基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(二)
2014-12-30 18:20
453 查看
该系列文章将分为四个部分:
第一部分,将对SPI子系统整体进行描述,同时给出SPI的相关数据结构,最后描述SPI总线的注册。基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(一)
第二部分,该文将对SPI的主控制器(master)驱动进行描述。 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(二)
第三部分,该文将对SPI设备驱动,也称protocol 驱动,进行讲解。基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(三)
第四部分,即本篇文章,通过SPI设备驱动留给用户层的API,我们将从上到下描述数据是如何通过SPI的protocol 驱动,由bitbang 中转,最后由master驱动将
数据传输出去。基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(四)
本文属于第二部分。
4. 主控制器驱动程序
4.1 定义 platform device
下列数据结构位于arch/arm/plat-s3c24XX/devs.c
[html] view
plaincopy
/* SPI (0) */
static struct resource s3c_spi0_resource[] = {
[0] = {
.start = S3C24XX_PA_SPI,
.end = S3C24XX_PA_SPI + 0x1f,
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[1] = {
.start = IRQ_SPI0,
.end = IRQ_SPI0,
.flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ,
}
};
static u64 s3c_device_spi0_dmamask = 0xffffffffUL;
struct platform_device s3c_device_spi0 = {
.name = "s3c2410-spi",
.id = 0,
.num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(s3c_spi0_resource),
.resource = s3c_spi0_resource,
.dev = {
.dma_mask = &s3c_device_spi0_dmamask,
.coherent_dma_mask = 0xffffffffUL
}
};
platform设备给出了spi0接口的寄存器地址资源以及IRQ资源。注意其设备名为s3c2410-spi。
4.2 定义platform driver
下列函数位于deivers/spi/s3c24xx.c。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
MODULE_ALIAS("platform:s3c2410-spi");
static struct platform_driver s3c24xx_spi_driver = {
.remove = __exit_p(s3c24xx_spi_remove),
.suspend = s3c24xx_spi_suspend,
.resume = s3c24xx_spi_resume,
.driver = {
.name = "s3c2410-spi",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
};
static int __init s3c24xx_spi_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_probe(&s3c24xx_spi_driver, s3c24xx_spi_probe);//设备不可热插拔,所以使用该函数,而不是platform_driver_register
}
static void __exit s3c24xx_spi_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&s3c24xx_spi_driver);
}
module_init(s3c24xx_spi_init);
module_exit(s3c24xx_spi_exit);
调用了platform_driver_probe注册platform驱动,注册完成以后将会调用platform的s3c24xx_spi_probe函数。
NOTE:platform驱动的name和platform device的name是相同的。
4.2.1 s3c24xx_spi_probe函数
下列函数位于deivers/spi/s3c24xx.c。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static int __init s3c24xx_spi_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct s3c2410_spi_info *pdata;
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw;
struct spi_master *master;
struct resource *res;
int err = 0;
/*分配master结构体,其中包括s3c24xx_spi结构的内存空间,使用master.dev.driver_data指向它*/
master = spi_alloc_master(&pdev->dev, sizeof(struct s3c24xx_spi));
if (master == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "No memory for spi_master\n");
err = -ENOMEM;
goto err_nomem;
}
/*获得s3c24xx_spi结构,并清0该结构*/
hw = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
memset(hw, 0, sizeof(struct s3c24xx_spi));
hw->master = spi_master_get(master); /*保存master结构体,同时增加引用计数*/
hw->pdata = pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data; /*获取s3c2410_spi_info结构体指针*/
hw->dev = &pdev->dev; /*保存platform设备的dev*/
if (pdata == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "No platform data supplied\n");
err = -ENOENT;
goto err_no_pdata;
}
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, hw); /*让platform_devuce.dev.driver_data 指向 s3c24xx_spi*/
init_completion(&hw->done); /*初始化completion*/
/* setup the master state. */ /*填充master结构体的两个字段*/
master->num_chipselect = hw->pdata->num_cs;
master->bus_num = pdata->bus_num;
/* setup the state for the bitbang driver */ /*填充bitbang字段*/
hw->bitbang.master = hw->master;
hw->bitbang.setup_transfer = s3c24xx_spi_setupxfer;
hw->bitbang.chipselect = s3c24xx_spi_chipsel;
hw->bitbang.txrx_bufs = s3c24xx_spi_txrx;
hw->bitbang.master->setup = s3c24xx_spi_setup;
dev_dbg(hw->dev, "bitbang at %p\n", &hw->bitbang);
/* find and map our resources */
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0); /*获取IO资源*/
if (res == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Cannot get IORESOURCE_MEM\n");
err = -ENOENT;
goto err_no_iores;
}
hw->ioarea = request_mem_region(res->start, (res->end - res->start)+1, /*申请IO内存*/
pdev->name);
if (hw->ioarea == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Cannot reserve region\n");
err = -ENXIO;
goto err_no_iores;
}
hw->regs = ioremap(res->start, (res->end - res->start)+1); /*建立映射*/
if (hw->regs == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Cannot map IO\n");
err = -ENXIO;
goto err_no_iomap;
}
hw->irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0); /*获取irq号*/
if (hw->irq < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "No IRQ specified\n");
err = -ENOENT;
goto err_no_irq;
}
err = request_irq(hw->irq, s3c24xx_spi_irq, 0, pdev->name, hw); /*申请spi中断,ISR为 s3c24xx_spi_irq*/
if (err) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Cannot claim IRQ\n");
goto err_no_irq;
}
hw->clk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "spi"); /*获取spi时钟*/
if (IS_ERR(hw->clk)) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "No clock for device\n");
err = PTR_ERR(hw->clk);
goto err_no_clk;
}
/* setup any gpio we can */
if (!pdata->set_cs) { /*没有定义分配CS管脚的函数*/
if (pdata->pin_cs < 0) { /*pin_cs为cs管脚*/
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "No chipselect pin\n");
goto err_register;
}
err = gpio_request(pdata->pin_cs, dev_name(&pdev->dev));/*申请IO地址*/
if (err) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Failed to get gpio for cs\n");
goto err_register;
}
hw->set_cs = s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs; /*给出分配cs管脚函数*/
gpio_direction_output(pdata->pin_cs, 1); /*设置该管脚为输出,貌似多次一举,在probe已经调用过该函数*/
} else
hw->set_cs = pdata->set_cs;
s3c24xx_spi_initialsetup(hw); /*spi控制器初始化*/
/* register our spi controller */
err = spi_bitbang_start(&hw->bitbang);
if (err) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Failed to register SPI master\n");
goto err_register;
}
return 0;
err_register:
if (hw->set_cs == s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs)
gpio_free(pdata->pin_cs);
clk_disable(hw->clk);
clk_put(hw->clk);
err_no_clk:
free_irq(hw->irq, hw);
err_no_irq:
iounmap(hw->regs);
err_no_iomap:
release_resource(hw->ioarea); /*先释放资源*/
kfree(hw->ioarea); /*再释放空间*/
err_no_iores:
err_no_pdata:
spi_master_put(hw->master);; /*减少引用计数*/
err_nomem:
return err;
}
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/**
* spi_alloc_master - allocate SPI master controller
* @dev: the controller, possibly using the platform_bus
* @size: how much zeroed driver-private data to allocate; the pointer to this
* memory is in the driver_data field of the returned device,
* accessible with spi_master_get_devdata().
