IBM DB2 Catalog使用及浅析
2014-04-10 22:49
239 查看
RHEL 6上配置LDAP服务器
了解LDAP的作用;
掌握LDAP的配置:基本配置、TLS加密;
掌握RedhatLinux上CA的配置;
LDAP(Lightweight Directory Access Protocol,轻量目录访问协议),于1993年获批准LDAPv1版。它作为X.500简化版本提供了很多自由特性(可以根据需要定制)。与X.500不同,LDAP支持TCP/IP,这对访问Internet是必须的。LDAP的核心规范在RFC中都有定义,所有与LDAP相关的RFC都可以在LDAPmanRFC网页中找到。LDAP目录以树状的层次结构来存储数据。如果对自顶向下的DNS树或UNIX文件的目录树比较熟悉,也就很容易掌握LDAP目录树这个概念了。就象DNS的主机名那样,LDAP目录记录的标识名(Distinguished Name,简称DN)是用来读取单个记录,以及回溯到树的顶部。
基准DN
LDAP目录树的最顶部就是根,也就是所谓的“基准DN"。用企业域名作为基准DN是现在常用的方式。如一个名为example.com的企业,其基准DN可以用:dc=example,dc=com的格式。这种格式也是以DNS域名为基础的,显得更加灵活。微软的AD就是使用的这种方式。
组织数据
在UNIX文件系统中,最顶层是根目录(root)。在根目录的下面有很多的文件和目录。象上面介绍的那样,LDAP目录也是用同样的方法组织起来的。在根目录下,要把数据从逻辑上区分开。因为历史上(X.500)的原因,大多数LDAP目录用OU从逻辑上把数据分开来。OU表示“Organization Unit",在X.500协议中是用来表示公司内部的机构:销售部、财务部,等等。现在LDAP还保留ou=这样的命名规则,但是扩展了分类的范围,可以分类为:ou=people, ou=groups, ou=devices,等等。更低一级的OU有时用来做更细的归类。例如:LDAP目录树(不包括单独的记录)可能会是这样的:
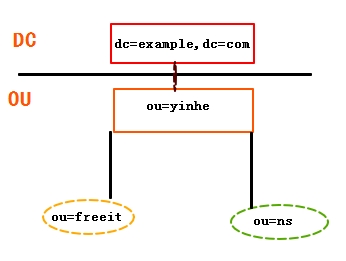
单独记录
在LDAP目录中的所有记录项都有一个唯一的DN(Distinguished Name).每一个LDAP记录的DN是由两部分组成的:相对DN(RDN)和记录在LDAP目录中的位置。RDN是DN中与目录树的结构无关的部分。在LDAP目录中存储的记录项都要有一个名字,这个名字通常存在cn(Common Name)这个属性里。因为几乎所有的东西都有一个名字,在LDAP中存储的对象都用它们的cn值作为RDN的基础。企业为员工设置一个用户账户的DN时,可以用基于cn或UID。如:example.com的员工gyh(登录名freeit_gyh)的DN:①基于姓名:cn=gyh,ou=ns,ou=yinhe,dc=example,dc=com;
②基于登录名:cn=freeit_gyh, ou=ns,ou=yinhe,dc=example,dc=com。
3.2.LDAP分类
Microsoft的Active Directory;
Novell的eDirectory;
Sun的iPlanet;
IBM/Lotus Domino Directory;
OpenLDAP;
Apache的Apache目录服务器;
Apple的OpenDirectory。
注:在LDAP中,schema用来指定一个目录中所包含的对象类型(objectClass)以及每一个对象类型中的每个必备或可选属性。Schema是一个数据模型,它被用来决定数据怎样被存储,被跟踪的数据是什么类型,存储在不同的条目下的数据之间的关系。Schema需要在使用目录服务前定义,在Openldap中其需要在ldap的主配置文件中指定,以用来决定本目录中使用到的对象类型。管理员可以根据需要设计schema,包括属性定义,类定义以及语法定义等部分。LDAPv3中在x.500标准的基础上定义了一个包含网络中大多常见对象的schema,这些对象包括国家、所在地、组织、人员、小组以及设备等。同时,LDAPc3中可以很方便地从目录中提出出schema,它正是一条记录中关于属性的声明部分。LDAP是一个用于为任何网络中本地组织个人和其他资源比如文件设备提供授权的软件协议。LDAP目录可以分布在许多服务器上。LDIF用来同步不同LDAP目录。同步LDAP目录的第一步是从LDAP目录中提取的全部内容或是部分内容并格式化这些内容填到LDIF文件里。LDIF文件然后被邮寄到目录同步遥控设备(DIRBOT)。经过几个不同的步骤之后,最终LDIF文件和源LDIF文件进行比较。这时就会确定在源记录中哪些记录会增加、删除、修改等更新的指令。然后会同步所有的LDAP目录。 LDIF文件有如下特性
以空行分割为一个定义;
以#开始的是注释行;
所有属性赋值方法为“属性:属性值”;
属性可以被重复赋值;
每行后面不允许有空格。
LDAP每条记录必须包含一个对象类型,且对象类型需要赋予至少一个值。每个值将用作一条LDAP记录进行数据存储的模板,模板中包含了一条记录中数个必须被赋值的属性和一系列可选的属性。如上个例子中,objectClass的值为:domain。ObjectClass有严格的等级之分,最顶层的类是top和alias。ObjectClass大致分为3类:结构性的(如:Person和organizationUnit);
辅助型的(如extensibeobject);
抽象型的(此类不能直接使用)。
具体的objectclass定义值请看官方文档。
属性相当于变量,它可以被赋值,就像是可以存放在一个单一类型信息的容器。属性可以自己定义,但不能定义同名属性。Objectcalss也是一种特殊的属性,它包含其他用到的属性以及自身。最常见的属性有:dc(domain Component,常用来指一个域名的一部分,如上述例子中的dc=example,dc=com),ou(organizationalUnit,组织单元),cn(common name,指定一个对象的名字,如用户,需要使用的全名),c(国家),mail(邮件地址)、telephoneNumber(指定电话)、UID(指定登录名)、sn(surname,指定一个人的姓)等。
说明:
将用户认证信息从系统文件迁移到LDAP目录中;
OpenLDAP客户端通过LDAP对用户进行身份验证;
数据保密:由于密码之类的身份验证数据会通过网络进行传输,因此需要使用TLS协议在整个LDAP环境中建立加密的数据通信。
正向解析文件配置
反向解析文件配置
重启named服务
三个主机都指向DNS
Station.example.com指向自己
server.example.com指向192.168.10.251
desktop.example.com指向192.168.10.251
最后,DNS服务器的防火墙一定要允许客户端向自己查询,为方便起见,我们直接清空iptables
安装openldap相关软件包
Openldap:包含Openldap配置文件、库和文档;
Openldap-servers:包含slapd和slurpd服务器、迁移脚本和相关文件。
Openldap-clients:包含客户端程序及用来访问和修改Open’ldap目录软件。
启动服务
5.4.2.主配置文件修改
查看主配置目录
Ldap实验中,我们要使用的配置文件为slapd.conf,但是此处主配置目录里没有(有些版本存在slapd.conf.bak,去掉.bak得到slapd.conf即可) slapd.conf。需要我们从其他地方(/usr/share/openldap-servers/slapd.conf.obsolete)复制模板来。如下:
把slapd.d改名,否则服务不会读slapd.conf,而是读slapd.d。后面的实验中也会报错
修改主配置文件的主机前缀和域
5.4.3.创建管理员密码
生成管理员密码,需要用到slappasswd命令工具,参数如下:
-s :指定密码
-h :指定对密码使用的散列算法(SSHA、SMD5、SHA)
Slappasswd –h {SSHA} –s redhat结果会将生成的密文通过标准输出,但由于该密文要在/etc/openldap/slapd.con文件中使用,所以直接将密码输出到openldap的主配置文件最尾行,以方便以后复制使用。下面我们就对管理员密码进行加密:
修改主配置文件,指定管理员密码
5.4.4.创建系统用户、组及配置NFS
此处创建的用户和组都是为后面转换为ldap用户做准备。配置nfs是为在客户端远程挂载时能够获取用户家目录。
创建组
创建用户家目录及用户
使用NFS共享家目录
5.4.5.把用户及组迁移到数据库文件
安装迁移工具migrationtools
查看目录
如上,/usr/share/migrationtools/有一些Perl脚本用于执行迁移的相关操作。这些perl脚本的配置信息包含在migrate_common.ph文件。这些脚本在RHEL中由openldap-servers软件提供。对于我们来说,只需修改命名前缀的变量使用条目的识别名就足够了,如下:
接下来,要生成一个目录结构模板文件(.ldif结尾),在该模板中定义了常用的目录结构,如果应用比较简单的话,可对模板进行简化(当然如果对LDIF文件及目录结构比较熟悉的话,也可手工编写)。
将LDIF文件的目录结构导入到schema(架构)中
导入系统中的组信息,本实验只导入组ldapgroups,因为所创建的ldap用户属于这个组
导入系统中的用户信息
注:
如果出现如下错误
ldap_bind:Invalid credentials (49)
可能有以下几种原因:
检查“cn=”条目是否给错;
