Android下的屏幕适配
2016-01-12 12:20
357 查看
什么是适配
适配 即当前应用在相同的手机上面显示相同的效果。
适配前需要首先确定当前手机所属像素密度类型(如:xhdpi、hdpi、mdpi等),下面以华为G700、模拟器为例,讲解如何计算像素密度。
案例一:
手机型号:G700
手机分辨率:1280*720 (注:手机两个直角边上分别放置了1280及720个像素点)
手机尺寸大小:5英寸(手机斜边长度)
假设a,b分别为两个直角边,c为斜边,由勾股定理可得出计算方式:sqrt(a*a+b*b)/c
计算结果:sqrt(1280*1280+720*720)/5 ≈ 293.72dpi
根据google官方文档说明得出,当前手机最接近320dpi,则将其归纳在xhdpi手机范围内,
即1dp=2px;
案例二:
手机型号:模拟器
手机分辨率:800*480(注:手机两个直角边上分别放置了800及480个像素点)
手机尺寸大小:3.7英寸(手机斜边大小)
计算结果:sqrt(800*800+480*480)/3.7 ≈ 252.15dpi
根据google官方文档(图1-1)得出,当前手机接近240dpi,则将其归纳在hdpi手机范围内,
即1dp=1.5px。
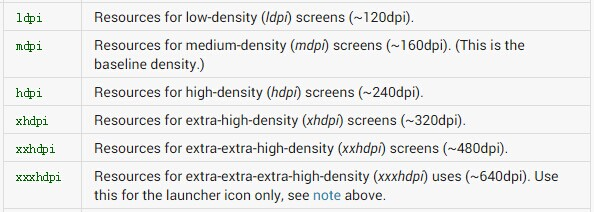
按照以上计算方式,大致可以将市场上的手机划分为5个像素密度等级,具体如下:
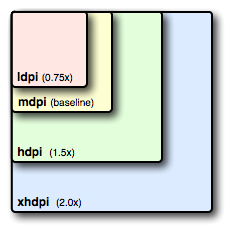
ldpi:120dpi,像素密度与dp转换关系为:1dp = 0.75px
mdpi:160dpi ,像素密度与dp转换关系为:1dp = 1px
hdpi:240dpi,像素密度与dp转换关系为:1dp = 1.5px
xhdpi:320dpi,像素密度与dp转换关系为:1dp = 2px
xxhdpi:480dpi,像素密度与dp转换关系为:1dp = 3px
如何适配
下面以华为手机G700和模拟器的对比,讲解如何进行屏幕适配,具体方式如下:
适配方式1:图片适配
不同像素密度的手机加载工程资源文件(res)中不同资源图片,以手机G700和模拟器为例,图片的布局代码如下所示:
若使用G700(xhdpi)加载a.jpg文件,该文件位于res/drawable-xhdpi文件夹下,显示效果如下:
若使用模拟器(hdpi)加载a.jpg文件,该文件位于res/drawable-hdpi文件夹下,显示效果如下:
适配方式2:dimens.xml文件适配
dimens.xml存在于工程资源(res)文件夹中不同values(如:value-1280x720、value-800x480)文件夹下,可用于指定控件大小,不同像素密度手机加载不同values文件夹下的dimens.xml文件,使用方式如下:
模拟器(hdpi):加载dimens.xml资源文件,位于res/value-800x480文件夹下
G700(xhdpi):加载dimens.xml资源文件,位于res/value-1280x720文件夹下
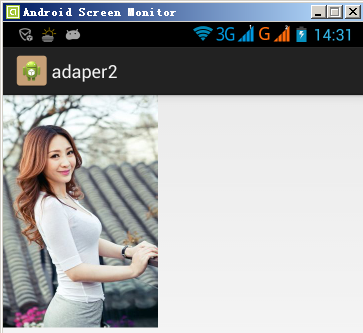
G700(xhdpi)显示的图片效果如下所示:
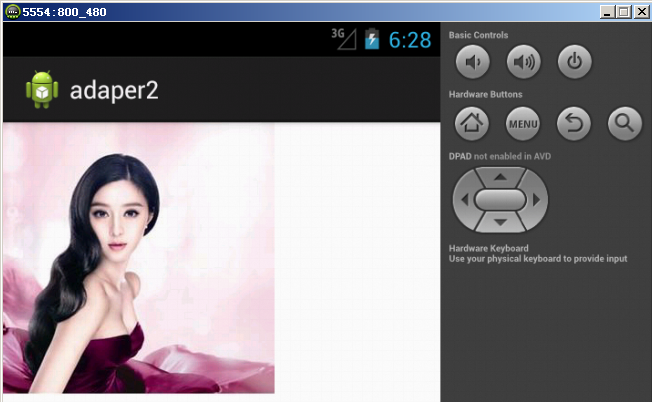
