双边滤波器的原理及实现
2015-12-14 16:52
344 查看
http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7616663
双边滤波器是什么?
双边滤波(Bilateral filter)是一种可以保边去噪的滤波器。之所以可以达到此去噪效果,是因为滤波器是由两个函数构成。一个函数是由几何空间距离决定滤波器系数。另一个由像素差值决定滤波器系数。可以与其相比较的两个filter:高斯低通滤波器(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaussian_filter)和α-截尾均值滤波器(去掉百分率为α的最小值和最大之后剩下像素的均值作为滤波器),后文中将结合公式做详细介绍。
双边滤波器中,输出像素的值依赖于邻域像素的值的加权组合,
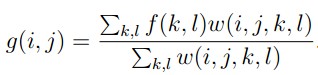
权重系数w(i,j,k,l)取决于定义域核
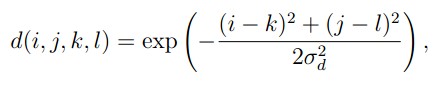
和值域核
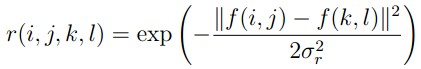
的乘积
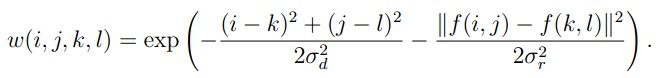
同时考虑了空间域与值域的差别,而Gaussian Filter和α均值滤波分别只考虑了空间域和值域差别。
=======================================================================
双边滤波器的实现(MATLAB):function B = bfilter2(A,w,sigma)
CopyRight:
% Douglas R. Lanman, Brown University, September 2006.
% dlanman@brown.edu, http://mesh.brown.edu/dlanman
具体请见function B = bfltGray(A,w,sigma_d,sigma_r)函数说明。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
%简单地说:
%A为给定图像,归一化到[0,1]的矩阵
%W为双边滤波器(核)的边长/2
%定义域方差σd记为SIGMA(1),值域方差σr记为SIGMA(2)
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Pre-process input and select appropriate filter.
function B = bfilter2(A,w,sigma)
% Verify that the input image exists and is valid.
if ~exist('A','var') || isempty(A)
error('Input image A is undefined or invalid.');
end
if ~isfloat(A) || ~sum([1,3] == size(A,3)) || ...
min(A(:)) < 0 || max(A(:)) > 1
error(['Input image A must be a double precision ',...
'matrix of size NxMx1 or NxMx3 on the closed ',...
'interval [0,1].']);
end
% Verify bilateral filter window size.
if ~exist('w','var') || isempty(w) || ...
numel(w) ~= 1 || w < 1
w = 5;
end
w = ceil(w);
% Verify bilateral filter standard deviations.
if ~exist('sigma','var') || isempty(sigma) || ...
numel(sigma) ~= 2 || sigma(1) <= 0 || sigma(2) <= 0
sigma = [3 0.1];
end
% Apply either grayscale or color bilateral filtering.
if size(A,3) == 1
B = bfltGray(A,w,sigma(1),sigma(2));
else
B = bfltColor(A,w,sigma(1),sigma(2));
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Implements bilateral filtering for grayscale images.
function B = bfltGray(A,w,sigma_d,sigma_r)
% Pre-compute Gaussian distance weights.
[X,Y] = meshgrid(-w:w,-w:w);
%创建核距离矩阵,e.g.
% [x,y]=meshgrid(-1:1,-1:1)
%
% x =
%
% -1 0 1
% -1 0 1
% -1 0 1
%
%
% y =
%
% -1 -1 -1
% 0 0 0
% 1 1 1
%计算定义域核
G = exp(-(X.^2+Y.^2)/(2*sigma_d^2));
% Create waitbar.
h = waitbar(0,'Applying bilateral filter...');
set(h,'Name','Bilateral Filter Progress');
% Apply bilateral filter.
