Codeforces 629E:Famil Door and Roads
2016-03-12 18:42
323 查看
E. Famil Door and Roads
time limit per test
5 seconds
memory limit per test
512 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Famil Door’s City map looks like a tree (undirected connected acyclic graph) so other people call it Treeland. There are n intersections
in the city connected by n - 1 bidirectional roads.
There are m friends of Famil Door living in the city. The i-th
friend lives at the intersection ui and
works at the intersection vi.
Everyone in the city is unhappy because there is exactly one simple path between their home and work.
Famil Door plans to construct exactly one new road and he will randomly choose one among n·(n - 1) / 2 possibilities. Note,
that he may even build a new road between two cities that are already connected by one.
He knows, that each of his friends will become happy, if after Famil Door constructs a new road there is a path from this friend home to work and back that doesn't visit the same road twice. Formally, there is a simple cycle containing both ui and vi.
Moreover, if the friend becomes happy, his pleasure is equal to the length of such path (it's easy to see that it's unique). For each of his friends Famil Door wants to know his expected pleasure, that is the expected length of the cycle containing both ui and vi if
we consider only cases when such a cycle exists.
Input
The first line of the input contains integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 100 000) —
the number of the intersections in the Treeland and the number of Famil Door's friends.
Then follow n - 1 lines describing bidirectional roads. Each of them contains two integers ai and bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n) —
the indices of intersections connected by the i-th road.
Last m lines of the input describe Famil Door's friends. The i-th
of these lines contain two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi) —
indices of intersections where the i-th friend lives and works.
Output
For each friend you should print the expected value of pleasure if he will be happy. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
Namely: let's assume that your answer is a, and the answer of the jury is b.
The checker program will consider your answer correct, if
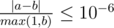
.
Examples
input
output
input
output
Note
Consider the second sample.
Both roads (1, 2) and (2, 3) work,
so the expected length if

Roads (1, 3) and (2, 3) make
the second friend happy. Same as for friend 1 the answer is 2.5
The only way to make the third friend happy is to add road (2, 3), so the answer is 3
还是记录一下这道题吧。。。题意是给出了一个树,在树中添加任意一条边,然后询问树中某两个点,形成环的长度的期望值。
u,v两点,k=lca(u,v)。
如果k==u||k==v,那么结果等于k上面的到k的距离之和/k上面的点的数量+u/v下面的点的距离之和/(u/v下面的点的数量)+u、v距离之和+1。
如果k不等于u或者v,那么结果等于u下面的点的距离之和/(u下面的点的数量)+v下面的点的距离之和/(v下面的点的数量v)+u、v距离之和+1。
另外,求到某一个点的距离的时候用到了之前搞过的树形dp。
代码:
time limit per test
5 seconds
memory limit per test
512 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Famil Door’s City map looks like a tree (undirected connected acyclic graph) so other people call it Treeland. There are n intersections
in the city connected by n - 1 bidirectional roads.
There are m friends of Famil Door living in the city. The i-th
friend lives at the intersection ui and
works at the intersection vi.
Everyone in the city is unhappy because there is exactly one simple path between their home and work.
Famil Door plans to construct exactly one new road and he will randomly choose one among n·(n - 1) / 2 possibilities. Note,
that he may even build a new road between two cities that are already connected by one.
He knows, that each of his friends will become happy, if after Famil Door constructs a new road there is a path from this friend home to work and back that doesn't visit the same road twice. Formally, there is a simple cycle containing both ui and vi.
Moreover, if the friend becomes happy, his pleasure is equal to the length of such path (it's easy to see that it's unique). For each of his friends Famil Door wants to know his expected pleasure, that is the expected length of the cycle containing both ui and vi if
we consider only cases when such a cycle exists.
Input
The first line of the input contains integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 100 000) —
the number of the intersections in the Treeland and the number of Famil Door's friends.
Then follow n - 1 lines describing bidirectional roads. Each of them contains two integers ai and bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n) —
the indices of intersections connected by the i-th road.
Last m lines of the input describe Famil Door's friends. The i-th
of these lines contain two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi) —
indices of intersections where the i-th friend lives and works.
Output
For each friend you should print the expected value of pleasure if he will be happy. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
Namely: let's assume that your answer is a, and the answer of the jury is b.
The checker program will consider your answer correct, if
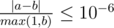
.
Examples
input
4 3 2 4 4 1 3 2 3 1 2 3 4 1
output
4.00000000 3.00000000 3.00000000
input
3 3 1 2 1 3 1 2 1 3 2 3
output
2.50000000 2.50000000 3.00000000
Note
Consider the second sample.
