安卓StateMachine分析举例---WifiStateMachine
2016-01-03 17:31
519 查看
WifiStateMachine创建:
创建在构造方法WifiStateMachine(Context context, String wlanInterface) 中实施:public WifiStateMachine(Context context, String wlanInterface) {
/*调用stateMachine类的构造方法完成状态机的构造,名字为WifiStateMachine*/
super("WifiStateMachine");
/*添加状态*/
addState(mDefaultState);
addState(mInitialState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartedState, mDefaultState);
addState(mDriverStartingState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mDriverStartedState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mScanModeState, mDriverStartedState);
addState(mConnectModeState, mDriverStartedState);
addState(mL2ConnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mObtainingIpState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mVerifyingLinkState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mCaptivePortalCheckState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mConnectedState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mDisconnectingState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mDisconnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWpsRunningState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWaitForP2pDisableState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mDriverStoppingState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mDriverStoppedState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mSupplicantStoppingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSoftApStartingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSoftApStartedState, mDefaultState);
addState(mTetheringState, mSoftApStartedState);
addState(mTetheredState, mSoftApStartedState);
addState(mUntetheringState, mSoftApStartedState);
/*设置初始状态*/
setInitialState(mInitialState);
/*设置状态日志记录*/
setLogRecSize(2000);
setLogOnlyTransitions(false);
/*开始状态机*/
start();
}在start方法中,调用completeConstruction方法完成构造,这个方法之前已经分析过,主要是完成状态机棧的搭建,并发送启动完成的消息,将状态机运行起来。状态机起来后,分别运行mDefaultState和mInitialState的状态的enter方法,在mDefaultState的方法中do nothing,在mInitialState的enter方法中,进行了wifi相关的初始化,这里不做关注:
public void enter() {
mWifiNative.unloadDriver();
if (mWifiP2pChannel == null) {
mWifiP2pChannel = new AsyncChannel();
mWifiP2pChannel.connect(mContext, getHandler(), mWifiP2pManager.getMessenger());
}
if (mWifiApConfigChannel == null) {
mWifiApConfigChannel = new AsyncChannel();
WifiApConfigStore wifiApConfigStore = WifiApConfigStore.makeWifiApConfigStore(
mContext, getHandler());
wifiApConfigStore.loadApConfiguration();
mWifiApConfigChannel.connectSync(mContext, getHandler(),wifiApConfigStore.getMessenger());
}
}至此WifiStateMachine创建成功,运行在InitialState状态,罗列一下各个状态之间的关系:
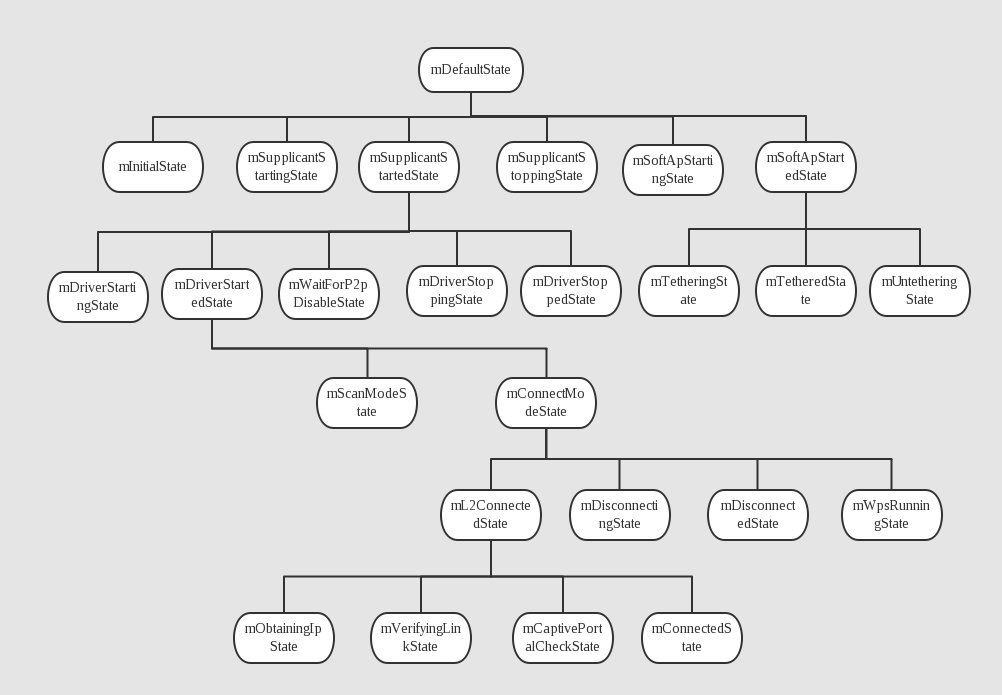
WifiStateMachine状态切换举例–开启AP:
调用setHostApRunning方法,开启AP功能,此方法发送CMD_START_AP消息状态机启动后处于InitialState状态,收到CMD_START_AP消息后:
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
switch (message.what) {
/*省略代码*/
case CMD_START_AP:
if (mWifiNative.loadDriver()) {
/*设置AP状态*/
setWifiApState(WIFI_AP_STATE_ENABLING);
