http://blog.httrack.com/blog/2013/08/23/catching-posix-signals-on-android/
To Report Or Not To ReportYou have a
nice application available on the Google Android Store and, as a
developer, you have access to nice features giving you basic statistics (the number of downloads, Android version breakdown, etc.), reviews, and a Crashes & ANRs section allowing to audit user crash reports (and Application hangs – that’s the ANR thing).
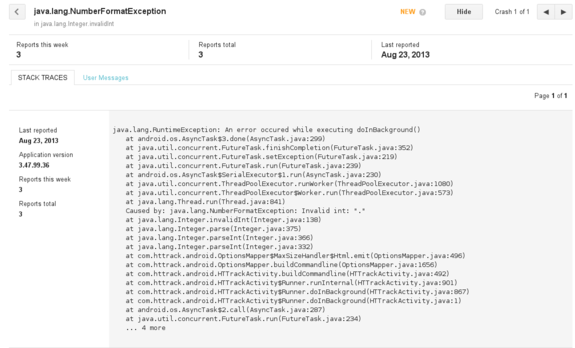
This is a rather basic feature (you do not have any details on the user’s phone, Android version, etc. – only a Java stack trace extract), but at least it allows you to quickly spot mistakes (such as
NullPointerException
, or in this case, a
NumberFormatException
), and the report is pretty straightforward for users (they only have click on the “Report” button in case of crash)
But what if your application is using
native code (through JNI) ? In such case, the application will just crash silently, giving the user no opportunity to report the bug to the upstream developer (you), which is
not cool (because the bug will remain unspotted, unless users are nice enough to email you, and have the know-how to provide you useful technical details, such as the address of the crash, which is kind of rare)
Catching the ProblemA first step is obviously to be able to detect common native crashes (
SIGSEGV
,
SIGBUS
, etc.) using signal handlers. On POSIX systems, this can be achieved by using
sigaction()
:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| struct sigaction sa;
struct sigaction sa_old;
memset(&sa, 0, sizeof(sa));
sigemptyset(&sa.sa_mask);
sa.sa_sigaction = my_handler;
sa.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;
if (sigaction(sig, &sa, &sa_old) == 0) {
...
}
|
First problem: we are typically running on small systems (Android …), and one source of error is the stack overflow. When the stack is full (too much recursion, too large objects on stack), you hit the last guard page, and the system will raise the
SIGSEGV
signal handler, running by default on the… same full stack, raising one more time the signal. Fortunately, you may register in any thread an alternative stack through the use of
sigaltstack
, which basically reserve some space in case of emergency (ie. the system will switch the stack pointer to this one in case of trouble, letting you handler run on a “fresh” stack).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
| stack_t stack;
memset(&stack, 0, sizeof(stack));
/* Reserver the system default stack size. We don't need that much by the way. */
stack.ss_size = SIGSTKSZ;
stack.ss_sp = malloc(stack.ss_size);
stack.ss_flags = 0;
/* Install alternate stack size. Be sure the memory region is valid until you revert it. */
if (stack.ss_sp != NULL && sigaltstack(&stack, NULL) == 0) {
...
}
|
Second problem: we’re hosted on a Java Virtual Machine, and some of these signals might already be caught. Typically,
SIGSEGV
might be regularly raised to address
NullPointerException
or as normal JIT processing (ie. executable pages might be flagged with a “no access” protection, and filled by the JIT compiler through a signal handler) – you have to make sure the original signal handler is called first, before messing up with it. If the signal was not processed, the original signal handler will generally return, or will call
abort()
(which is nice, because we have a last chance to catch it through a
SIGABRT
handler)
1
2
3
4
5
| static void my_handler(const int code, siginfo_t *const si, void *const sc) {
/* Call previous handler. */
old_handler.sa_sigaction(code, si, sc);
...
}
|
Third problem: we’re running on a multi-threaded process, and ideally we do not want to catch crashes from threads we do not own. We can address this issue by using
pthread_getspecific()
to have a thread-specific context. Well, this is actually a dirty solution:
pthread_getspecific()
is
not an async-signal-safe function, which means that if you are using it on a signal handler, you may have to prepare for unforeseen consequences. (I fail to see what could go wrong with this specific function, however – this is just a peek in a thread-specific address array. But yes, yes, we’re playing with fire, don’t kick me!)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
11
| static void my_handler(const int code, siginfo_t *const si, void *const sc) {
/* Call previous handler. */
old_handler.sa_sigaction(code, si, sc);
/* Get thread-specific context. */
my_struct *s = (my_struct*) pthread_getspecific(my_thread_var);
if (s != NULL) {
...
