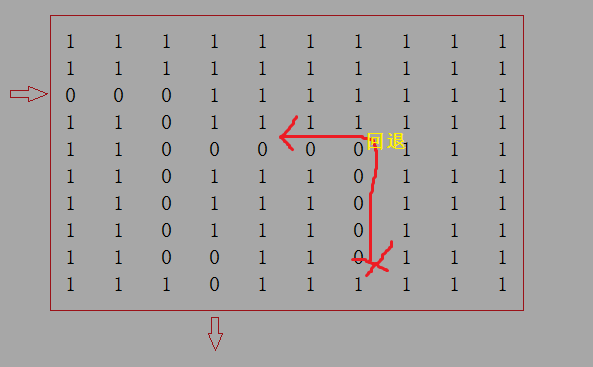
这里用 栈 主要是解决 如图所示 走不出去 会退时上一步(出栈) 位置的记录
以及 记录已经走过的路径(压栈)
扩展 :(1) 非递归法实现
(递归法 与 非递归 的 一点不同
递归法不会出现 尝试下一步失败后 退到上一步 再次尝试下一步时 不会出现 重复 尝试上一次走错的那个“下一步” 而 下面使用 栈的方式的 退栈时 下一步尝试还会判断 已走过不成功的情况【重复判断一次】)
(2) 多个出口 最短路问题 【在下面实现】
//-----------------Maze.h---------
#pragma once
#define N 10
#define MAZEPATH "MazeMap.txt"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <assert.h>
#include <stack>
struct Pos
{
int _row;
int _col;
};
void GetMaze(int* a, int n);
void PrintMaze(int* a, int n);
bool MazePath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry, stack<Pos>& path);
//-----------------Maze.cpp-----------
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
// 栈应用:迷宫(n*n)问题
#include "Maze.h"
void GetMaze(int* a, int n)
{
FILE* f_out = fopen(MAZEPATH, "r");
assert(f_out != NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; )
{
char ch = fgetc(f_out);
if (ch == '0' || ch == '1') //通路为0 不通路2
{
a[i*n + j] = ch - '0';
++j;
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
}
fclose(f_out);
}
void PrintMaze(int* a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++ )
{
cout<<a[i * n + j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
bool CheckIsAccess(const int *a, int n, const Pos& next) //判断路通不通
{
assert(a);
if (next._row >= 0 && next._row < n
&& next._col >= 0 && next._col < n
&& a[next._row * n + next._col] == 0)// 0 表示路通
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// const Pos entry 入口 , stack<Pos>& path 用于压路径的 栈
bool MazePath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry, stack<Pos>& path)
{
Pos cur = entry;
path.push(cur);
while (!path.empty()) // 无路走时栈空
{
a[cur._row * n + cur._col] = 2;// 走过的路标记 2
// 定义数组 最下边为 出口
if (cur._row == n - 1) // 判断是否到出口
{
return true;
}
Pos next = cur;
// 向上 探索
next._row--;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向右 探索
next = cur;
next._col++;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向下 探索
next = cur;
next._row++;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向左 探索
next = cur;
next._col--;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 走不通
a[cur._row * n + cur._col] = 5;// 标出错误路线
path.pop();
if (!path.empty())
{
cur = path.top();
}
}
return false;
}
//---------------------test.cpp----------------------
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Maze.h"
void TestMaze()
{
int a
= {};
GetMaze((int*)a, N);
PrintMaze((int*)a, N);
stack<Pos> path;
Pos entry = {2, 0};
MazePath((int*)a, N, entry, path);
cout<<"------------------------------"<<endl;
PrintMaze((int*)a, N);
}
int main()
{
TestMaze();
getchar();
return 0;
}
//--------------MazeMap.txt----------------
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
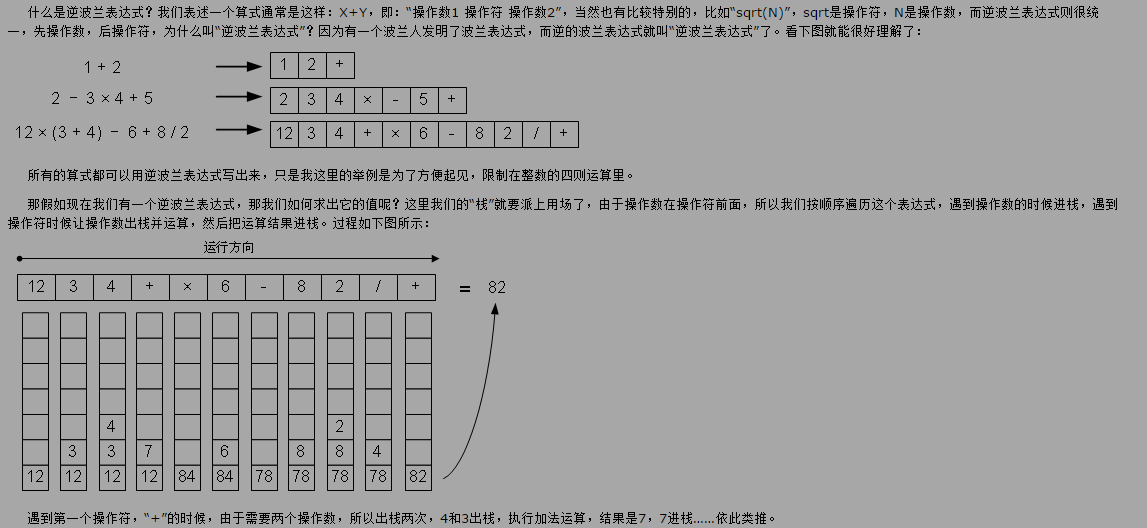
2、栈的应用2 逆波兰式计算
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
// 栈的应用 2 算数表达式求解
enum Type
{
OP_NUM,
OP_SYMBOL
};
struct Cell
{
Type type;
int value;
};
enum SYMBOL
{
ADD,
SUB,
