Linux ls 命令实现(简化版)
2014-05-07 08:21
639 查看
在学习linux系统编程的时候,实现了ls命令的简化版本。
实现的功能如下:
1. 每种文件类型有自己的颜色 (- 普通文件, d 目录文件, l 链接文件, c 字符设备文件, b 快设备文件, p 管道文件, s socket文件。共7种)
2. 支持的参数有 -hali (a: 显示隐藏文件, i: 显示inode节点号,l: 以列表形式显示文件的详细信息,h: 人类可读的文件大小显示)
3. 对于符号链接,显示出其指向的文件。
4. 设备文件,显示主设备号和次设备号,不显示文件大小(设备文件没有大小属性,对于设备号,不同的 *nix 存储方式可能不同)
5. 文件按照字典序排序显示。
程序说明:
1. 程序中大部分使用的都是linux系统调用和c标准库函数,只有文件排序用到了c++ stl 的vector和sort算法(好吧,我又偷懒了!)
2. lstat(): 获取文件的详细信息,inode, 权限, 连接数, uid, gid, size, time 等(对于符号链接文件,返回自身的信息,而不是目标文件的)
opendir(), readdir(), closedir(): 读取目录信息。
getpwuid(), getgrgid(): 通过uid, gid 获取用户和组的详细信息。
3. 对于不同文件类型的颜色,在Linux下可以使用env命令获取,也可以在程序中使用 extern char **environ 或 getenv() 获取。
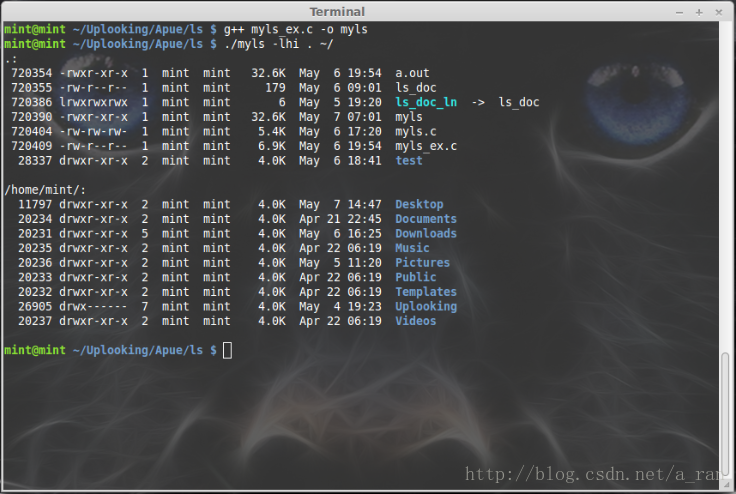
程序编译运行(见下图)
程序源码:
实现的功能如下:
1. 每种文件类型有自己的颜色 (- 普通文件, d 目录文件, l 链接文件, c 字符设备文件, b 快设备文件, p 管道文件, s socket文件。共7种)
2. 支持的参数有 -hali (a: 显示隐藏文件, i: 显示inode节点号,l: 以列表形式显示文件的详细信息,h: 人类可读的文件大小显示)
3. 对于符号链接,显示出其指向的文件。
4. 设备文件,显示主设备号和次设备号,不显示文件大小(设备文件没有大小属性,对于设备号,不同的 *nix 存储方式可能不同)
5. 文件按照字典序排序显示。
程序说明:
1. 程序中大部分使用的都是linux系统调用和c标准库函数,只有文件排序用到了c++ stl 的vector和sort算法(好吧,我又偷懒了!)