}
...
}
|
Fourth problem: we have to collect some basic information on the crash, especially the faulting address. Fortunately, the third argument of the
sigaction
callback is a pointer to a
ucontext_t
context collecting register values (and various other processor-specific details). On x86-64 architectures, the program counter will typically be saved in
uc_mcontext.gregs[REG_RIP]
; on ARM,
uc_mcontext.arm_pc
. Unfortunately, on Android, the
ucontext_t
structure is not defined in any system headers, and you’ll have to import one by yourself (I shamelessly copied the one from Richard Quirk). You also have to find out what was the binary where the program counter was actually running, to find out this code base address in memory, because a randomized address is not very useful for audit and debugging. The Linux-specific
dladdr()
function is fortunately giving you this information, with useful other ones (namely the nearest symbol matching the address, and the module base address, to compute a relative offset address). (Note: you can also get this information on Linux by snooping in
/proc/self/maps
, and checking the address ranges – it will at least provide you the base address)
1
2
3
4
56
7
| Dl_info info;
if (dladdr(addr, &info) != 0 && info.dli_fname != NULL) {
void * const nearest = info.dli_saddr;
const uintptr_t addr_relative =
((uintptr_t) addr - (uintptr_t) info.dli_fbase);
...
}
|
You have also the opportunity to catch a backtrace, with the same information, as long as you have a recent (ie. 4.1.1 or higher) Android version, using
libcorkscrew
library features. This library is not available on older Android releases, and besides, we do not want to get a backtrace of the current stack, but a backtrace of the stack provided in the crash context. Fortunately, we can dynamically load the
libcorkscrew.so
library to solve the first issue (using
dlopen
and
dlsym()
) and, for the second issue, import manually a nice function called
unwind_backtrace_signal_arch
, which does exactly what we want:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
11
12
| /*
* Describes a single frame of a backtrace.
*/
typedef struct {
uintptr_t absolute_pc; /* absolute PC offset */
uintptr_t stack_top; /* top of stack for this frame */
size_t stack_size; /* size of this stack frame */
} backtrace_frame_t;
ssize_t unwind_backtrace_signal_arch(siginfo_t* siginfo, void* sigcontext,
const map_info_t* map_info_list,
backtrace_frame_t* backtrace, size_t ignore_depth, size_t max_depth);
|
(We also need to import
acquire_my_map_info_list()
)
We can also, when corkscrew is there, use the advanced
get_backtrace_symbols
function to resolve symbols and demangle them:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| /*
* Describes the symbols associated with a backtrace frame.
*/
typedef struct {
uintptr_t relative_pc; /* relative frame PC offset from the start of the library, or the absolute PC if the library is unknown */
uintptr_t relative_symbol_addr; /* relative offset of the symbol from the start of the library or 0 if the library is unknown */
char* map_name; /* executable or library name, or NULL if unknown */
char* symbol_name; /* symbol name, or NULL if unknown */
char* demangled_name; /* demangled symbol name, or NULL if unknown */
} backtrace_symbol_t;
/*
* Gets the symbols for each frame of a backtrace.
* The symbols array must be big enough to hold one symbol record per frame.
* The symbols must later be freed using free_backtrace_symbols.
