自定义控件 仿应用宝 管理界面的标题栏缩放效果
2015-09-24 09:24
351 查看
最近看到应用宝管理界面里面那个能缩能放的标题栏很有意思,所以自己尝试简单模仿下。
先上效果图: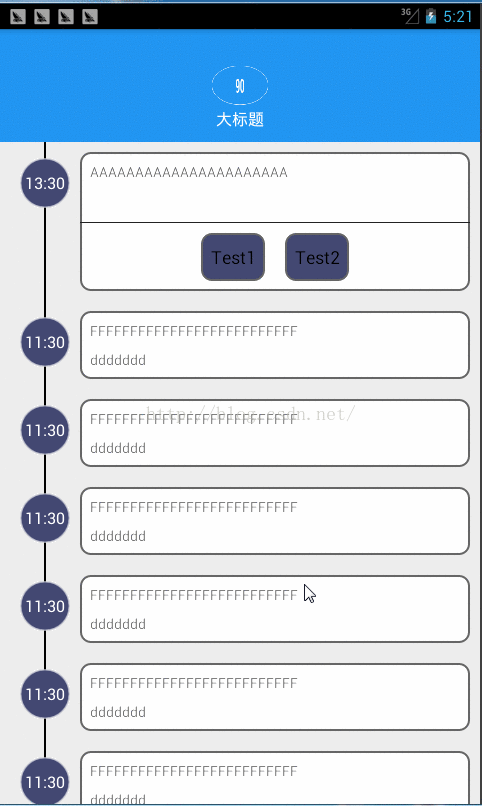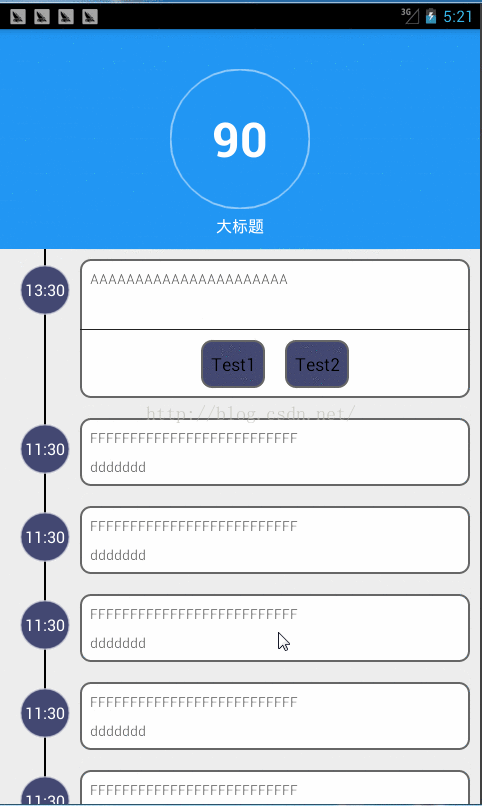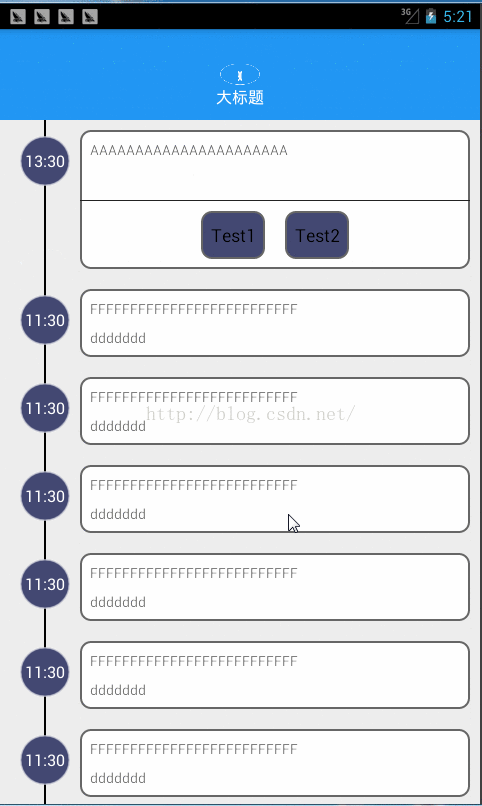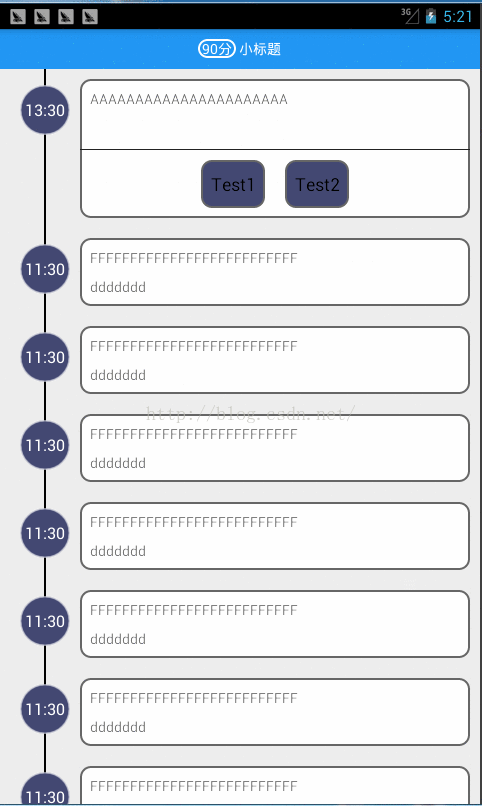
实现原理:
在listview里面设置ontouch监听,判断滑动方向和蓝色区域的状态,如果蓝色区域状态是显示最大且滑动方向向上,那么缩小该区域,如果蓝色区域最小,且滑动方向向下,则放大该区域。如果区域既不最大 也不最小,那么即可放大也可缩小。蓝色区域继承framelayout,小标题和大标题的visibile是相反设置的,也就是说只能显示一个标题。
结合代码:
开始做初始化:通过id获取两个标题栏View,并得到他们的高度和设置大标题View可见,小标题View不可见。这里需要注意一点:在绘制没有完成的情况下获取到的高度是0,那么就会出问题, 所以initData()函数要放在下面的地方执行。http://stackoverflow.com/questions/11946424/getmeasuredheight-and-width-returning-0-after-measure
这个网址做了详细解释
@Override
public void onWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus) {
super.onWindowFocusChanged(hasFocus);
if(bigHeaderView == null && smallHeaderView == null){
initData();
}
}private void initData() {
int bigHeaderViewId= getResources().getIdentifier("big_header_view", "id", getContext().getPackageName());
int smallHeaderViewId = getResources().getIdentifier("small_header_view", "id", getContext().getPackageName());
// System.out.println("bigHeaderViewId = " + bigHeaderViewId + " smallHeaderViewId = " + smallHeaderViewId);
if (bigHeaderViewId != 0 && smallHeaderViewId != 0) {
bigHeaderView = findViewById(bigHeaderViewId);
smallHeaderView = findViewById(smallHeaderViewId);
heightBV = bigHeaderView.getMeasuredHeight();
currentHeightBV = heightBV;
heightSV = smallHeaderView.getMeasuredHeight();