MUL,
DIV
};
int CountRNP(Cell* a,size_t size)
{
assert(a);
stack<int> s;
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (a[i].type == OP_NUM)
{
s.push(a[i].value);
}
else
{
int right = s.top();// 注意 压栈 与表达式 顺序不同
s.pop();
int left = s.top();
s.pop();
switch (a[i].value)
{
case ADD:
s.push(left + right);
break;
case SUB:
s.push(left - right);
break;
case MUL:
s.push(left * right);
break;
case DIV:
s.push(left / right);
break;
}
}
}
return s.top();
}
void TestRnp()
{
Cell a[] =
{
{OP_NUM, 12},
{OP_NUM, 3},
{OP_NUM, 4},
{OP_SYMBOL, ADD},
{OP_SYMBOL, MUL},
{OP_NUM, 6},
{OP_SYMBOL, SUB},
{OP_NUM, 8},
{OP_NUM, 2},
{OP_SYMBOL, DIV},
{OP_SYMBOL, ADD}
};
int ret = CountRNP(a, sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]));
}
int main()
{
TestRnp();
return 0;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////
////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//----------------迷宫 递归法(不用栈)---------
// 递归法 不需要栈
bool MazePath(int* a, int n, Pos cur)
{
// 定义数组 最下边为 出口
if (cur._row == n - 1 && a[cur._row * n + cur._col] == 0) // 判断是否到出口
{
a[cur._row * n +cur._col] = 2; // 2 表示此路可走
return true;
}
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, cur))
{
a[cur._row * n +cur._col] = 2; // 2 表示此【点】可走 下一步还不知道
Pos next_left = cur;
next_left._col--;
Pos next_right = cur;
next_right._col++;
Pos next_up = cur;
next_up._row--;
Pos next_down = cur;
next_down._row++;
bool next = (MazePath((int*)a, n, next_up)
|| MazePath((int*)a, n, next_right)
|| MazePath((int*)a, n, next_down)
|| MazePath((int*)a, n, next_left));
if (!next)
{
a[cur._row * n +cur._col] = 5; //5表示 下一步走不出去 把当前点从2变到五 表示这个点走不出去
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
else //cur 不能走
{
return false;
}
}
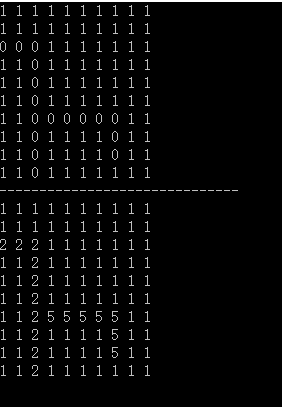
2 表示成功路线
5 表示 尝试失败的路线
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//--------------------迷宫 (最短路) ---------------
//-------------------Maze.h--------------------
#pragma once
#define N 10
#define DEBUGE 0 // 1 调试 0 不调试
#define MAZEPATH "MazeMap.txt"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <assert.h>
#include <stack>
struct Pos
{
int _row;
int _col;
};
//stack<Pos> MinPath;
void GetMaze(int* a, int n);
void PrintMaze(int* a, int n);
bool MazePath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry, stack<Pos>& path);
bool FindMinPath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry ,stack<Pos>& MinPath);
int GetCount(stack<Pos> path);
//---------------------------Maze.cpp-----------------
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
// 栈应用2:迷宫(n*n)问题
#include "Maze.h"
void GetMaze(int* a, int n)
{
FILE* f_out = fopen(MAZEPATH, "r");
assert(f_out != NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; )
{
char ch = fgetc(f_out);
if (ch == '0' || ch == '1') //通路为0 不通路2
{
a[i*n + j] = ch - '0';
++j;
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
}
fclose(f_out);
}
void PrintMaze(int* a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++ )
