机器视觉算法之物体方位特征提取
2015-11-02 22:26
411 查看
机器视觉算法之物体方位特征提取
在机器视觉处理中,我们经常要对检测到的物体的方位特征进行评估。比如说,我们要 OCR 识别一个字符串。那么这个字符串与x轴的夹角就很重要,我们需要这个信息把这个字符串转正,然后才方便识别。条形码识别也类似,尤其是当我们条形码不是很清晰时,首先将条形码转正,然后用各向异性的滤波器处理一下,可以让条形码变得更清晰易于读取。
这里给出一种基于统计参数的特征提取方法。这个方法已经有几十年历史了,算是个老方法,但是效果很不错,所以值得写篇文章来介绍介绍。
区域的矩
一片区域 R 的矩定义为:mp,q=∑(r,c)∈Rrpcq
当p 和q 都取 0 时,得到的就是这片区域的面积。也就是:
a=m0,0
矩还可以归一化,也就是用上面的定义再除以面积 a。
np,q=1a∑(r,c)∈Rrpcq
(n1,0,n0,1) 表示的是这片区域的重心。可以用它来描述区域的位置。
归一化的矩回随区域在图像中的位置不同而变化,要去除这个影响,可以用中心矩,中心矩只反映区域本身的特征。
μp,q=1a∑(r,c)∈R(r−n1,0)p(c−n0,1)q
二阶中心距有三个,分别是 μ2,0, μ1,1, μ0,2,用这三个参数再加上重心(n1,0,n0,1) 就可以估算出区域的范围和方位。
具体的方法是将这个区域当作一个椭圆区域,那么用上面5个参量就可以计算出椭圆的长短轴和旋转角度。具体公式如下:
r1=2(μ2,0+μ0,2+(μ2,0−μ0,2)2+4μ21,1−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−√)−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−√
r1=2(μ2,0+μ0,2−(μ2,0−μ0,2)2+4μ21,1−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−√)−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−√
θ=−12arctan2μ1,1μ0,2−μ2,0
椭圆的这几个参数的图形解释如下图:
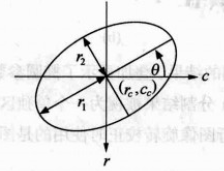
利用这几个参数就可以确定区域的方位和尺寸了。
比如我们有下面的一幅测试图像。
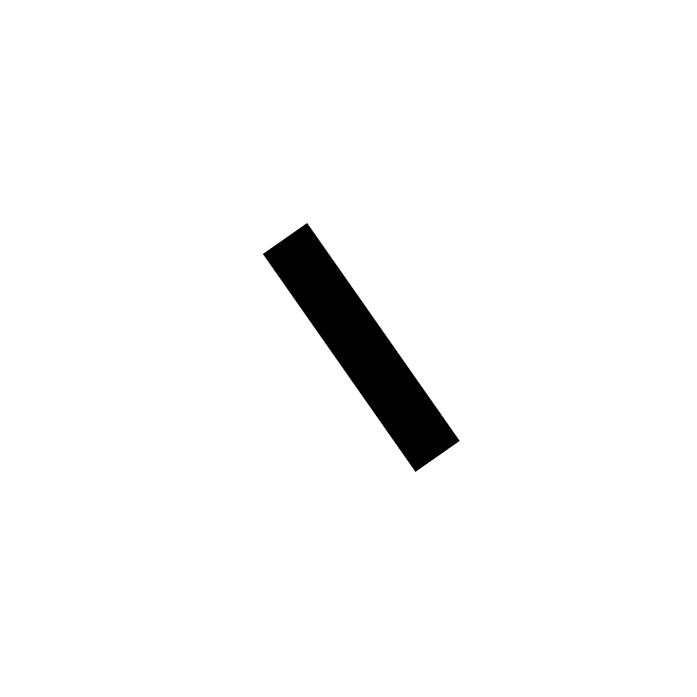
用上面方法计算出的椭圆如下:
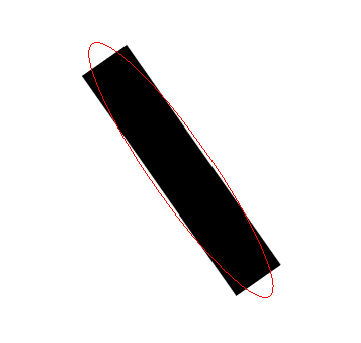
可以看出结果非常的好。尤其是旋转角度,计算的非常准确。
下面是我的测试代码,供参考。用到了些 Qt 的功能。
#include <QApplication>
#include <QImage>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QPainter>
#include "picturebox.h"
#include <math.h>
QImage threshold(const QImage &image, quint8 th)
{
int height = image.height();
int width = image.width();
QImage ret(width, height, QImage::Format_Indexed8);
ret.setColorCount(256);
for(int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
ret.setColor(i, qRgb(i, i, i));
}
for(int i = 0; i < height; i ++)
{
const uchar *pSrc = (uchar *)image.constScanLine(i);
uchar *pDest = (uchar *)ret.scanLine(i);
for( int j = 0; j < width; j ++)
{
pDest[j] = (pSrc[j] > th)? 255: 0;
}
}
return ret;
}
QImage toGray( const QImage &image )
{
int height = image.height();
int width = image.width();
QImage ret(width, height, QImage::Format_Indexed8);
ret.setColorCount(256);
for(int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
ret.setColor(i, qRgb(i, i, i));
}
qDebug () << image.format();
switch(image.format())
{
case QImage::Format_Indexed8:
case QImage::Format_Grayscale8:
for(int i = 0; i < height; i ++)
{
const uchar *pSrc = (uchar *)image.constScanLine(i);
uchar *pDest = (uchar *)ret.scanLine(i);
memcpy(pDest, pSrc, width);
}
break;
case QImage::Format_RGB32:
case QImage::Format_ARGB32:
case QImage::Format_ARGB32_Premultiplied:
for(int i = 0; i < height; i ++)
{
const QRgb *pSrc = (QRgb *)image.constScanLine(i);
uchar *pDest = (uchar *)ret.scanLine(i);
for( int j = 0; j < width; j ++)
{
pDest[j] = qGray(pSrc[j]);
}
}
break;
}
return ret;
}
QPointF center(const QImage &image, int value)
