高速排序 解析
2014-10-23 11:11
148 查看
高速排序法原理也是用了分治法,主要原理是将数组分为A[p..q-1] 和A[q+1..r],然后调整元素使得A[p..q-1]小于等于q,也小于等于A[q+1..r]。然后不断的递归,到最后就排序完毕。
上代码:
以下我们測试一组数组: 2 8 7 1 3 5 6 4

当中第一次分治法调用示意图例如以下:
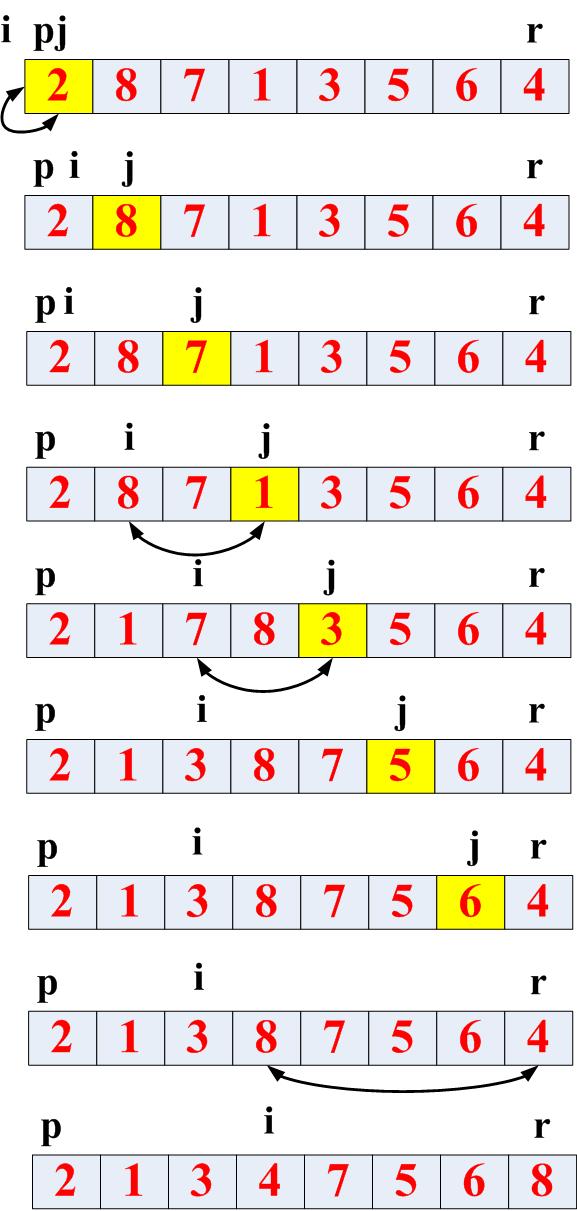
上代码:
// QuickSort.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/*函数声明*/
void QuickSort(int *A,int p,int r); //高速排序
int Partition(int *A,int p,int r); //分治法
void Display(int *a,int size); //打印函数
/*主函数*/
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int size,*a;
while(1)
{
cout<<"输入字符串长度:"<<endl;
cin>>size;
if(size > 0) {
cout<<"请输入"<<size<<"个待排序数字:"<<endl;
a = (int*)malloc(size*sizeof(int)); //a = new int [size];
for(int i=0; i<size; i++) //输入数组
{
cin>>a[i];
}
QuickSort(a,0,size-1); //调用高速排序函数
}
else
cout<<"输入长度错误!"<<endl;
Display(a,size); //打印数组
}
return 0;
}
/*函数定义*/
void QuickSort(int *A,int p,int r) //高速排序
{
int q;
if(p<r) //假设p 小于等于 r 那么就程序不运行
{
q = Partition(A,p,r); //调用分治法 找到q的值
QuickSort(A,p,q-1);
QuickSort(A,q+1,r);
}
}
int Partition(int *A,int p,int r) //分治法,作用就是将数组分为A[p..q-1] 和A[q+1..r]
{ //然后调整元素使得A[p..q-1]小于等于q,也小于等于A[q+1..r]
int x,i,j,temp;
x = A[r]; //将最后一个值保存在x中
i = p-1; //開始的时候将i 移动到数组的外面
for( j=p; j<=r-1; j++)
{
if(A[j]<=x)
{
i +=1;
temp = A[i]; //exchange
A[i] = A[j];
A[j] = temp;
}
}
temp = A[i+1]; //exchange
A[i+1] = A[r];
A[r] = temp;
return i+1; //返回q值
}
void Display(int *a,int size) //打印函数
{
cout<<"排序结果为:"<<endl;
for(int i=0; i<size; i++) //打印数组
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl<<endl;
}以下我们測试一组数组: 2 8 7 1 3 5 6 4

当中第一次分治法调用示意图例如以下:

相关文章推荐
- 高速排序 解析
- 冒泡排序原理全面解析
- 解析搜索引擎常用的排序技术
- 冒泡插入选择排序解析以及信号量机制
- 解析PHP中数组元素升序、降序以及重新排序的函数
- PHP函数asort()利用值排序的具体方式解析
- 解析PHP中数组元素升序、降序以及重新排序的函数
- 双调排序程序解析(可对任意长度的序列排序)
- 对java中集合类排序的解析
- jQuery之排序组件的深入解析
- 【转贴】Google搜索引擎命令解析—高速搜索
- 快速排序 解析
- List的排序。在一个list里面放入"1","2"..."10","11"...,"99999","100000",使用字符串大小的顺序与解析成的数字的大小进行排序
- 排序算法解析--冒泡排序,选择排序,快速排序
- lucene按某个字段排序代码解析
- More Effective C# 第21条、第22条 实例代码解析(可比较 可排序 自定义对象集合完整演示) IEquatable, IComparable,IEnumerable
- bit_map映射实现高速排序查找
- C#基础解析之Ⅳ 【数组和排序】
- Mysql中排序在SQL优化中的部分解析
- 浙江大学PAT上机题解析之3-09. 队列中的元素排序