// System.out.println("heightBV = " + heightBV + " heightSV = " + heightSV);
bigHeaderView.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
smallHeaderView.setVisibility(INVISIBLE);
state = BIG_HEADER_VIEW_STATE;
} else {
Log.e("Error Inform", "没有设置HeaderView Id");
}
}下面是改变蓝色区域大小的代码:
//根据滑动设置高度
public void setHeaderHeight(float dis) {
int height = (int)(currentHeightBV + dis);
if (height < heightSV) {
height = heightSV;
} else if (height > heightBV) {
height = heightBV;
}
if (bigHeaderView != null && bigHeaderView.getLayoutParams() != null) {
bigHeaderView.getLayoutParams().height = height;
System.out.println("height = " + height + " currentHeight = " + currentHeightBV);
//计算缩放比,有了缩放比,你就可以做很多其他事情,比如控制alpha变化,控制scale变化
//像有些标题栏是根据手势移动,来改变透明度的.
float scalePercent = (height - heightSV)*1.0f / (heightBV - heightSV);
setTextViewHeight(scalePercent);
bigHeaderView.requestLayout();
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "bigHeaderView = null");
}
if(height <= heightSV){
smallHeaderView.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
bigHeaderView.setVisibility(INVISIBLE);
state = SMALL_HEADER_VIEW_STATE;
} else {
smallHeaderView.setVisibility(INVISIBLE);
bigHeaderView.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
if(height == heightBV)
state = BIG_HEADER_VIEW_STATE;
else
state = MID_HEADER_VIEW_STATE;
}
}为了体验更好,在蓝色区域缩放到2/3以内大小的时候,自动缩小直到最小。我的实现方式是通过线程来慢慢改变高度,详见代码,注释很详细
/**
* 当位置大于heightSV 并且小于 heightBV*2/3的时候,执行平滑缩放
* 感觉自己用线程实现的平滑效果不是很好......