* Context: can sleep
*
* This call is used only by SPI master controller drivers, which are the
* only ones directly touching chip registers. It's how they allocate
* an spi_master structure, prior to calling spi_register_master().
*
* This must be called from context that can sleep. It returns the SPI
* master structure on success, else NULL.
*
* The caller is responsible for assigning the bus number and initializing
* the master's methods before calling spi_register_master(); and (after errors
* adding the device) calling spi_master_put() to prevent a memory leak.
*/
struct spi_master *spi_alloc_master(struct device *dev, unsigned size)
{
struct spi_master *master;
if (!dev)
return NULL;
master = kzalloc(size + sizeof *master, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!master)
return NULL;
device_initialize(&master->dev);
master->dev.class = &spi_master_class;
master->dev.parent = get_device(dev);
spi_master_set_devdata(master, &master[1]);
return master;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_alloc_master);
该函数首先为spi_master结构体以及s3c24xx_spi结构体分配了空间,同时,spi_master.dev.driver_data指向了s3c24xx_spi。
s3c24xx_spi结构如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
struct s3c24xx_spi {
/* bitbang has to be first */
struct spi_bitbang bitbang;
struct completion done;
void __iomem *regs;
int irq;
int len;
int count;
void (*set_cs)(struct s3c2410_spi_info *spi,
int cs, int pol);
/* data buffers */
const unsigned char *tx;
unsigned char *rx;
struct clk *clk;
struct resource *ioarea;
struct spi_master *master;
struct spi_device *curdev;
struct device *dev;
struct s3c2410_spi_info *pdata;
};
接着执行了该条语句:
hw->pdata = pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data; /*获取s3c2410_spi_info结构体指针*/
NOTE:在这里获取platform_device.dev.platform_data,也就是平台设备的相关数据,而在4.1小结中的arch/arm/plat-s3c24XX/devs.c文件中并没有发现platform_data的身影,因此这正式需要我们移植的地方。
随后初始化了completion,这个东东将用于实现同步I/O,详见下文。之后,为master定义了setup方法,为bitbang定义了3个方法。
接着获取了一系列的资源,同时注册了中断服务程序。接着调用s3c24xx_spi_initialsetup初始化控制器。我们来看下该函数。
该函数位于下列函数位于deivers/spi/s3c24xx.c。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static void s3c24xx_spi_initialsetup(struct s3c24xx_spi *hw)
{
/* for the moment, permanently enable the clock */
clk_enable(hw->clk); /*使能时钟*/
/* program defaults into the registers */
writeb(0xff, hw->regs + S3C2410_SPPRE); /*设置预分频系数,baudrate=pclk/2/(prescaler value+1)*/
writeb(SPPIN_DEFAULT, hw->regs + S3C2410_SPPIN);/*使能master out keep*/
writeb(SPCON_DEFAULT, hw->regs + S3C2410_SPCON);/*master, interrupt mode*/
if (hw->pdata) {
if (hw->set_cs == s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs) /*set_cs 在probe方法中设置为s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs*/
gpio_direction_output(hw->pdata->pin_cs, 1); /*设置该管脚为输出,貌似多次一举,在probe已经调用过该函数*/
*/
if (hw->pdata->gpio_setup)
hw->pdata->gpio_setup(hw->pdata, 1);
}
}
注意,这里设置了SPI0主控制器工作在master方式,使用中断模式。
最后调用了spi_bitbang_start函数,该函数非常重要,在下一小节中单独讲解。
4.2.2 spi_bitbang_start函数
下列函数位于drivers/spi/spi_bitbang.c
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/**
* spi_bitbang_start - start up a polled/bitbanging SPI master driver
* @bitbang: driver handle
*
* Caller should have zero-initialized all parts of the structure, and then
* provided callbacks for chip selection and I/O loops. If the master has
* a transfer method, its final step should call spi_bitbang_transfer; or,
* that's the default if the transfer routine is not initialized. It should
* also set up the bus number and number of chipselects.
*
* For i/o loops, provide callbacks either per-word (for bitbanging, or for
* hardware that basically exposes a shift register) or per-spi_transfer
* (which takes better advantage of hardware like fifos or DMA engines).
*
* Drivers using per-word I/O loops should use (or call) spi_bitbang_setup,
* spi_bitbang_cleanup and spi_bitbang_setup_transfer to handle those spi
* master methods. Those methods are the defaults if the bitbang->txrx_bufs
* routine isn't initialized.
*
* This routine registers the spi_master, which will process requests in a
* dedicated task, keeping IRQs unblocked most of the time. To stop
* processing those requests, call spi_bitbang_stop().
*/
int spi_bitbang_start(struct spi_bitbang *bitbang)
{
int status;
if (!bitbang->master || !bitbang->chipselect)
return -EINVAL;
INIT_WORK(&bitbang->work, bitbang_work); /*初始化工作,工作为bitbang_work*/
spin_lock_init(&bitbang->lock); /*初始化自旋锁*/
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&bitbang->queue); /*初始化链表头,链表为双向循环链表*/
if (!bitbang->master->transfer) /*master的transfer方法没有定义过*/
bitbang->master->transfer = spi_bitbang_transfer; /*使用spi_bitbang_transfe方法*/
if (!bitbang->txrx_bufs) { /*如果bitbang没有txrx_bufs方法,在probe函数中定义过该方法*/
bitbang->use_dma = 0;
bitbang->txrx_bufs = spi_bitbang_bufs;
if (!bitbang->master->setup) {
if (!bitbang->setup_transfer)
bitbang->setup_transfer =
spi_bitbang_setup_transfer;
bitbang->master->setup = spi_bitbang_setup;
bitbang->master->cleanup = spi_bitbang_cleanup;
}
} else if (!bitbang->master->setup) /*setup方法在probe函数中有定义*/
return -EINVAL;
/* this task is the only thing to touch the SPI bits */
bitbang->busy = 0;
bitbang->workqueue = create_singlethread_workqueue( /*创建工作队列*/
dev_name(bitbang->master->dev.parent));
if (bitbang->workqueue == NULL) {
status = -EBUSY;
goto err1;
}
/* driver may get busy before register() returns, especially
* if someone registered boardinfo for devices
*/
status = spi_register_master(bitbang->master); /*注册spi控制器*/
if (status < 0)
goto err2;
return status;
err2:
destroy_workqueue(bitbang->workqueue);
err1:
return status;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_bitbang_start);
在这里,定义了控制器的transfer方法为spi_bitbang_transfer。创建了一个工作队列和一个工作bitbang_work,同时创建了一个链表。这些东东的作用将在后面介绍。
最后,调用了spi_register_master函数,该函数将完成SPI控制器的注册,其中还牵涉到spi_device的注册。因此该函数也非常重要。我们来看看这个函数
下列函数位于drivers/spi/spi_bitbang.c
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/**
* spi_register_master - register SPI master controller
* @master: initialized master, originally from spi_alloc_master()
* Context: can sleep
*
* SPI master controllers connect to their drivers using some non-SPI bus,
* such as the platform bus. The final stage of probe() in that code
* includes calling spi_register_master() to hook up to this SPI bus glue.
