C. k-Tree
2016-03-08 18:08
190 查看
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Quite recently a creative student Lesha had a lecture on trees. After the lecture Lesha was inspired and came up with the tree of his own which he called a k-tree.
A k-tree is an infinite rooted tree where:
each vertex has exactly k children;
each edge has some weight;
if we look at the edges that goes from some vertex to its children (exactly k edges), then their weights will equal1, 2, 3, ..., k.
The picture below shows a part of a 3-tree.
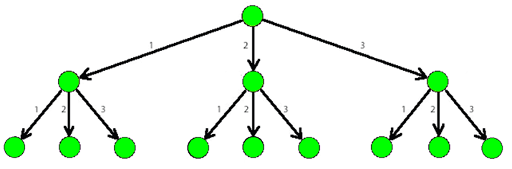
As soon as Dima, a good friend of Lesha, found out about the tree, he immediately wondered: "How many paths of total weight n (the
sum of all weights of the edges in the path) are there, starting from the root of a k-tree and also containing at least one edge of
weight at least d?".
Help Dima find an answer to his question. As the number of ways can be rather large, print it modulo 1000000007(109 + 7).
Input
A single line contains three space-separated integers: n, k and d (1 ≤ n, k ≤ 100; 1 ≤ d ≤ k).
Output
Print a single integer — the answer to the problem modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
input
output
解题说明:题意是给出K-Tree定义,每个结点都有恰好K个孩子,这棵树无限增长。每个节点到它K个孩子的K条边的权重刚好是1,2,3...,K。现在问有多少条路径,使得从根节点出发到达某个结点,经过的边权重之和恰好为n,并且经过的边至少有一条权重不小于d。做法是采用动态规划
dp[i][0]:表示权值和为i中不包含权值>=d的边。
dp[i][j]:表示权值和为i中包含权值>=d的边。
dp[i][0]+=dp[i-j][0] (j<d)
dp[i][1]+=dp[i-j][0] (j>=d)
dp[i][1]+=dp[i-j][1];
#include<cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#define MAX_N (100)
#define MOD (1000000007)
using namespace std;
int dp[2][MAX_N+1];
void build_dp(int n, int k, int d)
{
int j,m;
dp[0][0] = 1;
for ( j=1; j <= n; ++j )
{
for ( m=1; m <= k; ++m )
{
dp[0][j] += j-m >= 0 ? dp[0][j-m] : 0, dp[0][j] %= MOD;
}
}
for ( j=1; j <= n; ++j )
{
for ( m=1; m < d; ++m )
{
dp[1][j] += j-m >= 0 ? dp[1][j-m] : 0, dp[1][j] %= MOD;
}
for ( m=d; m <= k; ++m )
{
dp[1][j] += j-m >= 0 ? dp[0][j-m] : 0, dp[1][j] %= MOD;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n,k,d;
scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &k, &d);
build_dp(n, k, d);
printf("%d\n", dp[1]
);
return 0;
}
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Quite recently a creative student Lesha had a lecture on trees. After the lecture Lesha was inspired and came up with the tree of his own which he called a k-tree.
A k-tree is an infinite rooted tree where:
each vertex has exactly k children;
each edge has some weight;
if we look at the edges that goes from some vertex to its children (exactly k edges), then their weights will equal1, 2, 3, ..., k.
The picture below shows a part of a 3-tree.

As soon as Dima, a good friend of Lesha, found out about the tree, he immediately wondered: "How many paths of total weight n (the
sum of all weights of the edges in the path) are there, starting from the root of a k-tree and also containing at least one edge of
weight at least d?".
Help Dima find an answer to his question. As the number of ways can be rather large, print it modulo 1000000007(109 + 7).
Input
A single line contains three space-separated integers: n, k and d (1 ≤ n, k ≤ 100; 1 ≤ d ≤ k).
Output
Print a single integer — the answer to the problem modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Examples
input
3 3 2
output
3
input
3 3 3
output
1
input
4 3 2
output
6
input
4 5 2
output
7
解题说明:题意是给出K-Tree定义,每个结点都有恰好K个孩子,这棵树无限增长。每个节点到它K个孩子的K条边的权重刚好是1,2,3...,K。现在问有多少条路径,使得从根节点出发到达某个结点,经过的边权重之和恰好为n,并且经过的边至少有一条权重不小于d。做法是采用动态规划
dp[i][0]:表示权值和为i中不包含权值>=d的边。
dp[i][j]:表示权值和为i中包含权值>=d的边。
dp[i][0]+=dp[i-j][0] (j<d)
dp[i][1]+=dp[i-j][0] (j>=d)
dp[i][1]+=dp[i-j][1];
#include<cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#define MAX_N (100)
#define MOD (1000000007)
using namespace std;
int dp[2][MAX_N+1];
void build_dp(int n, int k, int d)
{
int j,m;
dp[0][0] = 1;
for ( j=1; j <= n; ++j )
{
for ( m=1; m <= k; ++m )
{
dp[0][j] += j-m >= 0 ? dp[0][j-m] : 0, dp[0][j] %= MOD;
}
}
for ( j=1; j <= n; ++j )
{
for ( m=1; m < d; ++m )
{
dp[1][j] += j-m >= 0 ? dp[1][j-m] : 0, dp[1][j] %= MOD;
}
for ( m=d; m <= k; ++m )
{
dp[1][j] += j-m >= 0 ? dp[0][j-m] : 0, dp[1][j] %= MOD;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n,k,d;
scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &k, &d);
build_dp(n, k, d);
printf("%d\n", dp[1]
);
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- mysql 数据库编译安装
- basic_iptables_how_to_for_ubuntu
- HomeWork2
- Ajax实现无刷新分页
- 支付宝集成
- Java网络编程(一)流
- 浅谈NSUserDefaults
- 推荐!手把手教你使用Git
- Python常用内置函数介绍【filter,map,reduce,apply,zip】
- 网页布局水平垂直技术
- Java单例模式七种实现方式
- [Cocos2d-x v3.x]序列帧动画
- 使用<c:if>标签处理页面数据
- 管理组
- Leetcode ☞ 234. Palindrome Linked List
- IE8及以下浏览器,关键字不能作为属性名称
- 一、各种WAV文件头格式
- EventBus源码解析 源码阅读记录
- 使用 Async 和 Await 的异步编程(C# 和 Visual Basic)[msdn.microsoft.com]
- Windows下Memcache的安装及PHP扩展配置方法