/*状态切换mSoftApStartingState*/
transitionTo(mSoftApStartingState);
} else {
loge("Failed to load driver for softap");
}
/*省略代码*/
}
}此消息处理函数处理完后,跳转到mSoftApStartingState
进入mSoftApStartingState的enter方法:
public void enter() {
final Message message = getCurrentMessage();
if (message.what == CMD_START_AP) {
final WifiConfiguration config = (WifiConfiguration) message.obj;
if (config == null) {
mWifiApConfigChannel.sendMessage(CMD_REQUEST_AP_CONFIG);
} else {
mWifiApConfigChannel.sendMessage(CMD_SET_AP_CONFIG, config);
/*开启AP*/
startSoftApWithConfig(config);
}
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Illegal transition to SoftApStartingState: " + message);
}
}startSoftApWithConfig开启AP成功后,会发送CMD_START_AP_SUCCESS消息,
SoftApStartingState状态下,处理此消息:
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
switch(message.what) {
//
case CMD_START_AP_SUCCESS:
/*设置AP状态*/
setWifiApState(WIFI_AP_STATE_ENABLED);
/*跳转到mSoftApStartedState*/
transitionTo(mSoftApStartedState);
break;
}
}CMD_START_AP_SUCCESS消息处理完后,跳转到mSoftApStartedState状态,执行该状态的enter方法。此状态下受到CMD_TETHER_STATE_CHANGE消息后处理:
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
switch(message.what) {
//
case CMD_TETHER_STATE_CHANGE:
TetherStateChange stateChange = (TetherStateChange) message.obj;
/*开启tethering*/
if (startTethering(stateChange.available)) {
transitionTo(mTetheringState);
}
break;
}
}开启startTethering成功后,跳转到mTetheringState状态,执行其enter方法:
public void enter() {
/*发送延时消息,超时时间5s*/
sendMessageDelayed(obtainMessage(CMD_TETHER_NOTIFICATION_TIMED_OUT,
++mTetherToken, 0), TETHER_NOTIFICATION_TIME_OUT_MSECS);
}处于mTetheringState状态下,收到CMD_TETHER_NOTIFICATION_TIMED_OUT超时消息,则启动tether失败,一步步切换,退回到init状态。如果在超时消息之前收到CMD_TETHER_STATE_CHANGE消息,则走如下 处理:
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
switch(message.what) {
/*省略代码*/
case CMD_TETHER_STATE_CHANGE:
TetherStateChange stateChange = (TetherStateChange) message.obj;
if (isWifiTethered(stateChange.active)) {
transitionTo(mTetheredState);
}
return HANDLED;
/*省略代码*/
}如果isWifiTethered返回成功则跳转到mTetheredState状态,并执行其enter方法。否则,超时消息到达后关闭ap。
至此整个状态机的状态历经如下切换,稳定在mThertheredState
mInitialState->mSoftApStartingState->mSoftApStartedState->mThetheringState->mThertheredState
若在mThertheredState状态下关闭AP,则按照如下流程切换
mThertheredState->mUntetheringState->mSoftApStartedState->mInitialState
这个流程中用到了deferMessage来实现相同消息的反复发送。在StateMachine章节已论述。
根据源码分析,弄清一个状态机代码流程的关键点是根据源码画出状态关系图,再根据状态逐个进行推演。如果是定位问题,可以重点使用dump功能,将状态迁徙的过程dump出来,再结合logcat进行分析。
相关文章推荐
- 使用C++实现JNI接口需要注意的事项
- Android IPC进程间通讯机制
- Android Manifest 用法
- [转载]Activity中ConfigChanges属性的用法
- Android之获取手机上的图片和视频缩略图thumbnails
- Android之使用Http协议实现文件上传功能
- Android学习笔记(二九):嵌入浏览器
- android string.xml文件中的整型和string型代替
- i-jetty环境搭配与编译
- android之定时器AlarmManager
- android wifi 无线调试
- Android Native 绘图方法
- Android java 与 javascript互访(相互调用)的方法例子
- android 代码实现控件之间的间距
- android FragmentPagerAdapter的“标准”配置
- Android"解决"onTouch和onClick的冲突问题
- android:installLocation简析
- android searchView的关闭事件
- SourceProvider.getJniDirectories