2. lstat(): 获取文件的详细信息,inode, 权限, 连接数, uid, gid, size, time 等(对于符号链接文件,返回自身的信息,而不是目标文件的)
opendir(), readdir(), closedir(): 读取目录信息。
getpwuid(), getgrgid(): 通过uid, gid 获取用户和组的详细信息。
3. 对于不同文件类型的颜色,在Linux下可以使用env命令获取,也可以在程序中使用 extern char **environ 或 getenv() 获取。
程序编译运行(见下图)

程序源码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <grp.h>
#include <pwd.h>
// c++
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#define BUF_SIZE 1024
#define COLOR_R (char*)"\33[0m"
#define COLOR_D (char*)"\33[01m\33[34m"
#define COLOR_L (char*)"\33[01m\33[36m"
#define COLOR_P (char*)"\33[40m\33[33m"
#define COLOR_B (char*)"\33[40m\33[33m"
#define COLOR_C (char*)"\33[40m\33[33m"
#define COLOR_S (char*)"\33[02m\33[35m"
#define RESET_CLOLR (char*)"\33[0m"
int get_option(const char *opt);
int show_ls();
int show_ls_one_path(const char *path);
int show_ls_file(const char *path, const char *name);
int show_ll_part(struct stat *p_stat, int bHuman);
void to_humen_size(char *buf, off_t size);
char get_file_type(mode_t st_mode);
void get_mode(char *buf, mode_t st_mode);
// global var
enum EOPT
{
E_a, E_i, E_l, E_h, E_num
};
int g_opt[E_num] = {0}; // order: -ailh
char *g_scolor;
vector<string> gv_path;
/* ls: ./a.out argv... */
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int i;
for (i = 1; i < argc; ++i)
{
if ('-' == argv[i][0])
{
if (-1 == get_option(argv[i]+1))
{
fprintf(stderr, "bad option!\n");
return 1;
}
}
else
{
gv_path.push_back(argv[i]);
}
}
if (0 == gv_path.size())
{
gv_path.push_back(".");
}
show_ls();
return 0;
}
/* -ailh */
int get_option(const char *opt)
{
while (*opt != '\0')
{
switch (*opt)
{
case 'a':
g_opt[E_a] = 1;
break;
case 'i':
g_opt[E_i] = 1;
break;
case 'l':
g_opt[E_l] = 1;
break;
case 'h':
g_opt[E_h] = 1;
break;
default:
return -1;
}
opt++;
}
return 0;
}
int show_ls()
{
for (vector<string>::iterator it = gv_path.begin();
it != gv_path.end(); ++it)
{
show_ls_one_path(it->c_str());
}
return 0;
}
int show_ls_one_path(const char *path)
{
DIR *dir;
dir = opendir(path);
if (NULL == dir)
{
// not a dir
if (ENOTDIR == errno)
{
char *p = rindex((char *)path, '/');
if (NULL == p)
{
show_ls_file("./", path);
}
else
{
char sdir[BUF_SIZE] = {'\0'};
strncpy(sdir, path, p-path);
show_ls_file(sdir, p+1);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
perror(path);
return -1;
}
if (gv_path.size() > 1)
{
fprintf(stdout, "%s:\n", path);
}
struct dirent *entry;
vector<string> v_name;
while (1)
{
entry = readdir(dir);
if (NULL == entry)
{
break;
}
// show conten depends on option(g_opt)
if (g_opt[E_a] != 1)
{
if ('.' == entry->d_name[0])
{
continue;
}
}
v_name.push_back(entry->d_name);
}
// sort filename
sort(v_name.begin(), v_name.end());
for (vector<string>::iterator it = v_name.begin();
it != v_name.end(); ++it)
{
show_ls_file(path, it->c_str());
}
fprintf(stdout, "\n");
closedir(dir);
}
int show_ls_file(const char *path, const char *name)
{
// stat
char full_path[BUF_SIZE];
int ret;
struct stat st_stat;
snprintf(full_path, BUF_SIZE, "%s/%s", path, name);
ret = lstat(full_path, &st_stat);
if (-1 == ret)
{
perror(full_path);
return -1;
}
if (1 == g_opt[E_i])
{
fprintf(stdout, "%7d ", (int)st_stat.st_ino);
}
if (1 == g_opt[E_l])
{
show_ll_part(&st_stat, g_opt[E_h]);
}
else
{
get_file_type(st_stat.st_mode);//get file color actually
}
// show filename with color
