hdu 1325 Is It A Tree? 判断是否是树 巨坑
2016-02-05 12:51
483 查看
每组数据,给出,一些有向边,从父亲指向儿子结点,每组数据以0 0 结尾,
整个输入以小于0的两个数结尾,判断每组数据是否是一棵树。
这个题目最坑的在于结尾的样例给的是-1 -1 ,结果习惯性的认为是-1 -1结尾,最后莫名其妙的wrong answer。
判定是否是一棵树:
0.空树可以是树。就是输入0 0 的一组也是数。
1.存在一个且仅有一个入度为0的结点。
2.其余结点的入度必须是1。
3.整个图必须是连通的。(用并查集实现,把有向边当作无向边)
下面证明如果不是空树,只要满足1、2、3三点就一定是一棵树。
我们建立一个集合S={},不断将点放入S
首先我们根据1可以找到仅有的一个根结点root,将root放入S,
因为所有点是连通的(根据3),而且root的入度为0,所以必须有从root出发边,假设连接到a1,将a放入S集合,那么因为a1的入度是1(根据2),所以S集合现在只能发出边,不能进入边,因为所有点连通,之后依次加入各点,直到所有点都放入S。
这个实质就是形成树的一个过程。
你可以发现这样形成的树,每个结点只有一个父结点,满足n=m+1,而且绝对无环。
Total Submission(s): 19561 Accepted Submission(s): 4385
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
A tree is a well-known data structure that is either empty (null, void, nothing) or is a set of one or more nodes connected by directed edges between nodes satisfying the following properties.
There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point.
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.
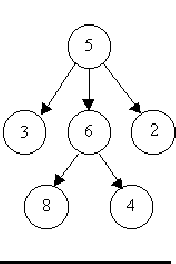
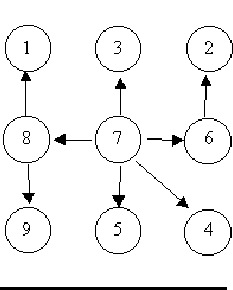
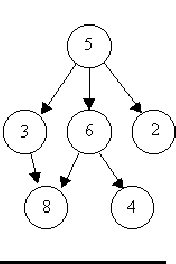
In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
[align=left]Input[/align]
The input will consist of a sequence of descriptions (test cases) followed by a pair of negative integers. Each test case will consist of a sequence of edge descriptions followed by a pair of zeroes Each edge description will consist
of a pair of integers; the first integer identifies the node from which the edge begins, and the second integer identifies the node to which the edge is directed. Node numbers will always be greater than zero.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For each test case display the line ``Case k is a tree." or the line ``Case k is not a tree.", where k corresponds to the test case number (they are sequentially numbered starting with 1).
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4
5 6 0 0
8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5
7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0
3 8 6 8 6 4
5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0
-1 -1
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
Case 1 is a tree.
Case 2 is a tree.
Case 3 is not a tree.
[align=left]Source[/align]
North Central North America 1997
整个输入以小于0的两个数结尾,判断每组数据是否是一棵树。
这个题目最坑的在于结尾的样例给的是-1 -1 ,结果习惯性的认为是-1 -1结尾,最后莫名其妙的wrong answer。
判定是否是一棵树:
0.空树可以是树。就是输入0 0 的一组也是数。
1.存在一个且仅有一个入度为0的结点。
2.其余结点的入度必须是1。
3.整个图必须是连通的。(用并查集实现,把有向边当作无向边)
下面证明如果不是空树,只要满足1、2、3三点就一定是一棵树。
我们建立一个集合S={},不断将点放入S
首先我们根据1可以找到仅有的一个根结点root,将root放入S,
因为所有点是连通的(根据3),而且root的入度为0,所以必须有从root出发边,假设连接到a1,将a放入S集合,那么因为a1的入度是1(根据2),所以S集合现在只能发出边,不能进入边,因为所有点连通,之后依次加入各点,直到所有点都放入S。
这个实质就是形成树的一个过程。
你可以发现这样形成的树,每个结点只有一个父结点,满足n=m+1,而且绝对无环。
Is It A Tree?