{
cout<<a[i * n + j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
bool CheckIsAccess(const int *a, int n, const Pos& next) //判断路通不通
{
assert(a);
if (next._row >= 0 && next._row < n
&& next._col >= 0 && next._col < n
&& a[next._row * n + next._col] == 0)// 0 表示路通
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// const Pos entry 入口 , stack<Pos>& path 用于压路径的 栈
bool MazePath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry, stack<Pos>& path)
{
Pos cur = entry;
path.push(cur);
while (!path.empty()) // 无路走时栈空
{
a[cur._row * n + cur._col] = 2;// 走过的路标记 2
// 定义数组 最下边为 出口
if (cur._row == n - 1) // 判断是否到出口
{
return true;
}
Pos next = cur;
// 向上 探索
next._row--;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向右 探索
next = cur;
next._col++;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向下 探索
next = cur;
next._row++;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向左 探索
next = cur;
next._col--;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 走不通
a[cur._row * n + cur._col] = 5;// 标出错误路线
path.pop();
if (!path.empty())
{
cur = path.top();
}
}
return false;
}
int GetCount(stack<Pos> path)
{
int count = 0;
while(!path.empty())
{
count += 1;
path.pop();
}
return count;
}
void huanyuan(int* a,int n, stack<Pos> Path) // Path不用引用
{
while(!Path.empty())
{
a[Path.top()._row * n + Path.top()._col] = 0;
Path.pop();
}
}
bool FindMinPath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry,stack<Pos>& MinPath)
{
bool next = false;
bool ret = false;
do
{
stack<Pos> path;
next = MazePath(a, n, entry, path);
//----------------debuge----------
#if DEBUGE
cout<<"-----------------------------"<<endl;
PrintMaze(a,n);
#endif
if (next)
{
if (MinPath.empty())
{
MinPath = path;
}
else
{
if (GetCount(MinPath) > GetCount(path))
{
MinPath = path; // 更新MinPath
}
}
huanyuan((int*)a, n, path);// 将已经走过的路 2 标记为 0
a[path.top()._row * n + path.top()._col] = 9; // 此出口已经堵住
//--------------debuge---------
#if DEBUGE
cout<<"-------------huanyuan----------------"<<endl;
PrintMaze(a,n);
#endif
ret = true;
}
}while(next);
if (ret)
{
huanyuan(a, n, MinPath);
//a[MinPath.top()._row * n + MinPath.top()._col] = 2; //打开这个最短路出口
}
return ret;
}
//--------------------------------test.cpp-----------------
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Maze.h"
void TestMaze()
{
int a
= {};
GetMaze((int*)a, N);
PrintMaze((int*)a, N);
stack<Pos> path;
stack<Pos> MinPath;
Pos entry = {2, 0};
FindMinPath((int*)a, N, entry ,MinPath);
cout<<"------------------------------"<<endl;
PrintMaze((int*)a, N);
}
int main()
{
TestMaze();
getchar();
return 0;
}
//----------------------------MazeMap.txt---------------------
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
运行图:
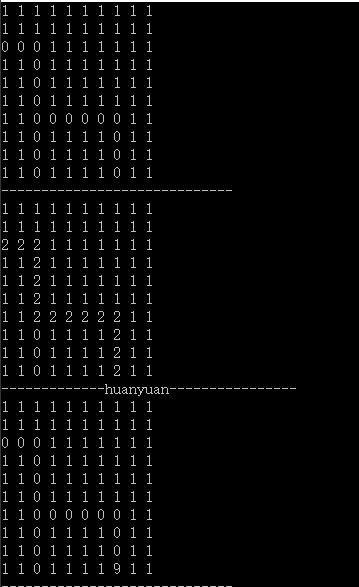
问题:一个n*n的0、1矩阵,0 表示可以走通,1表示不可以走 ,假定矩阵的下边是出口,给定矩阵的入口坐标,求出走出迷宫的路径

这里用 栈 主要是解决 如图所示 走不出去 会退时上一步(出栈) 位置的记录
以及 记录已经走过的路径(压栈)

扩展 :(1) 非递归法实现
(递归法 与 非递归 的 一点不同