*
* SPI controllers use board specific (often SOC specific) bus numbers,
* and board-specific addressing for SPI devices combines those numbers
* with chip select numbers. Since SPI does not directly support dynamic
* device identification, boards need configuration tables telling which
* chip is at which address.
*
* This must be called from context that can sleep. It returns zero on
* success, else a negative error code (dropping the master's refcount).
* After a successful return, the caller is responsible for calling
* spi_unregister_master().
*/
int spi_register_master(struct spi_master *master)
{
static atomic_t dyn_bus_id = ATOMIC_INIT((1<<15) - 1);
struct device *dev = master->dev.parent;
int status = -ENODEV;
int dynamic = 0;
if (!dev)
return -ENODEV;
/* even if it's just one always-selected device, there must
* be at least one chipselect
*/
if (master->num_chipselect == 0)
return -EINVAL;
/* convention: dynamically assigned bus IDs count down from the max */
if (master->bus_num < 0) {
/* FIXME switch to an IDR based scheme, something like
* I2C now uses, so we can't run out of "dynamic" IDs
*/
master->bus_num = atomic_dec_return(&dyn_bus_id);
dynamic = 1;
}
/* register the device, then userspace will see it.
* registration fails if the bus ID is in use.
*/
dev_set_name(&master->dev, "spi%u", master->bus_num);
status = device_add(&master->dev); /*注册设备*/
if (status < 0)
goto done;
dev_dbg(dev, "registered master %s%s\n", dev_name(&master->dev),
dynamic ? " (dynamic)" : "");
/* populate children from any spi device tables */
scan_boardinfo(master);
status = 0;
done:
return status;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_register_master);
该函数中,执行了相关的检查,然后注册了master设备,随后调用了scan_boardinfo。函数如下:
下列函数位于drivers/spi/spi.c
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/* FIXME someone should add support for a __setup("spi", ...) that
* creates board info from kernel command lines
*/
static void scan_boardinfo(struct spi_master *master)
{
struct boardinfo *bi;
mutex_lock(&board_lock);
/*以board_list为链表头,遍历所有的boardinfo结构,链表由spi_register_board_info添加*/
list_for_each_entry(bi, &board_list, list) {
struct spi_board_info *chip = bi->board_info;
unsigned n;
/*遍历该boardinfo指向的spi_board_info数组*/
for (n = bi->n_board_info; n > 0; n--, chip++) {
if (chip->bus_num != master->bus_num) /*通过bus_num对spi设备和master进行匹配*/
continue;
/* NOTE: this relies on spi_new_device to
* issue diagnostics when given bogus inputs
*/
/*执行到此,表示匹配完成,SPI设备由该SPI接口来控制,开始创建spi_device*/
(void) spi_new_device(master, chip);
}
}
mutex_unlock(&board_lock);
}
NOTE:这个函数通过boardinfo遍历的spi_board_info数组,而spi_board_info是在内核初始化过程中由spi_register_board_info进行注册的,在
linux/arch/arm/mach-s3c2440/mach-smdk2440.c中并没有调用过该函数,因此这也是需要移植的地方。
S3C2440共有两个接口:spi0和spi1。chip->bus_num表示该设备使用哪个spi接口,而master->bus_num正好表示了当前的接口。
该函数中,遍历spi_board_info,通过bus_num完成SPI设备和SPI控制器的匹配,匹配成功则开始建立spi_device设备,该过程通过调用spi_new_device实现。我们接着看下这个函数。
下列函数位于drivers/spi/spi.c
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/**
* spi_new_device - instantiate one new SPI device
* @master: Controller to which device is connected
* @chip: Describes the SPI device
* Context: can sleep
*
* On typical mainboards, this is purely internal; and it's not needed
* after board init creates the hard-wired devices. Some development
* platforms may not be able to use spi_register_board_info though, and
* this is exported so that for example a USB or parport based adapter
* driver could add devices (which it would learn about out-of-band).
*
* Returns the new device, or NULL.
*/
struct spi_device *spi_new_device(struct spi_master *master,
struct spi_board_info *chip)
{
struct spi_device *proxy;
int status;
/* NOTE: caller did any chip->bus_num checks necessary.
*
* Also, unless we change the return value convention to use
* error-or-pointer (not NULL-or-pointer), troubleshootability
* suggests syslogged diagnostics are best here (ugh).
*/
proxy = spi_alloc_device(master); /*分配spi_device结构,并初始化一些字段*/
if (!proxy)
return NULL;
WARN_ON(strlen(chip->modalias) >= sizeof(proxy->modalias));
/*从spi_board_info获取SPI从设备的参数*/
proxy->chip_select = chip->chip_select;
proxy->max_speed_hz = chip->max_speed_hz;
proxy->mode = chip->mode;
proxy->irq = chip->irq;
strlcpy(proxy->modalias, chip->modalias, sizeof(proxy->modalias));
proxy->dev.platform_data = (void *) chip->platform_data;
proxy->controller_data = chip->controller_data;
proxy->controller_state = NULL;
status = spi_add_device(proxy);
if (status < 0) {
spi_dev_put(proxy);
return NULL;
}
return proxy;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_new_device);
首先,创建了spi_device结构,让后通过板级信息spi_board_info将SPI从设备的相关信息复制给spi_device结构,从而完成了spi_device结构的定义,最后调用spi_add_device,完成spi_device的注册。
看下spi_add_device函数,该函数位于drivers/spi/spi.c
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/**
* spi_add_device - Add spi_device allocated with spi_alloc_device
* @spi: spi_device to register
*
* Companion function to spi_alloc_device. Devices allocated with
* spi_alloc_device can be added onto the spi bus with this function.
*
* Returns 0 on success; negative errno on failure
*/
int spi_add_device(struct spi_device *spi)
{
static DEFINE_MUTEX(spi_add_lock);
struct device *dev = spi->master->dev.parent;
int status;
/* Chipselects are numbered 0..max; validate. */
if (spi->chip_select >= spi->master->num_chipselect) {
dev_err(dev, "cs%d >= max %d\n",
spi->chip_select,
spi->master->num_chipselect);
return -EINVAL;
}
/* Set the bus ID string */
dev_set_name(&spi->dev, "%s.%u", dev_name(&spi->master->dev),
spi->chip_select);
/* We need to make sure there's no other device with this
* chipselect **BEFORE** we call setup(), else we'll trash
* its configuration. Lock against concurrent add() calls.
*/
mutex_lock(&spi_add_lock);
if (bus_find_device_by_name(&spi_bus_type, NULL, dev_name(&spi->dev))
!= NULL) {
dev_err(dev, "chipselect %d already in use\n",
spi->chip_select);
status = -EBUSY;
goto done;
}
/* Drivers may modify this initial i/o setup, but will
* normally rely on the device being setup. Devices
* using SPI_CS_HIGH can't coexist well otherwise...