fprintf(stdout, "%s", g_scolor);
fprintf(stdout, "%s ", name);
fprintf(stdout, RESET_CLOLR);
if (1 == g_opt[E_l] && 'l' == get_file_type(st_stat.st_mode))
{
// -> real file
char real_file[BUF_SIZE];
int path_size = readlink(full_path, real_file, BUF_SIZE);
real_file[path_size] = '\0';
fprintf(stdout, "-> %s", real_file);
}
if (1 == g_opt[E_l])
{
fprintf(stdout, "\n");
}
return 0;
}
/* show ll: mode, link num, user, group, size, time */
int show_ll_part(struct stat *p_stat, int bHuman)
{
// mode
char buf[BUF_SIZE];
get_mode(buf, p_stat->st_mode);
char file_type = buf[0];
fprintf(stdout, "%s", buf);
// link num
fprintf(stdout, " %d", p_stat->st_nlink);
// uid gid
// get_id_name(buf, p_stat->st_uid, "/etc/passwd");
// fprintf(stdout, " %s", buf);
// get_id_name(buf, p_stat->st_gid, "/etc/group");
// fprintf(stdout, " %s", buf);
struct passwd * st_user = getpwuid(p_stat->st_uid);
fprintf(stdout, " %s", st_user->pw_name);
struct group * st_group = getgrgid(p_stat->st_gid);
fprintf(stdout, " %s", st_group->gr_name);
// show dev id
if ('c' == file_type || 'b' == file_type/* || 'p' == file_type*/)
{
// dev_id
int major = 0xFF00 & p_stat->st_rdev;
major >>= 8;
int sub = 0x00FF & p_stat->st_rdev;
fprintf(stdout, "\t%4d,%4d", major, sub);
}
else // show file size
{
// -h bHuman size
off_t size = p_stat->st_size;
if (bHuman)
{
char buf[BUF_SIZE];
to_humen_size(buf, size);
fprintf(stdout, " %s", buf);
}
else
{
fprintf(stdout, " %9ld", size);
}
}
// time
char stime[BUF_SIZE] = {'\0'};
snprintf(stime, 13, "%s", 4+ctime(&p_stat->st_ctime));
fprintf(stdout, " %s ", stime);
return 0;
}
// -h option
void to_humen_size(char *buf, off_t size)
{
double tmp = size;
if (size >= 1024*1024*1024)
{
tmp /= 1024*1024*1024;
snprintf(buf, BUF_SIZE, "%5.1fG", tmp);
}
else if (size >= 1024*1024)
{
tmp /= 1024*1024;
snprintf(buf, BUF_SIZE, "%5.1fM", tmp);
}
else if (size >= 1024)
{
tmp /= 1024;
snprintf(buf, BUF_SIZE, "%5.1fK", tmp);
}
else
{
snprintf(buf, BUF_SIZE, "%6ld", size);
}
}
char get_file_type(mode_t st_mode)
{
if (S_ISREG(st_mode))
{
g_scolor = COLOR_R;
return '-';
}
if (S_ISDIR(st_mode))
{
g_scolor = COLOR_D;
return 'd';
}
if (S_ISCHR(st_mode))
{
g_scolor = COLOR_C;
return 'c';
}
if (S_ISBLK(st_mode))
{
g_scolor = COLOR_B;
return 'b';
}
if (S_ISFIFO(st_mode))
{
g_scolor = COLOR_P;
return 'p';
}
if (S_ISLNK(st_mode))
{
g_scolor = COLOR_L;
return 'l';
}
if (S_ISSOCK(st_mode))
{
g_scolor = COLOR_S;
return 's';
}
g_scolor = COLOR_R;
return '-';
}
// -rwx---...
void get_mode(char *buf, mode_t st_mode)
{
buf[0] = get_file_type(st_mode);
int i;
mode_t bit;
for (i = 3; i > 0; --i)
{
bit = st_mode & 0x01;
buf[i*3] = (1 == bit ? 'x' : '-');
st_mode >>= 1;
bit = st_mode & 0x01;
buf[i*3-1] = (1 == bit ? 'w' : '-');
st_mode >>= 1;
bit = st_mode & 0x01;
buf[i*3-2] = (1 == bit ? 'r' : '-');
st_mode >>= 1;
}
buf[10] = '\0';
}本文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/a_ran/article/details/25178417
相关文章推荐
- 使用C++实现JNI接口需要注意的事项
- android wifi 无线调试
- 10 篇对初学者和专家都有用的 Linux 命令教程
- Linux 与 Windows 对UNICODE 的处理方式
- Ubuntu12.04下QQ完美走起啊!走起啊!有木有啊!
- 解決Linux下Android开发真机调试设备不被识别问题
- 运维入门
- 运维提升
- Linux 自检和 SystemTap
- 动态清空 nohup 输出文件
- install scrapy with pip and easy_install
- Ubuntu Linux使用体验
- c语言实现hashmap(转载)
- Linux 信号signal处理机制
- linux下mysql添加用户
- 关于指针的一些事情
- Scientific Linux 5.5 图形安装教程
- 基于 Linux 集群环境上 GPFS 的问题诊断