检查“Enter LDAP Password:”是否输错;
检查/etc/openldap/slapd.conf中管理员密码行有无空格;
是否把slapd.d改名。
5.4.6.防火墙开放端口
我们可以查看下slapd的端口号
如上,slapd的端口号为389,所以,我们针对此端口号在防火墙开放即可。为方便实验,我们可以把iptables的缺省内容清空
5.4.7.查看LDAP用户
对于LDAP用户的查看,我们有两种方法,CLI和GUI界面。如下:
CLI界面查看LDAP用户
CLI查看LDAP用户,我们可以借助getent命令:getent passwd username
GUI界面查看用户
GUI界面查看LDAP用户比较麻烦,而且要用到http服务和PHP工具(phpldapadmin-1.2.3)
查看是否安装http服务
下载phpldapadmin-1.2.3工具,网站为:
http://osdn.jp/projects/sfnet_phpldapadmin/downloads/phpldapadmin-php5/1.2.3
本实验已经下载完毕,直接上传至ldap服务器的/var/www/html目录。
访问测试,直接输入http://192.168.10.250/myldap访问,如下:
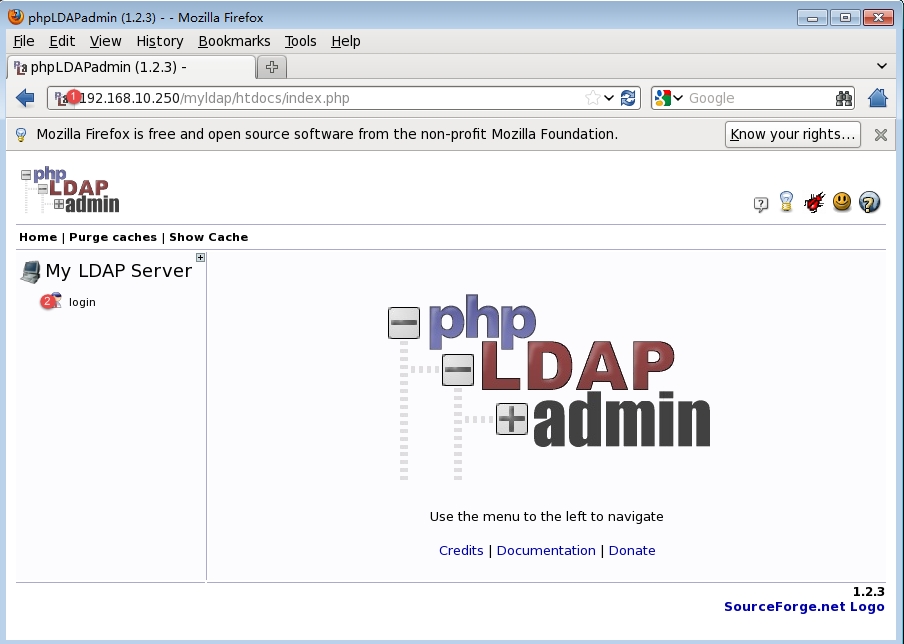
①输入http://192.168.10.250/myldap访问
②点击【login】转到登录界面
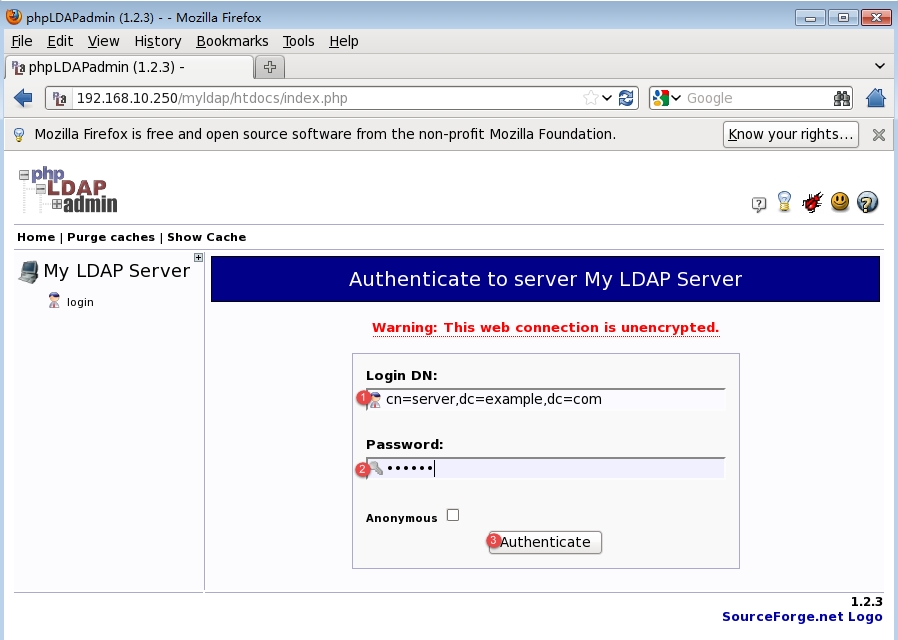
①输入完整的DN
②输入前面我们设置的管理员密码登录
③点击【Authenticate】登录
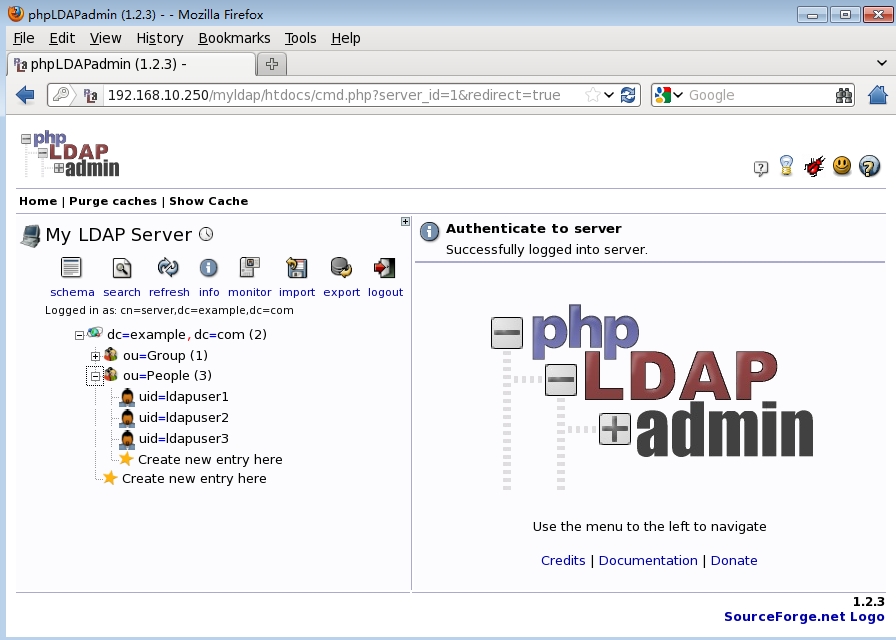
如上,登录后一次点开【dc=example,dc=com】--【ou=People】查看ldap用户。
直接在GUI界面输入命令system-config-authentication打开图形化界面
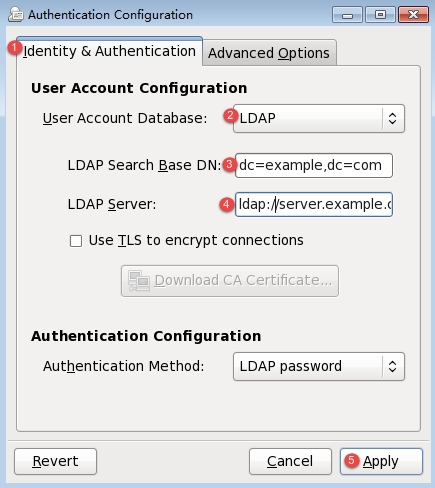
①选择【Identity&Authentication】
②选择【LDAP】
③填写DN,格式如上
④填写LDAP服务器的地址,以ldap://server.example.com(ldap://FQDN)的格式
⑤点击【Apply】完成设置
查看本地是否有ldap用户并登陆测试
如上,登陆成功后,没有用户家目录,这是因为我们还没有挂载远程用户的家目录,下面我们就通过LDAP服务器的NFS来挂载远程用户家目录,挂载到本地的/home/ldaphome
5.6.1.搭建CA
安装openssl软件包
创建存放证书的目录
查看主配置文件
创建索引文件及序号文件
生成CA私钥
参数:
umask 077:设置生成的文件的权限
genrsa:生成私钥
-out:私钥存放路径
2048:2048字节计算(默认为1024)
生成CA的公钥证书(自签证书的形式实现,自动在私钥中提取公钥放到自签证书中,用来验证所颁发证书的合法性。)
参数:
req:生成证书签署请求
-new:新请求
-key /path/to/keyfile:指定私钥文件位置,此处直接生成在当前目录
-out /path/to/somefile:指定证书文件存放在位置,此处直接生成在当前目录
-x509:生成自签证书
5.6.2.LDAP服务器创建密钥并生成请求文件
创建私钥
创建公钥证书
向CA申请证书
5.6.3.CA中心签发证书
5.6.4.LDAP服务器下载并安装证书
直接在CA上传送给LDAP服务器
LDAP服务器安装证书
5.6.5.CA发布公钥证书
安装vsftpd服务
共享公钥证书
5.6.6.客户端验证
测试前查看是否有证书
目录没有证书。
下面打开LDAP配置界面,添加TLS加密
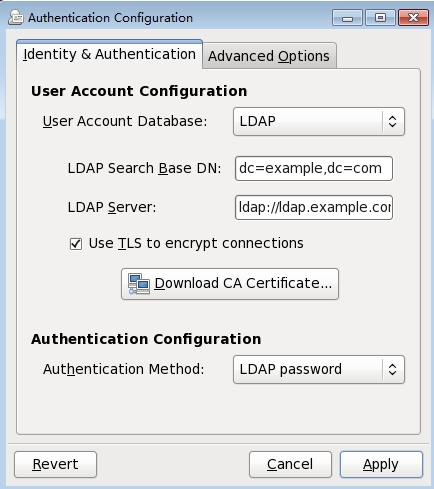
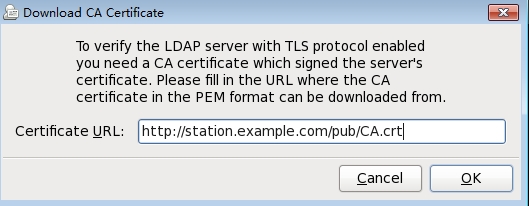
点击【OK】--【Apply】完成证书下载
再次查看是否有下载到的证书
下载成功。
验证用户
验证成功。这样就实验了LDAP的TLS加密,可以实现安全的通信了。
本文出自 “我就是天使” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://freeitgyh.blog.51cto.com/7297595/1655713
1.课程目标
了解LDAP服务(Linux上的AD);了解LDAP的作用;
掌握LDAP的配置:基本配置、TLS加密;
掌握RedhatLinux上CA的配置;
2.目录服务概述
目录服务对于网络的作用就像白页对电话系统的作用一样。目录服务将有关现实世界中的事物(如人、计算机、打印机等等)的信息存储为具有描述性属性的对象。人们可以使用该服务按名称查找对象或者像使用黄页一样,可使用它们查找服务。 网络上,特别是互联网中有各型各类的主机,有各种各样的资源, 这些东西杂散在网络中, 需要有一定的机制来访问这些资源, 得到相关的服务, 于是就有了目录服务. 随着网络中对象数量的增长,目录服务逐渐变得越来越重要。目录服务就像中心点,一个大的分布式目录围绕该中心运作。过去,目录服务主要用于命名和定位网络资源。现在,这些功能得到了扩展,目录服务也变成 Internet/Intranet 基础结构内的一个重要组件,提供类似参考目录、白页和黄页、电子邮件目录之类的服务。 总结一下,目录服务器的主要功能是提供资源与地址的对应关系, 比如你想找一台网上的共享打印机或主机时, 你只需要知道名字就可以了, 而不必去关心它真正的物理位置. 而目录服务器帮助维护这样的资源-地址映射3.LDAP概述
3.1.什么是LDAPLDAP(Lightweight Directory Access Protocol,轻量目录访问协议),于1993年获批准LDAPv1版。它作为X.500简化版本提供了很多自由特性(可以根据需要定制)。与X.500不同,LDAP支持TCP/IP,这对访问Internet是必须的。LDAP的核心规范在RFC中都有定义,所有与LDAP相关的RFC都可以在LDAPmanRFC网页中找到。LDAP目录以树状的层次结构来存储数据。如果对自顶向下的DNS树或UNIX文件的目录树比较熟悉,也就很容易掌握LDAP目录树这个概念了。就象DNS的主机名那样,LDAP目录记录的标识名(Distinguished Name,简称DN)是用来读取单个记录,以及回溯到树的顶部。
基准DN
LDAP目录树的最顶部就是根,也就是所谓的“基准DN"。用企业域名作为基准DN是现在常用的方式。如一个名为example.com的企业,其基准DN可以用:dc=example,dc=com的格式。这种格式也是以DNS域名为基础的,显得更加灵活。微软的AD就是使用的这种方式。
组织数据
在UNIX文件系统中,最顶层是根目录(root)。在根目录的下面有很多的文件和目录。象上面介绍的那样,LDAP目录也是用同样的方法组织起来的。在根目录下,要把数据从逻辑上区分开。因为历史上(X.500)的原因,大多数LDAP目录用OU从逻辑上把数据分开来。OU表示“Organization Unit",在X.500协议中是用来表示公司内部的机构:销售部、财务部,等等。现在LDAP还保留ou=这样的命名规则,但是扩展了分类的范围,可以分类为:ou=people, ou=groups, ou=devices,等等。更低一级的OU有时用来做更细的归类。例如:LDAP目录树(不包括单独的记录)可能会是这样的:

单独记录
在LDAP目录中的所有记录项都有一个唯一的DN(Distinguished Name).每一个LDAP记录的DN是由两部分组成的:相对DN(RDN)和记录在LDAP目录中的位置。RDN是DN中与目录树的结构无关的部分。在LDAP目录中存储的记录项都要有一个名字,这个名字通常存在cn(Common Name)这个属性里。因为几乎所有的东西都有一个名字,在LDAP中存储的对象都用它们的cn值作为RDN的基础。企业为员工设置一个用户账户的DN时,可以用基于cn或UID。如:example.com的员工gyh(登录名freeit_gyh)的DN:①基于姓名:cn=gyh,ou=ns,ou=yinhe,dc=example,dc=com;
②基于登录名:cn=freeit_gyh, ou=ns,ou=yinhe,dc=example,dc=com。
3.2.LDAP分类
Microsoft的Active Directory;
Novell的eDirectory;
Sun的iPlanet;
IBM/Lotus Domino Directory;
OpenLDAP;
Apache的Apache目录服务器;
Apple的OpenDirectory。
4.LDIF文件
LDIF(LDAP Data Interchange Format,轻量级目录交换格式)是一种ASCSI文件格式,用来交换数据并在LDAP服务器间进行数据同步。其最常用功能就是向目录导入或更改记录信息,这些信息需要按照LDAP中架构(schema)的格式进行组织,并会接受架构的检查,如果不符合其要求的格式将会出现报错信息。LDIF文件的内容如下:| dn:dc=example,dc=comdc:exampleobjectClass:topobjectClass:domain dn:ou=People,dc=example,dc=comou:PeopleobjectClass:topobjectClass:organizationakUnit dn:ou=Group,dc=example,dc=comou:GroupobjectClass:topobjectClass:organizationakUnit |