模拟器(hdpi)显示的图片效果如下所示:
适配方式3:布局文件适配
不同分辨率的手机,加载不同的布局文件已达到适配效果。创建多个layout(如:layout-1280x720、layout-800x480)文件夹用于存放不同像素密度手机所需布局文件。
模拟器(hdpi):加载activity_main.xml布局文件,位于res/layout-800x480文件夹下:
G700(xhdpi):加载activity_main.xml布局文件,位于res/layout-1280x720文件夹下:
G700(xhdpi)显示的图片效果如下:
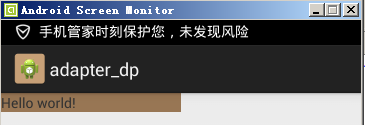
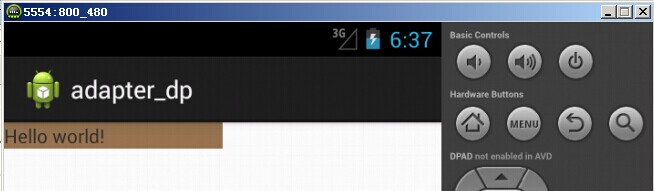
模拟器(hdpi)显示的图片效果如下所示:
适配方式4:java代码适配
通过android相应api获取当前手机的宽高像素值,按比例分配屏幕中控件的宽高以达到适配效果,下面是布局和实现功能的核心代码:
布局文件
G700(xhdpi)显示效果如下:
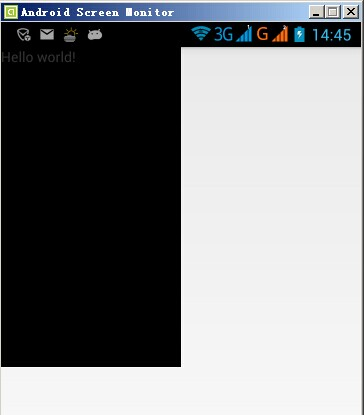
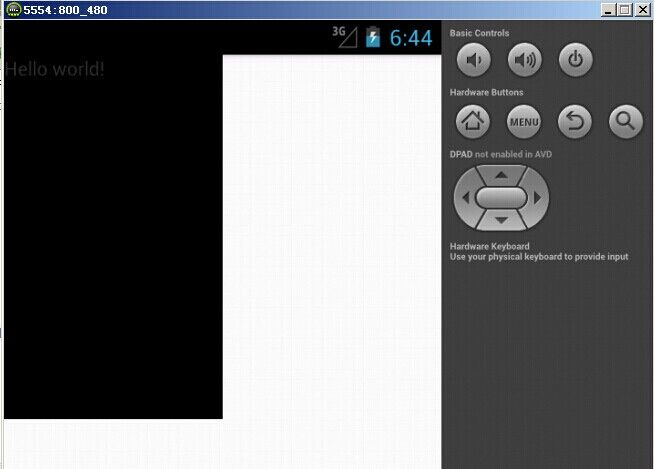
模拟器(hdpi)显示效果如下:
适配方式5:权重适配
通过android提供的(权重)剩余空间分配,达到适配效果。布局文件如下所示:
G700(xhdpi)显示的图片效果如下所示:
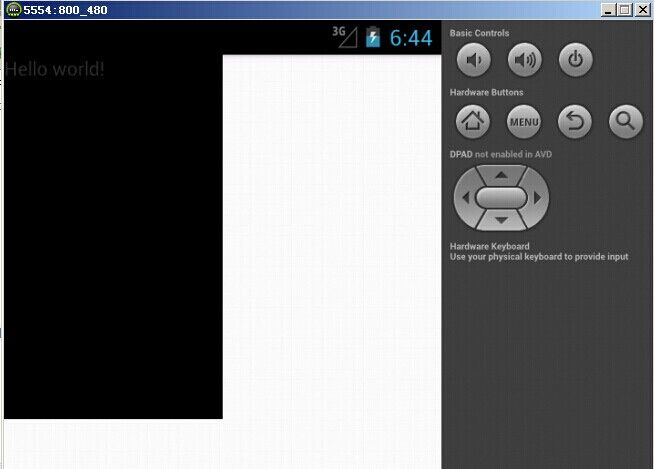
模拟器(hdpi)显示的图片效果如下所示:
适配 即当前应用在相同的手机上面显示相同的效果。
适配前需要首先确定当前手机所属像素密度类型(如:xhdpi、hdpi、mdpi等),下面以华为G700、模拟器为例,讲解如何计算像素密度。
案例一:
手机型号:G700
手机分辨率:1280*720 (注:手机两个直角边上分别放置了1280及720个像素点)
手机尺寸大小:5英寸(手机斜边长度)
假设a,b分别为两个直角边,c为斜边,由勾股定理可得出计算方式:sqrt(a*a+b*b)/c
计算结果:sqrt(1280*1280+720*720)/5 ≈ 293.72dpi
根据google官方文档说明得出,当前手机最接近320dpi,则将其归纳在xhdpi手机范围内,
即1dp=2px;
案例二:
手机型号:模拟器
手机分辨率:800*480(注:手机两个直角边上分别放置了800及480个像素点)
手机尺寸大小:3.7英寸(手机斜边大小)
计算结果:sqrt(800*800+480*480)/3.7 ≈ 252.15dpi
根据google官方文档(图1-1)得出,当前手机接近240dpi,则将其归纳在hdpi手机范围内,
即1dp=1.5px。
按照以上计算方式,大致可以将市场上的手机划分为5个像素密度等级,具体如下:
ldpi:120dpi,像素密度与dp转换关系为:1dp = 0.75px
mdpi:160dpi ,像素密度与dp转换关系为:1dp = 1px
hdpi:240dpi,像素密度与dp转换关系为:1dp = 1.5px
xhdpi:320dpi,像素密度与dp转换关系为:1dp = 2px
xxhdpi:480dpi,像素密度与dp转换关系为:1dp = 3px