%计算值域核H 并与定义域核G 乘积得到双边权重函数F
dim = size(A);
B = zeros(dim);
for i = 1:dim(1)
for j = 1:dim(2)
% Extract local region.
iMin = max(i-w,1);
iMax = min(i+w,dim(1));
jMin = max(j-w,1);
jMax = min(j+w,dim(2));
%定义当前核所作用的区域为(iMin:iMax,jMin:jMax)
I = A(iMin:iMax,jMin:jMax);%提取该区域的源图像值赋给I
% Compute Gaussian intensity weights.
H = exp(-(I-A(i,j)).^2/(2*sigma_r^2));
% Calculate bilateral filter response.
F = H.*G((iMin:iMax)-i+w+1,(jMin:jMax)-j+w+1);
B(i,j) = sum(F(:).*I(:))/sum(F(:));
end
waitbar(i/dim(1));
end
% Close waitbar.
close(h);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Implements bilateral filter for color images.
function B = bfltColor(A,w,sigma_d,sigma_r)
% Convert input sRGB image to CIELab color space.
if exist('applycform','file')
A = applycform(A,makecform('srgb2lab'));
else
A = colorspace('Lab<-RGB',A);
end
% Pre-compute Gaussian domain weights.
[X,Y] = meshgrid(-w:w,-w:w);
G = exp(-(X.^2+Y.^2)/(2*sigma_d^2));
% Rescale range variance (using maximum luminance).
sigma_r = 100*sigma_r;
% Create waitbar.
h = waitbar(0,'Applying bilateral filter...');
set(h,'Name','Bilateral Filter Progress');
% Apply bilateral filter.
dim = size(A);
B = zeros(dim);
for i = 1:dim(1)
for j = 1:dim(2)
% Extract local region.
iMin = max(i-w,1);
iMax = min(i+w,dim(1));
jMin = max(j-w,1);
jMax = min(j+w,dim(2));
I = A(iMin:iMax,jMin:jMax,:);
% Compute Gaussian range weights.
dL = I(:,:,1)-A(i,j,1);
da = I(:,:,2)-A(i,j,2);
db = I(:,:,3)-A(i,j,3);
H = exp(-(dL.^2+da.^2+db.^2)/(2*sigma_r^2));
% Calculate bilateral filter response.
F = H.*G((iMin:iMax)-i+w+1,(jMin:jMax)-j+w+1);
norm_F = sum(F(:));
B(i,j,1) = sum(sum(F.*I(:,:,1)))/norm_F;
B(i,j,2) = sum(sum(F.*I(:,:,2)))/norm_F;
B(i,j,3) = sum(sum(F.*I(:,:,3)))/norm_F;
end
waitbar(i/dim(1));
end
% Convert filtered image back to sRGB color space.
if exist('applycform','file')
B = applycform(B,makecform('lab2srgb'));
else
B = colorspace('RGB<-Lab',B);
end
% Close waitbar.
close(h);
调用方法:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
I=imread('einstein.jpg');
I=double(I)/255;
w = 5; % bilateral filter half-width
sigma = [3 0.1]; % bilateral filter standard deviations
I1=bfilter2(I,w,sigma);
subplot(1,2,1);
imshow(I);
subplot(1,2,2);
imshow(I1)
实验结果:

参考资料:
1.《Computer Vision Algorithms and Applications》
2. http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilaterale_Filterung
3.http://www.cs.duke.edu/~tomasi/papers/tomasi/tomasiIccv98.pdf
4. http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/CVonline/LOCAL_COPIES/MANDUCHI1/Bilateral_Filtering.html
5. http://mesh.brown.edu/dlanman
双边滤波器是什么?