递归法不会出现 尝试下一步失败后 退到上一步 再次尝试下一步时 不会出现 重复 尝试上一次走错的那个“下一步” 而 下面使用 栈的方式的 退栈时 下一步尝试还会判断 已走过不成功的情况【重复判断一次】)
(2) 多个出口 最短路问题 【在下面实现】
//-----------------Maze.h---------
#pragma once
#define N 10
#define MAZEPATH "MazeMap.txt"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <assert.h>
#include <stack>
struct Pos
{
int _row;
int _col;
};
void GetMaze(int* a, int n);
void PrintMaze(int* a, int n);
bool MazePath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry, stack<Pos>& path);
//-----------------Maze.cpp-----------
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
// 栈应用:迷宫(n*n)问题
#include "Maze.h"
void GetMaze(int* a, int n)
{
FILE* f_out = fopen(MAZEPATH, "r");
assert(f_out != NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; )
{
char ch = fgetc(f_out);
if (ch == '0' || ch == '1') //通路为0 不通路2
{
a[i*n + j] = ch - '0';
++j;
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
}
fclose(f_out);
}
void PrintMaze(int* a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++ )
{
cout<<a[i * n + j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
bool CheckIsAccess(const int *a, int n, const Pos& next) //判断路通不通
{
assert(a);
if (next._row >= 0 && next._row < n
&& next._col >= 0 && next._col < n
&& a[next._row * n + next._col] == 0)// 0 表示路通
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// const Pos entry 入口 , stack<Pos>& path 用于压路径的 栈
bool MazePath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry, stack<Pos>& path)
{
Pos cur = entry;
path.push(cur);
while (!path.empty()) // 无路走时栈空
{
a[cur._row * n + cur._col] = 2;// 走过的路标记 2
// 定义数组 最下边为 出口
if (cur._row == n - 1) // 判断是否到出口
{
return true;
}
Pos next = cur;
// 向上 探索
next._row--;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向右 探索
next = cur;
next._col++;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向下 探索
next = cur;
next._row++;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向左 探索
next = cur;
next._col--;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 走不通
a[cur._row * n + cur._col] = 5;// 标出错误路线
path.pop();
if (!path.empty())
{
cur = path.top();
}
}
return false;
}
//---------------------test.cpp----------------------
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Maze.h"
void TestMaze()
{
int a
= {};
GetMaze((int*)a, N);
PrintMaze((int*)a, N);
stack<Pos> path;
Pos entry = {2, 0};
MazePath((int*)a, N, entry, path);
cout<<"------------------------------"<<endl;
PrintMaze((int*)a, N);
}
int main()
{
TestMaze();
getchar();
return 0;
}
//--------------MazeMap.txt----------------
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
2、栈的应用2 逆波兰式计算

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
// 栈的应用 2 算数表达式求解
enum Type
{
OP_NUM,
OP_SYMBOL
};
struct Cell
{
Type type;
int value;
};
enum SYMBOL
{
ADD,
SUB,
MUL,
DIV
};
int CountRNP(Cell* a,size_t size)
{
assert(a);
stack<int> s;
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (a[i].type == OP_NUM)
{
s.push(a[i].value);