如何适配
下面以华为手机G700和模拟器的对比,讲解如何进行屏幕适配,具体方式如下:
适配方式1:图片适配
不同像素密度的手机加载工程资源文件(res)中不同资源图片,以手机G700和模拟器为例,图片的布局代码如下所示:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@drawable/a"/> </RelativeLayout>
若使用G700(xhdpi)加载a.jpg文件,该文件位于res/drawable-xhdpi文件夹下,显示效果如下:
若使用模拟器(hdpi)加载a.jpg文件,该文件位于res/drawable-hdpi文件夹下,显示效果如下:
适配方式2:dimens.xml文件适配
dimens.xml存在于工程资源(res)文件夹中不同values(如:value-1280x720、value-800x480)文件夹下,可用于指定控件大小,不同像素密度手机加载不同values文件夹下的dimens.xml文件,使用方式如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <!-- 不同的手机加载不同的dp --> <TextView android:background="#987654" android:layout_width="@dimen/width" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello_world" /> </LinearLayout>
模拟器(hdpi):加载dimens.xml资源文件,位于res/value-800x480文件夹下
<resources> <dimen name="width">160dp</dimen> </resources>
根据上述hdpi dp和px的转换关系1dp = 1.5px,则160dp = 240px,当前控件宽度应该位于屏幕中间位置。
G700(xhdpi):加载dimens.xml资源文件,位于res/value-1280x720文件夹下
<resources> <dimen name="width">180dp</dimen> </resources>
根据上述xhdpi 中dp和px的转换关系1dp = 2px,则180dp = 360px,当前控件宽度应该位于屏幕中间位置。
G700(xhdpi)显示的图片效果如下所示:

模拟器(hdpi)显示的图片效果如下所示:

适配方式3:布局文件适配
不同分辨率的手机,加载不同的布局文件已达到适配效果。创建多个layout(如:layout-1280x720、layout-800x480)文件夹用于存放不同像素密度手机所需布局文件。
模拟器(hdpi):加载activity_main.xml布局文件,位于res/layout-800x480文件夹下:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="800*480手机会去加载的布局文件" /> </RelativeLayout>
G700(xhdpi):加载activity_main.xml布局文件,位于res/layout-1280x720文件夹下:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="1280*720手机会去加载的布局文件" /> </RelativeLayout>
G700(xhdpi)显示的图片效果如下:

模拟器(hdpi)显示的图片效果如下所示:

适配方式4:java代码适配
通过android相应api获取当前手机的宽高像素值,按比例分配屏幕中控件的宽高以达到适配效果,下面是布局和实现功能的核心代码:
布局文件
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:background="#000000" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello_world" /> </RelativeLayout> activity中oncreate核心代码: TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv); //获取封装当前手机屏幕信息对象,用于存放宽高值 DisplayMetrics metrics = new DisplayMetrics(); //给当前屏幕设置宽高 getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(metrics); //获取高度 Constant.srceenHeight = metrics.heightPixels; //获取宽度 Constant.srceenWidth = metrics.widthPixels; Log.i(tag, "Constant.srceenHeight = "+Constant.srceenHeight); Log.i(tag, "Constant.srceenWidth = "+Constant.srceenWidth); //宽高各占50% RelativeLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams( (int)(Constant.srceenWidth*0.5+0.5), (int)(Constant.srceenHeight*0.5+0.5)); tv.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
G700(xhdpi)显示效果如下:

模拟器(hdpi)显示效果如下:

适配方式5:权重适配
通过android提供的(权重)剩余空间分配,达到适配效果。布局文件如下所示:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView android:background="#000000" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_height="match_parent"/> <TextView android:background="#123456" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_height="match_parent"/> </LinearLayout>
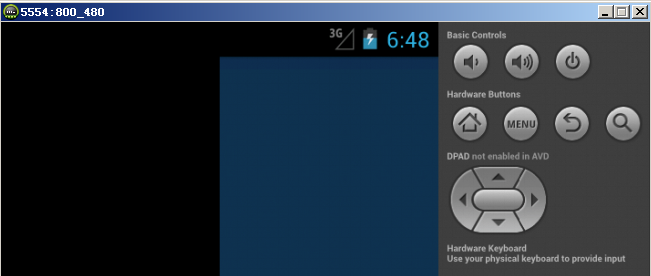
G700(xhdpi)显示的图片效果如下所示:

模拟器(hdpi)显示的图片效果如下所示:

相关文章推荐
- 关于android里的文件创建及读写问题
- android应用程序窗口框架学习(2)-view绘制流程源代码解析-setContentView与LayoutInflater加载解析机制源码分析
- [Andorid开发艺术探索 读书笔记]View的事件体系(一)
- Android编程使用Intent传递对象的方法分析
- Activity生命周期
- android 来电拦截
- Android中的几种小窗口实现
- Android实现QQ抢红包插件
- Android编程获取地理位置的经度和纬度实例
- Android中回调接口使用实例
- android用于打开各种文件的intent
- Android系统 小米/三星/索尼 应用启动图标未读消息数(BadgeNumber)动态提醒
- Android-四元数-控制VR设备的旋转
- 创建手机桌面的悬浮图标
- Android sdk等工具下载地址
- Android SD卡路径问题以及如何获取SDCard 内存
- 同步、更新、下载Android Source & SDK from 国内镜像站
- android应用程序窗口框架学习(1)-view绘制流程源代码解析
- Android常见XML属性解析
- Android编程实现监控apk安装,卸载,替换的方法