双边滤波(Bilateral filter)是一种可以保边去噪的滤波器。之所以可以达到此去噪效果,是因为滤波器是由两个函数构成。一个函数是由几何空间距离决定滤波器系数。另一个由像素差值决定滤波器系数。可以与其相比较的两个filter:高斯低通滤波器(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaussian_filter)和α-截尾均值滤波器(去掉百分率为α的最小值和最大之后剩下像素的均值作为滤波器),后文中将结合公式做详细介绍。
双边滤波器中,输出像素的值依赖于邻域像素的值的加权组合,
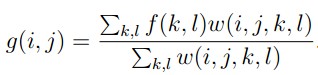
权重系数w(i,j,k,l)取决于定义域核
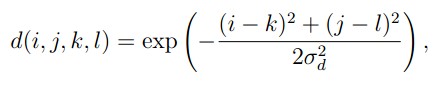
和值域核
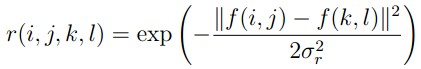
的乘积
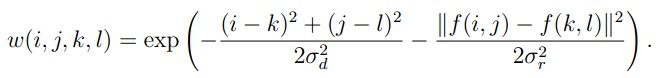
同时考虑了空间域与值域的差别,而Gaussian Filter和α均值滤波分别只考虑了空间域和值域差别。
=======================================================================
双边滤波器的实现(MATLAB):function B = bfilter2(A,w,sigma)
CopyRight:
% Douglas R. Lanman, Brown University, September 2006.
% dlanman@brown.edu, http://mesh.brown.edu/dlanman
具体请见function B = bfltGray(A,w,sigma_d,sigma_r)函数说明。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
%简单地说:
%A为给定图像,归一化到[0,1]的矩阵
%W为双边滤波器(核)的边长/2
%定义域方差σd记为SIGMA(1),值域方差σr记为SIGMA(2)
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Pre-process input and select appropriate filter.
function B = bfilter2(A,w,sigma)
% Verify that the input image exists and is valid.
if ~exist('A','var') || isempty(A)
error('Input image A is undefined or invalid.');
end
if ~isfloat(A) || ~sum([1,3] == size(A,3)) || ...
min(A(:)) < 0 || max(A(:)) > 1
error(['Input image A must be a double precision ',...
'matrix of size NxMx1 or NxMx3 on the closed ',...
'interval [0,1].']);
end
% Verify bilateral filter window size.
if ~exist('w','var') || isempty(w) || ...
numel(w) ~= 1 || w < 1
w = 5;
end
w = ceil(w);
% Verify bilateral filter standard deviations.
if ~exist('sigma','var') || isempty(sigma) || ...
numel(sigma) ~= 2 || sigma(1) <= 0 || sigma(2) <= 0
sigma = [3 0.1];
end
% Apply either grayscale or color bilateral filtering.
if size(A,3) == 1
B = bfltGray(A,w,sigma(1),sigma(2));
else
B = bfltColor(A,w,sigma(1),sigma(2));
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Implements bilateral filtering for grayscale images.
function B = bfltGray(A,w,sigma_d,sigma_r)
% Pre-compute Gaussian distance weights.
[X,Y] = meshgrid(-w:w,-w:w);
%创建核距离矩阵,e.g.
% [x,y]=meshgrid(-1:1,-1:1)
%
% x =
%
% -1 0 1
% -1 0 1
% -1 0 1
%
%
% y =
%
% -1 -1 -1
% 0 0 0
% 1 1 1
%计算定义域核
G = exp(-(X.^2+Y.^2)/(2*sigma_d^2));
% Create waitbar.
h = waitbar(0,'Applying bilateral filter...');
set(h,'Name','Bilateral Filter Progress');
% Apply bilateral filter.
%计算值域核H 并与定义域核G 乘积得到双边权重函数F
dim = size(A);
B = zeros(dim);
for i = 1:dim(1)
for j = 1:dim(2)
% Extract local region.
iMin = max(i-w,1);
iMax = min(i+w,dim(1));
jMin = max(j-w,1);
jMax = min(j+w,dim(2));
%定义当前核所作用的区域为(iMin:iMax,jMin:jMax)
I = A(iMin:iMax,jMin:jMax);%提取该区域的源图像值赋给I
% Compute Gaussian intensity weights.