以空行分割为一个定义;
以#开始的是注释行;
所有属性赋值方法为“属性:属性值”;
属性可以被重复赋值;
每行后面不允许有空格。
LDAP每条记录必须包含一个对象类型,且对象类型需要赋予至少一个值。每个值将用作一条LDAP记录进行数据存储的模板,模板中包含了一条记录中数个必须被赋值的属性和一系列可选的属性。如上个例子中,objectClass的值为:domain。ObjectClass有严格的等级之分,最顶层的类是top和alias。ObjectClass大致分为3类:结构性的(如:Person和organizationUnit);
辅助型的(如extensibeobject);
抽象型的(此类不能直接使用)。
具体的objectclass定义值请看官方文档。
属性相当于变量,它可以被赋值,就像是可以存放在一个单一类型信息的容器。属性可以自己定义,但不能定义同名属性。Objectcalss也是一种特殊的属性,它包含其他用到的属性以及自身。最常见的属性有:dc(domain Component,常用来指一个域名的一部分,如上述例子中的dc=example,dc=com),ou(organizationalUnit,组织单元),cn(common name,指定一个对象的名字,如用户,需要使用的全名),c(国家),mail(邮件地址)、telephoneNumber(指定电话)、UID(指定登录名)、sn(surname,指定一个人的姓)等。
5.OpenLDAP
5.1.简介
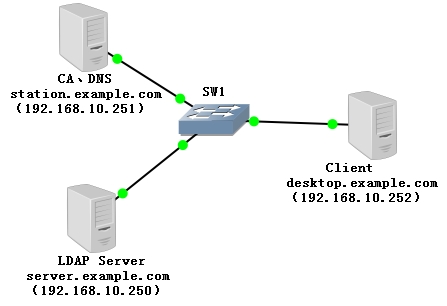
OpenLDAP用于实现基于LDAP的目录服务。不仅可以为所有需要提供身份验证的软件提供用户、组的相关信息,还可以提供通讯录等很多丰富的功能。由于OpenLDAP目录服务本身设计很多复杂的问题,所以相对于其他服务的配置难度较大。5.2.实验拓扑

说明:
将用户认证信息从系统文件迁移到LDAP目录中;
OpenLDAP客户端通过LDAP对用户进行身份验证;
数据保密:由于密码之类的身份验证数据会通过网络进行传输,因此需要使用TLS协议在整个LDAP环境中建立加密的数据通信。
5.3.配置DNS服务器
本实验需要用到DNS来解析LDAP服务器,所以在指定设备上安装DNS服务。因本实验不是重点讲解DNS实验,所以只展示正反向解析文件的内容。正向解析文件配置
| [root@station named]# vim named.example.zone $TTL 1D @ IN SOA ns.example.com. root ( 2015526 ; serial 1D ; refresh 1H ; retry 1W ; expire 3H ) ; minimum NS ns.example.com. ns IN A 192.168.10.251 station IN A 192.168.10.251 ldap IN A 192.168.10.250 server IN A 192.168.10.250 desktop IN A 192.168.10.252 |
| [root@station named]# vim named.example.rezone $TTL 3H @ IN SOA ns.example.com. root ( 2015526 ; serial 1D ; refresh 1H ; retry 1W ; expire 3H ) ; minimum NS ns.example.com. 251 IN PTR ns.example.com. 251 IN PTR station.example.com. 250 IN PTR ldap.example.com. 250 IN PTR server.example.com. 252 IN PTR desktop.example.com. |
| [root@station named]# service named restart Stopping named: umount: /var/named/chroot/var/named: device is busy. (In some cases useful info about processes that use the device is found by lsof(8) or fuser(1)) [ OK ] Starting named: [ OK ] |
Station.example.com指向自己
| [root@station named]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 DEVICE=eth0 TYPE=Ethernet UUID=4cac1aba-e6f6-4d28-827b-c68a4aff1e16 ONBOOT=yes NM_CONTROLLED=yes BOOTPROTO=none HWADDR=00:0C:29:8E:1C:39 IPADDR=192.168.10.251 PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=192.168.10.1 DNS1=192.168.10.251 DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=yes IPV6INIT=no NAME="eth0" ~ [root@station named]# /etc/init.d/NetworkManager restart Stopping NetworkManager daemon: [ OK ] Setting network parameters... [ OK ] Starting NetworkManager daemon: [ OK ] [root@station named]# cat /etc/resolv.conf # Generated by NetworkManager search example.com nameserver 192.168.10.251 |
| [root@server ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 DEVICE=eth0 TYPE=Ethernet UUID=ddae15a9-058f-434d-8331-fd68238fca6a ONBOOT=yes NM_CONTROLLED=yes BOOTPROTO=none HWADDR=00:0C:29:03:FC:20 IPADDR=192.168.10.250 PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=192.168.10.1 DNS1=192.168.10.251 DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=yes IPV6INIT=no NAME="eth0" ~ [root@server ~]# /etc/init.d/NetworkManager restart Stopping NetworkManager daemon: [ OK ] Setting network parameters... [ OK ] Starting NetworkManager daemon: [ OK ] [root@server ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf # Generated by NetworkManager search example.com nameserver 192.168.10.251 |
| [root@desktop ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 DEVICE=eth0 TYPE=Ethernet UUID=6edec324-05b6-48d7-9e97-f712647d9d06 ONBOOT=yes NM_CONTROLLED=yes BOOTPROTO=none HWADDR=00:0C:29:85:6D:5F IPADDR=192.168.10.252 PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=192.168.10.1 DNS1=192.168.10.251 DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=yes IPV6INIT=no NAME="eth0" ~ ~ [root@desktop ~]# /etc/init.d/NetworkManager restart Stopping NetworkManager daemon: [ OK ] Setting network parameters... [ OK ] Starting NetworkManager daemon: [ OK ] [root@desktop ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf # Generated by NetworkManager search example.com nameserver 192.168.10.251 |
| [root@station ~]# iptables -F [root@station ~]# iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination [root@station ~]# service iptables save iptables: Saving firewall rules to /etc/sysconfig/iptables: [ OK ] |
