Searching a 2D Sorted Matrix Part II
2015-09-10 12:27
393 查看
二维整型矩阵Table [m]
. 满足
Table[i][j] ≤ Table[i][j + 1],
Table[i][j] ≤ Table[i + 1][j]
在此中进行查找元素。
1.阶梯搜索
从右上角或者左下角开始,如下图红线所示的查找13的过程
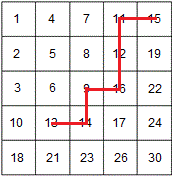
时间复杂度O(m+n)。
2.分治法
取矩阵的中心,将其划分成如下四个部分

如果查21,由于21》9,所以***部分排除。
复杂度推导
代码:
3.二分查找
用下面的方法可以将查找范围缩小到剩余的两部分。

a) 基于行的划分. The highlighted gray cells represents the traversed row (the middle row). The target 10 is
found between 9 and 16.

b)基于列的划分. The highlighted
gray cells represents the traversed column (the middle column). The target 10 is
found between 9 and 14.

c) 基于对角线的划分. The
highlighted gray cells represents the traversed diagonal. The target 10 is
found between 9and 17. Please note that diagonal-based binary
partition would fail in a non-square matrix (for the above example, it will not work in the two sub-matrices because they are non-square matrices).
If the target element equals one of the traversed cells, we immediately return the element as found. Otherwise we partition the matrix into two sub-matrices following the partition point we found. As it turns out, we need cn time
(linear time) to find such partition point, since we are essentially performing a linear search. Therefore, the complexity could be written as the following recurrence relation: (Note: I omitted the proof, as it is left as an exercise to the reader. )
复杂度:
. 满足
Table[i][j] ≤ Table[i][j + 1],
Table[i][j] ≤ Table[i + 1][j]
在此中进行查找元素。
1.阶梯搜索
从右上角或者左下角开始,如下图红线所示的查找13的过程

bool stepWise(int mat[][N_MAX], int N, int target,
int &row, int &col) {
if (target < mat[0][0] || target > mat[N-1][N-1]) return false;
row = 0;
col = N-1;
while (row <= N-1 && col >= 0) {
if (mat[row][col] < target)
row++;
else if (mat[row][col] > target)
col--;
else
return true;
}
return false;
}时间复杂度O(m+n)。
2.分治法
取矩阵的中心,将其划分成如下四个部分

如果查21,由于21》9,所以***部分排除。
复杂度推导
T(n) = 3T(n/2) + c,
= 3 [ 3T(n/4) + c ] + c
= 3 [ 3 [ 3T(n/8) + c ] + c ] + c
= 3k T(n/2k) + c (3k - 1)/2
= 3k ( T(n/2k) + c ) - c/2
Setting k = lg n,
T(n) = 3lg n ( T(1) + c ) - c/2
= O(3lg n)
= O(nlg 3) <== 3lg n = nlg 3
= O(n1.58)代码:
bool quadPart(int mat[][N_MAX], int M, int N, int target, int l, int u, int r, int d, int &targetRow, int &targetCol) {
if (l > r || u > d) return false;
if (target < mat[u][l] || target > mat[d][r]) return false;
int col = l + (r-l)/2;
int row = u + (d-u)/2;
if (mat[row][col] == target) {
targetRow = row;
targetCol = col;
return true;
} else if (l == r && u == d) {
return false;
}
if (mat[row][col] > target) {
return quadPart(mat, M, N, target, col+1, u, r, row, targetRow, targetCol) ||
quadPart(mat, M, N, target, l, row+1, col, d, targetRow, targetCol) ||
quadPart(mat, M, N, target, l, u, col, row, targetRow, targetCol);
} else {
return quadPart(mat, M, N, target, col+1, u, r, row, targetRow, targetCol) ||
quadPart(mat, M, N, target, l, row+1, col, d, targetRow, targetCol) ||
quadPart(mat, M, N, target, col+1, row+1, r, d, targetRow, targetCol);
}
}
bool quadPart(int mat[][N_MAX], int N, int target, int &row, int &col) {
return quadPart(mat, N, N, target, 0, 0, N-1, N-1, row, col);
}3.二分查找
用下面的方法可以将查找范围缩小到剩余的两部分。
ai < s < ai+1 , where ai is the ith traversed cell.

a) 基于行的划分. The highlighted gray cells represents the traversed row (the middle row). The target 10 is
found between 9 and 16.

b)基于列的划分. The highlighted
gray cells represents the traversed column (the middle column). The target 10 is
found between 9 and 14.

c) 基于对角线的划分. The
highlighted gray cells represents the traversed diagonal. The target 10 is
found between 9and 17. Please note that diagonal-based binary
partition would fail in a non-square matrix (for the above example, it will not work in the two sub-matrices because they are non-square matrices).
If the target element equals one of the traversed cells, we immediately return the element as found. Otherwise we partition the matrix into two sub-matrices following the partition point we found. As it turns out, we need cn time
(linear time) to find such partition point, since we are essentially performing a linear search. Therefore, the complexity could be written as the following recurrence relation: (Note: I omitted the proof, as it is left as an exercise to the reader. )
复杂度:
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + cn
= O(n lg n)bool binPart(int mat[][N_MAX], int M, int N, int target, int l, int u, int r, int d, int &targetRow, int &targetCol) { if (l > r || u > d) return false; if (target < mat[u][l] || target > mat[d][r]) return false; int mid = l + (r-l)/2; int row = u; while (row <= d && mat[row][mid] <= target) { if (mat[row][mid] == target) { targetRow = row; targetCol = mid; return true; } row++; } return binPart(mat, M, N, target, mid+1, u, r, row-1, targetRow, targetCol) || binPart(mat, M, N, target, l, row, mid-1, d, targetRow, targetCol);} bool binPart(int mat[][N_MAX], int N, int target, int &row, int &col) { return binPart(mat, N, N, target, 0, 0, N-1, N-1, row, col);}
相关文章推荐
- 空间域和频域结合的图像增强技术及实现
- lintcode-把排序数组转换为高度最小的二叉搜索树-177
- windows 10 开启vt-x
- cocos2d-x编译Andorid报错make: * No rule to make target
- 使用ascii方式得到26个字母
- HDU 4763 字符串的前中后三段公共子串
- TFS安装配置
- eDiary 日记本软件
- 为何新疆的股权投资企业所得税是12%,个人所得税是16%
- JSON.stringify几种可能的用法总结
- IOS图片效果模糊化
- Linux文件属主显示数字
- 字符串和date之间的相互转换方法
- Syslog4j如何实现接收日志
- 工业产品生产许可证审查费用已取消
- Java实现图的遍历(深搜与广搜)
- iOS 录屏大师启动页广告
- TortoiseSVN使用详解
- Android最佳性能实践(三)——高性能编码优化
- 快速提高Android开发效率的Web工具