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 19561 Accepted Submission(s): 4385
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
A tree is a well-known data structure that is either empty (null, void, nothing) or is a set of one or more nodes connected by directed edges between nodes satisfying the following properties.
There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point.
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.



In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
[align=left]Input[/align]
The input will consist of a sequence of descriptions (test cases) followed by a pair of negative integers. Each test case will consist of a sequence of edge descriptions followed by a pair of zeroes Each edge description will consist
of a pair of integers; the first integer identifies the node from which the edge begins, and the second integer identifies the node to which the edge is directed. Node numbers will always be greater than zero.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For each test case display the line ``Case k is a tree." or the line ``Case k is not a tree.", where k corresponds to the test case number (they are sequentially numbered starting with 1).
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4
5 6 0 0
8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5
7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0
3 8 6 8 6 4
5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0
-1 -1
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
Case 1 is a tree.
Case 2 is a tree.
Case 3 is not a tree.
[align=left]Source[/align]
North Central North America 1997
/**========================================== * This is a solution for ACM/ICPC problem * * @source:hdu 1325 * @type: * @author: wust_ysk * @blog: http://blog.csdn.net/yskyskyer123 * @email: 2530094312@qq.com *===========================================*/ #include<cstdio> #include<string> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<cmath> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int INF =0x3f3f3f3f; const int maxn= 1000000 ; int n,m; int in[maxn+5],out[maxn+5],maxi; bool vis[maxn+5]; int pre[maxn+5]; int find(int x) { return x==pre[x]?x:pre[x]=find(pre[x]); } void merge(int x,int y) { int rootx=find(x); int rooty=find(y); if(rootx==rooty) return; pre[rootx]=rooty; } int main() { int x,y,kase=0; while(~scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)&&x>=0&&y>=0) { maxi=0;n=0,m=0; if(x==0&&y==0) { printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",++kase); continue; } memset(in,0,sizeof in); memset(out,0,sizeof out); memset(vis,0,sizeof vis); out[x]++,in[y]++; maxi=max(maxi,x); maxi=max(maxi,y); if(!vis[x]) pre[x]=x; if(!vis[y]) pre[y]=y; vis[x]=1,vis[y]=1; merge(x,y); m++; while(~scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)&&x&&y ) { out[x]++,in[y]++; maxi=max(maxi,x); maxi=max(maxi,y); if(!vis[x]) pre[x]=x; if(!vis[y]) pre[y]=y; vis[x]=1,vis[y]=1; merge(x,y); m++; } int hasroot=0; bool ok_in=1, uni=1; for(int i=1;i<=maxi;i++) if(vis[i]) { n++; if(in[i]==0) hasroot++; else if(ok_in) ok_in=in[i]==1; if(uni) uni=uni&& (find(i)==find(maxi) ); } if(hasroot!=1||!ok_in||!uni) { printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n",++kase);continue; } printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",++kase); } return 0; }
相关文章推荐
- Android 开发体系图
- ios 将随意对象存进数据库
- Android 带password输入界面的Dialog实现机制
- UVa 11624 - Fire!
- systemd和systemctl
- 关于META-INF/services in JAR 的介绍
- 【CodeForces 312B】BUPT 2015 newbie practice #3A Archer
- junit设计模式--适配器模式
- noip2002-自由落体 2008.11.5
- noip2003传染病控制 2008.11.5
- junit设计模式--适配器模式
- linux下编译hadoop2.4.1源码
- VS2010中出现无法嵌入互操作类型
- JSP页面布局工具JWebBox升级到2.0版
- setInterval和setTimeout
- 人工智能、应用、程序
- Java [Leetcode 88]CMerge Sorted Array
- poj3233 Matrix Power Series (矩阵快速幂+二分)
- 关于accept 返回的socket的阻塞属性
- 字符串替换-K&R C 题3-2