5.4.OpenLDAP服务器配置
5.4.1.安装OpenLDAP安装openldap相关软件包
Openldap:包含Openldap配置文件、库和文档;
Openldap-servers:包含slapd和slurpd服务器、迁移脚本和相关文件。
Openldap-clients:包含客户端程序及用来访问和修改Open’ldap目录软件。
| [root@server ~]# yum -y install openldap* Loaded plugins: product-id, refresh-packagekit, security, subscription-manager This system is not registered to Red Hat Subscription Management. You can use subscription-manager to register. Setting up Install Process Package openldap-2.4.23-31.el6.x86_64 already installed and latest version Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package openldap-clients.x86_64 0:2.4.23-31.el6 will be installed ---> Package openldap-devel.x86_64 0:2.4.23-31.el6 will be installed --> Processing Dependency: cyrus-sasl-devel >= 2.1 for package: openldap-devel-2.4.23-31.el6.x86_64 ---> Package openldap-servers.x86_64 0:2.4.23-31.el6 will be installed --> Running transaction check ---> Package cyrus-sasl-devel.x86_64 0:2.1.23-13.el6_3.1 will be installed --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ……………… |
| [root@server ~]# /etc/init.d/slapd restart Stopping slapd: [FAILED] Starting slapd: [ OK ] [root@server ~]# chkconfig slapd on |
查看主配置目录
| [root@server ~]# cd /etc/openldap/ [root@server openldap]# ls certs ldap.conf schema slapd.d |
| [root@server openldap]# cp -p /usr/share/openldap-servers/slapd.conf.obsolete slapd.conf [root@server openldap]# ls certs ldap.conf schema slapd.conf slapd.d |
| [root@server openldap]# mv slapd.d slapd.d.bak [root@server openldap]# ls certs ldap.conf schema slapd.conf slapd.d.bak |
| 110 ####################################################################### 111 # database definitions 112 ####################################################################### 113 114 database bdb 115 suffix "dc=example,dc=com" //主机前缀 116 checkpoint 1024 15 117 rootdn "cn=server,dc=example,dc=com" //域 |
生成管理员密码,需要用到slappasswd命令工具,参数如下:
-s :指定密码
-h :指定对密码使用的散列算法(SSHA、SMD5、SHA)
Slappasswd –h {SSHA} –s redhat结果会将生成的密文通过标准输出,但由于该密文要在/etc/openldap/slapd.con文件中使用,所以直接将密码输出到openldap的主配置文件最尾行,以方便以后复制使用。下面我们就对管理员密码进行加密:
| [root@server ~]# slappasswd -h {SSHA} -s redhat >> /etc/openldap/slapd.conf [root@server ~]# tail /etc/openldap/slapd.conf index uidNumber,gidNumber,loginShell eq,pres index uid,memberUid eq,pres,sub index nisMapName,nisMapEntry eq,pres,sub # Replicas of this database #replogfile /var/lib/ldap/openldap-master-replog #replica host=ldap-1.example.com:389 starttls=critical # bindmethod=sasl saslmech=GSSAPI # authcId=host/ldap-master.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM {SSHA}7j3PDqWdCR5h5SHMHeGBt0Wj3UyqBWOS //由上面的redhat经SSHA算法转换得来 |
| 110 ####################################################################### 111 # database definitions 112 ####################################################################### 113 114 database bdb 115 suffix "dc=example,dc=com" 116 checkpoint 1024 15 117 rootdn "cn=server,dc=example,dc=com" 118 rootpw {SSHA}7j3PDqWdCR5h5SHMHeGBt0Wj3UyqBWOS //该密码即为上一步骤中使用命令slappasswd生成的。此处行首及中间不要加空格,rootpw与密码中间按tab键隔开 |
此处创建的用户和组都是为后面转换为ldap用户做准备。配置nfs是为在客户端远程挂载时能够获取用户家目录。
创建组
| [root@server ~]# groupadd ldapgroups |
| [root@server ~]# mkdir /home/ldaphome [root@server ~]# chmod 777 /home/ldaphome/ [root@server ~]# useradd -g ldapgroups -d /home/ldaphome/ldapuser1 ldapuser1 [root@server ~]# useradd -g ldapgroups -d /home/ldaphome/ldapuser2 ldapuser2 [root@server ~]# useradd -g ldapgroups -d /home/ldaphome/ldapuser3 ldapuser3 |
| [root@server ~]# vim /etc/exports /home/ldaphome 192.168.10.0/24(rw,sync) ~ //共享,但是只允许本域同网段的用户能够访问 [root@server ~]# /etc/init.d/nfs restart Shutting down NFS daemon: [FAILED] Shutting down NFS mountd: [FAILED] Shutting down NFS quotas: [FAILED] Starting NFS services: [ OK ] Starting NFS quotas: [ OK ] Starting NFS mountd: [ OK ] Stopping RPC idmapd: [ OK ] Starting RPC idmapd: [ OK ] Starting NFS daemon: [ OK ] //重启服务,让共享生效 |
安装迁移工具migrationtools