*/
status = spi->master->setup(spi); /*调用setup方法,即s3c24xx_spi_setup函数*/
if (status < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "can't %s %s, status %d\n",
"setup", dev_name(&spi->dev), status);
goto done;
}
/* Device may be bound to an active driver when this returns */
status = device_add(&spi->dev); /*注册SPI_device*/
if (status < 0)
dev_err(dev, "can't %s %s, status %d\n",
"add", dev_name(&spi->dev), status);
else
dev_dbg(dev, "registered child %s\n", dev_name(&spi->dev));
done:
mutex_unlock(&spi_add_lock);
return status;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_add_device);
在注册spi_device之前,调用了master的setup方法,该方法又将调用s3c24xx_spi_setupxfer和s3c24xx_spi_chipsel函数。
s3c24xx_spi_setupxfer函数计算预分频系数并写入寄存器。
s3c24xx_spi_chipsel函数用于禁止或使能CS信号。当使能CS信号时,要设置控制寄存器。这里调用是禁止CS信号。
下列代码位于deivers/spi/s3c24xx.c。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
#define SPCON_DEFAULT (S3C2410_SPCON_MSTR | S3C2410_SPCON_SMOD_INT)
#define SPPIN_DEFAULT (S3C2410_SPPIN_KEEP)
static inline struct s3c24xx_spi *to_hw(struct spi_device *sdev)
{
return spi_master_get_devdata(sdev->master);
}
static void s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs(struct s3c2410_spi_info *spi, int cs, int pol)
{
gpio_set_value(spi->pin_cs, pol);
}
static void s3c24xx_spi_chipsel(struct spi_device *spi, int value)
{
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw = to_hw(spi);
unsigned int cspol = spi->mode & SPI_CS_HIGH ? 1 : 0;
unsigned int spcon;
switch (value) {
case BITBANG_CS_INACTIVE: /*CS无效时*/
hw->set_cs(hw->pdata, spi->chip_select, cspol^1);/*即调用s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs使CS无效*/
break;
case BITBANG_CS_ACTIVE: /*CS有效时*/
spcon = readb(hw->regs + S3C2410_SPCON); /*获取目前SPCON寄存器的值*/
/*开始设置工作模式*/
if (spi->mode & SPI_CPHA)
spcon |= S3C2410_SPCON_CPHA_FMTB;
else
spcon &= ~S3C2410_SPCON_CPHA_FMTB;
if (spi->mode & SPI_CPOL)
spcon |= S3C2410_SPCON_CPOL_HIGH;
else
spcon &= ~S3C2410_SPCON_CPOL_HIGH;
/*激活时钟sck输出*/
spcon |= S3C2410_SPCON_ENSCK;
/* write new configration */
writeb(spcon, hw->regs + S3C2410_SPCON); /*保存新的配置*/
hw->set_cs(hw->pdata, spi->chip_select, cspol);/*即调用s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs使CS有效*/
break;
}
}
static int s3c24xx_spi_setupxfer(struct spi_device *spi,
struct spi_transfer *t)
{
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw = to_hw(spi);
unsigned int bpw;
unsigned int hz;
unsigned int div;
/*没有transfer,则使用spi_device进行配置*/
bpw = t ? t->bits_per_word : spi->bits_per_word;
hz = t ? t->speed_hz : spi->max_speed_hz;
if (bpw != 8) {
dev_err(&spi->dev, "invalid bits-per-word (%d)\n", bpw);
return -EINVAL;
}
div = clk_get_rate(hw->clk) / hz;
/* is clk = pclk / (2 * (pre+1)), or is it
* clk = (pclk * 2) / ( pre + 1) */
/*计算预分频系数*/
div /= 2;
if (div > 0)
div -= 1;
if (div > 255) /*只有8位*/
div = 255;
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "setting pre-scaler to %d (hz %d)\n", div, hz);
writeb(div, hw->regs + S3C2410_SPPRE); /*设置预分频系数*/
spin_lock(&hw->bitbang.lock); /*自旋锁加锁*/
if (!hw->bitbang.busy) { /*如果不忙*/
hw->bitbang.chipselect(spi, BITBANG_CS_INACTIVE);/*即调用s3c24xx_spi_chipsel使CS无效*/
/* need to ndelay for 0.5 clocktick ? */
}
spin_unlock(&hw->bitbang.lock);
return 0;
}
/* the spi->mode bits understood by this driver: */
#define MODEBITS (SPI_CPOL | SPI_CPHA | SPI_CS_HIGH)
static int s3c24xx_spi_setup(struct spi_device *spi) /*maser.setup方法*/
{
int ret;
if (!spi->bits_per_word)
spi->bits_per_word = 8; /*没有设置则使用8位*/
if (spi->mode & ~MODEBITS) { /*检查mode是否有错*/
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "setup: unsupported mode bits %x\n",
spi->mode & ~MODEBITS);
return -EINVAL;
}
ret = s3c24xx_spi_setupxfer(spi, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&spi->dev, "setupxfer returned %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%s: mode %d, %u bpw, %d hz\n",
__func__, spi->mode, spi->bits_per_word,
spi->max_speed_hz);
return 0;
}
至此,在probe函数中, 由spi_bitbang_start调用所引起的一系列函数调用都已讲解完毕。下面总结下整个调用过程:
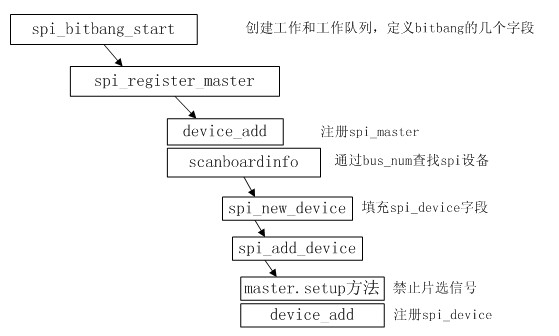
可以看到,调用spi_bitbang_start以后,spi_master和spi_device都将被注册到内核中。
下面来看下platform driver的其他几个方法。
4.2.3 remove,suspend以及resume方法
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static int __exit s3c24xx_spi_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw = platform_get_drvdata(dev);
platform_set_drvdata(dev, NULL);
spi_unregister_master(hw->master); /*注销spi主控制器*/
clk_disable(hw->clk); /*禁止时钟*/
clk_put(hw->clk); /*释放CLK*/
free_irq(hw->irq, hw); /*注销IRQ*/
iounmap(hw->regs); /*解除映射*/
if (hw->set_cs == s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs)
gpio_free(hw->pdata->pin_cs); /*释放用于cs的gpio*/
release_resource(hw->ioarea);
kfree(hw->ioarea);
spi_master_put(hw->master); /*减少master引用计数*/
return 0;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_PM /*如果定义了电源管理*/
static int s3c24xx_spi_suspend(struct platform_device *pdev, pm_message_t msg)
{
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
if (hw->pdata && hw->pdata->gpio_setup)
hw->pdata->gpio_setup(hw->pdata, 0);
clk_disable(hw->clk);
return 0;
}
static int s3c24xx_spi_resume(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
s3c24xx_spi_initialsetup(hw);
return 0;
}
#else
#define s3c24xx_spi_suspend NULL
#define s3c24xx_spi_resume NULL
#endif
至此,master 驱动的大体结构都已分析完毕,随后第三篇文章将介绍spi设备驱动
第一部分,将对SPI子系统整体进行描述,同时给出SPI的相关数据结构,最后描述SPI总线的注册。基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(一)
第二部分,该文将对SPI的主控制器(master)驱动进行描述。 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(二)
第三部分,该文将对SPI设备驱动,也称protocol 驱动,进行讲解。基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(三)
第四部分,即本篇文章,通过SPI设备驱动留给用户层的API,我们将从上到下描述数据是如何通过SPI的protocol 驱动,由bitbang 中转,最后由master驱动将
数据传输出去。基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(四)
本文属于第二部分。
4. 主控制器驱动程序
4.1 定义 platform device
下列数据结构位于arch/arm/plat-s3c24XX/devs.c
[html] view
plaincopy
/* SPI (0) */
static struct resource s3c_spi0_resource[] = {
[0] = {
.start = S3C24XX_PA_SPI,