}
else
{
int right = s.top();// 注意 压栈 与表达式 顺序不同
s.pop();
int left = s.top();
s.pop();
switch (a[i].value)
{
case ADD:
s.push(left + right);
break;
case SUB:
s.push(left - right);
break;
case MUL:
s.push(left * right);
break;
case DIV:
s.push(left / right);
break;
}
}
}
return s.top();
}
void TestRnp()
{
Cell a[] =
{
{OP_NUM, 12},
{OP_NUM, 3},
{OP_NUM, 4},
{OP_SYMBOL, ADD},
{OP_SYMBOL, MUL},
{OP_NUM, 6},
{OP_SYMBOL, SUB},
{OP_NUM, 8},
{OP_NUM, 2},
{OP_SYMBOL, DIV},
{OP_SYMBOL, ADD}
};
int ret = CountRNP(a, sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]));
}
int main()
{
TestRnp();
return 0;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////
////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//----------------迷宫 递归法(不用栈)---------
// 递归法 不需要栈
bool MazePath(int* a, int n, Pos cur)
{
// 定义数组 最下边为 出口
if (cur._row == n - 1 && a[cur._row * n + cur._col] == 0) // 判断是否到出口
{
a[cur._row * n +cur._col] = 2; // 2 表示此路可走
return true;
}
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, cur))
{
a[cur._row * n +cur._col] = 2; // 2 表示此【点】可走 下一步还不知道
Pos next_left = cur;
next_left._col--;
Pos next_right = cur;
next_right._col++;
Pos next_up = cur;
next_up._row--;
Pos next_down = cur;
next_down._row++;
bool next = (MazePath((int*)a, n, next_up)
|| MazePath((int*)a, n, next_right)
|| MazePath((int*)a, n, next_down)
|| MazePath((int*)a, n, next_left));
if (!next)
{
a[cur._row * n +cur._col] = 5; //5表示 下一步走不出去 把当前点从2变到五 表示这个点走不出去
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
else //cur 不能走
{
return false;
}
}

2 表示成功路线
5 表示 尝试失败的路线
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//--------------------迷宫 (最短路) ---------------
//-------------------Maze.h--------------------
#pragma once
#define N 10
#define DEBUGE 0 // 1 调试 0 不调试
#define MAZEPATH "MazeMap.txt"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <assert.h>
#include <stack>
struct Pos
{
int _row;
int _col;
};
//stack<Pos> MinPath;
void GetMaze(int* a, int n);
void PrintMaze(int* a, int n);
bool MazePath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry, stack<Pos>& path);
bool FindMinPath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry ,stack<Pos>& MinPath);
int GetCount(stack<Pos> path);
//---------------------------Maze.cpp-----------------
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
// 栈应用2:迷宫(n*n)问题
#include "Maze.h"
void GetMaze(int* a, int n)
{
FILE* f_out = fopen(MAZEPATH, "r");
assert(f_out != NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; )
{
char ch = fgetc(f_out);
if (ch == '0' || ch == '1') //通路为0 不通路2
{
a[i*n + j] = ch - '0';
++j;
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
}
fclose(f_out);
}
void PrintMaze(int* a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++ )
{
cout<<a[i * n + j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
bool CheckIsAccess(const int *a, int n, const Pos& next) //判断路通不通
{
assert(a);
if (next._row >= 0 && next._row < n