*/
void get_backtrace_symbols(const backtrace_frame_t* backtrace, size_t frames,
backtrace_symbol_t* backtrace_symbols);
|
Fifth problem: you need to pass all these useful information back to the Java Virtual Machine, and not only by calling directly some kind of callback, because you need to propagate a clean
RuntimeException
and unwind all Java frames, to have your final exception being reported through the Android framework. The only way to achieve that is by storing the exit point in your own code, using
setjmp
(actually
sigsetjmp
, because we’ll need to restore some masked signals), and using it in your signal handler to directly jump at the correct location. The
sigsetjmp
/
siglongjmp
functions are obviously not async-signal-safe (
see the remark on Application Usage of
sigaction()
), so this is a highly risky bet. Typically, if the crash happened in the middle of a
malloc()
call (because, say, the linked list of free blocks has been corrupted), you may find yourself triggering another
SIGSEGV
(which is the lesser of the evils) or worse, deadlocked, which is rather embarrassing because the user will have to find a way to kill the application by himself. For this reason, an
alarm()
call will be the first operation executed in case of emergency (and yes,
alarm()
is async-signal-safe – we can safely kill ourselves).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| static void my_handler(const int code, siginfo_t *const si, void *const sc) {
/* Call previous handler. */
old_handler.sa_sigaction(code, si, sc);
/* Trigger a time bomb. */
(void) alarm(30);
/* Get thread-specific context. */
my_struct *s = (my_struct*) pthread_getspecific(my_thread_var);
if (s != NULL) {
/* Store crash context for later. */
s->code = code;
s->si = *si;
s->uc = *(ucontext_t*) sc;
/* Jump back to initial location. */
siglongjmp(t->ctx, -1);
}
...
}
|
Is It Working ?Yes, and it’s much nicer to have
SIGSEGV
advertised through a clean stack:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| FATAL EXCEPTION: AsyncTask #5
java.lang.RuntimeException: An error occured while executing doInBackground()
at android.os.AsyncTask$3.done(AsyncTask.java:299)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.finishCompletion(FutureTask.java:352)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.setException(FutureTask.java:219)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:239)
at android.os.AsyncTask$SerialExecutor$1.run(AsyncTask.java:230)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1080)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:573)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:841)
Caused by: java.lang.Error: signal 11 (Address not mapped to object) at address 0x42 [at libhttrack.so:0xa024]
at com.httrack.android.jni.HTTrackLib.main(Native Method)
at com.httrack.android.HTTrackActivity$Runner.runInternal(HTTrackActivity.java:998)
at com.httrack.android.HTTrackActivity$Runner.doInBackground(HTTrackActivity.java:919)
at com.httrack.android.HTTrackActivity$Runner.doInBackground(HTTrackActivity.java:1)
at android.os.AsyncTask$2.call(AsyncTask.java:287)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:234)
... 4 more
Caused by: java.lang.Error: signal 11 (Address not mapped to object) at address 0x42 [at libhttrack.so:0xa024]
at data.app_lib.com_httrack_android_2.libhttrack_so.0xa024(Native Method)
at data.app_lib.com_httrack_android_2.libhttrack_so.0x705fc(hts_main2:0x8f74:0)
at data.app_lib.com_httrack_android_2.libhtslibjni_so.0x4cc8(HTTrackLib_main:0xf8:0)
at data.app_lib.com_httrack_android_2.libhtslibjni_so.0x52d8(Java_com_httrack_android_jni_HTTrackLib_main:0x64:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x1dc4c(dvmPlatformInvoke:0x70:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x4dcab(dvmCallJNIMethod(unsigned int const*, JValue*, Method const*, Thread*):0x18a:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x385e1(dvmCheckCallJNIMethod(unsigned int const*, JValue*, Method const*, Thread*):0x8:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x4f699(dvmResolveNativeMethod(unsigned int const*, JValue*, Method const*, Thread*):0xb8:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x27060(Native Method)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x2b580(dvmInterpret(Thread*, Method const*, JValue*):0xb8:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x5fcbd(dvmCallMethodV(Thread*, Method const*, Object*, bool, JValue*, std::__va_list):0x124:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x5fce7(dvmCallMethod(Thread*, Method const*, Object*, JValue*, ...):0x14:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x54a6f(Native Method)
at system.lib.libc_so.0xca58(__thread_entry:0x48:0)
at system.lib.libc_so.0xcbd4(pthread_create:0xd0:0)
|
Bonus: produce a relative address, and get the filename and line number for
FREE!
In the above stack, we know that the crash occurred somewhere inside the
hts_main2
function, which is not very precise. We have actually another very useful information: the crash was spotted inside
libhttrack.so
, at the relative address
0xa024
. This is a relative address, computed earlier with
dladdr()
, which means that you can find out exactly the source location if you kept some debugging information. Most people do not want them, because it increases the binary size by a unreasonable factor (especially when running on small embedded devices with 3G+ connectivity priced above gold ingots levels), and thus either strip them silently, or keep another “debug” build.