H = exp(-(I-A(i,j)).^2/(2*sigma_r^2));
% Calculate bilateral filter response.
F = H.*G((iMin:iMax)-i+w+1,(jMin:jMax)-j+w+1);
B(i,j) = sum(F(:).*I(:))/sum(F(:));
end
waitbar(i/dim(1));
end
% Close waitbar.
close(h);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Implements bilateral filter for color images.
function B = bfltColor(A,w,sigma_d,sigma_r)
% Convert input sRGB image to CIELab color space.
if exist('applycform','file')
A = applycform(A,makecform('srgb2lab'));
else
A = colorspace('Lab<-RGB',A);
end
% Pre-compute Gaussian domain weights.
[X,Y] = meshgrid(-w:w,-w:w);
G = exp(-(X.^2+Y.^2)/(2*sigma_d^2));
% Rescale range variance (using maximum luminance).
sigma_r = 100*sigma_r;
% Create waitbar.
h = waitbar(0,'Applying bilateral filter...');
set(h,'Name','Bilateral Filter Progress');
% Apply bilateral filter.
dim = size(A);
B = zeros(dim);
for i = 1:dim(1)
for j = 1:dim(2)
% Extract local region.
iMin = max(i-w,1);
iMax = min(i+w,dim(1));
jMin = max(j-w,1);
jMax = min(j+w,dim(2));
I = A(iMin:iMax,jMin:jMax,:);
% Compute Gaussian range weights.
dL = I(:,:,1)-A(i,j,1);
da = I(:,:,2)-A(i,j,2);
db = I(:,:,3)-A(i,j,3);
H = exp(-(dL.^2+da.^2+db.^2)/(2*sigma_r^2));
% Calculate bilateral filter response.
F = H.*G((iMin:iMax)-i+w+1,(jMin:jMax)-j+w+1);
norm_F = sum(F(:));
B(i,j,1) = sum(sum(F.*I(:,:,1)))/norm_F;
B(i,j,2) = sum(sum(F.*I(:,:,2)))/norm_F;
B(i,j,3) = sum(sum(F.*I(:,:,3)))/norm_F;
end
waitbar(i/dim(1));
end
% Convert filtered image back to sRGB color space.
if exist('applycform','file')
B = applycform(B,makecform('lab2srgb'));
else
B = colorspace('RGB<-Lab',B);
end
% Close waitbar.
close(h);
调用方法:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
I=imread('einstein.jpg');
I=double(I)/255;
w = 5; % bilateral filter half-width
sigma = [3 0.1]; % bilateral filter standard deviations
I1=bfilter2(I,w,sigma);
subplot(1,2,1);
imshow(I);
subplot(1,2,2);
imshow(I1)
实验结果:

参考资料:
1.《Computer Vision Algorithms and Applications》
2. http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilaterale_Filterung
3.http://www.cs.duke.edu/~tomasi/papers/tomasi/tomasiIccv98.pdf
4. http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/CVonline/LOCAL_COPIES/MANDUCHI1/Bilateral_Filtering.html
5. http://mesh.brown.edu/dlanman
相关文章推荐
- iOS恢复固件的方法
- Content Provider应用实例
- php gd库
- 宏
- php数组函数-array_reduce()
- Fragment与FragmentPagerAdapter的使用
- 第十三周项目5
- 第十四周 折半查找
- 第十六周--大数据集上排序算法性能的体验
- 第十六周 项目1.3- 验证算法
- 第十六周项目1-直接选择排序
- iOS开发之自定义导航栏返回按钮右滑返回手势失效的解决
- Git与Github折腾记-常用命令汇总
- Python基本内置数据类型有哪些?
- 第十四周-二叉排序树
- 第16周 项目1 - 验证算法
- 第十五周 项目1 冒泡排序
- 第14周项目3-是否二叉排序树
- Git与Github折腾记-常用命令汇总
- 1020 月饼 PAT