.end = S3C24XX_PA_SPI + 0x1f,
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[1] = {
.start = IRQ_SPI0,
.end = IRQ_SPI0,
.flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ,
}
};
static u64 s3c_device_spi0_dmamask = 0xffffffffUL;
struct platform_device s3c_device_spi0 = {
.name = "s3c2410-spi",
.id = 0,
.num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(s3c_spi0_resource),
.resource = s3c_spi0_resource,
.dev = {
.dma_mask = &s3c_device_spi0_dmamask,
.coherent_dma_mask = 0xffffffffUL
}
};
platform设备给出了spi0接口的寄存器地址资源以及IRQ资源。注意其设备名为s3c2410-spi。
4.2 定义platform driver
下列函数位于deivers/spi/s3c24xx.c。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
MODULE_ALIAS("platform:s3c2410-spi");
static struct platform_driver s3c24xx_spi_driver = {
.remove = __exit_p(s3c24xx_spi_remove),
.suspend = s3c24xx_spi_suspend,
.resume = s3c24xx_spi_resume,
.driver = {
.name = "s3c2410-spi",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
};
static int __init s3c24xx_spi_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_probe(&s3c24xx_spi_driver, s3c24xx_spi_probe);//设备不可热插拔,所以使用该函数,而不是platform_driver_register
}
static void __exit s3c24xx_spi_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&s3c24xx_spi_driver);
}
module_init(s3c24xx_spi_init);
module_exit(s3c24xx_spi_exit);
调用了platform_driver_probe注册platform驱动,注册完成以后将会调用platform的s3c24xx_spi_probe函数。
NOTE:platform驱动的name和platform device的name是相同的。
4.2.1 s3c24xx_spi_probe函数
下列函数位于deivers/spi/s3c24xx.c。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static int __init s3c24xx_spi_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct s3c2410_spi_info *pdata;
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw;
struct spi_master *master;
struct resource *res;
int err = 0;
/*分配master结构体,其中包括s3c24xx_spi结构的内存空间,使用master.dev.driver_data指向它*/
master = spi_alloc_master(&pdev->dev, sizeof(struct s3c24xx_spi));
if (master == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "No memory for spi_master\n");
err = -ENOMEM;
goto err_nomem;
}
/*获得s3c24xx_spi结构,并清0该结构*/
hw = spi_master_get_devdata(master);
memset(hw, 0, sizeof(struct s3c24xx_spi));
hw->master = spi_master_get(master); /*保存master结构体,同时增加引用计数*/
hw->pdata = pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data; /*获取s3c2410_spi_info结构体指针*/
hw->dev = &pdev->dev; /*保存platform设备的dev*/
if (pdata == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "No platform data supplied\n");
err = -ENOENT;
goto err_no_pdata;
}
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, hw); /*让platform_devuce.dev.driver_data 指向 s3c24xx_spi*/
init_completion(&hw->done); /*初始化completion*/
/* setup the master state. */ /*填充master结构体的两个字段*/
master->num_chipselect = hw->pdata->num_cs;
master->bus_num = pdata->bus_num;
/* setup the state for the bitbang driver */ /*填充bitbang字段*/
hw->bitbang.master = hw->master;
hw->bitbang.setup_transfer = s3c24xx_spi_setupxfer;
hw->bitbang.chipselect = s3c24xx_spi_chipsel;
hw->bitbang.txrx_bufs = s3c24xx_spi_txrx;
hw->bitbang.master->setup = s3c24xx_spi_setup;
dev_dbg(hw->dev, "bitbang at %p\n", &hw->bitbang);
/* find and map our resources */
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0); /*获取IO资源*/
if (res == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Cannot get IORESOURCE_MEM\n");
err = -ENOENT;
goto err_no_iores;
}
hw->ioarea = request_mem_region(res->start, (res->end - res->start)+1, /*申请IO内存*/
pdev->name);
if (hw->ioarea == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Cannot reserve region\n");
err = -ENXIO;
goto err_no_iores;
}
hw->regs = ioremap(res->start, (res->end - res->start)+1); /*建立映射*/
if (hw->regs == NULL) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Cannot map IO\n");
err = -ENXIO;
goto err_no_iomap;
}
hw->irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0); /*获取irq号*/
if (hw->irq < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "No IRQ specified\n");
err = -ENOENT;
goto err_no_irq;
}
err = request_irq(hw->irq, s3c24xx_spi_irq, 0, pdev->name, hw); /*申请spi中断,ISR为 s3c24xx_spi_irq*/
if (err) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Cannot claim IRQ\n");
goto err_no_irq;
}
hw->clk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "spi"); /*获取spi时钟*/
if (IS_ERR(hw->clk)) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "No clock for device\n");
err = PTR_ERR(hw->clk);
goto err_no_clk;
}
/* setup any gpio we can */
if (!pdata->set_cs) { /*没有定义分配CS管脚的函数*/
if (pdata->pin_cs < 0) { /*pin_cs为cs管脚*/
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "No chipselect pin\n");
goto err_register;
}
err = gpio_request(pdata->pin_cs, dev_name(&pdev->dev));/*申请IO地址*/
if (err) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Failed to get gpio for cs\n");
goto err_register;
}
hw->set_cs = s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs; /*给出分配cs管脚函数*/
gpio_direction_output(pdata->pin_cs, 1); /*设置该管脚为输出,貌似多次一举,在probe已经调用过该函数*/
} else
hw->set_cs = pdata->set_cs;
s3c24xx_spi_initialsetup(hw); /*spi控制器初始化*/
/* register our spi controller */
err = spi_bitbang_start(&hw->bitbang);
if (err) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Failed to register SPI master\n");
goto err_register;
}
return 0;
err_register:
if (hw->set_cs == s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs)
gpio_free(pdata->pin_cs);
clk_disable(hw->clk);
clk_put(hw->clk);
err_no_clk:
free_irq(hw->irq, hw);
err_no_irq:
iounmap(hw->regs);
err_no_iomap:
release_resource(hw->ioarea); /*先释放资源*/
kfree(hw->ioarea); /*再释放空间*/
err_no_iores:
err_no_pdata:
spi_master_put(hw->master);; /*减少引用计数*/
err_nomem:
return err;
}
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/**
* spi_alloc_master - allocate SPI master controller
* @dev: the controller, possibly using the platform_bus
* @size: how much zeroed driver-private data to allocate; the pointer to this
* memory is in the driver_data field of the returned device,
* accessible with spi_master_get_devdata().