*/
public void smoothSetHeaderHeight() {
currentHeightBV = bigHeaderView.getHeight();
final int timeCount = 1*200; //0.2秒钟 从heightBV*2/3 缩放到 heightSV
final float dis = -1 * (heightBV*2.0f/3.0f-heightSV)*1.0f/timeCount*10;
// System.out.println("currentHeightBV = " + currentHeightBV);
if(currentHeightBV > (heightBV*2 / 3) || currentHeightBV <= heightSV) {
return;
}
// System.out.println("dis = " + dis);
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < timeCount/10; i++) {
final float sumDis = i*dis + dis;
post(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
setHeaderHeight(sumDis);
}
});
try {
sleep(10); //为了体验好点,慢慢缩放
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
}下面贴上recycleview的事件监听代码
View.OnTouchListener onTouchListener = new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
int moveY = (int)event.getRawY(); //取得手指相对屏幕的Y坐标
if(event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN){
mDownY = event.getRawY(); //按下时候的坐标
}
if(event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE){
int dis = (int)(moveY - mDownY); //移动距离
// System.out.println("move distance = " + dis);
int state = scrollerHeaderLayout.getState(); //当前滑动状态
//下滑时候 需要做如下操作
if(dis > 0 && !recycleView.canScrollVertically(-1)
&& (state == ScrollerHeaderLayout.SMALL_HEADER_VIEW_STATE
|| state == ScrollerHeaderLayout.MID_HEADER_VIEW_STATE)){
// System.out.println("stateScrollerDir" + stateScrollerDir);
/**
* 这里逻辑是:如果你突然换方向移动,那么需要改变mDownY的坐标为"换方向的那个转折点"的Y标。
* 并初始化当前 scrollerHeaderLayout的高度。
*/
if(stateScrollerDir < 0) {
mDownY = moveY;
scrollerHeaderLayout.initCurrentHeightBV();
}
//改变移动状态
stateScrollerDir = 1;
dis = (int)(moveY - mDownY); //重新计算距离 :可能换方向移动了,原来计算的距离不对了.
scrollerHeaderLayout.setHeaderHeight(dis); //设置高度
return true;
}
//上滑 同下滑操作一样
if(dis < 0 && (state == ScrollerHeaderLayout.BIG_HEADER_VIEW_STATE
|| state == ScrollerHeaderLayout.MID_HEADER_VIEW_STATE)){
if(stateScrollerDir > 0) {
mDownY = moveY;
scrollerHeaderLayout.initCurrentHeightBV();
// System.out.println("mDownY = " + mDownY);
}
stateScrollerDir = -1;
dis = (int)(moveY - mDownY);
// System.out.println("-1 dis = " + dis);
scrollerHeaderLayout.setHeaderHeight(dis);
return true;
}
mDownY = event.getRawY();
}
if(event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP){
scrollerHeaderLayout.initCurrentHeightBV();
scrollerHeaderLayout.smoothSetHeaderHeight();
}
return false;
}
};总结:这里通过线程方式实现的自动缩放致最小高度,因为是匀速的,效果有点不太好...
相关文章推荐
- 使用C++实现JNI接口需要注意的事项
- Android IPC进程间通讯机制
- Android Manifest 用法
- [转载]Activity中ConfigChanges属性的用法
- Android之获取手机上的图片和视频缩略图thumbnails
- Android之使用Http协议实现文件上传功能
- Android学习笔记(二九):嵌入浏览器
- android string.xml文件中的整型和string型代替
- i-jetty环境搭配与编译
- android之定时器AlarmManager
- android wifi 无线调试
- Android Native 绘图方法
- Android java 与 javascript互访(相互调用)的方法例子
- android 代码实现控件之间的间距
- android FragmentPagerAdapter的“标准”配置
- Android"解决"onTouch和onClick的冲突问题
- android:installLocation简析
- android searchView的关闭事件
- SourceProvider.getJniDirectories
