day05_行转列,列转行操作示例
2016-03-21 21:02
309 查看
create table TEST_TB_GRADE
(
ID NUMBER(10) not null,
USER_NAME VARCHAR2(20 CHAR),
COURSE VARCHAR2(20 CHAR),
SCORE FLOAT
);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(1,'michael','语文',78);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(2,'michael','数学',95);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(3,'michael','英语',81);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(4,'xiaoxiao','语文',97);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(5,'xiaoxiao','数学',78);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(6,'xiaoxiao','英语',91);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(7,'zhangsan','语文',80);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(8,'zhangsan','数学',55);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(9,'zhangsan','英语',75);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(10,'lisi','语文',87);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(11,'lisi','数学',65);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(12,'lisi','英语',75);
commit;
初始数据如下图:
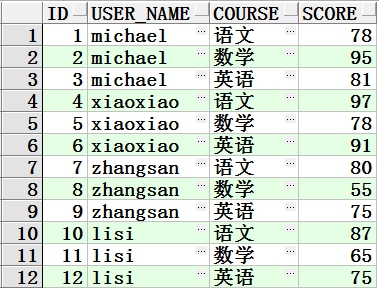
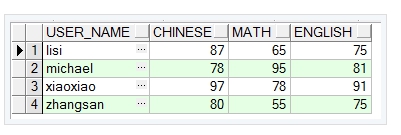
这就是最常见的行转列,主要原理是利用decode函数、聚集函数(sum),结合group by分组实现的,具体的sql如下
select t.user_name,
sum(decode(t.course, '语文', score,null)) as CHINESE,
sum(decode(t.course, '数学', score,null)) as MATH,
sum(decode(t.course, '英语', score,null)) as ENGLISH
from test_tb_grade t
group by t.user_name
order by t.user_name;
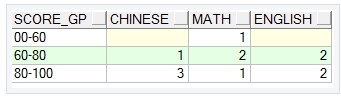
具体的实现sql如下:
Sql代码:
select t2.SCORE_GP,
sum(decode(t2.course, '语文', COUNTNUM,null)) as CHINESE,
sum(decode(t2.course, '数学', COUNTNUM,null)) as MATH,
sum(decode(t2.course, '英语', COUNTNUM,null)) as ENGLISH
from (
select t.course,
case when t.score <60 then '00-60'
when t.score >=60 and t.score <80 then '60-80'
when t.score >=80 then '80-100' end as SCORE_GP,
count(t.score) as COUNTNUM
FROM test_tb_grade t
group by t.course,
case when t.score <60 then '00-60'
when t.score >=60 and t.score <80 then '60-80'
when t.score >=80 then '80-100' end
order by t.course ) t2
group by t2.SCORE_GP
order by t2.SCORE_GP;
二、列转行表结构: TEST_TB_GRADE2
Sql代码:
create table TEST_TB_GRADE2
(
ID NUMBER(10) not null,
USER_NAME VARCHAR2(20 CHAR),
CN_SCORE FLOAT,
MATH_SCORE FLOAT,
EN_SCORE FLOAT
);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE2 values(1,'lisi',87,65,75);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE2 values(2,'michael',78,95,81);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE2 values(3,'xiaoxiao',97,78,91);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE2 values(4,'zhangsan',80,55,75);
commit;
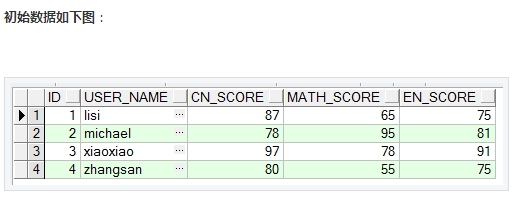
这就是最常见的列转行,主要原理是利用SQL里面的union,具体的sql语句如下:
Sql代码:
select user_name, 'CN_SCORE' COURSE, CN_SCORE as SCORE from test_tb_grade2
union
select user_name, 'MATH_SCORE' COURSE, MATH_SCORE as SCORE from test_tb_grade2
union
select user_name, 'EN_SCORE' COURSE, EN_SCORE as SCORE from test_tb_grade2
order by user_name, COURSE;
也可以利用【insert all into ... select】来实现
create table laowang(id number);
create table shuangshuang(id number);
create table xiaoming(id number);
create table dashi(id number);
insert all into ... select
insert all
into laowang
into shuangshuang
into xiaoming
into dashi
select OBJECT_ID from all_objects;
,首先需要先建一个表TEST_TB_GRADE3:
Sql代码:
create table TEST_TB_GRADE3
(
USER_NAME VARCHAR2(20 CHAR),
COURSE VARCHAR2(20 CHAR),
SCORE FLOAT
);
再执行下面的sql:
Sql代码:
insert all
into test_tb_grade3(USER_NAME,COURSE,SCORE) values(user_name, '语文', CN_SCORE)
into test_tb_grade3(USER_NAME,COURSE,SCORE) values(user_name, '数学', MATH_SCORE)
into test_tb_grade3(USER_NAME,COURSE,SCORE) values(user_name, '英语', EN_SCORE)
select user_name, CN_SCORE, MATH_SCORE, EN_SCORE from test_tb_grade2;
commit;
来自为知笔记(Wiz)
(
ID NUMBER(10) not null,
USER_NAME VARCHAR2(20 CHAR),
COURSE VARCHAR2(20 CHAR),
SCORE FLOAT
);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(1,'michael','语文',78);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(2,'michael','数学',95);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(3,'michael','英语',81);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(4,'xiaoxiao','语文',97);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(5,'xiaoxiao','数学',78);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(6,'xiaoxiao','英语',91);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(7,'zhangsan','语文',80);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(8,'zhangsan','数学',55);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(9,'zhangsan','英语',75);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(10,'lisi','语文',87);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(11,'lisi','数学',65);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE values(12,'lisi','英语',75);
commit;
初始数据如下图:

1.2、 如果需要实现如下的查询效果图:

这就是最常见的行转列,主要原理是利用decode函数、聚集函数(sum),结合group by分组实现的,具体的sql如下
select t.user_name,
sum(decode(t.course, '语文', score,null)) as CHINESE,
sum(decode(t.course, '数学', score,null)) as MATH,
sum(decode(t.course, '英语', score,null)) as ENGLISH
from test_tb_grade t
group by t.user_name
order by t.user_name;
1.3、延伸
如果要实现对各门功课的不同分数段进行统计,效果图如下:
具体的实现sql如下:
Sql代码:
select t2.SCORE_GP,
sum(decode(t2.course, '语文', COUNTNUM,null)) as CHINESE,
sum(decode(t2.course, '数学', COUNTNUM,null)) as MATH,
sum(decode(t2.course, '英语', COUNTNUM,null)) as ENGLISH
from (
select t.course,
case when t.score <60 then '00-60'
when t.score >=60 and t.score <80 then '60-80'
when t.score >=80 then '80-100' end as SCORE_GP,
count(t.score) as COUNTNUM
FROM test_tb_grade t
group by t.course,
case when t.score <60 then '00-60'
when t.score >=60 and t.score <80 then '60-80'
when t.score >=80 then '80-100' end
order by t.course ) t2
group by t2.SCORE_GP
order by t2.SCORE_GP;
二、列转行表结构: TEST_TB_GRADE2
Sql代码:
create table TEST_TB_GRADE2
(
ID NUMBER(10) not null,
USER_NAME VARCHAR2(20 CHAR),
CN_SCORE FLOAT,
MATH_SCORE FLOAT,
EN_SCORE FLOAT
);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE2 values(1,'lisi',87,65,75);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE2 values(2,'michael',78,95,81);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE2 values(3,'xiaoxiao',97,78,91);
insert into TEST_TB_GRADE2 values(4,'zhangsan',80,55,75);
commit;


这就是最常见的列转行,主要原理是利用SQL里面的union,具体的sql语句如下:
Sql代码:
select user_name, 'CN_SCORE' COURSE, CN_SCORE as SCORE from test_tb_grade2
union
select user_name, 'MATH_SCORE' COURSE, MATH_SCORE as SCORE from test_tb_grade2
union
select user_name, 'EN_SCORE' COURSE, EN_SCORE as SCORE from test_tb_grade2
order by user_name, COURSE;
也可以利用【insert all into ... select】来实现
create table laowang(id number);
create table shuangshuang(id number);
create table xiaoming(id number);
create table dashi(id number);
insert all into ... select
insert all
into laowang
into shuangshuang
into xiaoming
into dashi
select OBJECT_ID from all_objects;
,首先需要先建一个表TEST_TB_GRADE3:
Sql代码:
create table TEST_TB_GRADE3
(
USER_NAME VARCHAR2(20 CHAR),
COURSE VARCHAR2(20 CHAR),
SCORE FLOAT
);
再执行下面的sql:
Sql代码:
insert all
into test_tb_grade3(USER_NAME,COURSE,SCORE) values(user_name, '语文', CN_SCORE)
into test_tb_grade3(USER_NAME,COURSE,SCORE) values(user_name, '数学', MATH_SCORE)
into test_tb_grade3(USER_NAME,COURSE,SCORE) values(user_name, '英语', EN_SCORE)
select user_name, CN_SCORE, MATH_SCORE, EN_SCORE from test_tb_grade2;
commit;
来自为知笔记(Wiz)
相关文章推荐
- MySQL在windows系统中修改datadir路径后无法启动问题,报错1067
- PHP 版本 支付
- C/C++ 之 异常处理机制核心观点
- 整理的Python3数据类型
- 受限波尔滋曼机RBM
- 02.1android 广播总结
- 1012 Problem L
- Android 欢迎界面淡出动画效果(Animation)
- day5_vm_concat实现字段合并
- day05_oracle分析函数
- 软件工程-读书笔记(1-3章)
- IOS-音乐
- DAY2 160321
- 【机房重构】——数据库设计
- 将Tomcat源码导入Eclipse的标准步骤
- 安装cocoapods
- 状态压缩dp入门题 poj3254
- 深入理解PHP Opcode缓存原理
- android中的Application作用
- day5_查看表主外键关系