* Context: can sleep
*
* This call is used only by SPI master controller drivers, which are the
* only ones directly touching chip registers. It's how they allocate
* an spi_master structure, prior to calling spi_register_master().
*
* This must be called from context that can sleep. It returns the SPI
* master structure on success, else NULL.
*
* The caller is responsible for assigning the bus number and initializing
* the master's methods before calling spi_register_master(); and (after errors
* adding the device) calling spi_master_put() to prevent a memory leak.
*/
struct spi_master *spi_alloc_master(struct device *dev, unsigned size)
{
struct spi_master *master;
if (!dev)
return NULL;
master = kzalloc(size + sizeof *master, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!master)
return NULL;
device_initialize(&master->dev);
master->dev.class = &spi_master_class;
master->dev.parent = get_device(dev);
spi_master_set_devdata(master, &master[1]);
return master;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_alloc_master);
该函数首先为spi_master结构体以及s3c24xx_spi结构体分配了空间,同时,spi_master.dev.driver_data指向了s3c24xx_spi。
s3c24xx_spi结构如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
struct s3c24xx_spi {
/* bitbang has to be first */
struct spi_bitbang bitbang;
struct completion done;
void __iomem *regs;
int irq;
int len;
int count;
void (*set_cs)(struct s3c2410_spi_info *spi,
int cs, int pol);
/* data buffers */
const unsigned char *tx;
unsigned char *rx;
struct clk *clk;
struct resource *ioarea;
struct spi_master *master;
struct spi_device *curdev;
struct device *dev;
struct s3c2410_spi_info *pdata;
};
接着执行了该条语句:
hw->pdata = pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data; /*获取s3c2410_spi_info结构体指针*/
NOTE:在这里获取platform_device.dev.platform_data,也就是平台设备的相关数据,而在4.1小结中的arch/arm/plat-s3c24XX/devs.c文件中并没有发现platform_data的身影,因此这正式需要我们移植的地方。
随后初始化了completion,这个东东将用于实现同步I/O,详见下文。之后,为master定义了setup方法,为bitbang定义了3个方法。
接着获取了一系列的资源,同时注册了中断服务程序。接着调用s3c24xx_spi_initialsetup初始化控制器。我们来看下该函数。
该函数位于下列函数位于deivers/spi/s3c24xx.c。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static void s3c24xx_spi_initialsetup(struct s3c24xx_spi *hw)
{
/* for the moment, permanently enable the clock */
clk_enable(hw->clk); /*使能时钟*/
/* program defaults into the registers */
writeb(0xff, hw->regs + S3C2410_SPPRE); /*设置预分频系数,baudrate=pclk/2/(prescaler value+1)*/
writeb(SPPIN_DEFAULT, hw->regs + S3C2410_SPPIN);/*使能master out keep*/
writeb(SPCON_DEFAULT, hw->regs + S3C2410_SPCON);/*master, interrupt mode*/
if (hw->pdata) {
if (hw->set_cs == s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs) /*set_cs 在probe方法中设置为s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs*/
gpio_direction_output(hw->pdata->pin_cs, 1); /*设置该管脚为输出,貌似多次一举,在probe已经调用过该函数*/
*/
if (hw->pdata->gpio_setup)
hw->pdata->gpio_setup(hw->pdata, 1);
}
}
注意,这里设置了SPI0主控制器工作在master方式,使用中断模式。
最后调用了spi_bitbang_start函数,该函数非常重要,在下一小节中单独讲解。
4.2.2 spi_bitbang_start函数
下列函数位于drivers/spi/spi_bitbang.c
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/**
* spi_bitbang_start - start up a polled/bitbanging SPI master driver
* @bitbang: driver handle
*
* Caller should have zero-initialized all parts of the structure, and then
* provided callbacks for chip selection and I/O loops. If the master has
* a transfer method, its final step should call spi_bitbang_transfer; or,
* that's the default if the transfer routine is not initialized. It should
* also set up the bus number and number of chipselects.
*
* For i/o loops, provide callbacks either per-word (for bitbanging, or for
* hardware that basically exposes a shift register) or per-spi_transfer
* (which takes better advantage of hardware like fifos or DMA engines).
*
* Drivers using per-word I/O loops should use (or call) spi_bitbang_setup,
* spi_bitbang_cleanup and spi_bitbang_setup_transfer to handle those spi
* master methods. Those methods are the defaults if the bitbang->txrx_bufs
* routine isn't initialized.
*
* This routine registers the spi_master, which will process requests in a
* dedicated task, keeping IRQs unblocked most of the time. To stop
* processing those requests, call spi_bitbang_stop().
*/
int spi_bitbang_start(struct spi_bitbang *bitbang)
{
int status;
if (!bitbang->master || !bitbang->chipselect)
return -EINVAL;
INIT_WORK(&bitbang->work, bitbang_work); /*初始化工作,工作为bitbang_work*/
spin_lock_init(&bitbang->lock); /*初始化自旋锁*/
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&bitbang->queue); /*初始化链表头,链表为双向循环链表*/
if (!bitbang->master->transfer) /*master的transfer方法没有定义过*/
bitbang->master->transfer = spi_bitbang_transfer; /*使用spi_bitbang_transfe方法*/
if (!bitbang->txrx_bufs) { /*如果bitbang没有txrx_bufs方法,在probe函数中定义过该方法*/
bitbang->use_dma = 0;
bitbang->txrx_bufs = spi_bitbang_bufs;
if (!bitbang->master->setup) {
if (!bitbang->setup_transfer)
bitbang->setup_transfer =
spi_bitbang_setup_transfer;
bitbang->master->setup = spi_bitbang_setup;
bitbang->master->cleanup = spi_bitbang_cleanup;
}
} else if (!bitbang->master->setup) /*setup方法在probe函数中有定义*/
return -EINVAL;
/* this task is the only thing to touch the SPI bits */
bitbang->busy = 0;
bitbang->workqueue = create_singlethread_workqueue( /*创建工作队列*/
dev_name(bitbang->master->dev.parent));
if (bitbang->workqueue == NULL) {
status = -EBUSY;
goto err1;
}
/* driver may get busy before register() returns, especially
* if someone registered boardinfo for devices
*/
status = spi_register_master(bitbang->master); /*注册spi控制器*/
if (status < 0)
goto err2;
return status;
err2:
destroy_workqueue(bitbang->workqueue);
err1:
return status;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_bitbang_start);
在这里,定义了控制器的transfer方法为spi_bitbang_transfer。创建了一个工作队列和一个工作bitbang_work,同时创建了一个链表。这些东东的作用将在后面介绍。
最后,调用了spi_register_master函数,该函数将完成SPI控制器的注册,其中还牵涉到spi_device的注册。因此该函数也非常重要。我们来看看这个函数
下列函数位于drivers/spi/spi_bitbang.c
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/**
* spi_register_master - register SPI master controller
* @master: initialized master, originally from spi_alloc_master()
* Context: can sleep
*
* SPI master controllers connect to their drivers using some non-SPI bus,
* such as the platform bus. The final stage of probe() in that code
* includes calling spi_register_master() to hook up to this SPI bus glue.