You have an extremely simple alternative way: build once your libraries with all debugging symbols, including line numbers and macro information (
-g3
), and instead of stripping them, split the debugging sections on a separate file (say, a
.dbg
file). To let various tools such as
gdb
or
addr2line
behave gently, you have a way to “tell” them that the
.so
actually has a debug
.dbg
related file, through the
.gnu_debuglink
ELF section.
Here’s what you typically need to do to split your library into a stripped version plus a debug symbol file:
1
2
3
4
56
7
8
| # copy all debugging sections to dbg file
objcopy --only-keep-debug mylib.so mylib.dbg
# strip debug sections
objcopy --strip-debug mylib.so
# wipe any existing ELF .gnu_debuglink section if any
objcopy --remove-section .gnu_debuglink mylib.so
# set the .gnu_debuglink to the dbg file
objcopy --add-gnu-debuglink=mylib.dbg mylib.so
|
The nice
.dbg
file can then be kept for debugging purpose:
1
2
3
4
| cd /build-archives/httrack/armv7/3.47.99.35
./toolchains/arm-linux-androideabi-4.7/prebuilt/linux-x86_64/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-addr2line -C -f -e libhttrack.so 0xa024
fourty_two
src/htscoremain.c:111
|
Okay, but Is It Really Safe ?A typical crash may have a great variety of causes (Captain Obvious to the rescue!). My own experience, though, shows that NULL pointer dereferencing, dangling pointers, and other isolated crash spots due to bad code logic are a very common cause of crashes. Yes, you will still have troubles when dealing with corrupted allocators, or when breaking in the middle of a async-signal-safe call (leaving mutexes locked, and more generally a dirty state that will hit you back later), but the alternate solution is to die immediately (the default behavior), so trying to do gentle emergency steps can not do any harm.
I Want To Test It!You can check out the “
CoffeeCatch” library
code on GitHub – you can either merge the
.c
file in your project(s), or build it as a standalone library ; this tiny library has no exotic external dependencies. Make sure all your libraries are built with the
-funwind-tables
compiler flag to produce frame unwind information for all functions (add if necessary
LOCAL_CFLAGS := -funwind-tables
to your
Android.mk
file). Note that
-funwind-tables
does
not produce significant data size overhead in normal situations – so rest well my friend.
The use is pretty straightforward – for JNI code, a simple macro
COFFEE_TRY_JNI
, taking the
JNIEnv
environment pointer as a first argument, and a code block as a second argument, will do the trick. For code outside JNI, you have to enclose protected code with COFFEE_TRY()/COFFEE_CATCH()/COFFEE_END() as in the example below.
In all cases, make sure the block is enclosed in a dedicated function without any local variables lying around (because the saved context does not include registers, AFAIK, especially volatile registers, which might be wiped before calling
sigsetjmp
, and whose saved values are in unknown location in the stack).
The JNI flavor:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| /** The potentially dangerous function. **/
jint call_dangerous_function(JNIEnv* env, jobject object) {
// ... do dangerous things!
return 42;
}
/** Protected function stub. **/
void foo_protected(JNIEnv* env, jobject object, jint *retcode) {
/* Try to call 'call_dangerous_function', and raise proper Java Error upon
* fatal error (SEGV, etc.). **/
COFFEE_TRY_JNI(env, *retcode = call_dangerous_function(env, object));
}
/** Regular JNI entry point. **/
jint Java_com_example_android_MyNative_foo(JNIEnv* env, jobject object) {
jint retcode = 0;
foo_protected(env, object, &retcode);
return retcode;
}
|
The standard flavor:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
910
| static __attribute__ ((noinline)) void demo(int *fault) {
COFFEE_TRY() {
recurse_madness(42);
*fault = 0;
} COFFEE_CATCH() {
const char*const message = coffeecatch_get_message();
snprintf(string_buffer, sizeof(string_buffer), "%s", message);
*fault = 1;
} COFFEE_END();
}
|
TL;DR: so far, no native crash has been reported on Android for HTTrack. But I’m ready to collect them in case of need :)