Both roads (1, 2) and (2, 3) work,
so the expected length if

Roads (1, 3) and (2, 3) make
the second friend happy. Same as for friend 1 the answer is 2.5
The only way to make the third friend happy is to add road (2, 3), so the answer is 3
还是记录一下这道题吧。。。题意是给出了一个树,在树中添加任意一条边,然后询问树中某两个点,形成环的长度的期望值。
u,v两点,k=lca(u,v)。
如果k==u||k==v,那么结果等于k上面的到k的距离之和/k上面的点的数量+u/v下面的点的距离之和/(u/v下面的点的数量)+u、v距离之和+1。
如果k不等于u或者v,那么结果等于u下面的点的距离之和/(u下面的点的数量)+v下面的点的距离之和/(v下面的点的数量v)+u、v距离之和+1。
另外,求到某一个点的距离的时候用到了之前搞过的树形dp。
代码:
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <deque>
#include <set>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define INF 0x3fffffffffffffff
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 2 * 100000 + 5;
const int maxm = 19;
struct ed
{
int w;
int to;
int next;
}edge[maxn];
int n, m, edgen;
int lca[maxn][20], head[maxn], deep[maxn], dis[maxn];
ll sz[maxn], sumdown[maxn], sumall[maxn], vis[maxn];
void addedge(int from, int to, int w)
{
edgen++;
edge[edgen].to = to;
edge[edgen].w = w;
edge[edgen].next = head[from];
head[from] = edgen;
}
void init()
{
edgen = 0;
memset(edge, -1, sizeof(edge));
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
memset(deep, 0, sizeof(deep));
memset(sz, 0, sizeof(sz));
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
memset(sumdown, 0, sizeof(sumdown));
memset(sumall, 0, sizeof(sumall));
}
void dfs(int x)
{
vis[x] = 1;
sz[x] = 1;
sumdown[x] = 0;
int i, j, k;
for (i = head[x]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next)
{
k = edge[i].to;
if (vis[k] == 0)
{
deep[k] = deep[x] + 1;
lca[k][0] = x;
for (j = 1; j < maxm; j++)
{
int fa = lca[k][j - 1];
if (fa == 0)continue;
lca[k][j] = lca[fa][j - 1];
}
dfs(k);
sumdown[x] += sumdown[k] + sz[k];
sz[x] += sz[k];
}
}
}
void dfs2(int x)
{
vis[x] = 1;
int i, j, k;
for (i = head[x]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next)
{
k = edge[i].to;
if (vis[k] == 0)
{
sumall[k] = sumall[x] + n - sz[k] - sz[k];
dfs2(k);
}
}
}
int up(int x, int d)
{
int i;
for (i = maxm - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (d < (1 << i))continue;
x = lca[x][i];
d = d - (1 << i);
}
return x;
}
int LCA(int x, int y)
{
if (deep[x] > deep[y])
{
swap(x, y);
}
y = up(y, deep[y] - deep[x]);
if (x == y)return x;
int i;
for (i = maxm - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (lca[x][i] != lca[y][i])
{
x = lca[x][i];
y = lca[y][i];
}
}
return lca[x][0];
}
void cal(int x, int y)
{
int i, j, k;
int v = LCA(x, y);
double sum = deep[x] + deep[y] - 2 * deep[v] + 1;
if (v == x)
{
k = up(y, deep[y] - deep[x] - 1);
sum += (double)(sumall[x] - sumdown[k] - sz[k]) / (double)(n - sz[k]);
}
else
{
sum += (double)(sumdown[x]) / (double)(sz[x]);
}
if (v == y)
{
k = up(x, deep[x] - deep[y] - 1);
sum += (double)(sumall[y] - sumdown[k] - sz[k]) / (double)(n - sz[k]);
}
else
{
sum += (double)(sumdown[y]) / (double)(sz[y]);
}
printf("%.12f\n", sum);
}
void solve()
{
int i, j, k;
int u, v, w;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
addedge(u, v, 0);
addedge(v, u, 0);
}
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
deep[1] = 1;
lca[1][0] = 1;
dfs(1);
sumall[1] = sumdown[1];
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
vis[1] = 1;
dfs2(1);
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
cal(u, v);
}
}
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("i.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("o.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
init();
solve();
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- onlien_judge_1368
- Hive分布式安装
- 常见HTTP状态码
- 支持向量机分类入门实用指南
- 回答一个关于OSM技术栈的问题
- python 实现用ISBN从豆瓣获取图书信息
- iOS UIAppearance使用详解
- 《大数据时代:生活、工作与思维的大变革》读书笔记3(完)
- POJ 3126 Prime Path 筛法+最短路
- Bellmanford 最短路(1)
- 利用adaboost元算法提高分类性能
- 集合框架-Map练习-记录字母出现的次数
- Ubuntu14.04(从Nginx官方源)安装Nginx稳定版预编译包
- Spring使用util Schema
- 第二周学习进度
- Java 信号量 Semaphore 介绍
- 合并排序
- 数据库学习:for xml path
- PHP判断素数,循环,筛选——默认可执行时间秒数,默认可执行空间。用来测试运行效率
- Linux内核分析-构造一个简单的Linux系统MenuOS