| [root@server ~]# yum -y install migrationtools Loaded plugins: product-id, refresh-packagekit, security, subscription-manager This system is not registered to Red Hat Subscription Management. You can use subscription-manager to register. Setting up Install Process Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package migrationtools.noarch 0:47-7.el6 will be installed --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ……….. |
| [root@server ~]# cd /usr/share/migrationtools/ [root@server migrationtools]# ls migrate_aliases.pl migrate_group.pl migrate_all_netinfo_offline.sh migrate_hosts.pl migrate_all_netinfo_online.sh migrate_netgroup_byhost.pl migrate_all_nis_offline.sh migrate_netgroup_byuser.pl migrate_all_nis_online.sh migrate_netgroup.pl migrate_all_nisplus_offline.sh migrate_networks.pl migrate_all_nisplus_online.sh migrate_passwd.pl migrate_all_offline.sh migrate_profile.pl migrate_all_online.sh migrate_protocols.pl migrate_automount.pl migrate_rpc.pl migrate_base.pl migrate_services.pl migrate_common.ph migrate_slapd_conf.pl migrate_fstab.pl |
| [root@server migrationtools]# vim migrate_common.ph ……………. 70 # Default DNS domain 71 $DEFAULT_MAIL_DOMAIN = "example.com"; 72 73 # Default base 74 $DEFAULT_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com"; 75 76 # Turn this on for inetLocalMailReceipient 77 # sendmail support; add the following to 78 # sendmail.mc (thanks to Petr@Kristof.CZ): 79 ##### CUT HERE ##### ………. |
| [root@server migrationtools]# pwd /usr/share/migrationtools [root@server migrationtools]# ./migrate_base.pl >example.ldif //生成此文件后要进行简化及修改,如下 [root@server migrationtools]# vim example.ldif dn: dc=example,dc=com dc: example objectClass: top objectClass: domain dn: ou=People,dc=example,dc=com ou: People objectClass: top objectClass: organizationalUnit dn: ou=Group,dc=example,dc=com ou: Group objectClass: top objectClass: organizationalUnit ~ |
| [root@server migrationtools]# ldapadd -x -D "cn=server,dc=example,dc=com" -W -f example.ldif Enter LDAP Password: adding new entry "dc=example,dc=com" adding new entry "ou=People,dc=example,dc=com" adding new entry "ou=Group,dc=example,dc=com" |
| [root@server migrationtools]# pwd /usr/share/migrationtools [root@server migrationtools]# grep ldapgroups /etc/group >group.txt [root@server migrationtools]# ./migrate_group.pl group.txt >group.ldif [root@server migrationtools]# cat group.ldif dn: cn=ldapgroups,ou=Group,dc=example,dc=com objectClass: posixGroup objectClass: top cn: ldapgroups userPassword: {crypt}x gidNumber: 501 [root@server migrationtools]# ldapadd -x -D "cn=server,dc=example,dc=com" -W -f group.ldif Enter LDAP Password: adding new entry "cn=ldapgroups,ou=Group,dc=example,dc=com" //导入组信息成功 |
| [root@server migrationtools]# grep ldapuser1 /etc/passwd >user.txt [root@server migrationtools]# ./migrate_passwd.pl user.txt >user.ldif [root@server migrationtools]# grep ldapuser2 /etc/passwd >user.txt [root@server migrationtools]# ./migrate_passwd.pl user.txt >>user.ldif [root@server migrationtools]# grep ldapuser3 /etc/passwd >user.txt [root@server migrationtools]# ./migrate_passwd.pl user.txt >>user.ldif [root@server migrationtools]# cat user.ldif dn: uid=ldapuser1,ou=People,dc=example,dc=com uid: ldapuser1 cn: ldapuser1 objectClass: account objectClass: posixAccount objectClass: top objectClass: shadowAccount userPassword: {crypt}!! shadowLastChange: 16581 shadowMin: 0 shadowMax: 99999 shadowWarning: 7 loginShell: /bin/bash uidNumber: 501 gidNumber: 501 homeDirectory: /home/ldaphome/ldapuser1 dn: uid=ldapuser2,ou=People,dc=example,dc=com uid: ldapuser2 cn: ldapuser2 objectClass: account objectClass: posixAccount objectClass: top objectClass: shadowAccount userPassword: {crypt}!! shadowLastChange: 16581 shadowMin: 0 shadowMax: 99999 shadowWarning: 7 loginShell: /bin/bash uidNumber: 502 gidNumber: 501 homeDirectory: /home/ldaphome/ldapuser2 dn: uid=ldapuser3,ou=People,dc=example,dc=com uid: ldapuser3 cn: ldapuser3 objectClass: account objectClass: posixAccount objectClass: top objectClass: shadowAccount userPassword: {crypt}!! shadowLastChange: 16581 shadowMin: 0 shadowMax: 99999 shadowWarning: 7 loginShell: /bin/bash uidNumber: 503 gidNumber: 501 homeDirectory: /home/ldaphome/ldapuser3 [root@server migrationtools]# ldapadd -x -D "cn=server,dc=example,dc=com" -W -f user.ldif Enter LDAP Password: adding new entry "uid=ldapuser1,ou=People,dc=example,dc=com" adding new entry "uid=ldapuser2,ou=People,dc=example,dc=com" adding new entry "uid=ldapuser3,ou=People,dc=example,dc=com" //导入用户信息成功 |
