MapReduce-输入数据整块处理
2015-11-12 16:46
375 查看
通常编程时会使用TextInputFormat作为输入方式(记录是按行输入的)
现通过自定义方法实现整个数据文件输入
适用场景:在map阶段检验数据是否有序
运行环境:windows下VM虚拟机,centos 6.5系统,hadoop2.2.0,三节点 ,java 1.7
原数据:
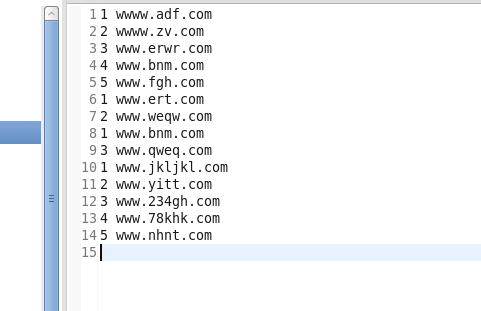
第一步:自定义wholeFileInputFormat方法继承FileInputFormat
第二步:自定义wholeFileRecordReader类
第三步:在具体场景中使用
可以看出针对多行数据只执行了一次map任务
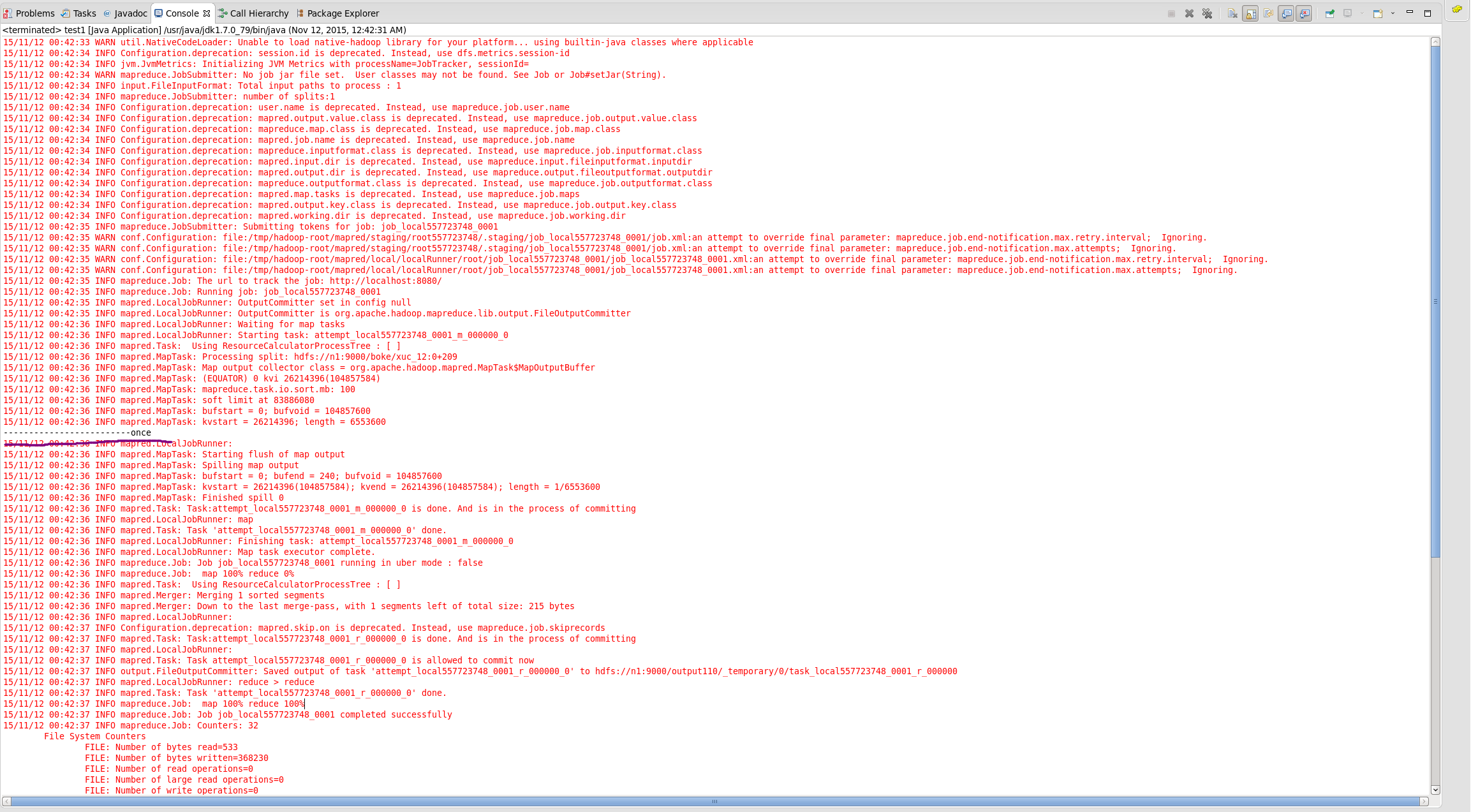
现通过自定义方法实现整个数据文件输入
适用场景:在map阶段检验数据是否有序
运行环境:windows下VM虚拟机,centos 6.5系统,hadoop2.2.0,三节点 ,java 1.7
原数据:

第一步:自定义wholeFileInputFormat方法继承FileInputFormat
//这个例子是以<NullWritable,BytesWritable>为输入<key,value>类型
public class wholeFileInputFormat extends FileInputFormat<NullWritable,BytesWritable>{
//重写isSplitable方法是为了对于输入文件不进行分片操作
protected boolean isSplitable(JobContext context,Path filename)
{
//返回false就可以实现不分片
return false;
}
//这个类是创建读取文件内容实例(返回值)
public RecordReader<NullWritable,BytesWritable> createRecordReader(
InputSplit split ,TaskAttemptContext context)throws IOException,InterruptedException
{
//这里需要自定义一个读取方式,代码在下面
wholeFileRecordReader reader=new wholeFileRecordReader();
//传入job配置信息和split分片信息
reader.initialize(split, context);
//
return reader;
}
}第二步:自定义wholeFileRecordReader类
//指定输入key,value类型
public class wholeFileRecordReader extends RecordReader<NullWritable,BytesWritable>{
//fileSplit是分片信息(文件位置,文件字节数)注:这里的分片只有1个
private FileSplit fileSplit;
private Configuration conf;
//这存的是文件内容,也是输出结果
private BytesWritable value=new BytesWritable();
//这是一个标志,用来表示数据是否被处理过
private boolean processed=false;
//通过context和分片信息初始化
public void initialize(InputSplit split,TaskAttemptContext context)throws IOException,InterruptedException
{
this.fileSplit=(FileSplit)split;
this.conf=context.getConfiguration();
}
//相当于迭代器的next()方法,读取文件内容
public boolean nextKeyValue()throws IOException,InterruptedException
{
if(!processed)
{
//根据文件的字节大小创建一个字节数组
byte[] contents =new byte[(int)fileSplit.getLength()];
//获取文件的位置
Path file=fileSplit.getPath();
//获取一个HDFS的系统实例
FileSystem fs=file.getFileSystem(conf);
//文件输入流
FSDataInputStream in=null;
try
{
//文件输入流指向文件
in=fs.open(file);
//IOUtils的readFully方法把文件内容写入contents数组中
IOUtils.readFully(in, contents, 0, contents.length);
//把数据放到上面定义过的BytesWritable类型的value(用于输出)
value.set(contents, 0, contents.length);
}finally
{
IOUtils.closeStream(in);
}
//这里赋值true表示数据被处理过了