*
* SPI controllers use board specific (often SOC specific) bus numbers,
* and board-specific addressing for SPI devices combines those numbers
* with chip select numbers. Since SPI does not directly support dynamic
* device identification, boards need configuration tables telling which
* chip is at which address.
*
* This must be called from context that can sleep. It returns zero on
* success, else a negative error code (dropping the master's refcount).
* After a successful return, the caller is responsible for calling
* spi_unregister_master().
*/
int spi_register_master(struct spi_master *master)
{
static atomic_t dyn_bus_id = ATOMIC_INIT((1<<15) - 1);
struct device *dev = master->dev.parent;
int status = -ENODEV;
int dynamic = 0;
if (!dev)
return -ENODEV;
/* even if it's just one always-selected device, there must
* be at least one chipselect
*/
if (master->num_chipselect == 0)
return -EINVAL;
/* convention: dynamically assigned bus IDs count down from the max */
if (master->bus_num < 0) {
/* FIXME switch to an IDR based scheme, something like
* I2C now uses, so we can't run out of "dynamic" IDs
*/
master->bus_num = atomic_dec_return(&dyn_bus_id);
dynamic = 1;
}
/* register the device, then userspace will see it.
* registration fails if the bus ID is in use.
*/
dev_set_name(&master->dev, "spi%u", master->bus_num);
status = device_add(&master->dev); /*注册设备*/
if (status < 0)
goto done;
dev_dbg(dev, "registered master %s%s\n", dev_name(&master->dev),
dynamic ? " (dynamic)" : "");
/* populate children from any spi device tables */
scan_boardinfo(master);
status = 0;
done:
return status;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_register_master);
该函数中,执行了相关的检查,然后注册了master设备,随后调用了scan_boardinfo。函数如下:
下列函数位于drivers/spi/spi.c
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/* FIXME someone should add support for a __setup("spi", ...) that
* creates board info from kernel command lines
*/
static void scan_boardinfo(struct spi_master *master)
{
struct boardinfo *bi;
mutex_lock(&board_lock);
/*以board_list为链表头,遍历所有的boardinfo结构,链表由spi_register_board_info添加*/
list_for_each_entry(bi, &board_list, list) {
struct spi_board_info *chip = bi->board_info;
unsigned n;
/*遍历该boardinfo指向的spi_board_info数组*/
for (n = bi->n_board_info; n > 0; n--, chip++) {
if (chip->bus_num != master->bus_num) /*通过bus_num对spi设备和master进行匹配*/
continue;
/* NOTE: this relies on spi_new_device to
* issue diagnostics when given bogus inputs
*/
/*执行到此,表示匹配完成,SPI设备由该SPI接口来控制,开始创建spi_device*/
(void) spi_new_device(master, chip);
}
}
mutex_unlock(&board_lock);
}
NOTE:这个函数通过boardinfo遍历的spi_board_info数组,而spi_board_info是在内核初始化过程中由spi_register_board_info进行注册的,在
linux/arch/arm/mach-s3c2440/mach-smdk2440.c中并没有调用过该函数,因此这也是需要移植的地方。
S3C2440共有两个接口:spi0和spi1。chip->bus_num表示该设备使用哪个spi接口,而master->bus_num正好表示了当前的接口。
该函数中,遍历spi_board_info,通过bus_num完成SPI设备和SPI控制器的匹配,匹配成功则开始建立spi_device设备,该过程通过调用spi_new_device实现。我们接着看下这个函数。
下列函数位于drivers/spi/spi.c
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/**
* spi_new_device - instantiate one new SPI device
* @master: Controller to which device is connected
* @chip: Describes the SPI device
* Context: can sleep
*
* On typical mainboards, this is purely internal; and it's not needed
* after board init creates the hard-wired devices. Some development
* platforms may not be able to use spi_register_board_info though, and
* this is exported so that for example a USB or parport based adapter
* driver could add devices (which it would learn about out-of-band).
*
* Returns the new device, or NULL.
*/
struct spi_device *spi_new_device(struct spi_master *master,
struct spi_board_info *chip)
{
struct spi_device *proxy;
int status;
/* NOTE: caller did any chip->bus_num checks necessary.
*
* Also, unless we change the return value convention to use
* error-or-pointer (not NULL-or-pointer), troubleshootability
* suggests syslogged diagnostics are best here (ugh).
*/
proxy = spi_alloc_device(master); /*分配spi_device结构,并初始化一些字段*/
if (!proxy)
return NULL;
WARN_ON(strlen(chip->modalias) >= sizeof(proxy->modalias));
/*从spi_board_info获取SPI从设备的参数*/
proxy->chip_select = chip->chip_select;
proxy->max_speed_hz = chip->max_speed_hz;
proxy->mode = chip->mode;
proxy->irq = chip->irq;
strlcpy(proxy->modalias, chip->modalias, sizeof(proxy->modalias));
proxy->dev.platform_data = (void *) chip->platform_data;
proxy->controller_data = chip->controller_data;
proxy->controller_state = NULL;
status = spi_add_device(proxy);
if (status < 0) {
spi_dev_put(proxy);
return NULL;
}
return proxy;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_new_device);
首先,创建了spi_device结构,让后通过板级信息spi_board_info将SPI从设备的相关信息复制给spi_device结构,从而完成了spi_device结构的定义,最后调用spi_add_device,完成spi_device的注册。
看下spi_add_device函数,该函数位于drivers/spi/spi.c
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/**
* spi_add_device - Add spi_device allocated with spi_alloc_device
* @spi: spi_device to register
*
* Companion function to spi_alloc_device. Devices allocated with
* spi_alloc_device can be added onto the spi bus with this function.
*
* Returns 0 on success; negative errno on failure
*/
int spi_add_device(struct spi_device *spi)
{
static DEFINE_MUTEX(spi_add_lock);
struct device *dev = spi->master->dev.parent;
int status;
/* Chipselects are numbered 0..max; validate. */
if (spi->chip_select >= spi->master->num_chipselect) {
dev_err(dev, "cs%d >= max %d\n",
spi->chip_select,
spi->master->num_chipselect);
return -EINVAL;
}
/* Set the bus ID string */
dev_set_name(&spi->dev, "%s.%u", dev_name(&spi->master->dev),
spi->chip_select);
/* We need to make sure there's no other device with this
* chipselect **BEFORE** we call setup(), else we'll trash
* its configuration. Lock against concurrent add() calls.
*/
mutex_lock(&spi_add_lock);
if (bus_find_device_by_name(&spi_bus_type, NULL, dev_name(&spi->dev))
!= NULL) {
dev_err(dev, "chipselect %d already in use\n",
spi->chip_select);
status = -EBUSY;
goto done;
}
/* Drivers may modify this initial i/o setup, but will
* normally rely on the device being setup. Devices
* using SPI_CS_HIGH can't coexist well otherwise...