&& next._col >= 0 && next._col < n
&& a[next._row * n + next._col] == 0)// 0 表示路通
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// const Pos entry 入口 , stack<Pos>& path 用于压路径的 栈
bool MazePath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry, stack<Pos>& path)
{
Pos cur = entry;
path.push(cur);
while (!path.empty()) // 无路走时栈空
{
a[cur._row * n + cur._col] = 2;// 走过的路标记 2
// 定义数组 最下边为 出口
if (cur._row == n - 1) // 判断是否到出口
{
return true;
}
Pos next = cur;
// 向上 探索
next._row--;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向右 探索
next = cur;
next._col++;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向下 探索
next = cur;
next._row++;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 向左 探索
next = cur;
next._col--;
if (CheckIsAccess(a, n, next))
{
cur = next;
path.push(cur);
continue;
}
// 走不通
a[cur._row * n + cur._col] = 5;// 标出错误路线
path.pop();
if (!path.empty())
{
cur = path.top();
}
}
return false;
}
int GetCount(stack<Pos> path)
{
int count = 0;
while(!path.empty())
{
count += 1;
path.pop();
}
return count;
}
void huanyuan(int* a,int n, stack<Pos> Path) // Path不用引用
{
while(!Path.empty())
{
a[Path.top()._row * n + Path.top()._col] = 0;
Path.pop();
}
}
bool FindMinPath(int* a, int n, const Pos entry,stack<Pos>& MinPath)
{
bool next = false;
bool ret = false;
do
{
stack<Pos> path;
next = MazePath(a, n, entry, path);
//----------------debuge----------
#if DEBUGE
cout<<"-----------------------------"<<endl;
PrintMaze(a,n);
#endif
if (next)
{
if (MinPath.empty())
{
MinPath = path;
}
else
{
if (GetCount(MinPath) > GetCount(path))
{
MinPath = path; // 更新MinPath
}
}
huanyuan((int*)a, n, path);// 将已经走过的路 2 标记为 0
a[path.top()._row * n + path.top()._col] = 9; // 此出口已经堵住
//--------------debuge---------
#if DEBUGE
cout<<"-------------huanyuan----------------"<<endl;
PrintMaze(a,n);
#endif
ret = true;
}
}while(next);
if (ret)
{
huanyuan(a, n, MinPath);
//a[MinPath.top()._row * n + MinPath.top()._col] = 2; //打开这个最短路出口
}
return ret;
}
//--------------------------------test.cpp-----------------
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Maze.h"
void TestMaze()
{
int a
= {};
GetMaze((int*)a, N);
PrintMaze((int*)a, N);
stack<Pos> path;
stack<Pos> MinPath;
Pos entry = {2, 0};
FindMinPath((int*)a, N, entry ,MinPath);
cout<<"------------------------------"<<endl;
PrintMaze((int*)a, N);
}
int main()
{
TestMaze();
getchar();
return 0;
}
//----------------------------MazeMap.txt---------------------
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
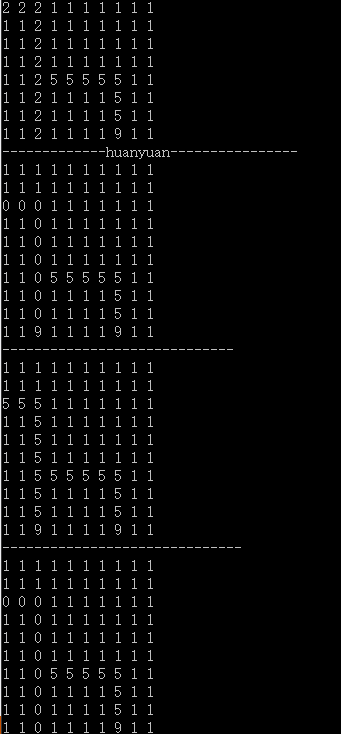
运行图:


相关文章推荐
- 使用C++实现JNI接口需要注意的事项
- 关于指针的一些事情
- c++ primer 第五版 笔记前言
- share_ptr的几个注意点
- Linux C函数参考手册(PDF版)
- C# partial关键字说明
- Lua中调用C++函数示例
- Lua教程(十七):C API简介
- 简单谈谈lua和c的交互
- Lua教程(一):在C++中嵌入Lua脚本
- Lua教程(二):C++和Lua相互传递数据示例
- C#中的委托数据类型简介
- C++联合体转换成C#结构的实现方法
- C#编写的艺术字类实例代码
- C#实现打造气泡屏幕保护效果
- 举例讲解C#编程中委托的实例化使用
- 使用C#代码获取存储过程返回值
- C++高级程序员成长之路
- C++编写简单的打靶游戏