processed=true;
//返回true,表示方法执行成功
return true;
}
//数据被处理过了,不用被再次读取数据,方法调用返回false
return false;
}
//下面是继承RecordReader需要实现的几个方法
//key值的返回结果
public NullWritable getCurrentKey()throws IOException,InterruptedException
{
return NullWritable.get();
}
//value的返回结果
public BytesWritable getCurrentValue()throws IOException,InterruptedException
{
return value;
}
//判断数据是否成功处理
public float getProgress()throws IOException
{
return processed?1.0f:0.0f;
}
//关闭
public void close()throws IOException{}
}第三步:在具体场景中使用
public class test1 extends Configured implements Tool{
public static class Map extends Mapper<NullWritable,BytesWritable,Text,BytesWritable>
{
private Text filenameKey;
//setup类每次在执行map方法之前都会被调用,通常用来初始化
protected void setup(Context context)throws IOException,InterruptedException
{
//这段话其实就是让finenameKey记录输入文件所在的hdfs位置,可有可无
InputSplit split=context.getInputSplit();
Path path=((FileSplit)split).getPath();
filenameKey=new Text(path.toString());
}
public void map(NullWritable key,BytesWritable value,Context context)throws IOException,InterruptedException
{
context.write(filenameKey, value);
//通过这个输出观察map任务调用了几次(TextoutputFormat是一行调用一次)
System.out.println("-------------------------once");
}
}
public int run(String[] args)throws Exception
{
Configuration conf=getConf();
Job job=new Job(conf,"test11");
job.setJarByClass(test1.class);
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(wholeFileInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(SequenceFileOutputFormat.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(BytesWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
return job.isSuccessful()?1:0;
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
int rsa=ToolRunner.run(new Configuration(), new test1(), args);
System.exit(rsa);
}
}可以看出针对多行数据只执行了一次map任务

相关文章推荐
- 详解HDFS Short Circuit Local Reads
- Hadoop_2.1.0 MapReduce序列图
- 使用Hadoop搭建现代电信企业架构
- 单机版搭建Hadoop环境图文教程详解
- hadoop常见错误以及处理方法详解
- hadoop 单机安装配置教程
- hadoop的hdfs文件操作实现上传文件到hdfs
- hadoop实现grep示例分享
- Apache Hadoop版本详解
- linux下搭建hadoop环境步骤分享
- hadoop client与datanode的通信协议分析
- hadoop中一些常用的命令介绍
- Hadoop单机版和全分布式(集群)安装
- 用PHP和Shell写Hadoop的MapReduce程序
- hadoop map-reduce中的文件并发操作
- Hadoop1.2中配置伪分布式的实例
- java结合HADOOP集群文件上传下载
- 用python + hadoop streaming 分布式编程(一) -- 原理介绍,样例程序与本地调试
- Hadoop安装感悟
- hadoop安装lzo