*/
status = spi->master->setup(spi); /*调用setup方法,即s3c24xx_spi_setup函数*/
if (status < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "can't %s %s, status %d\n",
"setup", dev_name(&spi->dev), status);
goto done;
}
/* Device may be bound to an active driver when this returns */
status = device_add(&spi->dev); /*注册SPI_device*/
if (status < 0)
dev_err(dev, "can't %s %s, status %d\n",
"add", dev_name(&spi->dev), status);
else
dev_dbg(dev, "registered child %s\n", dev_name(&spi->dev));
done:
mutex_unlock(&spi_add_lock);
return status;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_add_device);
在注册spi_device之前,调用了master的setup方法,该方法又将调用s3c24xx_spi_setupxfer和s3c24xx_spi_chipsel函数。
s3c24xx_spi_setupxfer函数计算预分频系数并写入寄存器。
s3c24xx_spi_chipsel函数用于禁止或使能CS信号。当使能CS信号时,要设置控制寄存器。这里调用是禁止CS信号。
下列代码位于deivers/spi/s3c24xx.c。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
#define SPCON_DEFAULT (S3C2410_SPCON_MSTR | S3C2410_SPCON_SMOD_INT)
#define SPPIN_DEFAULT (S3C2410_SPPIN_KEEP)
static inline struct s3c24xx_spi *to_hw(struct spi_device *sdev)
{
return spi_master_get_devdata(sdev->master);
}
static void s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs(struct s3c2410_spi_info *spi, int cs, int pol)
{
gpio_set_value(spi->pin_cs, pol);
}
static void s3c24xx_spi_chipsel(struct spi_device *spi, int value)
{
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw = to_hw(spi);
unsigned int cspol = spi->mode & SPI_CS_HIGH ? 1 : 0;
unsigned int spcon;
switch (value) {
case BITBANG_CS_INACTIVE: /*CS无效时*/
hw->set_cs(hw->pdata, spi->chip_select, cspol^1);/*即调用s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs使CS无效*/
break;
case BITBANG_CS_ACTIVE: /*CS有效时*/
spcon = readb(hw->regs + S3C2410_SPCON); /*获取目前SPCON寄存器的值*/
/*开始设置工作模式*/
if (spi->mode & SPI_CPHA)
spcon |= S3C2410_SPCON_CPHA_FMTB;
else
spcon &= ~S3C2410_SPCON_CPHA_FMTB;
if (spi->mode & SPI_CPOL)
spcon |= S3C2410_SPCON_CPOL_HIGH;
else
spcon &= ~S3C2410_SPCON_CPOL_HIGH;
/*激活时钟sck输出*/
spcon |= S3C2410_SPCON_ENSCK;
/* write new configration */
writeb(spcon, hw->regs + S3C2410_SPCON); /*保存新的配置*/
hw->set_cs(hw->pdata, spi->chip_select, cspol);/*即调用s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs使CS有效*/
break;
}
}
static int s3c24xx_spi_setupxfer(struct spi_device *spi,
struct spi_transfer *t)
{
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw = to_hw(spi);
unsigned int bpw;
unsigned int hz;
unsigned int div;
/*没有transfer,则使用spi_device进行配置*/
bpw = t ? t->bits_per_word : spi->bits_per_word;
hz = t ? t->speed_hz : spi->max_speed_hz;
if (bpw != 8) {
dev_err(&spi->dev, "invalid bits-per-word (%d)\n", bpw);
return -EINVAL;
}
div = clk_get_rate(hw->clk) / hz;
/* is clk = pclk / (2 * (pre+1)), or is it
* clk = (pclk * 2) / ( pre + 1) */
/*计算预分频系数*/
div /= 2;
if (div > 0)
div -= 1;
if (div > 255) /*只有8位*/
div = 255;
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "setting pre-scaler to %d (hz %d)\n", div, hz);
writeb(div, hw->regs + S3C2410_SPPRE); /*设置预分频系数*/
spin_lock(&hw->bitbang.lock); /*自旋锁加锁*/
if (!hw->bitbang.busy) { /*如果不忙*/
hw->bitbang.chipselect(spi, BITBANG_CS_INACTIVE);/*即调用s3c24xx_spi_chipsel使CS无效*/
/* need to ndelay for 0.5 clocktick ? */
}
spin_unlock(&hw->bitbang.lock);
return 0;
}
/* the spi->mode bits understood by this driver: */
#define MODEBITS (SPI_CPOL | SPI_CPHA | SPI_CS_HIGH)
static int s3c24xx_spi_setup(struct spi_device *spi) /*maser.setup方法*/
{
int ret;
if (!spi->bits_per_word)
spi->bits_per_word = 8; /*没有设置则使用8位*/
if (spi->mode & ~MODEBITS) { /*检查mode是否有错*/
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "setup: unsupported mode bits %x\n",
spi->mode & ~MODEBITS);
return -EINVAL;
}
ret = s3c24xx_spi_setupxfer(spi, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&spi->dev, "setupxfer returned %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%s: mode %d, %u bpw, %d hz\n",
__func__, spi->mode, spi->bits_per_word,
spi->max_speed_hz);
return 0;
}
至此,在probe函数中, 由spi_bitbang_start调用所引起的一系列函数调用都已讲解完毕。下面总结下整个调用过程:

可以看到,调用spi_bitbang_start以后,spi_master和spi_device都将被注册到内核中。
下面来看下platform driver的其他几个方法。
4.2.3 remove,suspend以及resume方法
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static int __exit s3c24xx_spi_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw = platform_get_drvdata(dev);
platform_set_drvdata(dev, NULL);
spi_unregister_master(hw->master); /*注销spi主控制器*/
clk_disable(hw->clk); /*禁止时钟*/
clk_put(hw->clk); /*释放CLK*/
free_irq(hw->irq, hw); /*注销IRQ*/
iounmap(hw->regs); /*解除映射*/
if (hw->set_cs == s3c24xx_spi_gpiocs)
gpio_free(hw->pdata->pin_cs); /*释放用于cs的gpio*/
release_resource(hw->ioarea);
kfree(hw->ioarea);
spi_master_put(hw->master); /*减少master引用计数*/
return 0;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_PM /*如果定义了电源管理*/
static int s3c24xx_spi_suspend(struct platform_device *pdev, pm_message_t msg)
{
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
if (hw->pdata && hw->pdata->gpio_setup)
hw->pdata->gpio_setup(hw->pdata, 0);
clk_disable(hw->clk);
return 0;
}
static int s3c24xx_spi_resume(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct s3c24xx_spi *hw = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
s3c24xx_spi_initialsetup(hw);
return 0;
}
#else
#define s3c24xx_spi_suspend NULL
#define s3c24xx_spi_resume NULL
#endif
至此,master 驱动的大体结构都已分析完毕,随后第三篇文章将介绍spi设备驱动
相关文章推荐
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(三)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(一)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(二)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(四)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(一)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(一)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(三)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(二) .
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(二)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(一)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(二)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(四)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(一)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(三)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(四)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(一)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(三)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(三)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(四)
- 基于S3C2440的嵌入式Linux驱动——SPI子系统解读(四)