如果出现如下错误
ldap_bind:Invalid credentials (49)
可能有以下几种原因:
检查“cn=”条目是否给错;
检查“Enter LDAP Password:”是否输错;
检查/etc/openldap/slapd.conf中管理员密码行有无空格;
是否把slapd.d改名。
5.4.6.防火墙开放端口
我们可以查看下slapd的端口号
| [root@server ~]# netstat -tunlp |grep slapd tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:389 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4474/slapd tcp 0 0 :::389 :::* LISTEN 4474/slapd |
| [root@server ~]# iptables -F [root@server ~]# iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination [root@server ~]# service iptables save iptables: Saving firewall rules to /etc/sysconfig/iptables: [ OK ] |
对于LDAP用户的查看,我们有两种方法,CLI和GUI界面。如下:
CLI界面查看LDAP用户
CLI查看LDAP用户,我们可以借助getent命令:getent passwd username
| [root@server ~]# getent passwd |grep ldapuser ldapuser1:x:501:501::/home/ldaphome/ldapuser1:/bin/bash ldapuser2:x:502:501::/home/ldaphome/ldapuser2:/bin/bash ldapuser3:x:503:501::/home/ldaphome/ldapuser3:/bin/bash |
GUI界面查看LDAP用户比较麻烦,而且要用到http服务和PHP工具(phpldapadmin-1.2.3)
查看是否安装http服务
| [root@server ~]# rpm -qa |grep httpd httpd-tools-2.2.15-26.el6.x86_64 httpd-2.2.15-26.el6.x86_64 //已经安装,直接启动 [root@server ~]# /etc/init.d/httpd restart Stopping httpd: [FAILED] Starting httpd: httpd: apr_sockaddr_info_get() failed for server.example.com httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using 127.0.0.1 for ServerName [ OK ] [root@server ~]# chkconfig httpd on |
http://osdn.jp/projects/sfnet_phpldapadmin/downloads/phpldapadmin-php5/1.2.3
本实验已经下载完毕,直接上传至ldap服务器的/var/www/html目录。
| [root@server ~]# cd /var/www/html/ [root@server html]# ls phpldapadmin-1.2.3.zip [root@server html]# unzip phpldapadmin-1.2.3.zip [root@server html]# ls phpldapadmin-1.2.3 phpldapadmin-1.2.3.zip [root@server html]# mv phpldapadmin-1.2.3 myldap //改个名方便访问 [root@server html]# cd myldap/config/ [root@server config]# ls config.php.example [root@server config]# cp -p config.php.example config.php [root@server config]# ls config.php config.php.example ----------------------安装辅助工具---------------------------- [root@server config]# yum -y install php-ldap php ----------------------------重启httpd服务----------------------- [root@server html]# /etc/init.d/httpd restart Stopping httpd: [ OK ] Starting httpd: httpd: apr_sockaddr_info_get() failed for server.example.com httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using 127.0.0.1 for ServerName [ OK ] |

①输入http://192.168.10.250/myldap访问
②点击【login】转到登录界面

①输入完整的DN
②输入前面我们设置的管理员密码登录
③点击【Authenticate】登录

如上,登录后一次点开【dc=example,dc=com】--【ou=People】查看ldap用户。
5.5.客户端配置
打开LDAP配置界面直接在GUI界面输入命令system-config-authentication打开图形化界面

①选择【Identity&Authentication】
②选择【LDAP】
③填写DN,格式如上
④填写LDAP服务器的地址,以ldap://server.example.com(ldap://FQDN)的格式
⑤点击【Apply】完成设置
查看本地是否有ldap用户并登陆测试
| [root@desktop ~]# id ldapuser1 uid=501(ldapuser1) gid=501(ldapgroups) groups=501(ldapgroups) 或 [root@desktop ~]# getent passwd ldapuser1 ldapuser1:*:501:501:ldapuser1:/home/ldaphome/ldapuser1:/bin/bash [root@desktop ~]# su ldapuser1 bash-4.1$ //登陆之后没有家目录 |
| [root@desktop ~]# mount -t nfs 192.168.10.250:/home/ldaphome /home/ldaphome [root@desktop ~]# df Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/sda2 60475476 3454812 53948664 7% / tmpfs 506272 0 506272 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 198337 33144 154953 18% /boot /dev/sda3 5039616 141084 4642532 3% /home 192.168.10.250:/home/ldaphome 5039616 141184 4642432 3% /home/ldaphome [root@desktop ~]# su - ldapuser1 [ldapuser1@desktop ~]$ //挂载之后,再次登录,用户拥有了家目录 |
5.6.LDAP的TLS加密
与HTTP一样,LDAP默认情况下使用明文进行传输,但是,实际生产环境中,我们队数据的加密性要求较高,所以建议使用SSL对LDAP数据通信进行保护。下面,我们就来配置LDAP的TLS加密。5.6.1.搭建CA
安装openssl软件包
| [root@station ~]# yum -y install openssl* //使用此命令安装openssl软件包 |
| [root@station ~]# mkdir /etc/openldap/.cakey |