{
if(image.isNull() || image.format() != QImage::Format_Indexed8)
{
return QPointF(-1, -1);
}
int width = image.width();
int height = image.height();
int x_mean = 0;
int y_mean = 0;
int count = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < height; j ++)
{
const uchar * p = image.constScanLine(j);
for(int i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
if( p[i] == value )
{
x_mean += i;
y_mean += j;
count++;
}
}
}
return QPointF((double)x_mean / count, (double)y_mean / count);
}
struct ELLIPSE_PARA
{
double x_mean; //椭圆的中心坐标 x
double y_mean; //椭圆的中心坐标 y
double r1; //椭圆的长轴半径
double r2; //椭圆的短轴半径
double theta; //椭圆的长轴与 x 轴的夹角(逆时针)
};
/**
* @brief ellipseFit 将一片区域当作椭圆来估计五个几何参数
* @param image
* @param value
* @param para
*/
bool ellipseFit(const QImage &image, int value, ELLIPSE_PARA * para)
{
if(image.isNull() || image.format() != QImage::Format_Indexed8)
{
return false;
}
QPointF c = center(image, value);
int width = image.width();
int height = image.height();
double n01 = c.x();
double n10 = c.y();
double mu20 = 0.0;
double mu02 = 0.0;
double mu11 = 0.0;
int count = 0;
for(int row = 0; row < height; row ++)
{
const uchar * p = image.constScanLine(row);
for(int col = 0; col < width; col++)
{
if( p[col] == value )
{
mu02 += (col - n01) * (col - n01);
mu20 += (row - n10) * (row - n10);
mu11 += (col - n01) * (row - n10);
count ++;
}
}
}
if(count == 0)
{
return false;
}
mu20 /= count;
mu02 /= count;
mu11 /= count;
double t1 = mu20 + mu02;
double t2 = mu20 - mu02;
double t3 = sqrt(t2 * t2 + 4 * mu11 * mu11);
double r1 = sqrt(2 * ( t1 + t3) );
double r2 = sqrt(2 * ( t1 - t3) );
double theta = - atan2(2 * mu11, mu02 - mu20) / 2.0;
para->r1 = r1;
para->r2 = r2;
para->theta = theta;
para->x_mean = n01;
para->y_mean = n10;
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
QImage image("D:/test55.png");
QImage imageGray = toGray(image);
//imageGray = threshold(imageGray, 128);
ELLIPSE_PARA para;
ellipseFit(imageGray, 0, ¶);
qDebug() << para.r1;
qDebug() << para.r2;
qDebug() << para.theta * 180 / 3.14159;
QPointF c(para.x_mean, para.y_mean);
qDebug() << c;
QPainter painter(&image);
painter.setPen(Qt::red);
painter.translate(c);
painter.rotate(-para.theta * 180 / 3.14159);
painter.drawEllipse(QPointF(0, 0), para.r1, para.r2 );
PictureBox box;
box.setImage(image);
box.show();
return a.exec();
}
相关文章推荐
- 利用矢量计算快速判定一点在直线的哪一侧
- 大幅面多相机高精度定位及测量解决方案
- 读书计划与交流的期望
- 在机器视觉领域中为何选择基于瑞芯微Rockchip PX2主控芯片?
- Halcon学习之四:有关图像生成的函数
- Halcon学习之二:摄像头获取图像和相关参数
- Halcon学习之五:有关图像的定义域的函数
- Halcon学习之七:改变图像的现实方式和大小
- 分享一些OpenCV实现立体视觉的经验
- 在OpenCV中用cvCalibrateCamera2进行相机标定
- 机器视觉方向的大牛介绍
- 机器人demo
- 机器视觉系统硬件部分
- 普及机器视觉,每日一贴
- 机器视觉的一些链接
- 本人常用资源整理(ing...)
- 图像处理与计算机视觉:基础,经典以及最近发展
- 工业相机和数码相机的六大区别
- 如何选择工业相机?听听专家怎么说
- 远心工业镜头与普通工业镜头的区别