| [root@station ~]# vim /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf 39 #################################################################### 40 [ CA_default ] 41 42 dir = /etc/pki/CA //根目录 # Where everything is kept 43 certs = $dir/certs //公钥目录 # Where the issued certs are kept 44 crl_dir = $dir/crl //过期、吊销证书目录 # Where the issued crl are kept 45 database = $dir/index.txt //证书签名记录文件 # database index file. 46 #unique_subject = no # Set to 'no' to allow creation of 47 # several ctificates with same subj ect. 48 new_certs_dir = $dir/newcerts //新公钥证书目录 # default place for new certs. 49 50 certificate = $dir/CA.crt # The CA certificate //公钥证书名修改之后创建时要对应 51 serial = $dir/serial //每次签名序号自动加1 # The current serial number 52 crlnumber = $dir/crlnumber # the current crl number 53 # must be commented out to leave a V1 CRL 54 crl = $dir/crl.pem # The current CRL 55 private_key = $dir/private/CA.key # The private key //私钥,修改名称之后创建时要对应名称 …………….. 84 [ policy_match ] 85 countryName = match 86 stateOrProvinceName = match 87 organizationName = match 88 organizationalUnitName = optional 89 commonName = supplied 90 emailAddress = optional …………………….. 129 countryName = Country Name (2 letter code) 130 countryName_default = CN //修改默认的国家名 131 countryName_min = 2 132 countryName_max = 2 133 134 stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name) 135 stateOrProvinceName_default = Hubei //修改默认的省份 136 137 localityName = Locality Name (eg, city) 138 localityName_default = Wuhan //修改默认的城市 139 140 0.organizationName = Organization Name (eg, company) 141 0.organizationName_default = Example, Inc. |
| [root@station ~]# cd /etc/pki/CA/ [root@station CA]# touch index.txt //创建索引文件,匹配证书编号 [root@station CA]# echo 01 >serial //输入一个编号,记录CA办理了多少证书 //编号从1开始 |
| [root@station CA]# pwd /etc/pki/CA [root@station CA]#( umask 077; openssl genrsa -out private/CA.key) Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus ...........................................++++++ .....................++++++ e is 65537 (0x10001) //生成后在/etc/pki/CA/private下 |
umask 077:设置生成的文件的权限
genrsa:生成私钥
-out:私钥存放路径
2048:2048字节计算(默认为1024)
生成CA的公钥证书(自签证书的形式实现,自动在私钥中提取公钥放到自签证书中,用来验证所颁发证书的合法性。)
| [root@station ~]# openssl req -new -x509 -key /etc/pki/CA/private/CA.key –out CA.crt You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [CN]:CN //国家 State or Province Name (full name) [Hubei]:Hubei //省 Locality Name (eg, city) [Wuhan]:Wuhan //地区 Organization Name (eg, company) [Example, Inc.]: //公司名称 //以上四项可以不填,默认与配置文件一样 Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:IT //公司部门名称 Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:station.example.com //服务器的主机名 Email Address []: //管理员邮箱 |
req:生成证书签署请求
-new:新请求
-key /path/to/keyfile:指定私钥文件位置,此处直接生成在当前目录
-out /path/to/somefile:指定证书文件存放在位置,此处直接生成在当前目录
-x509:生成自签证书
5.6.2.LDAP服务器创建密钥并生成请求文件
创建私钥
| [root@server ~]# openssl genrsa -out server-ldap.key Generating RSA private key, 512 bit long modulus .......++++++++++++ .++++++++++++ e is 65537 (0x10001) |
| [root@server ~]# openssl req -new -key server-ldap.key -out server-ldap.csr You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [CN]:CN State or Province Name (full name) [Hubei]:Hubei Locality Name (eg, city) [Wuhan]:Wuhan Organization Name (eg, company) [Example, Inc.]: Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:IT Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:server.example.com Email Address []: Please enter the following 'extra' attributes to be sent with your certificate request A challenge password []:redhat An optional company name []: |
| [root@server ~]# scp server-ldap.csr station:/tmp //把申请证书的信息文件传给CA The authenticity of host 'station (192.168.10.251)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is 69:62:46:3c:64:75:ac:5e:8a:b9:c8:59:4d:41:e5:e3. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added 'station,192.168.10.251' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. Address 192.168.10.251 maps to ns.example.com, but this does not map back to the address - POSSIBLE BREAK-IN ATTEMPT! root@station's password: server-ldap.csr 100% 501 0.5KB/s 00:00 |
| [root@station CA]# openssl ca -in /tmp/server-ldap.csr -out /tmp/server-ldap.crt Using configuration from /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf Check that the request matches the signature Signature ok Certificate Details: Serial Number: 1 (0x1) Validity Not Before: Nov 29 13:06:23 2013 GMT Not After : Nov 29 13:06:23 2014 GMT Subject: countryName = CN stateOrProvinceName = Hubei organizationName = Yinhe organizationalUnitName = IT commonName = server.example.com X509v3 extensions: X509v3 Basic Constraints: CA:FALSE Netscape Comment: OpenSSL Generated Certificate X509v3 Subject Key Identifier: 45:B7:28:37:6A:E5:53:1D:28:3B:D9:5F:B8:34:4C:BB:A7:A5:C7:87 X509v3 Authority Key Identifier: keyid:3B:A4:E2:47:47:6A:1E:17:1D:F1:6C:2B:31:3D:30:6F:94:F9:3B:1F Certificate is to be certified until Nov 29 13:06:23 2014 GMT (365 days) Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y 1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y Write out database with 1 new entries Data Base Updated [root@station CA]# ls /tmp/ keyring-GUquK5 pulse-UhvcMecHJjx0 server-ldap.csr yum.log orbit-gdm seahorse-9nqjTF virtual-root.aM2PSS pulse-INwxEV04N430 server-ldap.crt virtual-root.loj5D4 |
直接在CA上传送给LDAP服务器
| [root@station CA]# scp /tmp/server-ldap.crt 192.168.10.250:/root/ The authenticity of host '192.168.10.250 (192.168.10.250)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is af:63:d5:cf:76:af:71:02:22:3f:0d:7c:7e:eb:73:5e. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '192.168.10.250' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. root@192.168.10.250's password: server-ldap.crt 100% 2386 2.3KB/s 00:00 [root@station CA]# scp CA.crt 192.168.10.250:/root/ root@192.168.10.250's password: CA.crt 100% 790 0.8KB/s 00:00 |
| [root@server ~]# cp -p CA.crt /etc/pki/CA/certs/ [root@server ~]# cp -p server-ldap.* /etc/pki/CA/certs/ //以上两步是把证书文件复制到配置文件规定的目录 [root@server ~]# vim /etc/openldap/ldap.conf # # LDAP Defaults # # See ldap.conf(5) for details # This file should be world readable but not world writable. #BASE dc=example,dc=com #URI ldap://ldap.example.com ldap://ldap-master.example.com:666 #SIZELIMIT 12 #TIMELIMIT 15 #DEREF never URI ldap://127.0.0.1/ BASE dc=example,dc=com TLS_CACERTDIR /etc/openldap/certs ……………. [root@server ~]#vim /etc/openldap/slapd.conf ……………… 66 TLSCACertificatePath /etc/openldap/certs/CA.crt 67 TLSCertificateFile /etc/openldap/certs/server-ldap.crt 68 TLSCertificateKeyFile /etc/openldap/certs/server-ldap.key |
安装vsftpd服务
| [root@station tmp]# yum -y install httpd* Loaded plugins: product-id, refresh-packagekit, security, subscription-manager This system is not registered to Red Hat Subscription Management. You can use subscription-manager to register. Setting up Install Process Package httpd-2.2.15-26.el6.x86_64 already installed and latest version Package httpd-tools-2.2.15-26.el6.x86_64 already installed and latest version Resolving Dependencies ………………. [root@server tmp]# cd /var/www/html [root@server html]# mkdir pub [root@server html]# ls pub [root@station CA]# /etc/init.d/httpd restart Stopping httpd: [FAILED] Starting httpd: [ OK ] [root@server html]# chkconfig httpd on |
| [root@station CA]# cp /etc/pki/CA/CA.crt /var/www/html |
测试前查看是否有证书
| [root@desktop CA]# cd /etc/openldap/ cacerts [root@desktop cacerts]# ls [root@desktop cacerts]# |
下面打开LDAP配置界面,添加TLS加密


点击【OK】--【Apply】完成证书下载
再次查看是否有下载到的证书
| [root@desktop cacerts]# ls 406c48b7.0 authconfig_downloaded.pem |
验证用户
| [root@desktop ~]# id ldapuser1 uid=501(ldapuser1) gid=501 groups=501 [root@desktop ~]# id ldapuser2 uid=502(ldapuser2) gid=501 groups=501 [root@desktop ~]# id ldapuser3 uid=503(ldapuser3) gid=501 groups=501 |
本文出自 “我就是天使” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://freeitgyh.blog.51cto.com/7297595/1655713
相关文章推荐
- IBM DB2 Catalog使用及浅析
- DB2 Catalog使用及浅析
- IBM DB2 Catalog & Uncatalog使用
- 使用IBM Data Studio 管理DB2
- 使用 IBM Data Studio 开发调试 DB2 存储过程
- DB2 Catalog 使用简介
- 使用 Java 5 RowSet 新特性访问 IBM DB2 数据库
- php中使用IBM-DB2
- IBM DB2 数据库使用小技巧
- 编程使用c#连接到IBM db2的两种方式
- 使用重定向恢复克隆 DB2 数据库(摘自IBM developerWorks)
- IBM DB2学习笔记:日期以及时间的使用
- 使用 Hibernate 将 Java 对象持久保存到 IBM DB2 通用数据库中
- 使用 XForms 和 Ruby on Rails 开发小型门诊管理系统,第 1 部分: 安装配置 IBM DB2 9 pureXML
- 原创-IBM DB2学习笔记-1:日期以及时间的使用
- 使用DB2报错:ERROR [42818] [IBM][DB2/NT] SQL0401N The data types of the operands for the operation "=" a
- 使用 IBM DB2 Migration Toolkit 迁移数据
- Python yield 使用浅析 (ibm-developerworks)
- BuildForge使用默认的DB2 Express运行时出现ERROR [IBM][CLI Driver][DB2/6000] SQL0964C The transaction log for the database is full. SQLSTATE
- IBM DB2 数据库使用小技巧
